Abstract
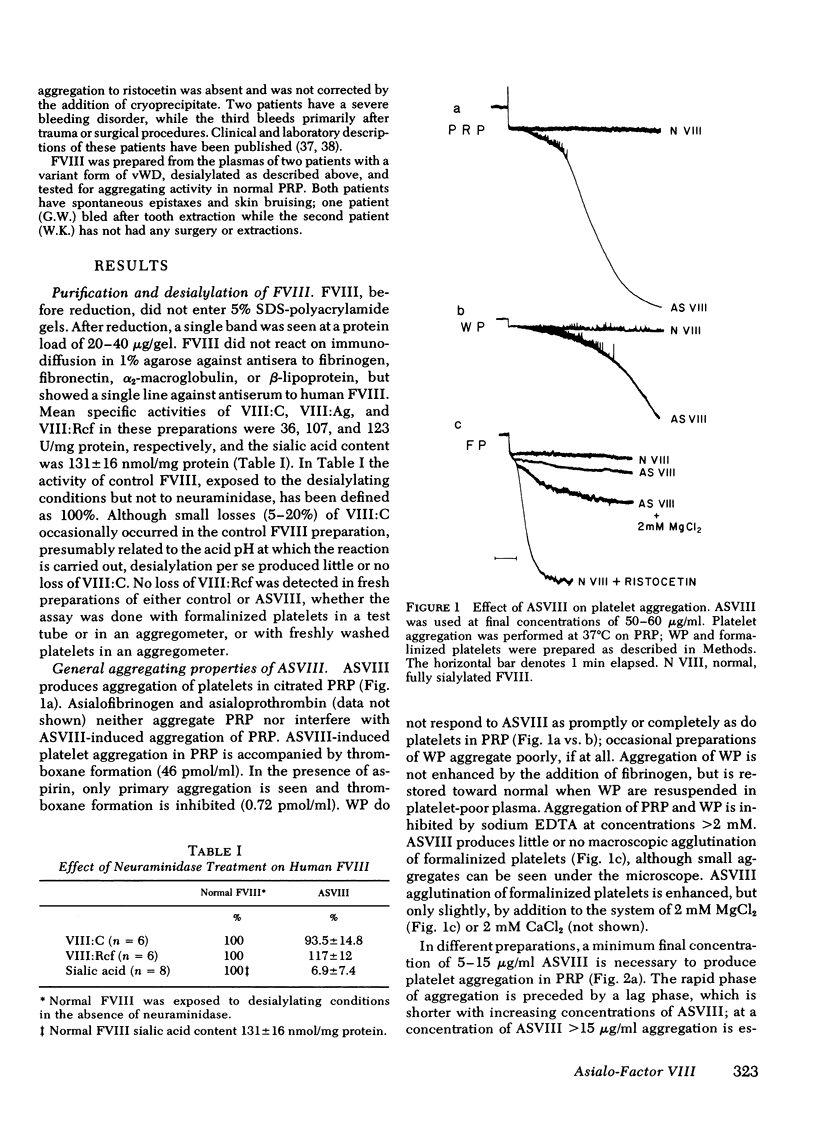
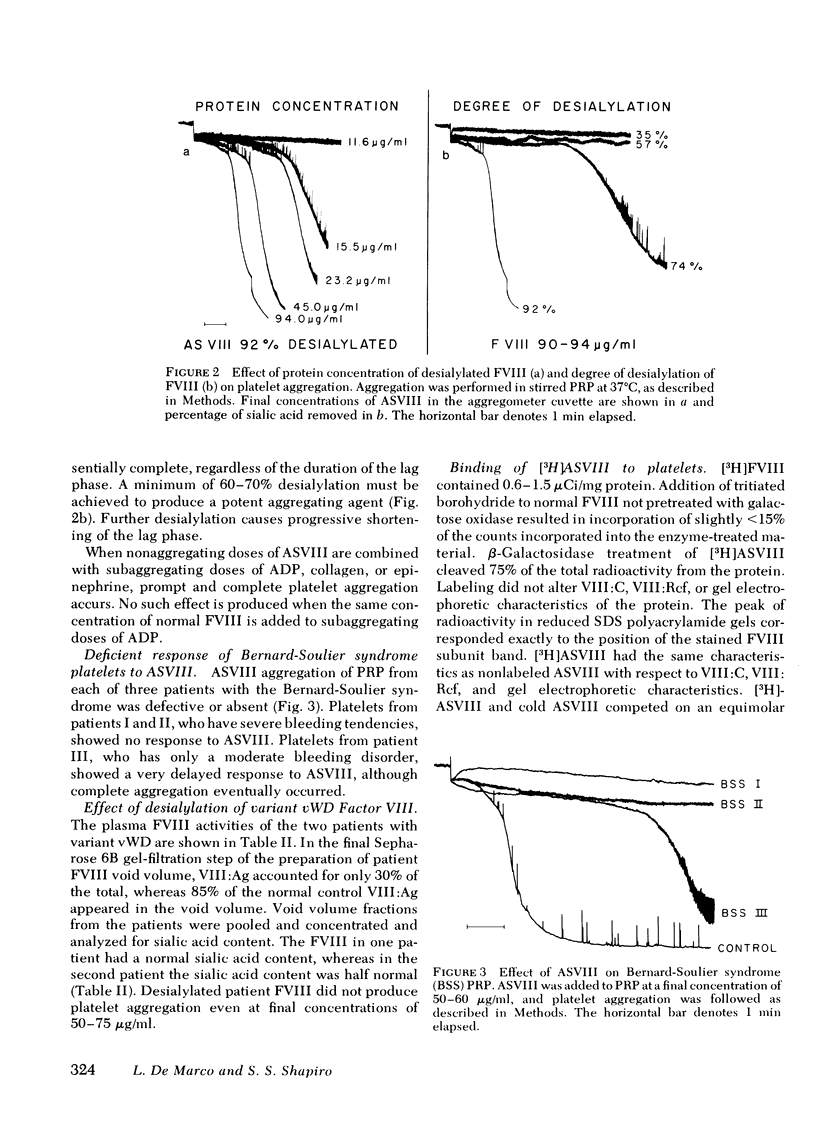
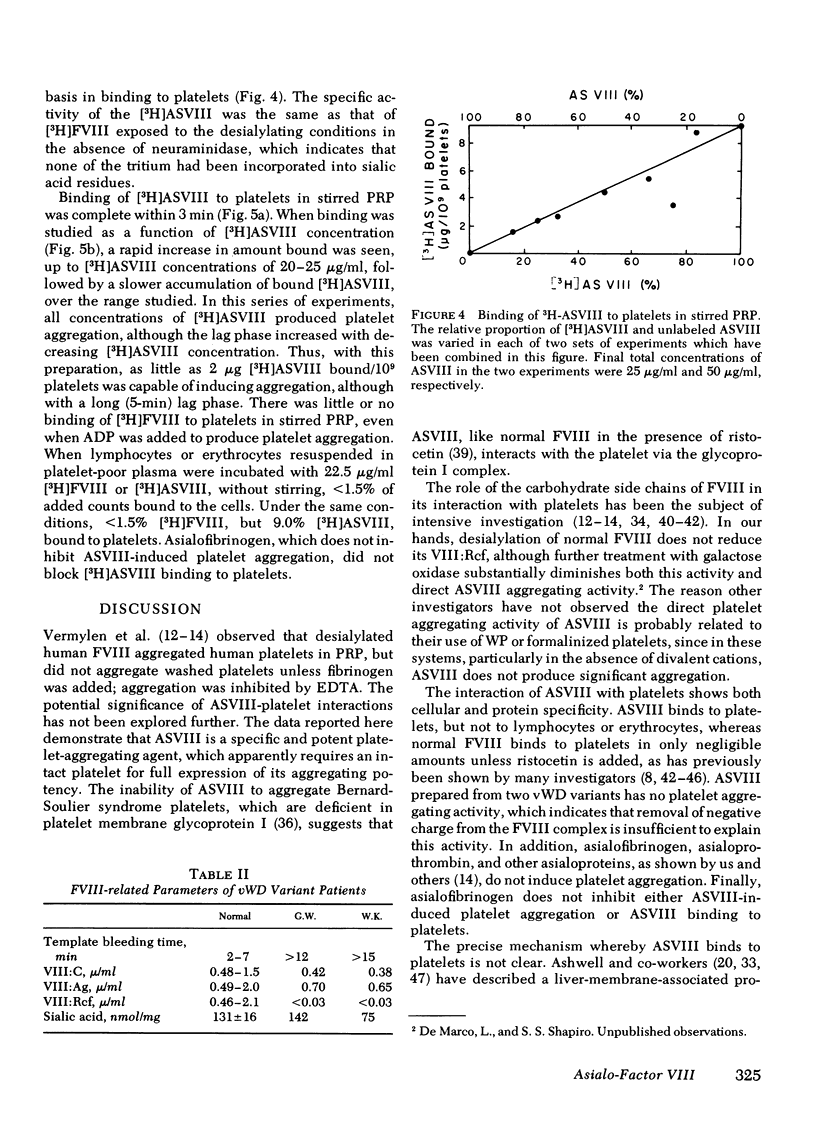
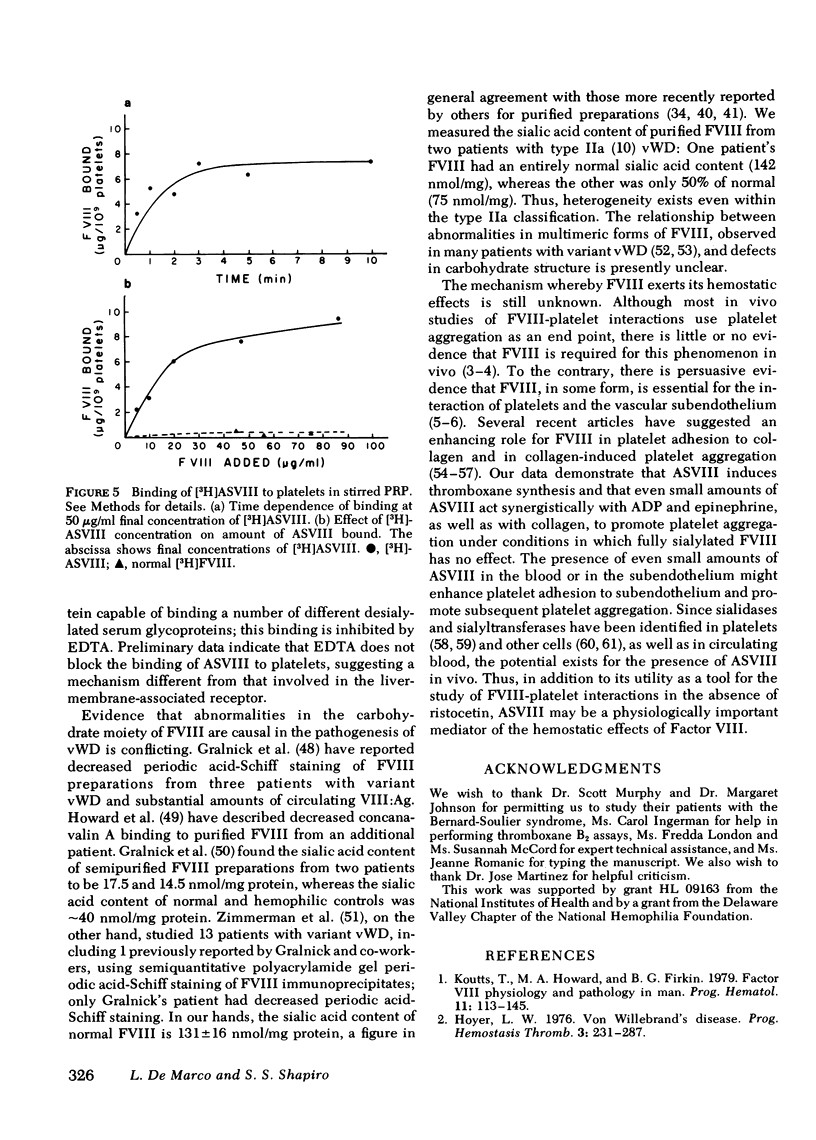
Human Factor VIII desialylated by treatment with Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase (ASVIII) aggregated human platelets in the absence of ristocetin in platelet-rich plasma and, to a lesser extent, in washed platelet suspensions. Aggregation is accompanied by thromboxane formation and is completely inhibited by EDTA. Aspirin blocks the second phase of aggregation and abolishes thromboxane production. Subaggregating doses of ASVIII and of either ADP, epinephrine, or collagen produce prompt and complete platelet aggregation. Bernard-Soulier syndrome platelets either did not aggregate with ASVIII (Two cases) or showed markedly decreased aggregation (one cases). Factor VIII complex was prepared from the plasma of two patients with variant von Willebrand's disease (sialic acid content 142 and 75 nmol/mg, respectively); neither protein generated platelet-aggregating activity upon desialylation. [3H]ASVIII binds rapidly to platelets and 37 degrees C, while tritiated, fully sialylated factor VIII binds to a negligible extent. As little as 1--2 micrograms ASVIII bound/10(9) platelets is capable of inducing platelet aggregation. ASVIII may be a useful tool for investigating platelet-Factor VIII interactions in the absence of ristocetin. Furthermore, desialylated Factor VIII might play a physiologic role in Factor VIII-mediated platelet reactions in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain J. P., Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Platelets fixed with paraformaldehyde: a new reagent for assay of von Willebrand factor and platelet aggregating factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):318–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baugh R. F., Jacoby J. C., Brown J. E. Collagen-induced platelet aggregation is enhanced by bovine von Willebrand factor. Thromb Res. 1979;16(1-2):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt P. M., Brinkhous K. M., Culp H. R., Krauss J. S., Roberts H. R. Antihemophilic factor concentrate therapy in von Willebrand disease. Dissociation of bleeding-time factor and ristocetin-cofactor activities. JAMA. 1976 Dec 13;236(24):2770–2772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B. Identification, purification and characteristics of glycosidases of human blood platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 20;258(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90984-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B. Platelet adhesiveness and aggregation. II. Surface sialic