Abstract
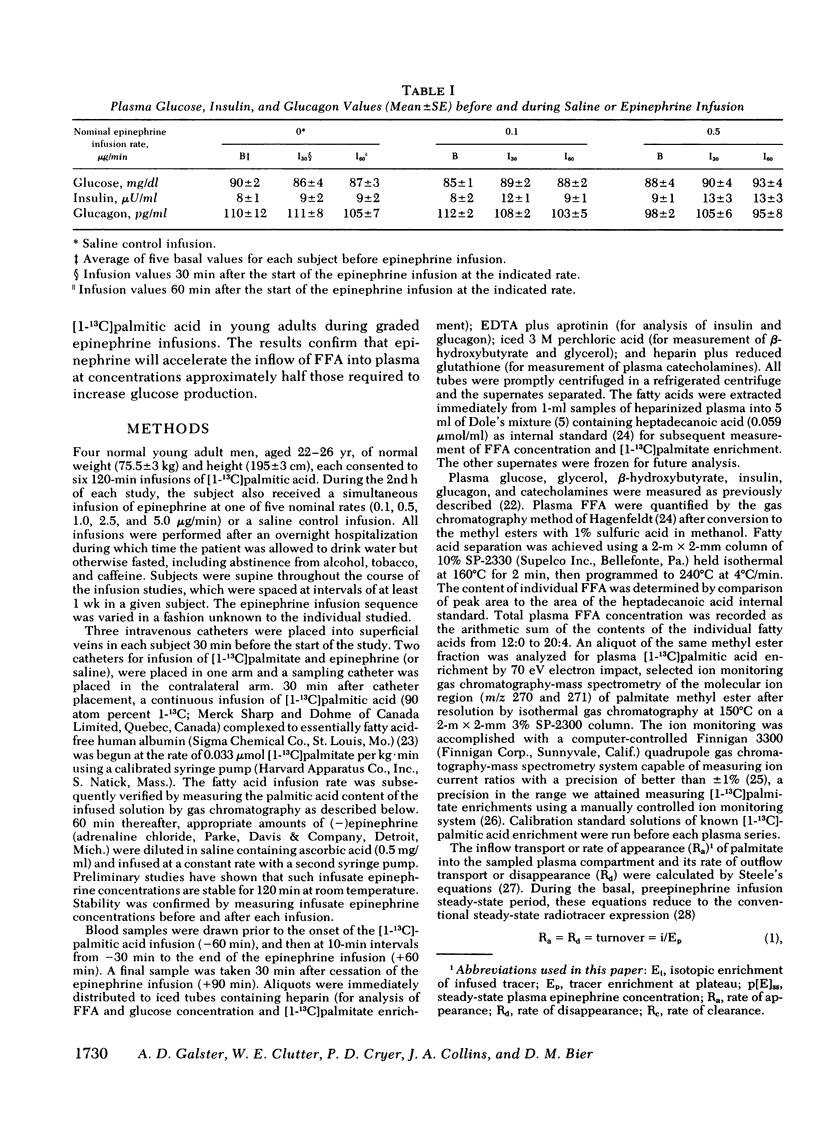
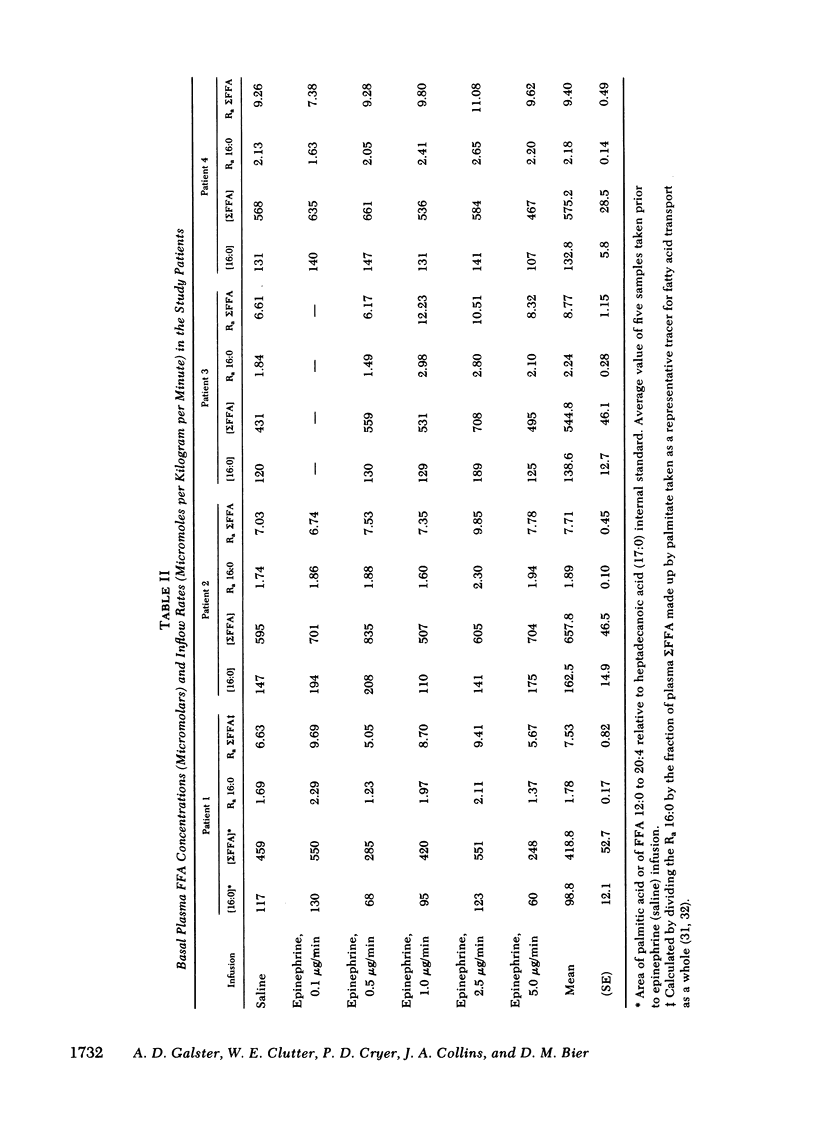
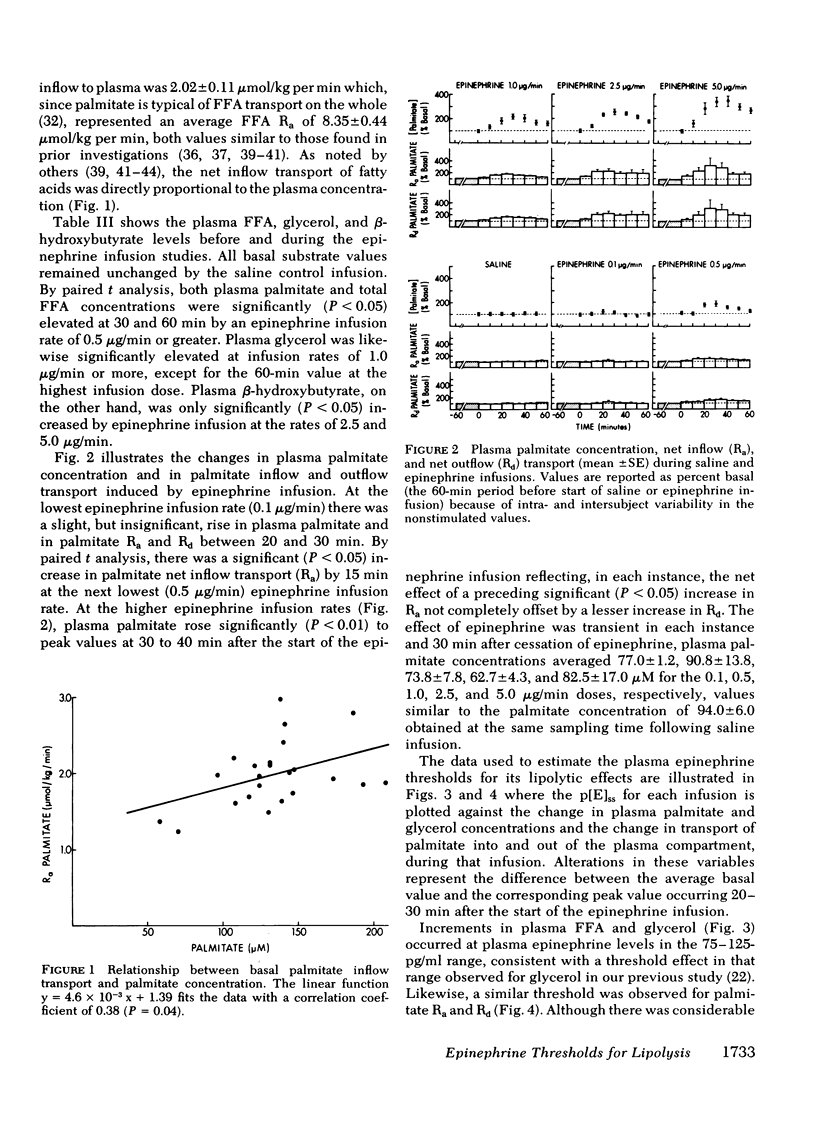
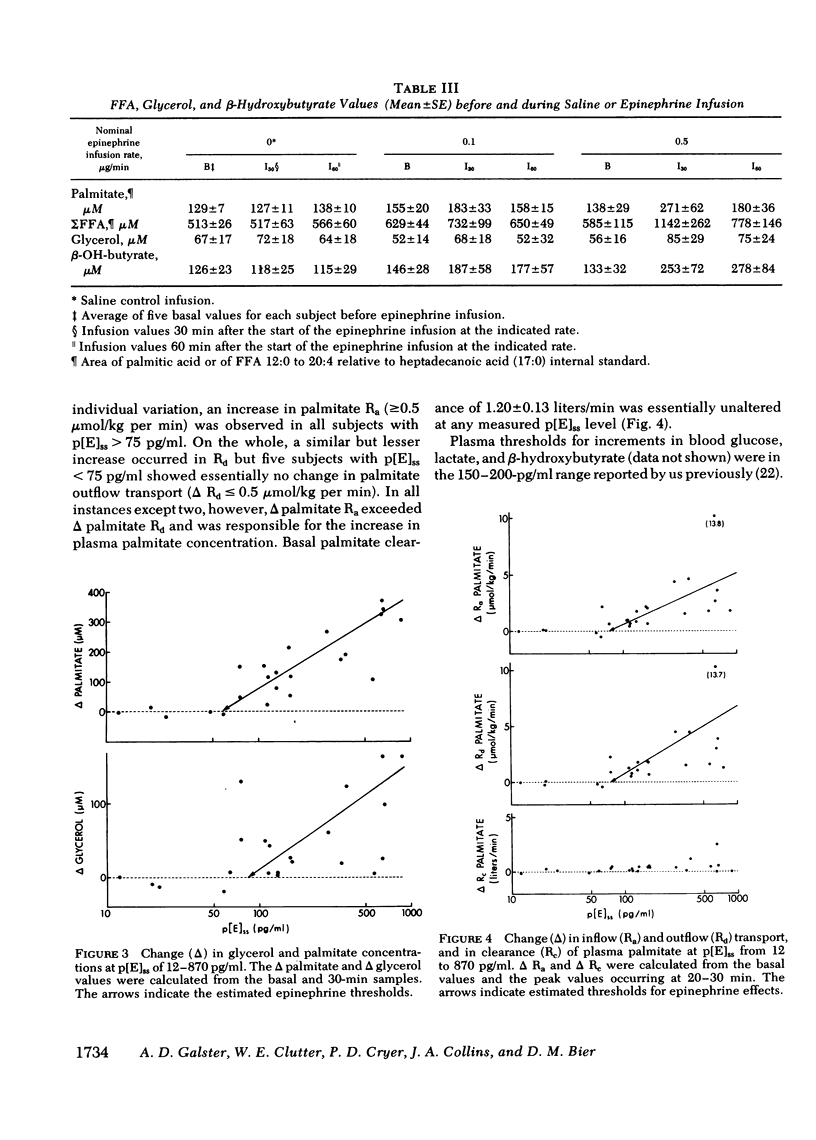
To determine the plasma epinephrine thresholds for its lipolytic effect, 60-min epinephrine infusions at nominal rates of 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.5, and 5.0 micrograms/min were performed in each of four normal young adult men while they also received a simultaneous infusion of [1-13C]palmitic acid to estimate inflow transport of plasma free fatty acids. These 20 infusions resulted in steady-state plasma epinephrine concentrations ranging from 12 to 870 pg/ml. Plasma epinephrine thresholds for changes in blood glucose, lactate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate were in the 150--200-pg/ml range reported by us previously (Clutter, W. E., D. M. Bier, S. D. Shah, and P. E. Cryer. 1980. J. Clin. Invest. 66: 94--101.). Increments in plasma glycerol and free fatty acids and in the inflow and outflow transport of palmitate, however, occurred at lower plasma epinephrine thresholds in the range of 75 to 125 pg/ml. Palmitate clearance was unaffected at any steady-state epinephrine level produced. These data indicate that (a) the lipolytic effects of epinephrine occur at plasma levels approximately threefold basal values and (b) lipolysis is more sensitive than glycogenolysis to increments in plasma epinephrine.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG D. T., STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., DUNN A., BISHOP J. S., DE BODO R. C. Regulation of plasma free fatty acid turnover. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jul;201:9–15. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIERMAN E. L., SCHWARTZ I. L., DOLE V. P. Action of insulin on release of fatty acids from tissue stores. Am J Physiol. 1957 Nov;191(2):359–362. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.191.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOGDONOFF M. D., LINHART J. W., KLEIN R. J., ESTES E. H., Jr The specific structure of compounds effecting fat mobilization in man. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1993–1996. doi: 10.1172/JCI104425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker N., Schotz M. C. Quantitative aspects of free fatty acid metabolism in the fasted rat. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):646–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P., Bergman H., Varnauskas E., Lindholm B. Lipid mobilization in relation to body composition in man. Metabolism. 1969 Oct;18(10):840–851. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. E., 3rd, Giamber S. R., Mager M., Lebovitz H. E. Lactate inhibition of lipolysis in exercising man. Metabolism. 