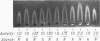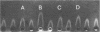Abstract
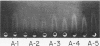
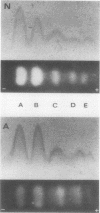
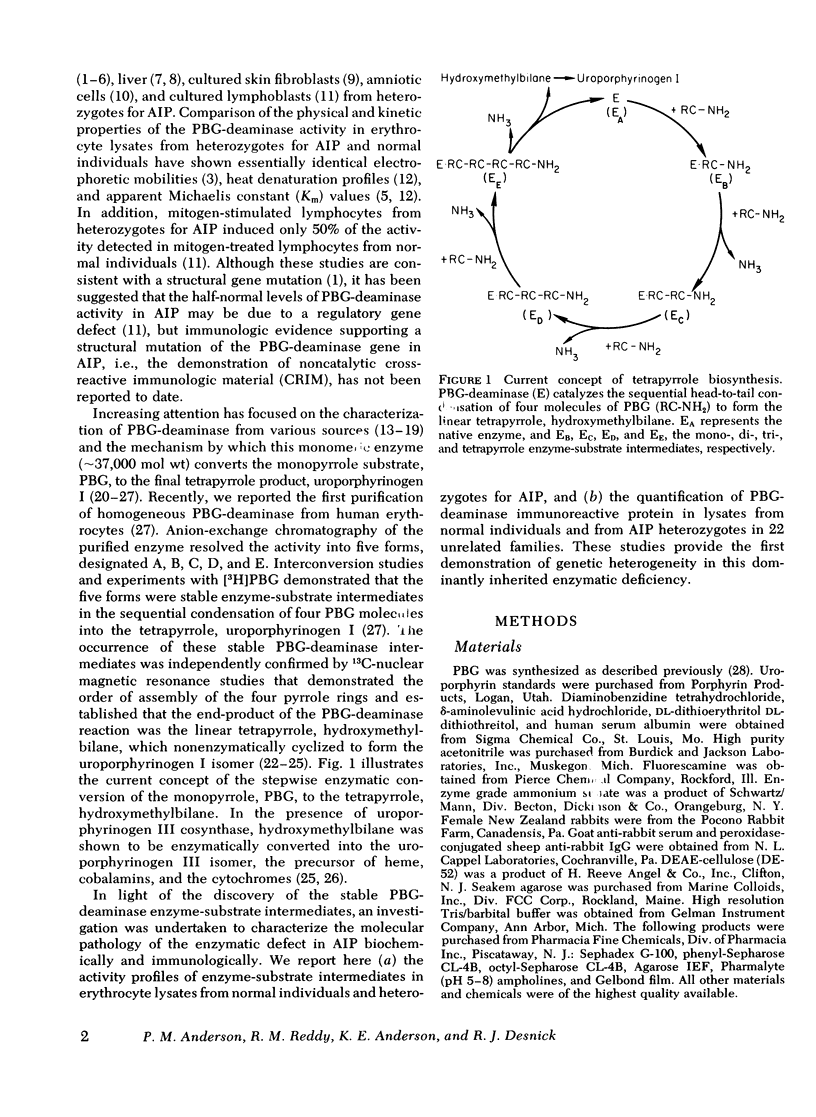
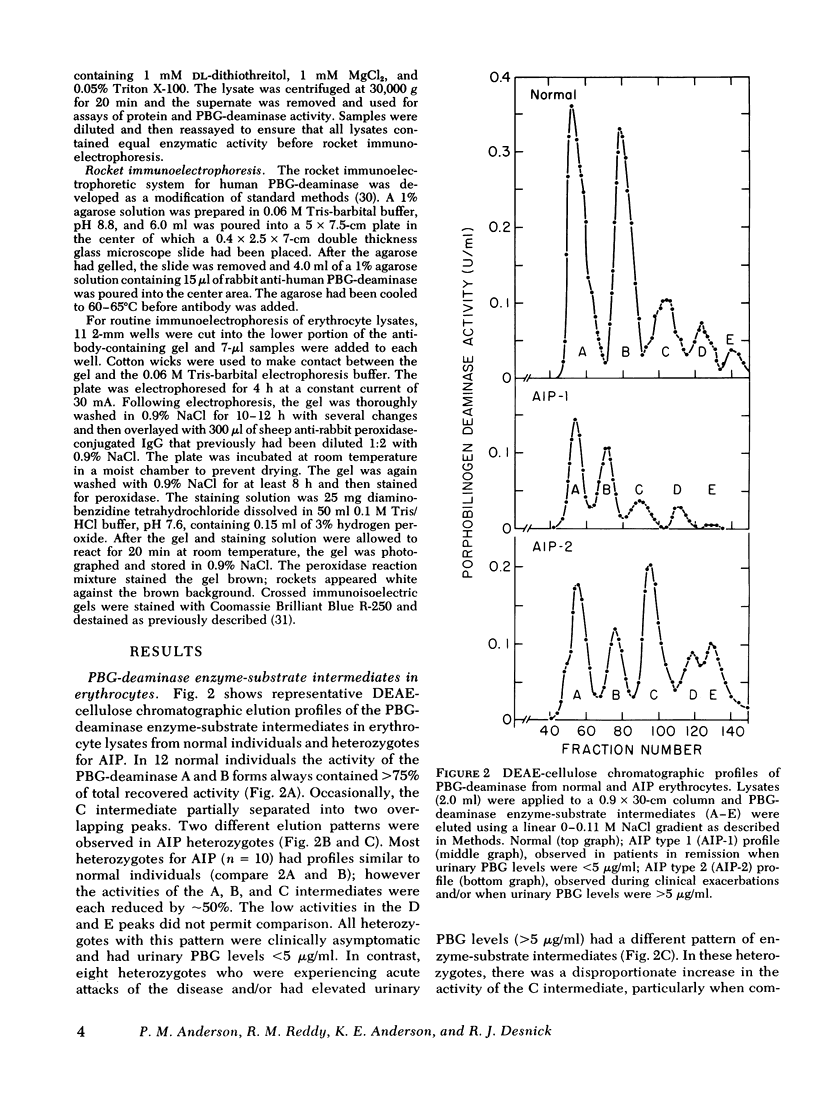
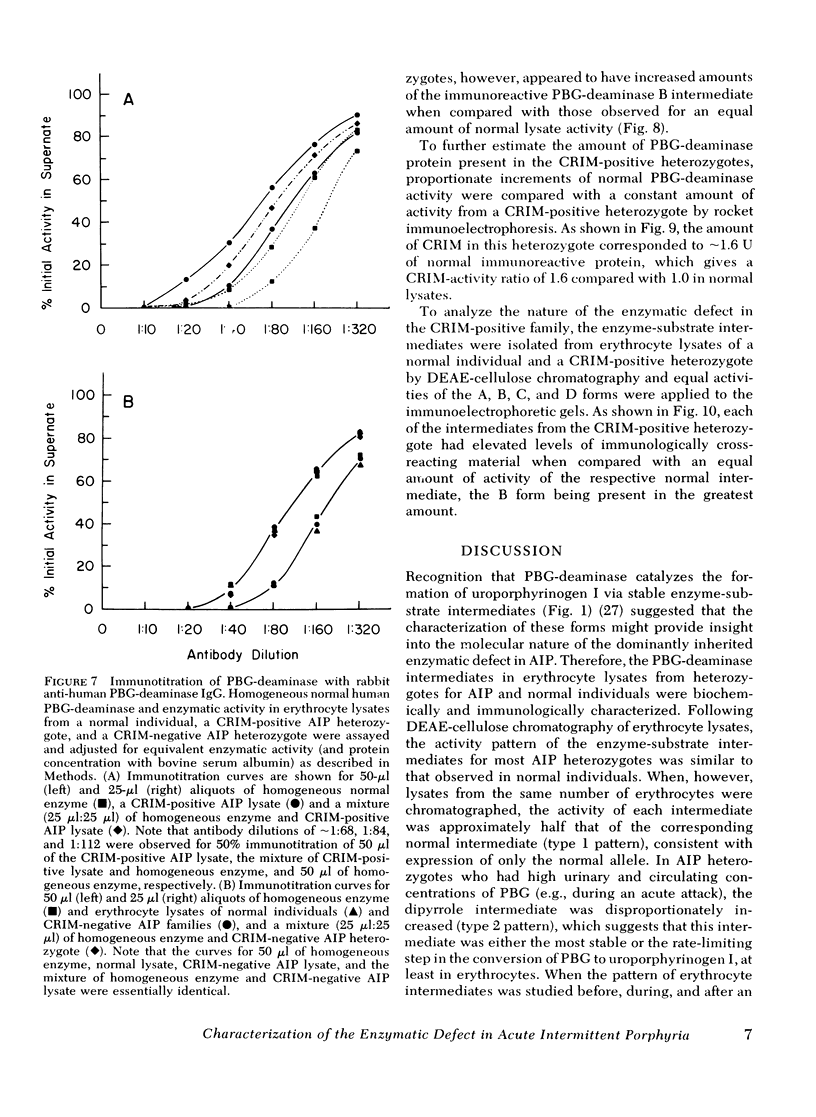
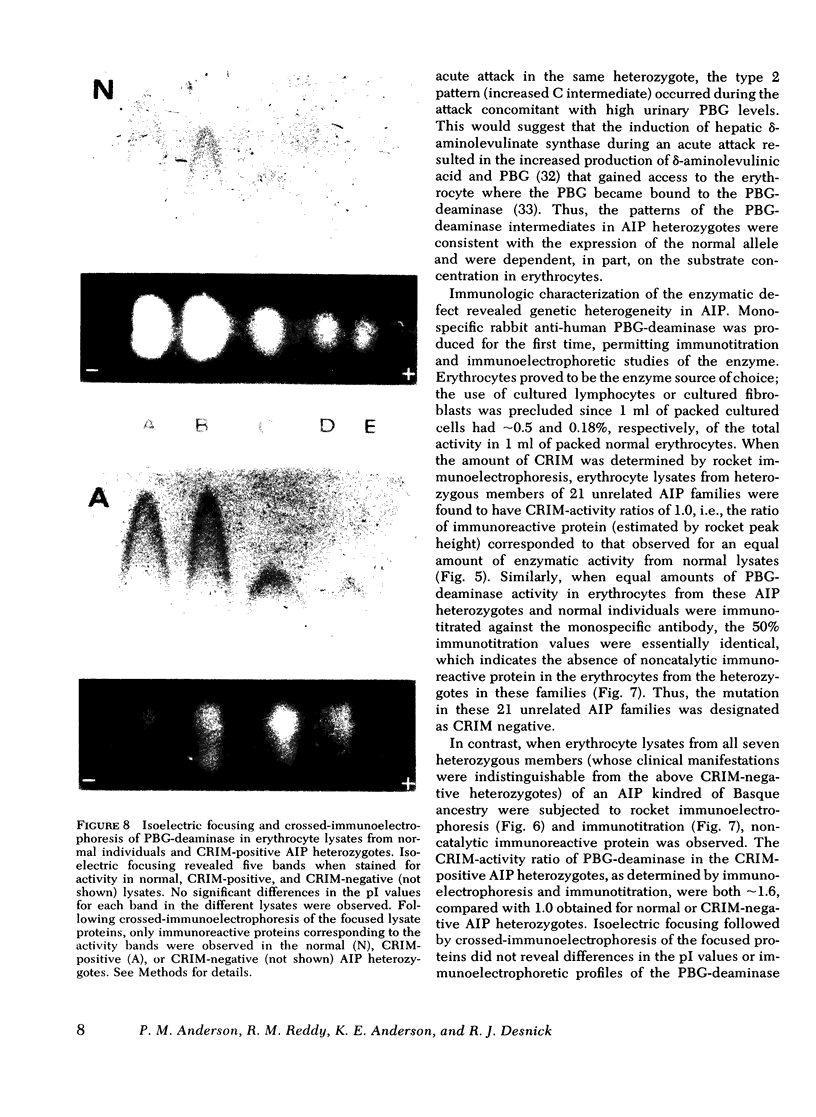
The molecular pathology of the porphobilinogen (PBG)-deaminase deficiency in heterozygotes for acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) was investigated by means of biochemical and immunologic techniques. The stable enzyme-substrate intermediates (A, B, C, D, and E) of PBG-deaminase were separated by anion-exchange chromatography of erythrocyte lysates from heterozygotes for AIP and normal individuals. In normal lysates, the intermediates eluted in a characteristic pattern with decreasing amounts of activity (A > B > C > D > E), the combined A and B intermediates representing >75% of total recovered activity. In contrast, two different profiles were observed in lysates from heterozygotes for AIP. In most heterozygotes, the elution profile was similar to that of normal individuals, but each intermediate was reduced ∼50%. A second profile in which the C intermediate had disproportionately higher activity than the A or B intermediates was observed in asymptomatic heterozygotes with high urinary levels of PBG (>5 μg/ml) as well as in heterozygotes during acute attacks. These findings suggested that the C intermediate (the dipyrrole-enzyme intermediate) may be rate limiting in the stepwise conversion of the monopyrrole, PBG, to the linear tetrapyrrole, hydroxymethylbilane. To investigate further the nature of the enzymatic defect in AIP, sensitive immunotitration and immunoelectrophoretic assays were developed with the aid of a rabbit anti-human PBG-deaminase IgG preparation produced against the homogeneous enzyme. Equal amounts of erythrocyte lysate activity from 32 heterozygotes for AIP from 22 unrelated families and 35 normal individuals were immunoelectrophoresed. There were no detectable differences in the amounts of cross-reactive immunologic material (CRIM) in lysates from the normal individuals and 25 heterozygotes from 21 of the 22 unrelated families with AIP. In contrast, when equal enzymatic activities were coimmunoelectrophoresed, all seven heterozygotes from one family had ∼ 1.6 times the amount of CRIM compared with that detected in normal lysates. Consistent with these findings, immunotitration studies also demonstrated