acid, glycoprotein: N-acetylneuraminic acid transferase, and neuraminidase of human blood platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 25;279(3):456–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caen J. P., Nurden A. T., Jeanneau C., Michel H., Tobelem G., Levy-Toledano S., Sultan Y., Valensi F., Bernard J. Bernard-Soulier syndrome: a new platelet glycoprotein abnormality. Its relationship with platelet adhesion to subendothelium and with the factor VIII von Willebrand protein. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Apr;87(4):586–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. The effects of ristocetin and von Willebrand factor on platelet electrophoretic mobility. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1168–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI109032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Coller B. S., Sultan Y. Carbohydrate deficiency of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor Protein in von Willebrand's disease variants. Science. 1976 Apr 2;192(4234):56–59. doi: 10.1126/science.1083071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R. Factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein. Galactose a cryptic determinant of von Willebrand factor activity. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):496–499. doi: 10.1172/JCI109152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Sultan Y., Coller B. S. Von Willebrand's disease: combined qualitative and quantitative abnormalities. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 5;296(18):1024–1030. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197705052961802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. The proteolytic nature of commercial samples of galactose oxidase. Purification of the enzyme by a simple affinity method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 8;438(2):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauptman S. P., Kansu E., Serno M., Godfrey S. Human macromolecular insoluble cold globulin (MICG). I. T-cell origin of T-MICG and null cell origin of N-MICG. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):158–171. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovig T., Stormorken H. Ultrastructural studies on the platelet plug formation in bleeding time wounds from normal individuals and patients with von Willebrand's disease. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1974;Suppl 248:105–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Hendrix L., Firkin B. G. Further studies on the factor VIII of a patient with a variant form of von Willebrand's disease. Thromb Res. 1979;14(4-5):609–619. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Von Willebrand's disease. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:231–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G., Stockert R. J., Morell A. G. The isolation and properties of a rabbit liver binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORGENSEN L., BORCHGREVINK C. F. THE HAEMOSTATIC MECHANISM IN PATIENTS WITH HAEMORRHAGIC DISEASES. A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF WOUNDS MADE FOR PRIMARY AND SECONDARY BLEEDING TIME TESTS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1964;60:55–82. doi: 10.1111/apm.1964.60.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAZAL L. A., AMSEL S., MILLER O. P., TOCANTINS L. M. THE PREPARATION AND SOME PROPERTIES OF FIBRINOGEN PRECIPITATED FROM HUMAN PLASMA BY GLYCINE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Aug-Sep;113:989–994. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. J., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Demonstration and characterization of specific binding sites for factor VIII/von Willebrand factor on human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):656–664. doi: 10.1172/JCI109348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. J., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Platelet receptors for human Factor VIII/von Willebrand protein: functional correlation of receptor occupancy and ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5317–5320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby E. P. Factor VIII-associated platelet aggregation. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Dec 15;38(4):1054–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koutts J., Howard M. A., Firkin B. G. Factor VIII physiology and pathology in man. Prog Hematol. 1979;11:115–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Johnson M. M., Aster R. H. Absence of the platelet receptor for drug-dependent antibodies in the Bernard-Soulier syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):716–719. doi: 10.1172/JCI109181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewy R. I., Smith J. B., Silver M. J., Saia J., Walinsky P., Wiener L. Detection of thromboxane B2 in peripheral blood of patients with Prinzmetal's angina. Prostaglandins Med. 1979 Apr;2(4):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(79)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane D. E., Stibbe J., Kirby E. P., Zucker M. B., Grant R. A., McPherson J. Letter: A method for assaying von Willebrand factor (ristocetin cofactor). Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Sep 30;34(1):306–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Obert B., Pietu G., Lavergne J. M., Zimmerman T. S. Multimeric structure of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in von Willebrand's disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Apr;95(4):590–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Gregoriadis G., Scheinberg I. H., Hickman J., Ashwell G. The role of sialic acid in determining the survival of glycoproteins in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1461–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Irvine R. A., Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H., Ashwell G. Physical and chemical studies on ceruloplasmin. V. Metabolic studies on sialic acid-free ceruloplasmin in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):155–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A. G., Van den Hamer C. J., Scheinberg I. H., Ashwell G. Physical and chemical studies on ceruloplasmin. IV. Preparation of radioactive, sialic acid-free ceruloplasmin labeled with tritium on terminal D-galactose residues. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3745–3749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin R. J., Chen A. F., Narayanan A. S., Raye C., Moss R. A., Srikantaiah M. V., Barajas L. Platelet adhesion to collagen in normal and von Willebrand's disease subjects. Thromb Res. 1980 Mar 1;17(5):719–728. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90375-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morisato D. K., Gralnick H. R. Selective binding of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein to human platelets. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Jaffe E. A., Weksler B. B. Immunoinhibition of ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):143–148. doi: 10.1172/JCI108612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J., Johnson A. J., Karpatkin M. H., Puszkin S. Methods for the production of clinically effective intermediate- and high-purity factor-VIII concentrates. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jul;21(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyman D. Von Willebrand factor dependent platelet aggregation and adsorption of factor VIII related antigen by collagen. Thromb Res. 1980 Jan 1;17(1-2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOL J. G., GERSHGOLD E. J., PAPPENHAGEN A. R. HIGH-POTENCY ANTIHAEMOPHILIC FACTOR CONCENTRATE PREPARED FROM CRYOGLOBULIN PRECIPITATE. Nature. 1964 Jul 18;203:312–312. doi: 10.1038/203312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., CRUM J. D. ACTIVATION OF HAGEMAN FACTOR BY SOLUTIONS OF ELLAGIC ACID. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Mar;63:359–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Saito H. Letter: Bleeding in von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 9;290(19):1089–1089. doi: 10.1056/nejm197405092901921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld L., Kirby E. P. The effects of neuraminidase treatment on the biological activities of factor VIII. Thromb Res. 1979;15(1-2):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Pareti F. I., Mannucci P. M., Ciavarella N., Zimmerman T. S. Heightened interaction between platelets and factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in a new subtype of von Willebrand's disease. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 8;302(19):1047–1051. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005083021902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Variant von Willebrand's disease: characterization of two subtypes by analysis of multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in plasma and platelets. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1318–1325. doi: 10.1172/JCI109795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Bolhuis P. A., Sixma J. J. Human blood platelet adhesion to artery subendothelium is mediated by factor VIII-Von Willebrand factor bound to the subendothelium. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):636–638. doi: 10.1038/279636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Trip M. D., Jenkins C. S., Kahlé L. H., Sturk A., ten Cate J. W. Studies on the mechanism of ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation: binding of factor VIII to platelets. Br J Haematol. 1979 Sep;43(1):99–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb03725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodetz J. M., Paulson J. C., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Carbohydrate on human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Impairment of function by removal of specific galactose residues. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7202–7206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Nishioka J., Hashimoto S. Identical binding site on human platelets for von Willebrand factor and bovine platelet aggregating factor. Thromb Res. 1980 Jan 1;17(1-2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Studies on human antihemophilic factor. Evidence for a covalently linked subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):925–937. doi: 10.1172/JCI108369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THELIN G. M., WGNER R. H. Sedimentation of plasma antihemophilic factor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Oct;95:70–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp T. B., Baumgartner H. R., Meyer D. Antibody to human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor inhibits collagen-induced platelet aggregation and release. Thromb Res. 1980 Jan 1;17(1-2):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermylen J., Bottecchia D., Szpilman H. Factor VIII and human platelet aggregation. III. Further studies on aggregation of humna platelets by neuraminidase-treated human factor VIII. Br J Haematol. 