Abstract
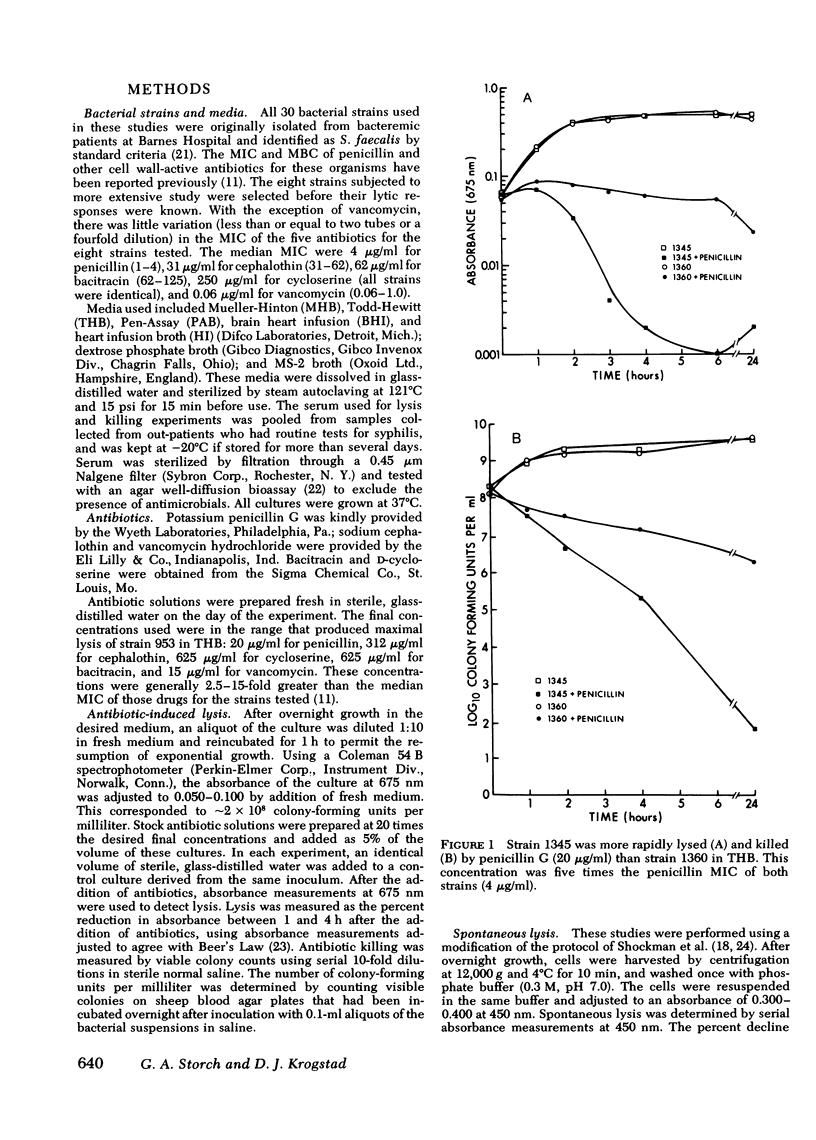
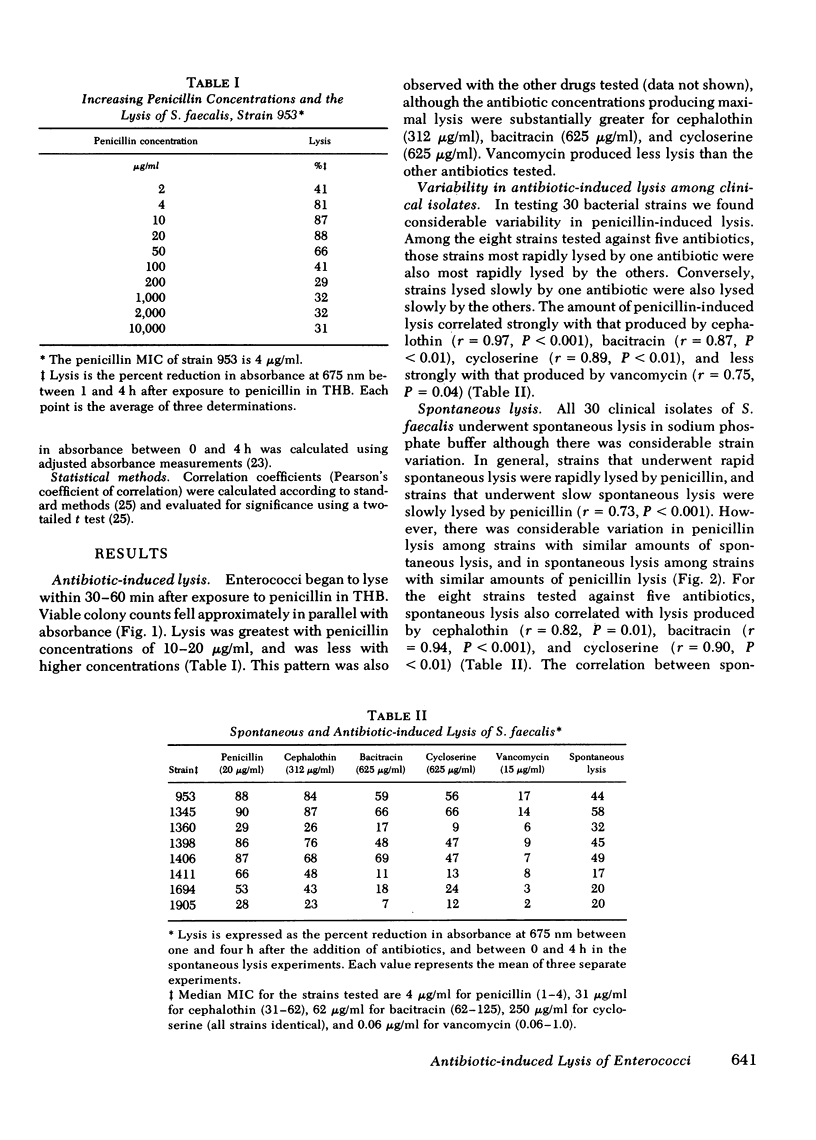
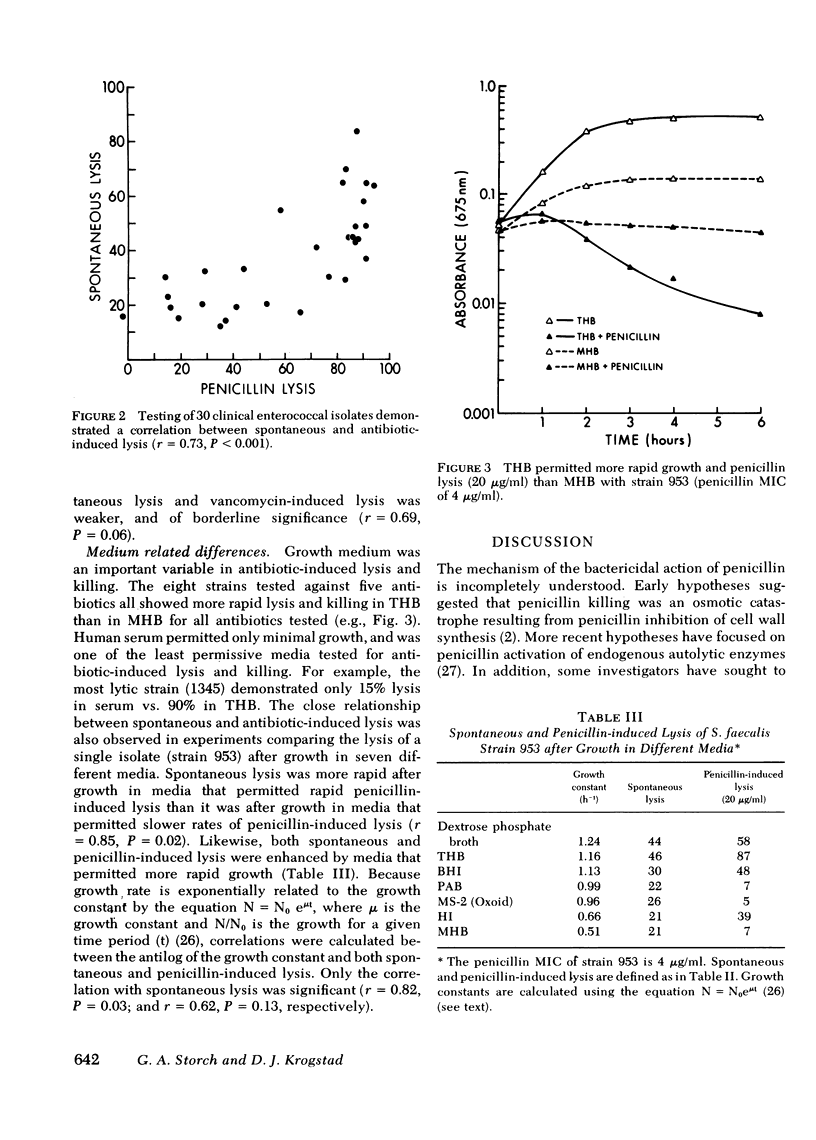
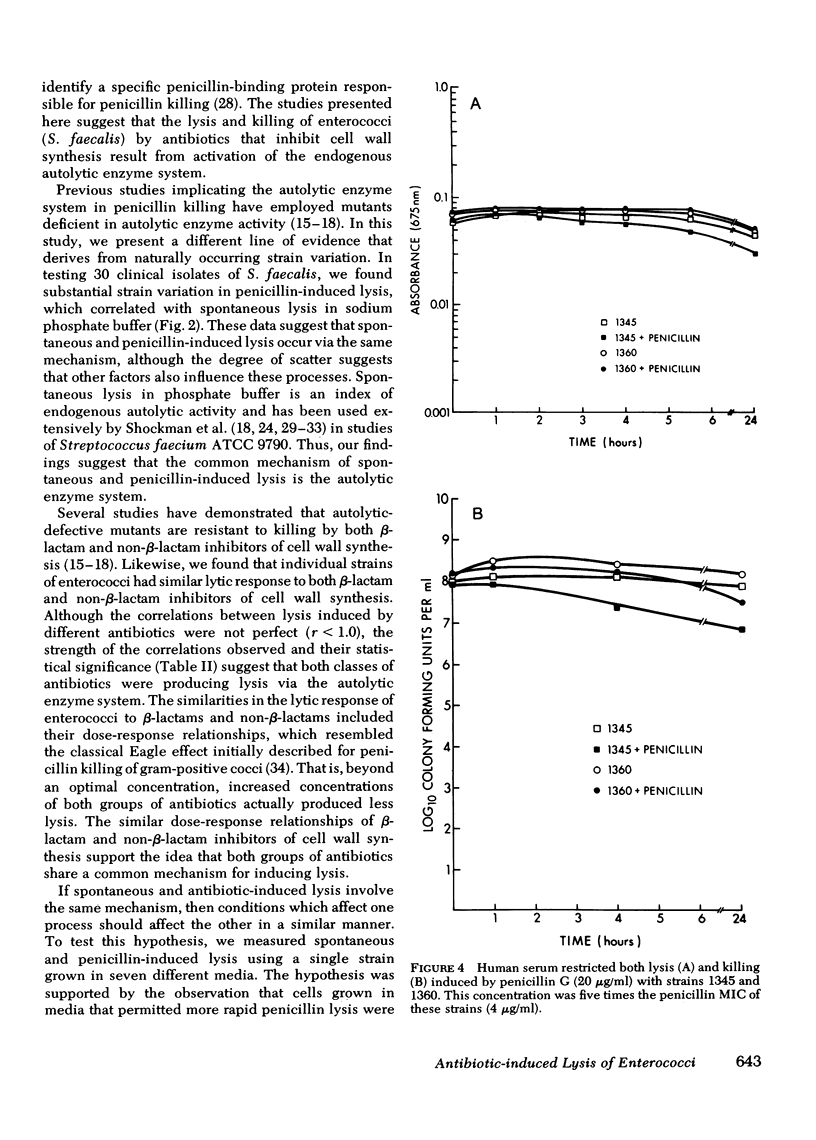
Enterococci are resistant to penicillin killing in vivo and in vitro. Because some bacteria resistant to penicillin killing have reduced autolytic activity, we examined the lysis of clinical enterococcal isolates suspended in buffer (spontaneous lysis), and compared it with their susceptibility to antibiotic-induced lysis and killing. We found significant correlations between spontaneous and antibiotic-induced lysis, using five antibiotics that inhibit cell wall synthesis (penicillin, cephalothin, bacitracin, cycloserine, and vancomycin). Among isolates, strains more rapidly lysed by one antibiotic were more rapidly lysed by the other antibiotics, and more susceptible to spontaneous lysis. In studies involving a single strain grown in different media, spontaneous lysis also correlated closely with antibiotic-induced lysis. These results are consistent with a common mechanism for spontaneous and antibiotic-induced lysis, such as the autolytic enzyme system. Human serum was one of the least permissive media tested for enterococcal growth and antibiotic-induced lysis and killing. We suggest that the inhibitory effect of human serum on growth and the activation of the enterococcal autolytic enzyme system may be a critical factor in the resistance of enterococcal endocarditis to treatment with penicillin alone.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayusawa D., Yoneda Y., Yamane K., Maruo B. Pleiotropic phenomena in autolytic enzyme(s) content, flagellation, and simultaneous hyperproduction of extracellular alpha-amylase and protease in a Bacillus subtilis mutant. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):459–469. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.459-469.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best G. K., Best N. H., Koval A. V. Evidence for participation of autolysins in bactericidal action of oxacillin on Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):825–830. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornett J. B., Shockman G. D. Cellular lysis of Streptococcus faecalis induced with triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.153-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Recognition of group D streptococcal species of human origin by biochemical and physiological tests. