Abstract
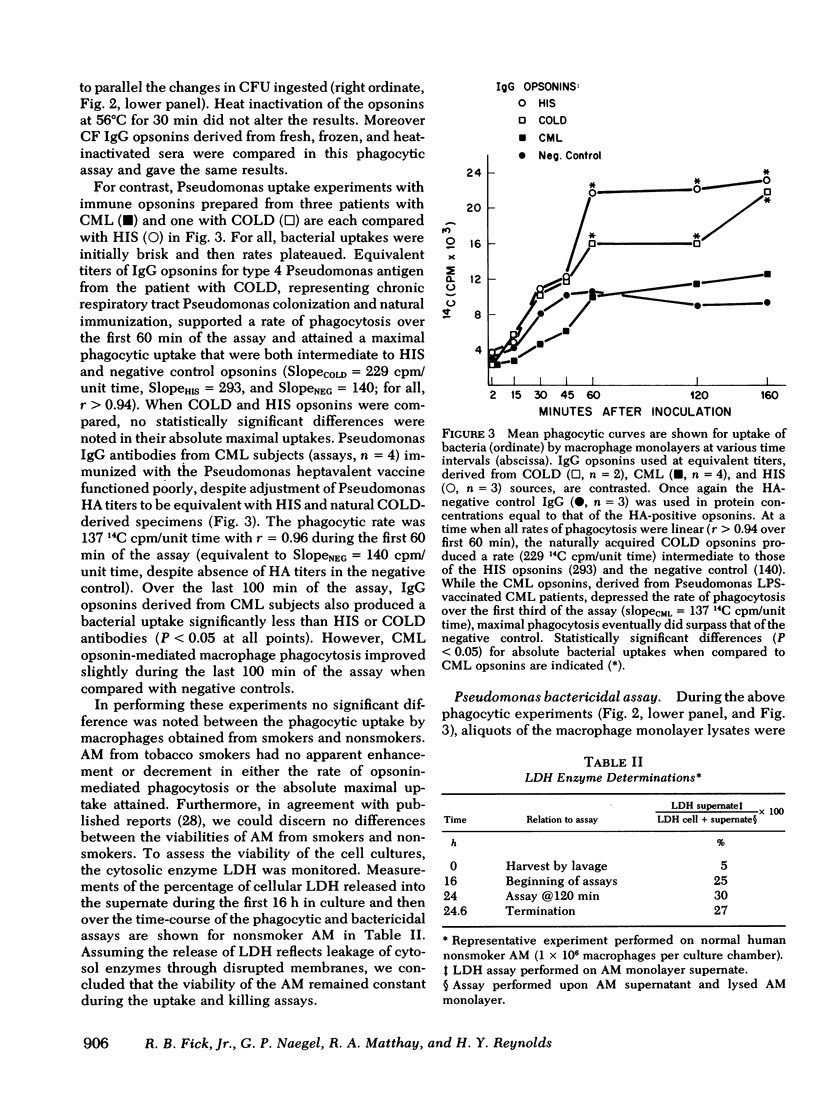
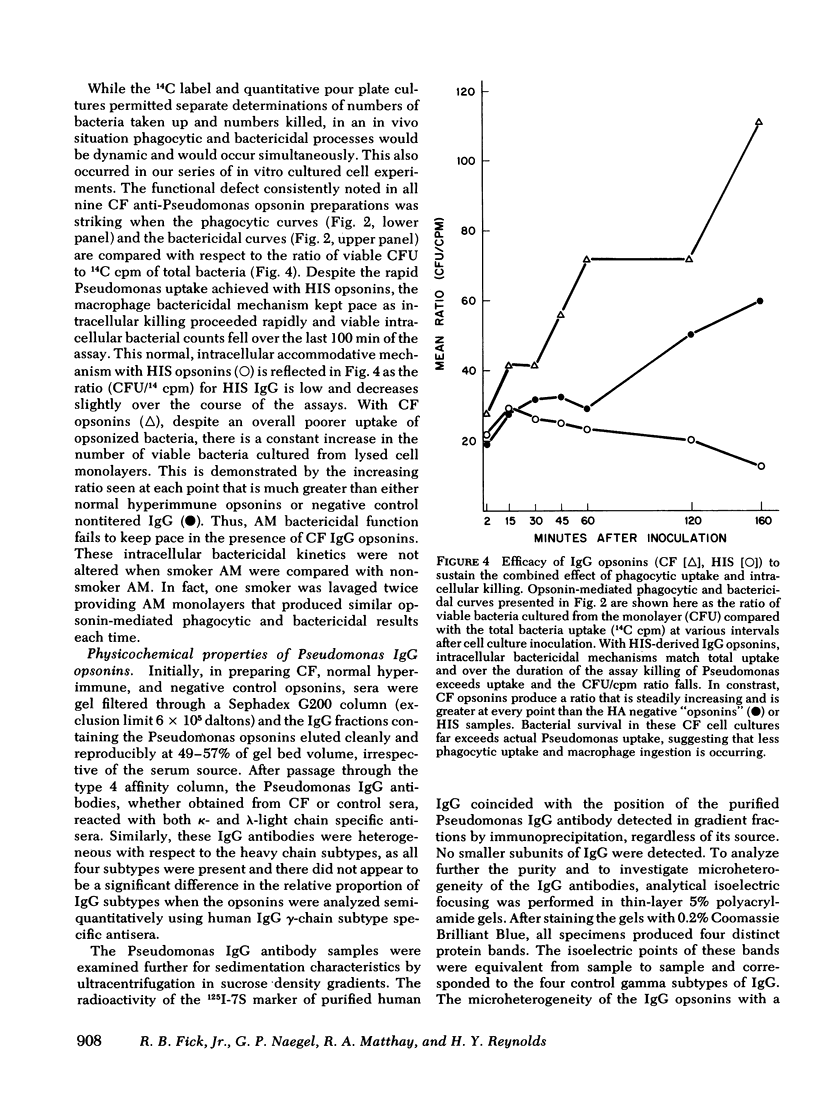
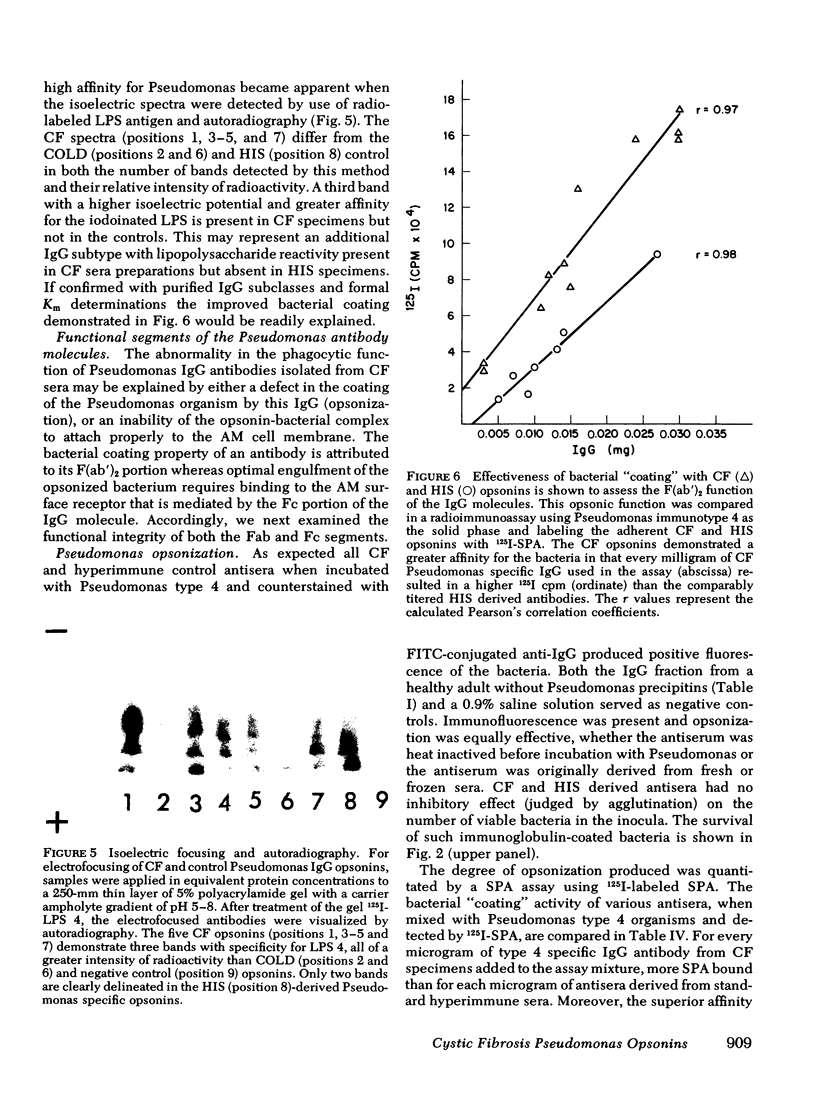
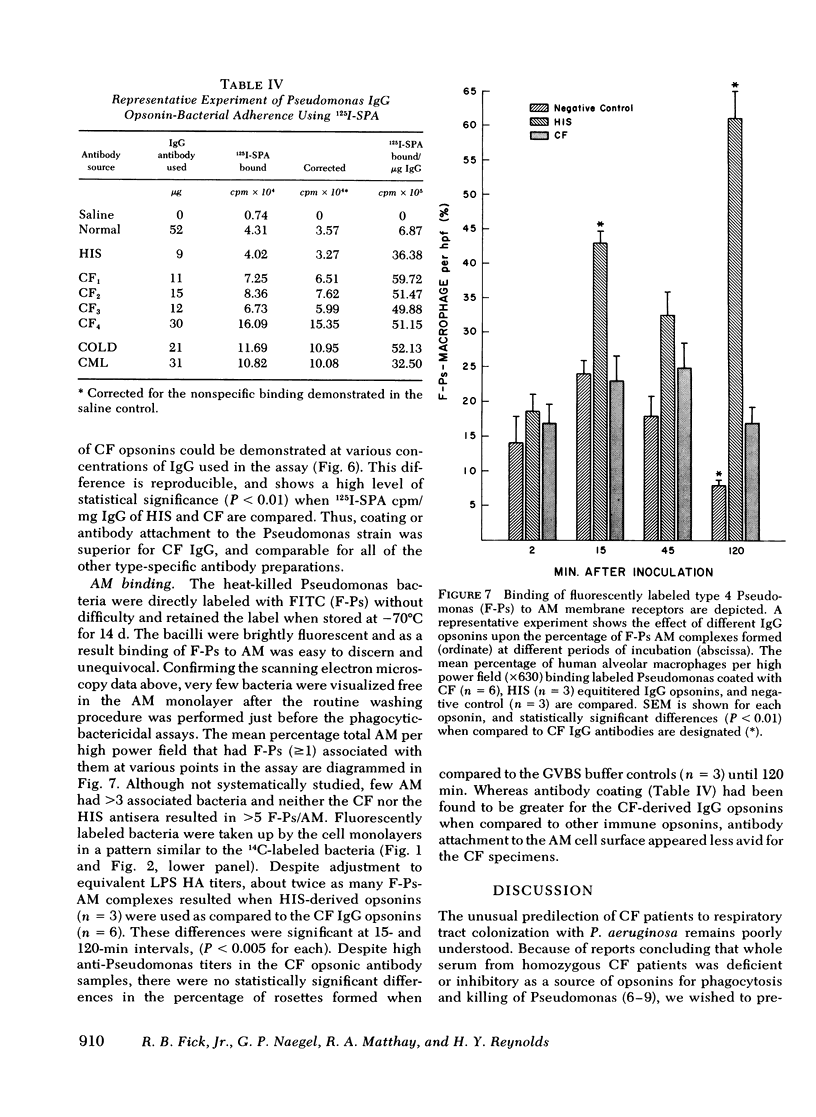
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection plays a primary pathogenetic role in the chronic respiratory tract disease of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. Despite pronounced humoral immune responses, reflected by high levels of antibodies against Pseudomonas in serum and in sputum, the antibodies do not eliminate this bacterium. In the present study we have used affinity chromatography with a lipopolysaccharide substituted immunoadsorbent gel to isolate high titers (meanCF = 1:256) of immunotype specific Pseudomonas IgG antibodies from the sera of nine CF subjects, and have evaluated the functional ability of these antibodies to promote phagocytosis and intracellular killing of P. aeruginosa in an in vitro human alveolar macrophage culture system. The phagocytic and intracellular bactericidal kinetics revealed that CF IgG antibodies function in an inhibitory fashion. Both the rate of phagocytosis (rateCF = 204 cpm/unit time) and absolute bacterial uptakes maximal at 120 min (uptakeCF = 18 x 10(3) 14C cpm) were inhibited compared with appropriate positive controls (hyperimmune serum, HIS; [rateHIS = 399; uptakeHIS = 29 x 10(3), P less than 0.005]). The ability of such CF-derived opsonins to potentiate macrophage intracellular bactericidal processes was mildly impaired (bacterial survivalCF = 15 x 10(3) colony forming units (CFU)/min, survivalHIS = 9 x 10(3)). Further characterization of this defect, assessed with functional studies of the Fab and Fc portions of the immunoglobulin molecule, revealed an impairment in the attachment of these specific antibodies to the alveolar macrophage membrane Fc gamma receptors. Preliminary studies of the physical-chemical properties of these immunoglobulins were normal. The expression of this inhibitory activity in vivo may facilitate Pseudomonas colonization and the subsequent established infections in the respiratory tracts of CF subjects.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. The macrophage receptor for IgG: number and affinity of binding sites. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1455–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggar W. D., Holmes B., Good R. A. Opsonic defect in patients with cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1716–1719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson A. B., Michael J. G. Contribution of humoral and cellular factors to the resistance to experimental infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. I. Interaction between immunoglobulins, heat-labile serum factors, and phagocytic cells in the killing of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):462–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.462-467.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxerbaum B., Kagumba A., Matthews L. W. Selective inhibition of phagocytic activity of rabbit alveolar macrophages by cystic fibrosis serum. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Oct;108(4):777–783. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.4.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. B., Cline M. J. The human alveolar macrophage: isolation, cultivation in vitro, and studies of morphologic and functional characteristics. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1390–1398. doi: 10.1172/JCI106622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover J. H., Conod E. J., Hirschhorn K. Letter: Complement components in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 29;2(7844):1501–1501. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92768-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J. K., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Opsonin-independent phagocytosis of activators of the alternative complement pathway by human monocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1132–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Sant'Agnese P. A., Davis P. B. Research in cystic fibrosis (first of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 26;295(9):481–485. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608262950905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Jr, Naegel G. P., Reynolds H. Y. Use of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide immunoadsorbents to prepare high potency, mono-specific antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38(1-2):103–116. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand J. A., Fauci A. S., Green I., Frank M. M. A simple method for the determination of complement receptor-bearing mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):595–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G. N., Rehm S. R., Pierce A. K. The effect of complement depletion on lung clearance of bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):373–378. doi: 10.1172/JCI109138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz M., Lubec G. Complement in cystic fibrosis. Eur J Pediatr. 1978 Jan 17;127(2):133–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00445769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P. Immunological aspects of cystic fibrosis. Bibl Paediatr. 1967;86:144–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanessian S., Regan W., Watson D., Haskell T. H. Isolation and characterization of antigenic components of a new heptavalent Pseudomonas vaccine. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 17;229(7):209–210. doi: 10.1038/newbio229209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M. The binding of human IgG subclasses to human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Jun;2(3):257–261. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinman L. M., Stevens C. A., Matthay R. A., Gee J. B. Elastase and lysozyme activities in human alveolar macrophages. Effects of cigarette smoking. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):263–271. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holby N., Olling S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Bactericidal effect of serum from normal individuals and patients with cystic fibrosis on P. aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis or other diseases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Apr;85(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb D., Reid L. The tracheobronchial submucosal glands in cystic fibrosis: a qualitative and quantitative histochemical study. Br J Dis Chest. 1972 Oct;66(4):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(72)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Zwet T. L., Daha M. R., van Furth R. Requirement of extracellular complement and immunoglobulin for intracellular killing of micro-organisms by human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):772–784. doi: 10.1172/JCI109362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W. W., Naegel