similar quantities of noncatalytic CRIM in lysates from this AIP family. When equal activities of the individual A, B, C, and D enzyme-substrate intermediates from normal and CRIM-positive erythrocytes were immunoelectrophoresed, increased amounts of immunoreactive protein were observed for each intermediate, B > A ≃ C ≃ D, from the CRIM-positive AIP variants. On the basis of these findings, it is hypothesized that the enzymatic defect in the CRIM-positive AIP family resulted from a mutation in the structural gene for PBG-deaminase which altered the catalytic as well as a substrate binding site. These studies of the enzymatic defect provide the first demonstration of genetic heterogeneity in AIP.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P. M., Desnick R. J. Purification and properties of delta-aminolevulinate dehydrase from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6924–6930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P. M., Desnick R. J. Purification and properties of uroporphyrinogen I synthase from human erythrocytes. Identification of stable enzyme-substrate intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1993–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battersby A. R., Fookes C. J., Matcham G. W., McDonald E. Biosynthesis of the pigments of life: formation of the macrocycle. Nature. 1980 May 1;285(5759):17–21. doi: 10.1038/285017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battersby A. R. The discovery of nature's biosynthetic pathways. Experientia. 1978 Jan 15;34(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF01921870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beratis N. G., LaBadie G. U., Hirschhorn K. Characterization of the molecular defect in infantile and adult acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1264–1274. doi: 10.1172/JCI109247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonkowsky H. L., Tschudy D. P., Weinbach E. C., Ebert P. S., Doherty J. M. Porphyrin synthesis and mitochondrial respiration in acute intermittent porphyria: studies using cultured human fibroblasts. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jan;85(1):93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie M. J., Moore M. R., Goldberg A. Enzyme abnormalities in the porphyrias. Lancet. 1977 Oct 1;2(8040):699–701. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90507-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corash L. M., Piomelli S., Chen H. C., Seaman C., Gross E. Separation of erythrocytes according to age on a simplified density gradient. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jul;84(1):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. C., Neuberger A. Polypyrroles formed from porphobilinogen and amines by uroporphyrinogen synthetase of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):471–492. doi: 10.1042/bj1330471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman B., Frydman R. B., Valasinas A., Levy S., Feinstein G. The mechanism of uroporphyrinogen biosynthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:371–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman R. B., Frydman B. Purification and properties of porphobilinogen deaminase from wheat germ. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jan;136(1):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Bogorad L. The purification and properties of uroporphyrinogen I synthases and uroporphyrinogen III cosynthase. Interactions between the enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:401–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. M., Berry A. Preuroporphyrinogen, a universal intermediate in the biosynthesis of uroporphyrinogen III. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 24;112(1):86–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. M., Seehra J. S. The biosynthesis of uroporphyrinogen III: order of assembly of the four porphobilinogen molecules in the formation of the tetrapyrrole ring. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 15;104(2):364–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80853-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. M., Shemin D. Purification and properties of uroporphyrinogen I synthetase from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):1019–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Holland J. P., Dozy A. M., Charache S., Kazazian H. H. Deletion of the beta-globin structure gene in hereditary persistence of foetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):162–163. doi: 10.1038/258162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Holland J. P., Dozy A. M., Varmus H. E. Demonstration of non-functional beta-globin mRNA in homozygous beta (0) thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor J. A., Turner P. H., Nienhuis A. W. Beta Thalassemia: mutations which affect processing of the beta-Globin mRNA precursor. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnussen C. R., Levine J. B., Doherty J. M., Cheesman J. O., Tschudy D. P. A red cell enzyme method for the diagnosis of acute intermittent porphyria. Blood. 1974 Dec;44(6):857–868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer U. A., Strand L. J., Doss M., Rees A. C., Marver H. S. Intermittent acute porphyria--demonstration of a genetic defect in porphobilinogen metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jun 15;286(24):1277–1282. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197206152862401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyagi K., Cardinal R., Bossenmaier I., Watson C. J. The serum porphobilinogen and hepatic porphobilinogen deaminase in normal and porphyric individuals. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Nov;78(5):683–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyagi K., Kaneshima M., Kawakami J., Nakada F., Petryka Z. J., Watson C. J. Uroporphyrinogen I synthase from human erythrocytes: separation, purification, and properties of isoenzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6172–6176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prager E. M., Wilson A. C. The dependence of immunological cross-reactivity upon sequence resemblance among lysozymes. I. Micro-complement fixation studies. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5978–5989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Shander M. H., Manley J. L., Gefter M. L., Maniatis T. Structure and in vitro transcription of human globin genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1329–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.6158093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell C. S., Rockwell P. The effects of sulfhydryl reagents on the activity of wheat germ uroporphyrinogen I synthase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80643-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancovich H. A., Battle A. M., Grinstein M. Porphyrin biosynthesis. VI. Separation and purification of porphobilinogen deaminase and uroporphyrinogen isomerase from cow liver. Porphobilinogenase an allosteric enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Sep 30;191(1):130–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Granick S., Bickers D. R., Bradlow H. L., Kappas A. A microassay for uroporphyrinogen I synthase, one of three abnormal enzyme activities in acute intermittent porphyria, and its application to the study of the genetics of this disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):732–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Solish G., Levere R. D., Kappas A. Studies in porphyria. IV. Expression of the gene defect of acute intermittent porphyria in cultured human skin fibroblasts and amniotic cells: prenatal diagnosis of the porphyric trait. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):722–731. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Zalar G. L., Kappas A. Studies in porphyria. VII. Induction of uroporphyrinogen-I synthase and expression of the gene defect of acute intermittent porphyria in mitogen-stimulated human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):499–508. doi: 10.1172/JCI108961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. I., Hos K. S., Kajiwara M., Takahashi T. Letter: Biosynthesis of uroporphyrinogen III from porphobilinogen. Resolution of the enigmatic "switch" mechanism. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Mar 17;98(6):1589–1591. doi: 10.1021/ja00422a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens E., Frydman R. B., Frydman B. Separation of porphobilinogen deaminase and uroporphyrinogen 3 cosynthetase from human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 24;158(3):496–498. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand L. J., Felsher B. F., Redeker A. G., Marver H. S. Heme biosynthesis in intermittent acute prophyria: decreased hepatic conversion of porphobilinogen to porphyrins and increased delta aminolevulinic acid synthetase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1315–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand L. J., Meyer U. A., Felsher B. F., Redeker A. G., Marver H. S. Decreased red cell uroporphyrinogen I synthetase activity in intermittent acute porphyria. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2530–2536. doi: 10.1172/JCI107068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton H. E., Wagner R. P. Mutation and enzyme function in humans. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:187–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSCHUDY D. P., PERLROTH M. G., MARVER H. S., COLLINS A., HUNTER G., Jr, RECHCIGL M., Jr ACUTE INTERMITTENT PORPHYRIA: THE FIRST "OVERPRODUCTION DISEASE" LOCALIZED TO A SPECIFIC ENZYME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:841–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Recent developments in the molecular genetics of human hemoglobin. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):467–479. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]