Abstract
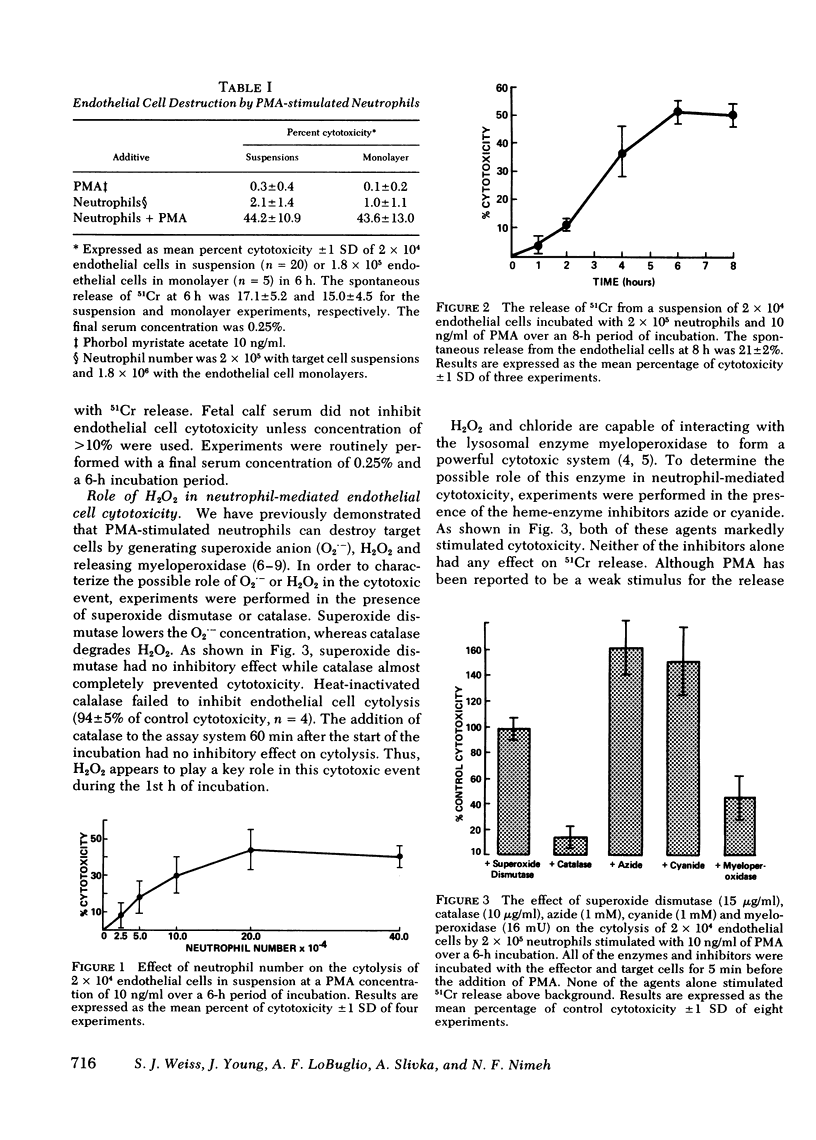
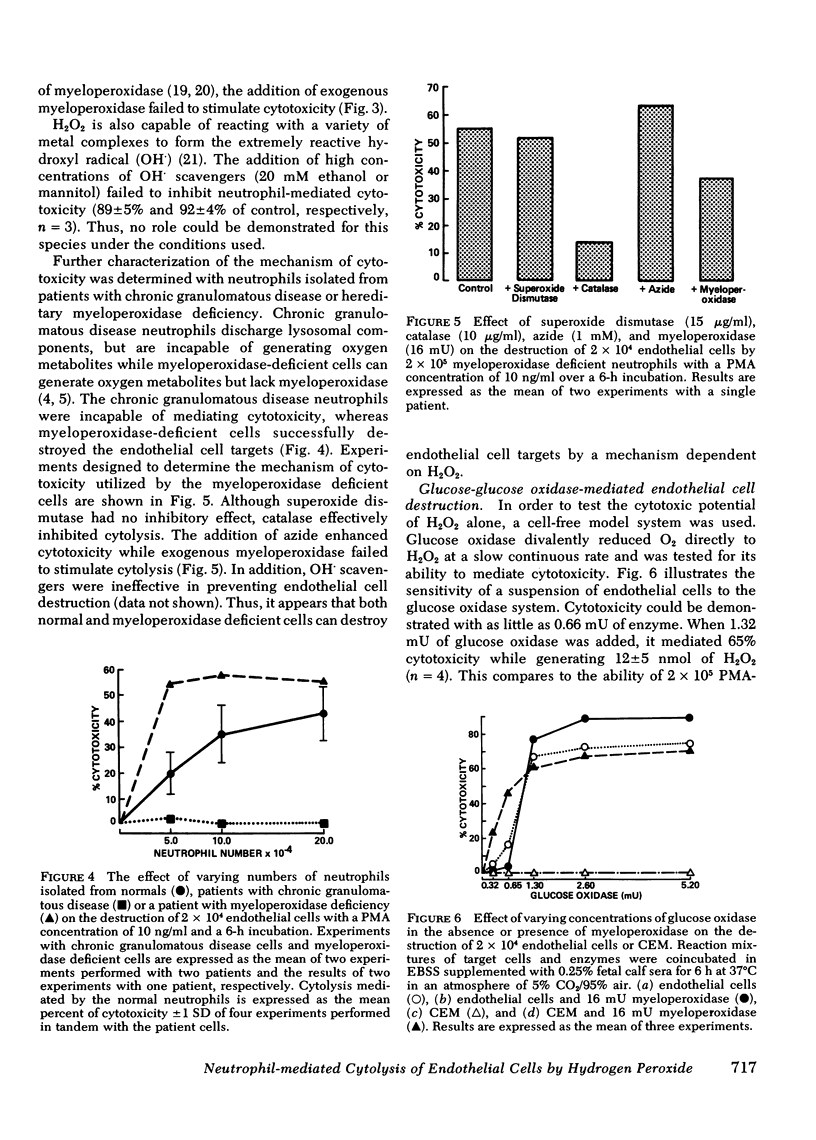
Human neutrophils stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate were able to destroy suspensions or monolayers of cultured human endothelial cells. Neutrophil-mediated cytotoxicity was related to phorbol myristate acetate concentration, time of incubation and neutrophil number. Cytolysis was prevented by the addition of catalase, while superoxide dismutase had no effect on cytotoxicity. The addition of the heme-enzyme inhibitors, azide or cyanide, markedly stimulated neutrophil-mediated damage while exogenous myeloperoxidase failed to stimulate cytolysis. Neutrophils isolated from patients with chronic granulomatous disease did not destroy the endothelial cell targets while myeloperoxidase-deficient neutrophils successfully mediated cytotoxicity. Endothelial cell damage mediated by the myeloperoxidase deficient cells was also inhibited by catalase but not superoxide dismutase. The addition of purified myeloperoxidase to the deficient cells did not stimulate cytotoxicity. Glucose-glucose oxidase, an enzyme system capable of generating hydrogen peroxide, could replace the neutrophil as the cytotoxic mediator. The addition of myeloperoxidase at low concentrations of glucose oxidase did not increase cytolysis, but at the higher concentrations of glucose oxidase it stimulated cytotoxicity. The destruction of endothelial cells by the glucose oxidase-myeloperoxidase system was inhibited by the addition of hypochlorous acid scavengers. In contrast, neutrophil-mediated cytolysis was not effectively inhibited by the hypochlorous acid scavengers. Based on these observations, we propose that human neutrophils can destroy cultured human endothelial cells by generating cytotoxic quantities of hydrogen peroxide.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. A., Szejda P. Mechanisms of killing of newborn larvae of Trichinella spiralis by neutrophils and eosinophils. Killing by generators of hydrogen peroxide in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1558–1564. doi: 10.1172/JCI109616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Myeloperoxidase--H2O2--halide system: cytotoxic effect on human blood leukocytes. Blood. 1977 Jul;50(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Neutrophil-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity: role of the peroxidase system. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1442–1447. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Neutrophil-platelet interaction mediated by myeloperoxidase and hydrogen peroxide. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):399–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Role of the myeloperoxidase-H2O2-halide system in concanavalin A-induced tumor cell killing by human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2605–2610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S., Johnston R. B., Jr Effect of phorbol myristate acetate on the oxidative metabolism of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1976 Apr;47(4):545–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Massaro D. Oxygen toxicity. Am J Med. 1980 Jul;69(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90509-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Ross R. Pathogenesis of arterial vascular disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1979 Spring;5(4):274–292. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1087159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Pabalan S., Schultz J. The subunit structure of crystalline canine myeloperoxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 23;493(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Schultz J. Studies on the chlorinating activity of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homan-Müller J. W., Weening R. S., Roos D. Production of hydrogen peroxide by phagocytizing human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):198–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Clark R. A. Hemolysis and iodination of erythrocyte components by a myeloperoxidase-mediated system. Blood. 1975 May;45(5):699–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Hamon C. B. Role of myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial systems in intact leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Aug;12(2):170–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Oxygen metabolism and the toxic properties of phagocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Sep;93(3):480–489. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-3-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Leukocyte myeloperoxidase deficiency and disseminated candidiasis: the role of myeloperoxidase in resistance to Candida infection. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1478–1488. doi: 10.1172/JCI106114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Silverstein S. C., Brukner L. H., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. II. Hydrogen peroxide as a mediator of cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):100–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Chemiluminescence and superoxide production by myeloperoxidase-deficient leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):50–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI108458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Hydroxyl radical generation by polymorphonuclear leukocytes measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1725–1729. doi: 10.1172/JCI109637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 12;295(7):369–377. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608122950707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 19;295(8):420–425. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608192950805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sbarra A. J., Selvaraj R. J., Paul B. B., Poskitt P. K., Mitchell G. W., Jr, Louis F., Asbell M. A. Granulocyte biochemistry and a hydrogen peroxide-dependent microbicidal system. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1977;13:29–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Levy P. C., Lobuglio A. F. Human monocyte cytotoxicity to tumor cells. I. Antibody-dependent cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):573–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka A., LoBuglio A. F., Weiss S. J. A potential role for hypochlorous acid in granulocyte-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, chloride antimicrobial system: nitrogen-chlorine derivatives of bacterial components in bactericidal action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.522-531.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurman R. G., Ley H. G., Scholz R. Hepatic microsomal ethanol oxidation. Hydrogen peroxide formation and the role of catalase. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb;25(3):420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., PALADE G. E. NEW CYTOPLASMIC COMPONENTS IN ARTERIAL ENDOTHELIA. J Cell Biol. 1964 Oct;23:101–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., LoBuglio A. F. An oxygen-dependent mechanism of neutrophil-mediated cytotoxicity. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):1020–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., LoBuglio A. F., Kessler H. B. Oxidative mechanisms of monocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):584–587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Rustagi P. K., LoBuglio A. F. Human granulocyte generation of hydroxyl radical. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):316–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. The role of superoxide in the destruction of erythrocyte targets by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9912–9917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Estensen R. D. Selective labilization of specific granules in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by phorbol myristate acetate. Am J Pathol. 1974 Apr;75(1):45–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgliczynski J. M., Selvaraj R. J., Paul B. B., Stelmaszynska T., Poskitt P. K., Sbarra A. J. Chlorination by the myeloperoxidase-H2O2-Cl- antimicrobial system at acid and neutral pH. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Mar;154(3):418–422. doi: 10.3181/00379727-154-39684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