G. P., Matthay R. A., Reynolds H. Y. Alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor: kinetics of in vitro production and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):268–276. doi: 10.1172/JCI109668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. B., Lewiston N. J. Immune complexes and humoral response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jan;121(1):23–29. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey S. A., Root R. K., Schreiber A. D. The role of antibody and complement in phagocytosis by rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):896–903. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington J. E., Reynolds H. Y., Wood R. E., Robinson R. A., Levine A. S. Use of a Pseudomonas Aeruginosa vaccine in pateints with acute leukemia and cystic fibrosis. Am J Med. 1975 May;58(5):629–636. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90498-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. M., Dresser D. W. Antibody isoelectric spectra visualized by antigen-coated erythrocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Nov;3(11):738–740. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. Studies on the immunoglobulins which stimulate the ingestion of glutaraldehyde-treated red cells attached to macrophages. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1115–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Atkinson J. P., Newball H. H., Frank M. M. Receptors for immunoglobulin and complement on human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1813–1819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Johnson J. S. Structural units of canine serum and secretory immunoglobulin A. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 20;10(15):2821–2827. doi: 10.1021/bi00791a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Kazmierowski J. A., Newball H. H. Specificity of opsonic antibodies to enhance phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by human alveolar macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):376–385. doi: 10.1172/JCI108102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Newball H. H. Analysis of proteins and respiratory cells obtained from human lungs by bronchial lavage. