Abstract
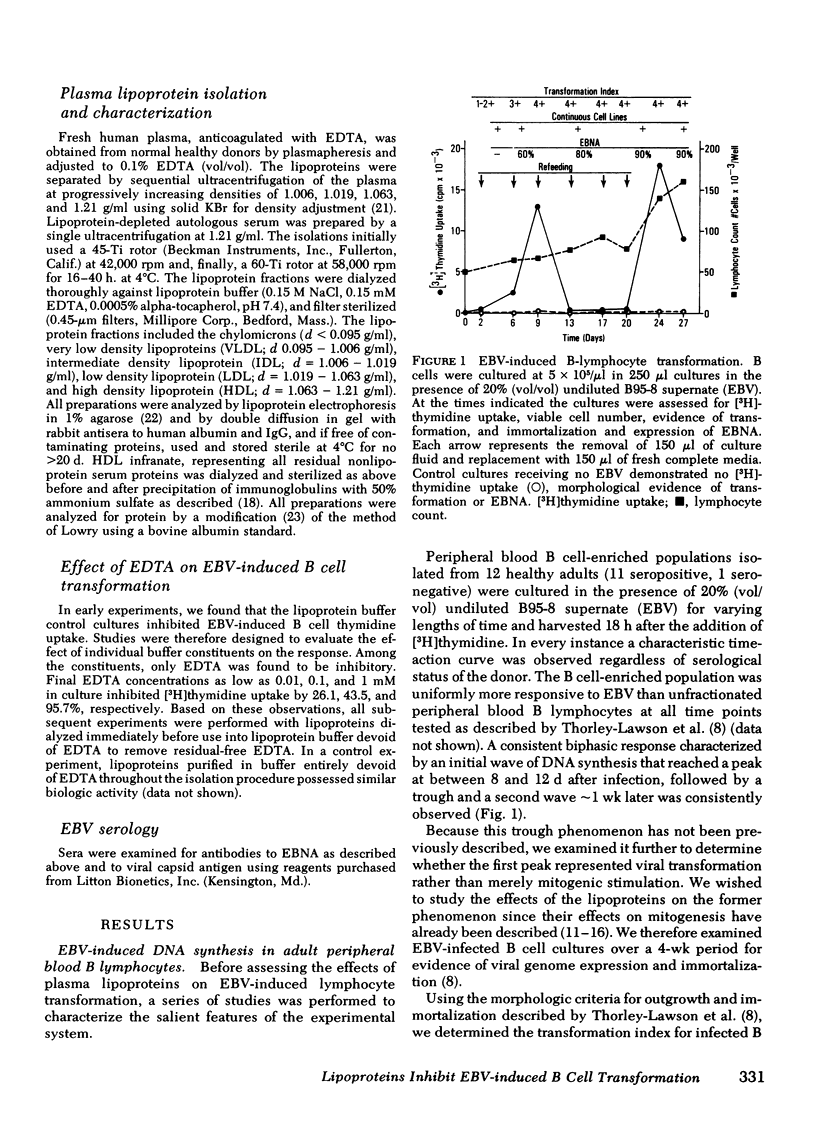
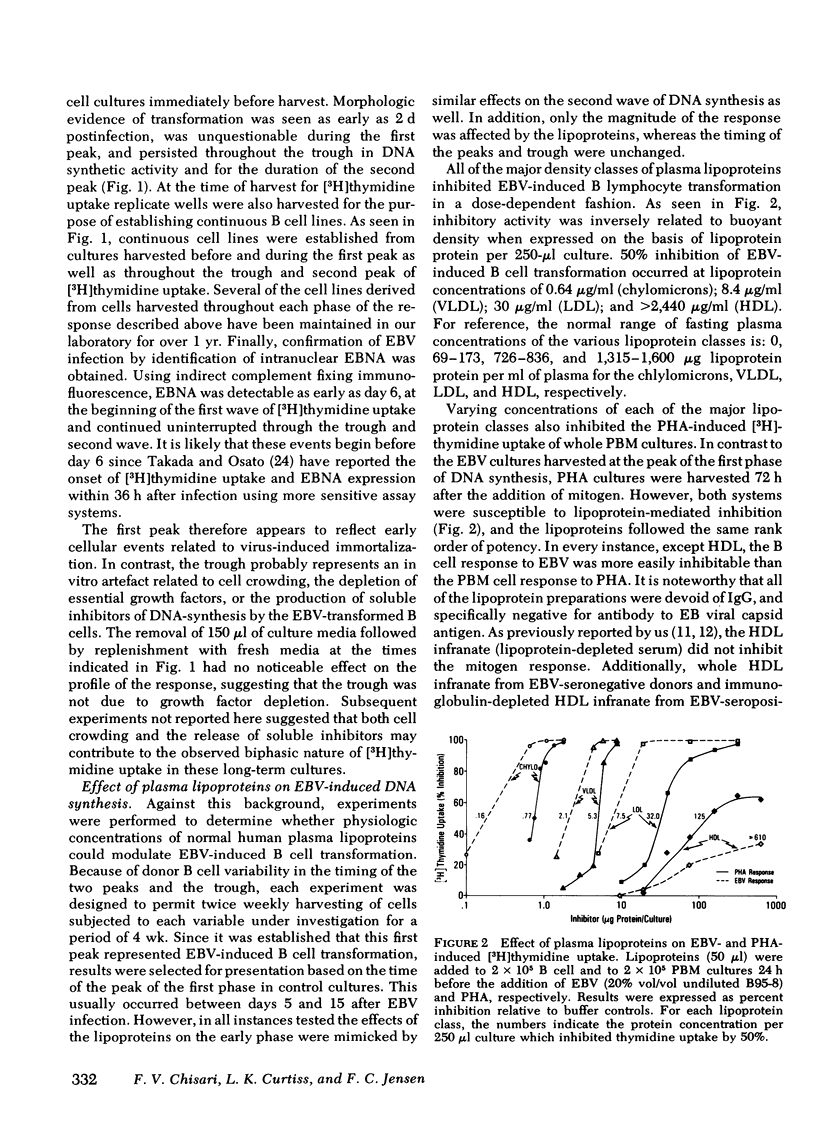
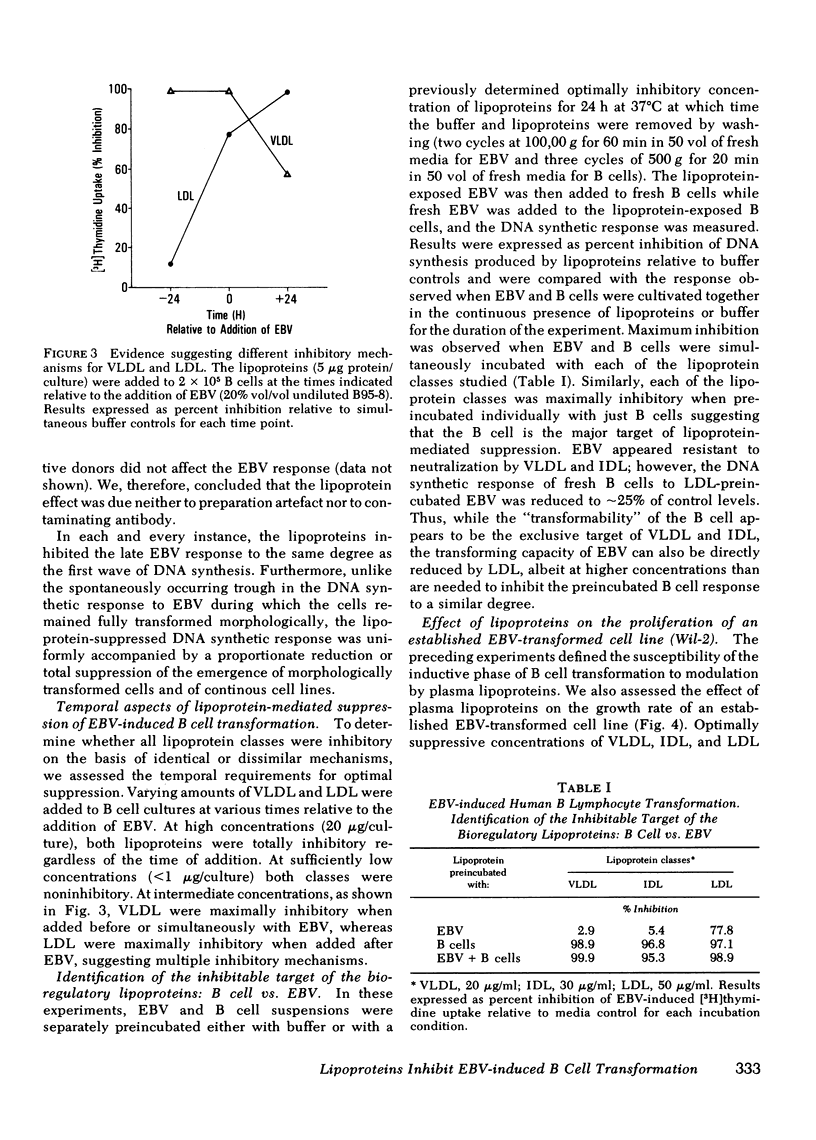
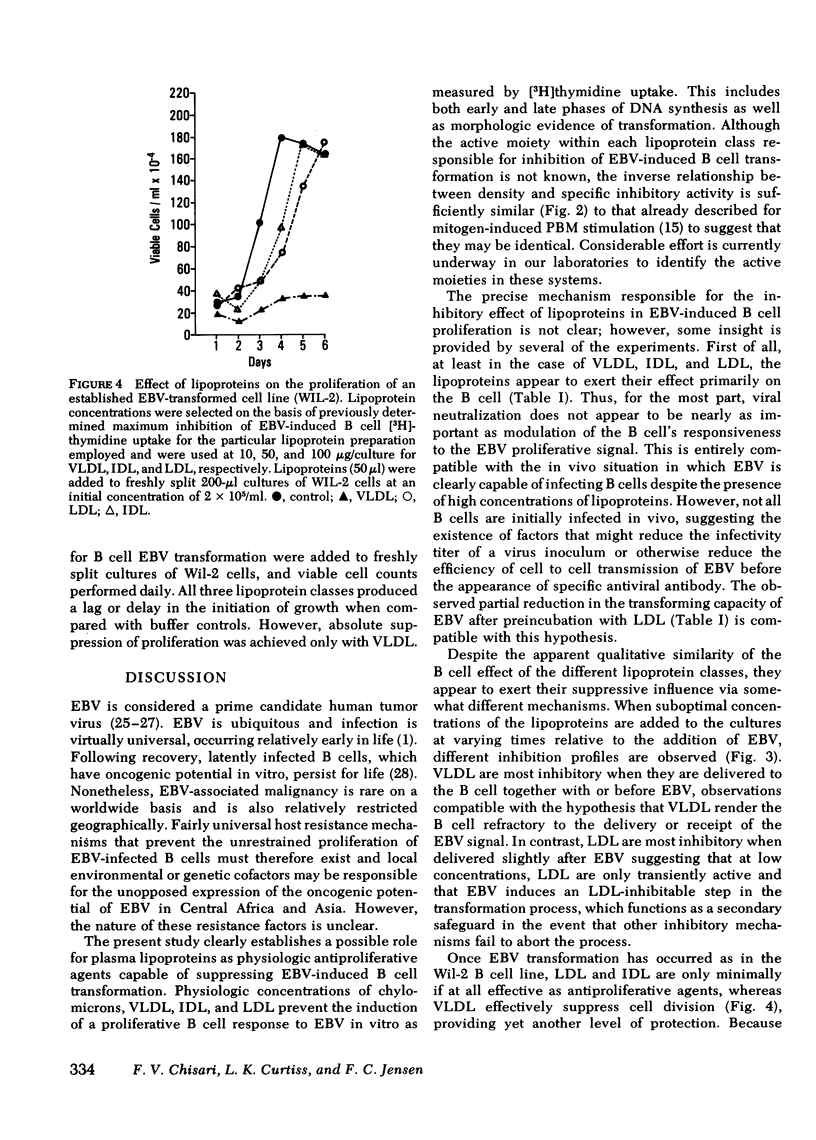
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced immortalization of adult human B lymphocytes is suppressed by physiologic concentrations of human plasma lipoproteins. Several inhibitory mechanisms appear to be operative. First, low density lipoproteins (LDL) directly reduce the ability of EBV to transform human B cells. Second, LDL as well as intermediate and very low density lipoproteins modulate early inductive events rendering the B cell refractory to transforming signals from EBV. Third, LDL also selectively inhibit an EBV-inducible step that occurs within 24 h after transformation. Finally, very low density lipoproteins can abrogate the ongoing, cellular proliferation of EBV-transformed, established B cell lines. The plasma lipoproteins may therefore prevent the emergence of EBV-transformed malignant B cell clones in vivo. Conceivably, on this basis, environmental and genetic influences on plasma lipoprotein concentrations may affect the global distribution of Burkitt's lymphoma, a lymphoid malignancy putatively caused by EBV.