1976 Oct;34(2):321–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermylen J., De Gaetano G., Donati M. B., Verstraete M. Platelet-aggregating activity in neuraminidase-treated human cryoprecipitates: its correlation with factor-VIII-related antigen. Br J Haematol. 1974 Apr;26(4):645–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermylen J., Donati M. B., De Gaetano G., Verstraete M. Aggregation of human platelets by bovine or human factor VIII: role of carbohydrate side chains. Nature. 1973 Jul 20;244(5412):167–168. doi: 10.1038/244167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N. Albumin density gradient separation and washing of platelets and the study of platelet coagulant activities. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):205–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N., Mills D. C., Pareti F. I., Stewart G. J., Macfarlane D. E., Johnson M. M., Egan J. J. Hereditary giant platelet syndrome. Absence of collagen-induced coagulant activity and deficiency of factor-XI binding to platelets. Br J Haematol. 1975 Apr;29(4):639–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb02750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Baumgartner H. R., Tschopp T. B., Turitto V. T., Cohen D. Correction by factor VIII of the impaired platelet adhesion to subendothelium in von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1978 Feb;51(2):267–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Hoyer L. W., Rickles F. R., Varma A., Rogers J. Quantitative assay of a plasma factor deficient in von Willebrand's disease that is necessary for platelet aggregation. Relationship to factor VIII procoagulant activity and antigen content. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2708–2716. doi: 10.1172/JCI107465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Hoyer L. W., Dickson L., Edgington T. S. Determination of the von Willebrand's disease antigen (factor VIII-related antigen) in plasma by quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jul;86(1):152–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Voss R., Edgington T. S. Carbohydrate of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in von Willebrand's disease. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1298–1302. doi: 10.1172/JCI109585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