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1131–1139. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1131-1139.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Canepari P., Satta G., Coyette J. Identification of the lethal target of benzylpenicillin in Streptococcus faecalis by in vivo penicillin binding studies. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):70–72. doi: 10.1038/287070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Lopez R., Tomasz A. Suppression of lytic effect of beta lactams on Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3293–3297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt W. L., Seligman S. J., Deigh R. A. Kinetics of the synergism of penicillin-streptomycin and penicillin-kanamycin for enterococci and its relationship to L-phase variants. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 May;67(5):792–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D. Site of initiation of cellular autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis as seen by electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):504–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.504-512.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinks R. P., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Cellular autolytic activity in synchronized populations of Streptococcus faecium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):822–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.822-829.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd, Roberts R. B., Sande M. A. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental enterococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Nov;8(5):564–570. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.5.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jawetz E., Gunnison J. B., Coleman V. R. The Combined Action of Penicillin with Streptomycin or Chloromycetin on Enterococci in Vitro. Science. 1950 Mar 10;111(2880):254–256. doi: 10.1126/science.111.2880.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D. Antibiotic treatment of streptococcal endocarditis. Am J Med. 1980 Nov;69(5):650–652. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90412-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Korfhagen T. R., Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Swartz M. N. Plasmid-mediated resistance to antibiotic synergism in enterococci. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1645–1653. doi: 10.1172/JCI109085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Pargwette A. R. Defective killing of enterococci: a common property of antimicrobial agents acting on the cell wall. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):965–968. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez R., Ronda-Lain C., Tapia A., Waks S. B., Tomasz A. Suppression of the lytic and bactericidal effects of cell wallinhibitory antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):697–706. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto J. Y., Wilson W. R., Wright A. J., Geraci J. E., Washington J. A., 2nd Synergy of penicillin and decreasing concentration of aminoglycosides against enterococci from patients with infective endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):944–947. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Watson B. K., Kunz L. J. Endocarditis due to group D streptococci. Comparison of disease caused by streptococcus bovis with that produced by the enterococci. Am J Med. 1974 Aug;57(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Weinberg A. N. Studies on antibiotic synergism against enterococci. I. Bacteriologic studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 May;77(5):821–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M., Shockman G. D. Relationship between the location of autolysin, cell wall synthesis, and the development of resistance to cellular autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis after inhibition of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):457–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.457-466.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS W. C., TOMPSETT R. Treatment of enterococcal endocarditis and bacteremia; results of combined therapy with penicillin and streptomycin. Am J Med. 1951 Mar;10(3):278–299. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., Forsberg C. W. Role of autolysins in the killing of bacteria by some bactericidal antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1235–1243. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1235-1243.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wheeler N., Laverdiere M., Blazevic D., Wilkinson B. J. A new type of penicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1977 Feb 26;1(8009):443–447. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayare M., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Influence of macromolecular biosynthesis on cellular autolysis in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.337-344.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D., Conover M. J., Kolb J. J., Phillips P. M., Riley L. S., Toennies G. LYSIS OF STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81(1):36–43. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.1.36-43.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shungu D. L., Cornett J. B., Shockman G. D. Morphological and physiological study of autolytic-defective Streptococcus faecium strains. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):598–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.598-608.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L. The actions of penicillin and other antibiotics on bacterial cell wall synthesis. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1973 Aug;133(2):63–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Baker C. N., Facklam R. R. Antibiotic susceptibility of Streptococcus bovis and other group D streptococci causing endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):228–233. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Albino A., Zanati E. Multiple antibiotic resistance in a bacterium with suppressed autolytic system. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):138–140. doi: 10.1038/227138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Biological consequences of the replacement of choline by ethanolamine in the cell wall of Pneumococcus: chanin formation, loss of transformability, and loss of autolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):86–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. From penicillin-binding proteins to the lysis and death of bacteria: a 1979 view. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 May-Jun;1(3):434–467. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The role of autolysins in cell death. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):439–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters R. E., Litwack K. D., Hewitt W. L. Relation between dose and levels of gentamicin in blood. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S90–S95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



