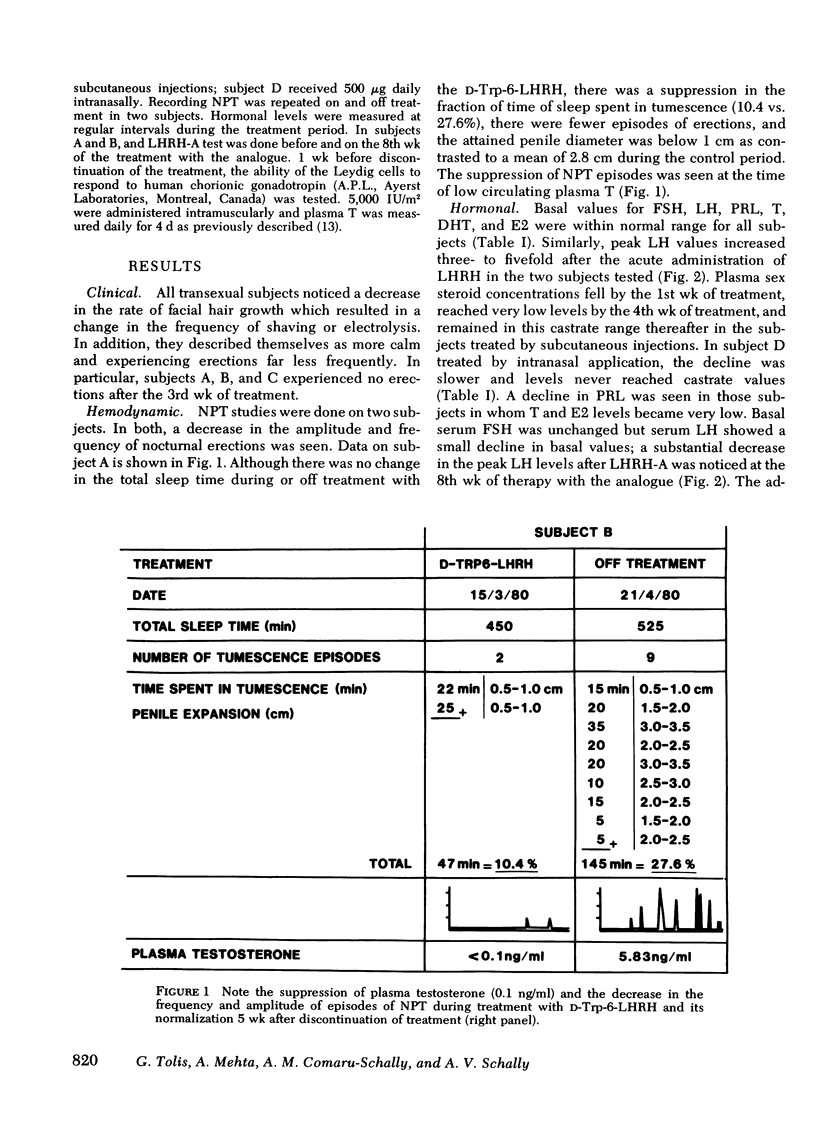
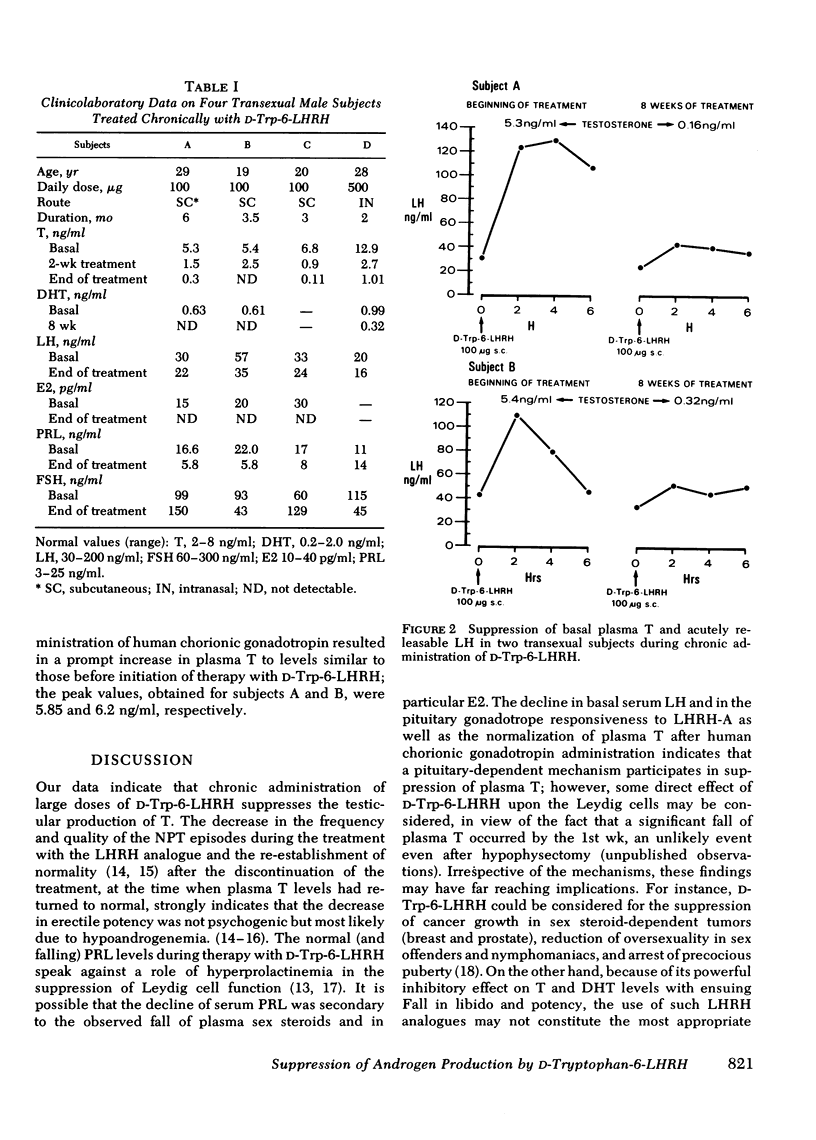
Abstract
Four male transsexual subjects were given a superactive luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analogue, D-tryptophan-6-LHRH at daily doses of 100 micrograms for 3--6 mo. A decrease in beard growth, acne, and erectile potency was noted; the latter was documented objectively with the recordings of nocturnal penile tumescence episodes. Plasma testosterone and dihydrotestosterone levels fell to castrate values; basal prolactin and luteinizing hormone levels showed a small decline, whereas the acutely releasable luteinizing hormone was significantly suppressed. A rise of plasma testosterone from castrate to normal levels was demonstrable with the use of human chorionic gonadotropin. Discontinuation of treatment led to a normalization of erectile potency and plasma testosterone. The suppression of Leydig cell function by D-tryptophan-6-LHRH might have wide application in reproductive biology and in endocrine-dependent neoplasia (where it could replace surgical castration).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert A., Rosemberg E., Ross G. T., Paulsen C. A., Ryan R. J. Report of the National Pituitary Agency collaborative study on the radioimmunoassay of FSH and LH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Aug;28(8):1214–1219. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-8-1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auclair C., Kelly P. A., Labrie F., Coy D. H., Schally A. V. Inhibition of testicular luteinizing hormone receptor level by treatment with a potent luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist of human chorionic gonadotropin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):855–862. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91579-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bélanger A., Caron S., Picard V. Simultaneous radioimmunoassay of progestins, androgens and estrogens in rat testis. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Feb;13(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter J. N., Tyson J. E., Tolis G., Van Vliet S., Faiman C., Friesen H. G. Prolactin-screening tumors and hypogonadism in 22 men. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 19;299(16):847–852. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810192991602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley W. F., Jr, Comite F., Vale W., Rivier J., Loriaux D. L., Cutler G. B., Jr Therapeutic use of pituitary desensitization with a long-acting lhrh agonist: a potential new treatment for idiopathic precocious puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Feb;52(2):370–372. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-2-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber D., Swerdloff R. S. Male contraception; synergism of gonadotropin-releasing hormone analog and testosterone in suppressing gonadotropin. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):936–938. doi: 10.1126/science.6773142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh A. J., Erickson G. F. Extra-pituitary inhibition of testicular function by luteinising hormone releasing hormone. Nature. 1979 Sep 6;281(5726):66–67. doi: 10.1038/281066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang P., Guyda H., Friesen H. A radioimmunoassay for human prolactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1902–1906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo Jaramillo C., Pérez-Infante V., López Maciá A., Salgado A. C., Coy D. H., Schally A. V. Serum LH, FSH and testosterone response to the administration of a new LH-RH analog, D-Trp6-LH-RH, in normal men. Int J Fertil. 1977;22(2):77–84. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikhail G., Wu C. H., Ferin M., Vande Wiele R. L. Radioimmunoassay of plasma estrone and estradiol. Steroids. 1970 Mar;15(3):333–352. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(70)80053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Donald R. A., Espiner E. A., Stronach S. The effects of prolonged administration of D-Ser (TBU)6-LH-RH-EA10 (HOE 766) in subjects with hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1979 Nov;11(5):553–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1979.tb03108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spark R. F., White R. A., Connolly P. B. Impotence is not always psychogenic. Newer insights into hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal dysfunction. JAMA. 1980 Feb 22;243(8):750–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tharandt L., Schulte H., Benker G., Hackenberg K., Reinwein D. Treatment of isolated gonadotropin deficiency in men with synthetic LR-RH and a more potent analogue of LH-RH. Neuroendocrinology. 1977;24(3-4):195–207. doi: 10.1159/000122708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wass J. A., Besser G. M., Gomez-Pan A., Scanlon M. F., Hall R., Kastin A. J., Coy D. H., Schally A. V. Comparison of long-acting analogues of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone in man. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1979 Apr;10(4):419–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1979.tb02098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegelmann W., Solbach H. G., Kley H. K., Krüskemper H. L. LH- and FSH response to long-term application of LH-RH analogue in normal males. Horm Metab Res. 1977 Nov;9(6):521–522. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