1974 Jun;23(6):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns T. W., Mohs J. M., Langley P. E., Yawn R., Chase G. R. Regulation of human lipolysis. In vivo observations on the role of adrenergic receptors. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):338–341. doi: 10.1172/JCI107556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J. Plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine in untreated diabetics, during fasting and after insulin administration. Diabetes. 1974 Jan;23(1):1–8. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Videbaek J. Plasma catecholamines and carbohydrate metabolism in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):278–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI107763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutter W. E., Bier D. M., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Epinephrine plasma metabolic clearance rates and physiologic thresholds for metabolic and hemodynamic actions in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):94–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI109840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Haymond M. W., Santiago J. V., Shah S. D. Norepinephrine and epinephrine release and adrenergic mediation of smoking-associated hemodynamic and metabolic events. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 9;295(11):573–577. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609092951101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Isotope-derivative measurements of plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine in man. Diabetes. 1976 Nov;25(11):1071–1082. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.11.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E. Physiology and pathophysiology of the human sympathoadrenal neuroendocrine system. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 21;303(8):436–444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008213030806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Santiago J. V., Shah S. Measurement of norepinephrine and epinephrine in small volumes of human plasma by a single isotope derivative method: response to the upright posture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Dec;39(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-6-1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. P., Berman M., Steinberg D. Kinetic studies of plasma free fatty acid and triglyceride metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1560–1579. doi: 10.1172/JCI106122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINE M. B., WILLIAMS R. H. Effect of fasting, epinephrine and glucose and insulin on hepatic uptake of nonesterified fatty acids. Am J Physiol. 