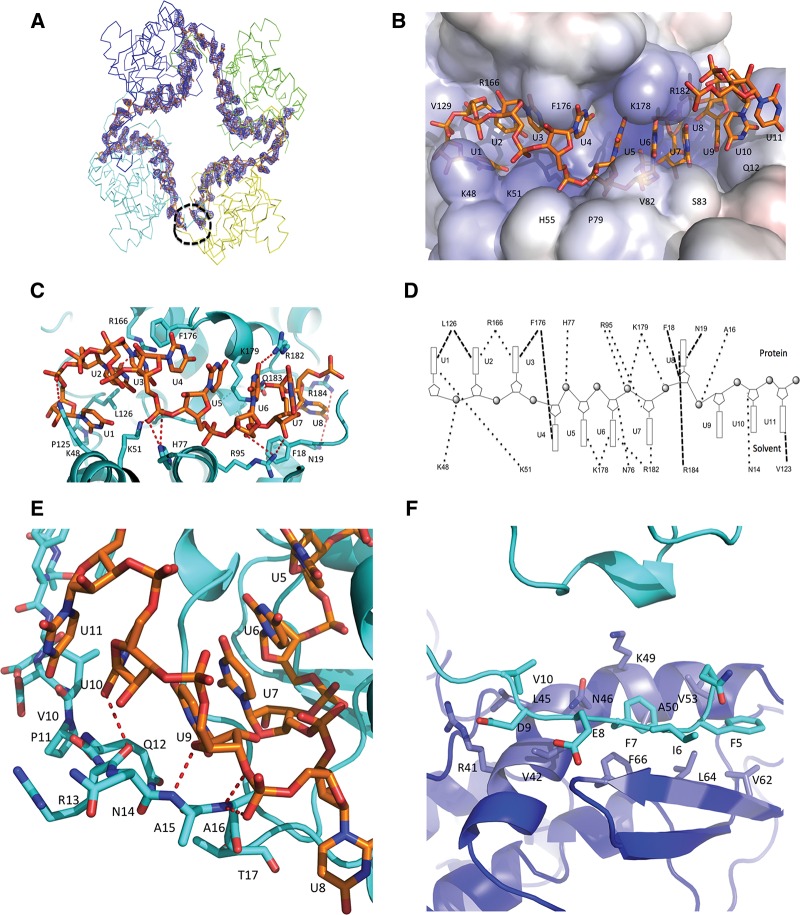
FIGURE 2.
SBV N–RNA interactions. (A) Unbiased Fo–Fc electron density map of the 42-nt polyU contoured at 3 σ. The electron density is shown in blue and the RNA is shown in stick form in orange. The four protomers are shown in ribbon form. The black dotted circle shows the RNA gap. (B) Electrostatic potential surface map showing RNA binding in a SBV N protomer. The RNA is shown as stick form in orange. One protomer binds 11 nt of RNA with 8 nt in the RNA-binding cleft and 3 nt to the N-terminal arm. Bases U1 to U3 face into protein inside the RNA-binding cleft, bases U4 to U7 point outside the RNA-binding cleft and are exposed to solvent, while base U8 is bent into the bottom of the binding cleft and faces the protein. (C) Interaction between the RNA and residues of the RNA-binding cleft. The RNA forms an “S” shape in the RNA-binding cleft. The RNA is shown as stick form in orange, while amino acids of the RNA-binding cleft are shown in cyan. (D) Schematic diagram showing interactions between RNA and amino acids in SBV N. Bases oriented to the top indicate those that face into protein in the RNA-binding cleft, while the bases oriented toward the bottom indicate the bases exposed to solvent. The dark dotted lines show the interactions. (E) Interaction of the N-terminal arm and the RNA. Bases U9–U11 interact with atoms of the main chain of the N-terminal arm. Base U9 is stacked above base U7. The RNA is shown in orange and the protein in cyan. (F) The N-terminal arm binds to another hydrophobic area of a neighboring protomer. In particular, residues F7 and F66 form π–π interaction. The N-terminal arm is in cyan and the hydrophobic area of the neighboring protomer is in blue.