Abstract
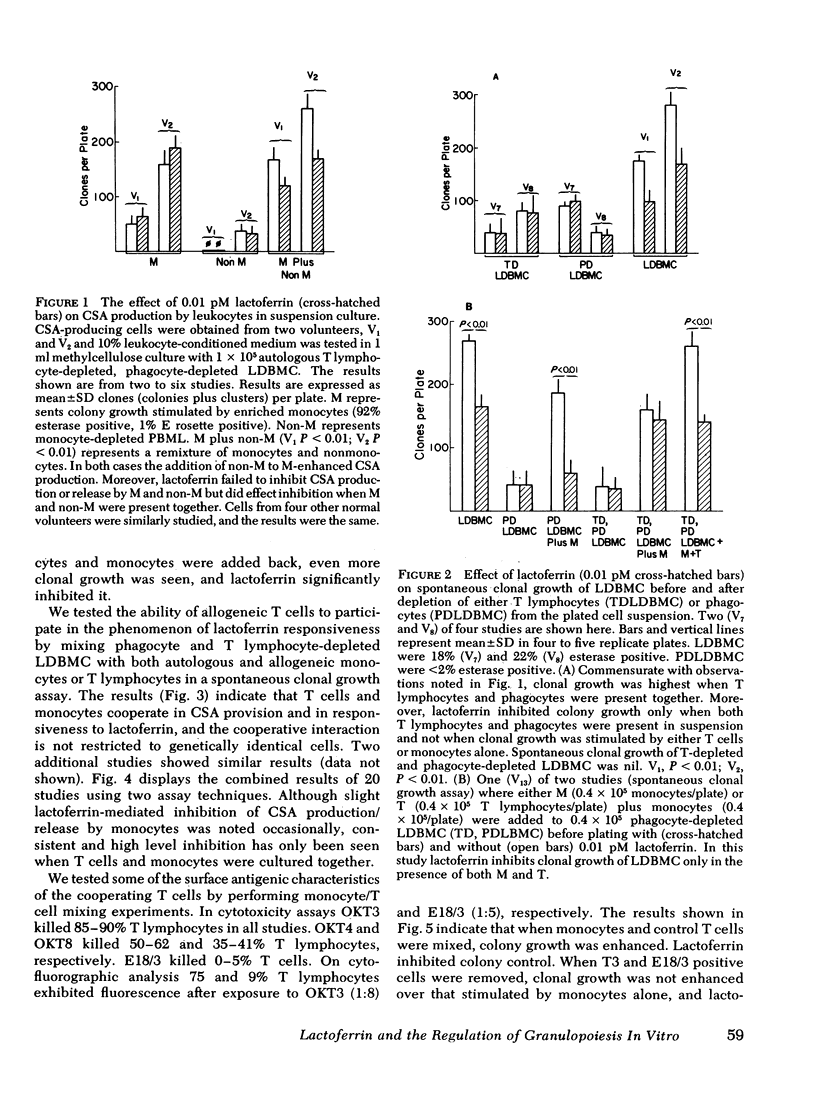
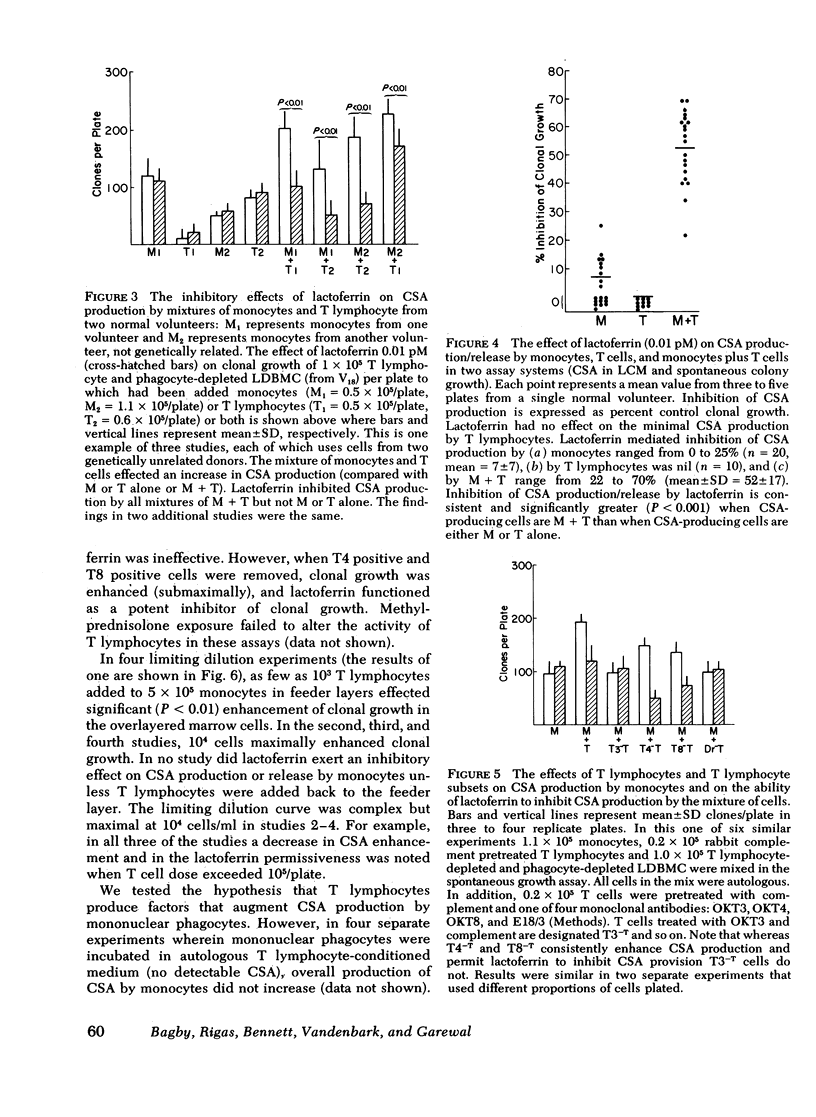
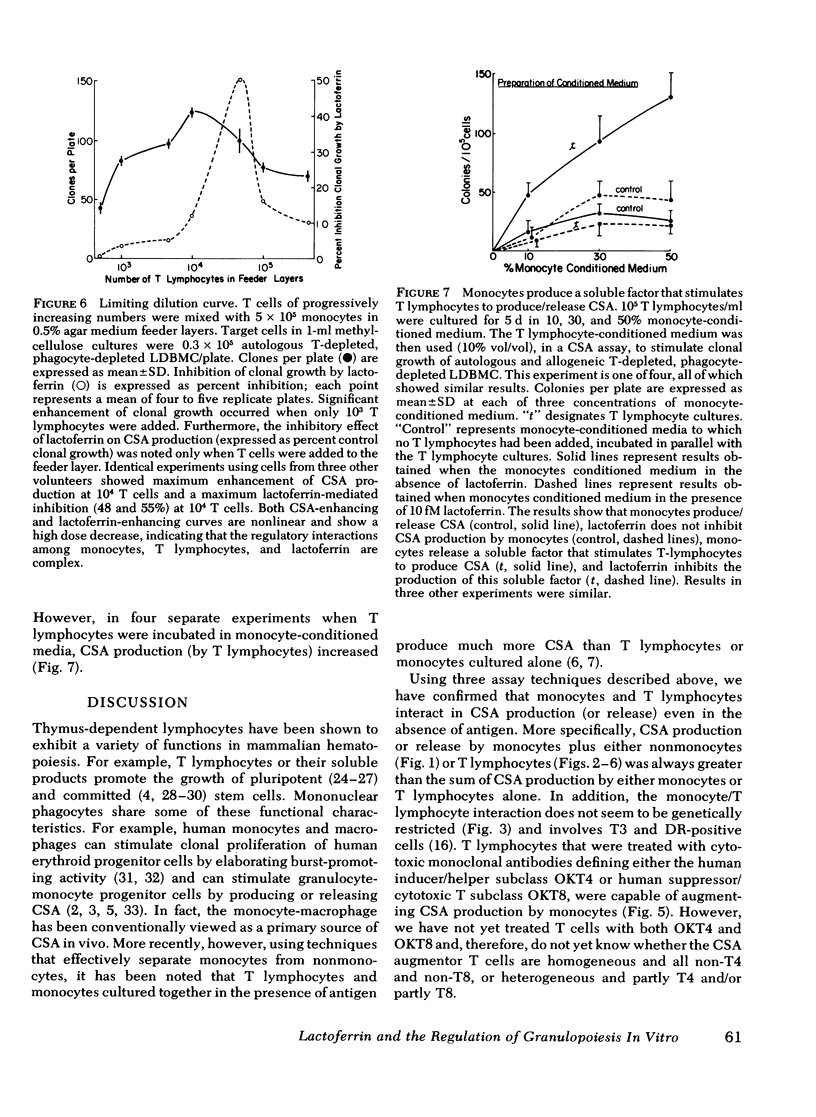
Colony-stimulating activities (CSA) are potent granulopoietic stimulators in vitro. Using clonogenic assay techniques, we analyzed the degree to which mononuclear phagocytes and T lymphocytes cooperate in the positive (production/release of CSA) and feedback (inhibition of CSA production/release) regulation of granulopoiesis. We measured the effect of lactoferrin (a putative feedback regulator of CSA production) on CSA provision in three separate assay systems wherein granulocyte colony growth of marrow cells from 22 normal volunteers was stimulated by (a) endogenous CSA-producing cells in the marrow cells suspension, (b) autologous peripheral blood leukocytes in feeder layers, and (c) medium conditioned by peripheral blood leukocytes. The CSA-producing cell populations in each assay were varied by using cell separation techniques and exposure of isolated T lymphocytes to methylprednisolone or to monoclonal antibodies to surface antigens and complement. We noted that net CSA production increased more than twofold when a small number of unstimulated T lymphocytes were added to monocyte cultures. Lactoferrin's inhibitory effect was also T lymphocyte dependent. The T lymphocytes that interact with monocytes and lactoferrin to inhibit CSA production are similar to those that augment CSA production because their activities are neither genetically restricted not glucocorticoid sensitive, and both populations express HLA-DR (Ia-like) and T3 antigens but not T4 or T8 antigens. These findings are consistent with results of our studies on the mechanism of lactoferrin's inhibitory effect with indicate that mononuclear phagocytes produce both CSA and soluble factors that stimulate T lymphocytes to produce CSA, and that lactoferrin does not suppress monocyte CSA production, but does completely suppress production or release by monocytes of those factors that stimulate T lymphocytes to produce CSA. We conclude that mononuclear phagocytes and a subset of T lymphocytes exhibit important complex interactions in the regulation of granulopoiesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainscough E. W., Brodie A. M., Plowman J. E., Bloor S. J., Loehr J. S., Loehr T. M. Studies on human lactoferrin by electron paramagnetic resonance, fluorescence, and resonance Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 19;19(17):4072–4079. doi: 10.1021/bi00558a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aye M. T. Erythroid colony formation in cultures of human marrow: effect of leukocyte conditioned medium. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Apr;91(1):69–77. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. C., Jr, Gabourel J. D. Neutropenia in three patients with rheumatic disorders. Suppression of granulopoiesis by control-sensitive thymus-dependent lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):72–82. doi: 10.1172/JCI109465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby G. C., Jr, Goodnight S. H., Mooney W. M., Richert-Boe K. Prednisone-responsive aplastic anemia: a mechanism of glucocorticoid action. Blood. 1979 Aug;54(2):322–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Mohla C. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the measurement of lactoferrin in human plasma: variations with age, sex, and disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jul;88(1):156–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., DeSousa M., Smithyman A., Ralph P., Hamilton J., Kurland J. I., Bognacki J. Specificity and modulation of the action of lactoferrin, a negative feedback regulator of myelopoiesis. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):324–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., DeSousa M., Smithyman A., Ralph P., Hamilton J., Kurland J. I., Bognacki J. Specificity and modulation of the action of lactoferrin, a negative feedback regulator of myelopoiesis. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):324–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E. Lactoferrin acts on Ia-like antigen-positive subpopulations of human monocytes to inhibit production of colony stimulatory activity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1717–1720. doi: 10.1172/JCI109635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Smithyman A., Eger R. R., Meyers P. A., de Sousa M. Identification of lactoferrin as the granulocyte-derived inhibitor of colony-stimulating activity production. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1052–1067. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burek V., Plavljanić D., Slamberger S., Vitale B. Studies on the mechanism of allogeneic disease in mice. I. The influence of bone marrow T lymphocytes on the differentiation and proliferation of hemopoietic stem cells. Exp Hematol. 1977 Nov;5(6):465–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Metcalf D. The nature and action of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factors. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):947–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., Engelman E. G., Benike C. J., McDevitt H. O. Ia antigens on alloreactive T cells in man detected by monoclonal antibodies. Evidence for synthesis of HLA-D/DR molecules of the responder type. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):127s–136s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervenick P. A., LoBuglio A. F. Human blood monocytes: stimulators of granulocyte and mononuclear colony formation in vitro. Science. 1972 Oct 13;178(4057):164–166. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4057.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervenick P. A., LoBuglio A. F. Human blood monocytes: stimulators of granulocyte and mononuclear colony formation in vitro. Science. 1972 Oct 13;178(4057):164–166. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4057.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Cline M. J. Identification of the colony-stimulating cell in human peripheral blood. J Clin Invest. 1972 Nov;51(11):2981–2983. doi: 10.1172/JCI107124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. W., Burch K. T., Basford N. L. Graft-vs.-Host activity of thymocytes: relationship to the role of thymocytes in hemopoiesis. Blood. 1972 Jun;39(6):850–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellmann A., Th'ng K. H., Goldman J. M. Production of colony stimulating activity in mixed mononuclear cell culture. Br J Haematol. 1980 Jun;45(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb07144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai K., Itoh K., Hinuma S., Tada M. Pretreatment of plastic Petri dishes with fetal calf serum. A simple method for macrophage isolation. J Immunol Methods. 1979;29(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung P., Goldstein G., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Monoclonal antibodies defining distinctive human T cell surface antigens. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):347–349. doi: 10.1126/science.314668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffell M. S., Spitznagel J. K. Association of lactoferrin with lysozyme in granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):761–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.761-765.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendes N. F., Tolnai M. E., Silveira N. P., Gilbertsen R. B., Metzgar R. S. Technical aspects of the rosette tests used to detect human complement receptor (B) and sheep erythrocyte-binding (T) lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Sep;111(3):860–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. G., Chess L., Hillman D. G., Clarke B., Breard J., Merler E., Housman D. E. Human erythroid burst-forming unit: T-cell requirement for proliferation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):324–339. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. W., Metcalf D. Production of colony-stimulating factor in mitogen-stimulated lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Current concepts in immunology: Regulation of the immune response--inducer and suppressor T-lymphocyte subsets in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 14;303(7):370–373. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008143030704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Chervenick P. A. Release of colony-stimulating activity from thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):520–527. doi: 10.1172/JCI107958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck R. K., Boegel F., Pope F., Waheed A. Binding of colony stimulating factor by sterile filtration membranes. Exp Hematol. 1978 Apr;6(4):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah R. G., Caporale L. H., Moore M. A. Characterization of colony-stimulating activity produced by human monocytes and phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocytes. Blood. 1977 Nov;50(5):811–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucco M. M., Garotta G., Stocker J. W., Ceppellini R. Murine monoclonal antibodies against HLA structures. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:219–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma D. S., Spitzer G., Zander A. R., Fisher R., McCredie K. B., Dicke K. A. T lymphocyte and monocyte-macrophage interaction in colony-stimulating activity elaboration in man. Blood. 1979 Dec;54(6):1376–1383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor-Jedrzejczak W., Sharkie S., Ahmed A., Sell K. W., Santos G. W. Theta-sensitive cell and erythropoiesis: identification of a defect in W/Wv anemic mice. Science. 1977 Apr 15;196(4287):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.322288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., McCune J. M., Fu S. M., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Two types of Ia-positive T cells. Synthesis and exchange of Ia antigens. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):89s–98s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipori D., Trainin N. The role of a thymus humoral factor in the proliferation of bone marrow CFU-S from thymectomized mice. Exp Hematol. 1975 Nov;3(6):389–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman K. S. Stimulation of human BFU(E) by products of human monocytes and lymphocytes. Exp Hematol. 1980 Aug;8(7):924–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