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chisari F. V. Immunoregulatory properties of human plasma in very low density lipoproteins. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2129–2136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Routenberg J. A., Edgington T. S. Mechanisms responsible for defective human T-lymphocyte sheep erythrocyte rosette function associated with hepatitis B virus infections. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1227–1238. doi: 10.1172/JCI108391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., DeHeer D. H., Edgington T. S. In vivo suppression of the primary immune response by a species of low density serum lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):648–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Regulatory serum lipoproteins: regulation of lymphocyte stimulation by a species of low density lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1452–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deal D. R., Gerber P., Chisari F. V. Heterotransplantation of two human lymphoid cell lines transformed in vitro by Epstein-Barr virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Oct;47(4):771–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl V., Henle G., Henle W., Kohn G. Demonstration of a herpes group virus in cultures of peripheral leukocytes from patients with infectious mononucleosis. J Virol. 1968 Jul;2(7):663–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.7.663-669.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G. Recent progress in Epstein-Barr virus research. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:421–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Diehl V. Relation of Burkitt's tumor-associated herpes-ytpe virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):94–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Niederman J. C., Andrews L. L. Prolonged oropharyngeal excretion of Epstein-Barr virus after infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):229–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misko I. S., Moss D. J., Pope J. H. HLA antigen-related restriction of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4247–4250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse J. H., Witte L. D., Goodman D. S. Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation stimulated by lectins and allogeneic cells by normal plasma lipoproteins. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1791–1803. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shope T., Dechairo D., Miller G. Malignant lymphoma in cottontop marmosets after inoculation with Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2487–2491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Osato T. Analysis of the transformation of human lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. I. Sequential occurrence from the virus-determined nuclear antigen synthesis, to blastogenesis, to DNA synthesis. Intervirology. 1979;11(1):30–39. doi: 10.1159/000149009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Chess L., Strominger J. L. Suppression of in vitro Epstein-Barr virus infection. A new role for adult human T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):495–508. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Magrath I., Koski I., Dooley N., Blaese M. Activation of suppressor T cells during Epstein-Barr-virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 22;301(21):1133–1137. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911223012101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell C. C., Taunton O. D., Twomey J. J. Inhibition of lymphoproliferation by hyperlipoproteinemic plasma. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):950–954. doi: 10.1172/JCI108548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