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):559–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Thompson R. E. Pulmonary host defenses. II. Interaction of respiratory antibodies with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):369–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. Macrophage heterogeneity in receptor activity: the activation of macrophage Fc receptor function in vivo and in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):976–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas V., Shelokov A., Forland M. Antibody-coated bacteria in the urine and the site of urinary-tract infection. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 14;290(11):588–590. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403142901102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Boxerbaum B., Demko C. A., Kuchenbrod P. J., Dearborn D. G., Wood R. E. Inhibitory effect of cystic fibrosis serum on pseudomonas phagocytosis by rabbit and human alveolar macrophages. Pediatr Res. 1979 Sep;13(9):1085–1088. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197909000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Wood R. E., Tandler B., Dearborn D. G., Boxerbaum B., Kuchenbrod P. J. Ultrastructure and function of alveolar macrophages from cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr Res. 1980 May;14(5):715–721. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198005000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallwork J. C., Brenchley P., McCarthy J., Allan J. D., Moss D., Ward A. M., Holzel A., Williams R. F., McFarlane H. Some aspects of immunity in patients with cystic fibrosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):303–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. In-vitro interaction of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and serum factors. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):257–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. In-vitro interaction of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and serum factors. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):257–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Williams R. L. Serotyping of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):521–526. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.521-526.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]