1960 Sep;199:403–406. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.3.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDRICKSON D. S., GORDON R. S., Jr The metabolism of albumin-bound C14-labeled unesterified fatty acids in normal human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1504–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI103742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN H. M., KNOBIL E. Effect of adrenergic blocking agents on fatty acid mobilization during fasting. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Nov;102:493–495. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN H. M., KNOBIL E. Mobilization of fatty acids by epinephrine in normal and hypophysectomized rhesus monkeys. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jan;100(1):195–197. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON R. S., Jr, CHERKES A. Unesterified fatty acid in human blood plasma. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):206–212. doi: 10.1172/JCI103265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbo H., Holst J. J., Christensen N. J. Glucagon and plasma catecholamine responses to graded and prolonged exercise in man. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Jan;38(1):70–76. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Charles M. A., Grodsky G. M. Regulation of pancreatic insulin and glucagon secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:353–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Stimulation of glucagon secretion by epinephrine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Sep;37(3):479–481. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Tsalikian E., Karam J. H. Studies on the mechanism of epinephrine-induced hyperglycemia in man. Evidence for participation of pancreatic glucagon secretion. Diabetes. 1976 Jan;25(1):65–71. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenke L. D., Craig J. C., Bier D. M. An improved selected ion recording system for precise isotope ratio determination. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1980 Sep;7(9):381–384. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200070905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L. A gas chromatographic method for the determination of individual free fatty acids in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Feb;13(2):266–268. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L. Metabolism of free fatty acids and ketone bodies during exercise in normal and diabetic man. Diabetes. 1979 Jan;28 (Suppl 1):66–70. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.1.s66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L. Turnover of individual free fatty acids in man. Fed Proc. 1975 Dec;34(13):2246–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L., Wahren J., Pernow B., Räf L. Uptake of individual free fatty acids by skeletal muscle and liver in man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2324–2330. doi: 10.1172/JCI107043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L., Wahren J. Turnover of plasma-free arachidonic and oleic acids in resting and exercising human subjects. Metabolism. 1975 Jul;24(7):799–806. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall S. E., Saunders J., Sönksen P. H. Glucose and free fatty acid turnover in normal subjects and in diabetic patients before and after insulin treatment. Diabetologia. 1979 May;16(5):297–306. doi: 10.1007/BF01223618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Balasse E. O., Segel N., Basso L. V. Splanchnic metabolism of free fatty acids and production of triglycerides of very low density lipoproteins in normotriglyceridemic and hypertriglyceridemic humans. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):2017–2035. doi: 10.1172/JCI106422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz B., Jr, Miller H. I., Rodahl K. Lipid and carbohydrate metabolism during exercise. Fed Proc. 1966 Jul-Aug;25(4):1415–1420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James E., Meschia G., Battaglia F. C. A-V differences of free fatty acids and glycerol in the ovine umbilical circulation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):823–826. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN R. F., ESTES E. H., Jr, BOGDONOFF M. D. Effect of norepinephrine on plasma free fatty acids level in man. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Mar;16:342–344. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.2.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCELROY W. T., Jr, SPITZER J. J. Effects of adrenergic blocking agents on plasma free fatty acid concentrations. Am J Physiol. 1961 Feb;200:318–322. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.2.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. E., Ben-Galim E., Bier D. M. Determination of stable isotopic enrichment in individual plasma amino acids by chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1979 Jan;51(1):80–84. doi: 10.1021/ac50037a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORTH R. D., WILLIAMS R. H. Response of plasma NEFA levels to epinephrine infusions in normal and obese women. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 May;104:119–120. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passon P. G., Peuler J. D. A simplified radiometric assay for plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):618–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90517-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle M. C., Ryan W. G., Schwartz T. B. Human plasma free fatty acid concentration at rest and after norepinephrine infusion: effect of preceding physical activity. Metabolism. 1972 Nov;21(11):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R., Haymond M., Cryer P., Gerich J. Differential effects of epinephrine on glucose production and disposal in man. Am J Physiol. 1979 Oct;237(4):E356–E362. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.4.E356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOTZ M. C., PAGE I. H. Effect of norepinephrine and epinephrine on nonesterified fatty acid concentration in plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:624–626. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAFRIR E., SUSSMAN K. E., STEINBERG D. Role of the pituitary and the adrenal in the mobilization of free fatty acids and lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1960 Oct;1:459–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg A. B., Shah S. D., Haymond M. W., Cryer P. E. Norepinephrine: hormone and neurotransmitter in man. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):E252–E256. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.3.E252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tancredi R. G., Dagenais G. R., Zierler K. L. Free fatty acid metabolism in the forearm at rest: muscle uptake and adipose tissue release of free fatty acids. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1976 May;138(5):167–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN K., JOSEPH J. D., MAYERSON H. S. Kinetics of vascular and extravascular protein exchange in unbled and bled dogs. Am J Physiol. 1956 Jan;184(1):175–182. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.184.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe B. M., Havel J. R., Marliss E. B., Kane J. P., Seymour J., Ahuja S. P. Effects of a 3-day fast and of ethanol on splanchnic metabolism of FFA, amino acids, and carbohydrates in healthy young men. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):329–340. doi: 10.1172/JCI108284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Allsop J. R., Burke J. F. Glucose metabolism in man: responses to intravenous glucose infusion. Metabolism. 1979 Mar;28(3):210–220. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Evans J. E., Mullany C. J., Burke J. F. Measurement of plasma free fatty acid turnover and oxidation using [1-13C]palmitic acid. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1980 Apr;7(4):168–171. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200070407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


