Abstract
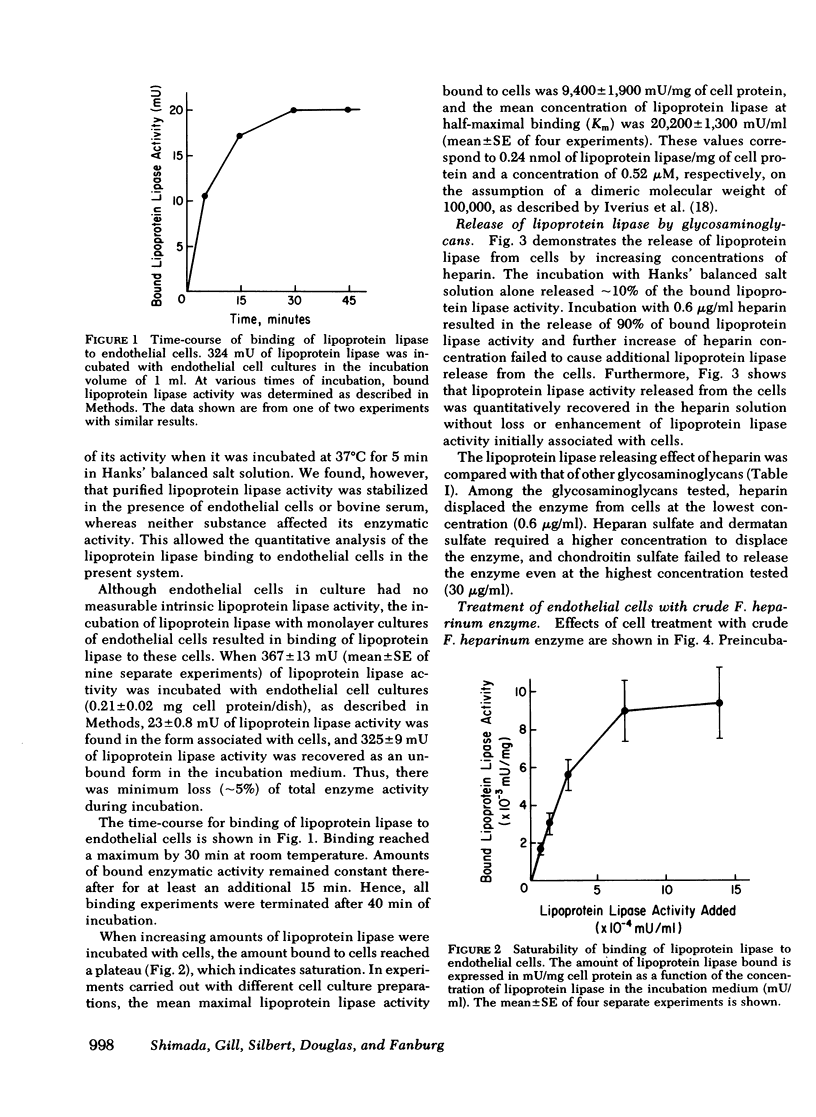
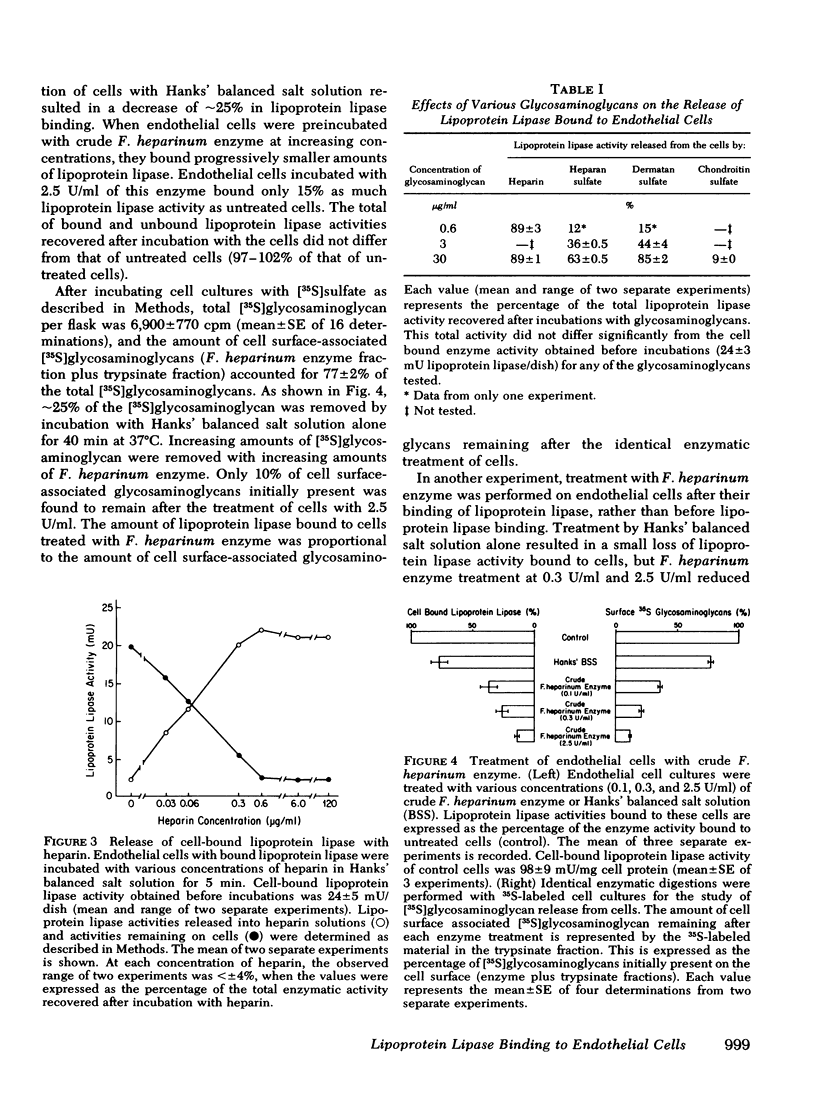
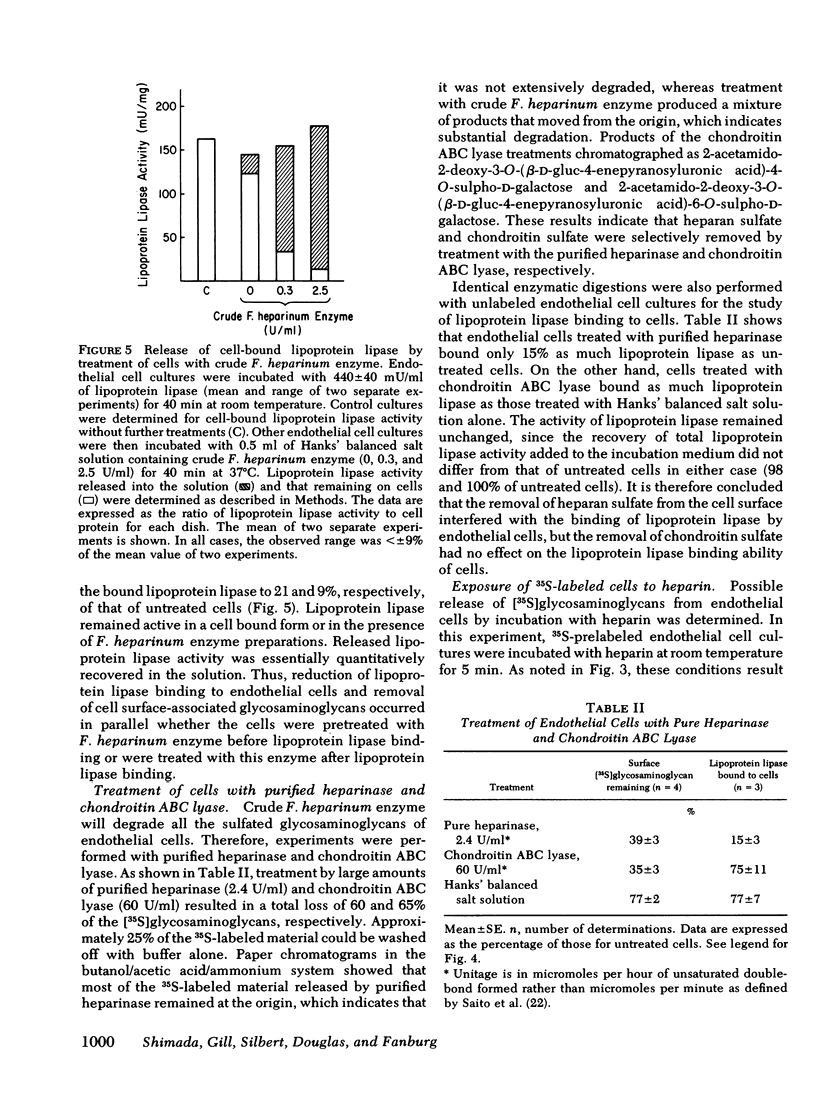
It has been postulated that lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme important in the uptake of fatty acids into tissues, is bound to the vascular endothelial cell surface and that this binding occurs through attachment to heparinlike glycosaminoglycans. Furthermore, it is thought that heparin releases the enzyme from its attachment to the endothelium into the circulation. These hypotheses have never been tested directly in cell systems in vitro. In the present study we have directly evaluated the interaction of lipoprotein lipase, purified from bovine skim milk with monolayer cultures of endothelial cells, isolated from bovine pulmonary artery. Endothelial cells in primary culture had no intrinsic lipoprotein lipase activity but were able to bind lipoprotein lipase quantitatively. The binding reached equilibrium and was saturable at 0.24 nmol of lipoprotein lipase/mg of cell protein. The concentration of lipoprotein lipase at half-maximal binding was 0.52 microM. Bound lipoprotein lipase could be detached from cultured cells by increasing concentrations of heparin, and at and above 0.6 microgram/ml of heparin, 90% of the cell-bound lipoprotein lipase activity was released. Heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate released the enzyme to a lesser extent and chondroitin sulfate caused little, if any, release of lipoprotein lipase. The release of lipoprotein lipase with heparin was not associated with a release of [3S]glycosaminoglycans from 35S-prelabeled cells. Reductions of lipoprotein lipase binding to endothelial cells and of cell surface-associated [3S]glycosaminoglycans in 35S-prelabeled cells occurred in parallel both when cells were pretreated with crude Flavobacterium heparinum enzyme before lipoprotein lipase binding and when cells were treated with this enzyme after lipoprotein lipase binding. The removal of heparan sulfate from the cell surface by purified heparinase totally inhibited the binding of lipoprotein lipase by endothelial cells, but the removal of chondroitin sulfate by chondroitin ABC lyase had no effect on this binding. These results provide direct evidence for lipoprotein lipase attachment to endothelial cells through heparan sulfate on the cell surface, and provide evidence for the release of lipoprotein lipase by heparin through a detachment from this binding site.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T., Hök M., Riesenfeld J., Lindahl U. Interaction of lipoprotein lipase with native and modified heparin-like polysaccharides. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj1890625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T. Interaction of lipoprotein lipase with heparin-Sepharose. Evaluation of conditions for affinity binding. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):109–119. doi: 10.1042/bj1670109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P., Karlsson M., Pertoft H., Pettersson P., Sjöström L., Smith U. Isolation and characterization of cells from rat adipose tissue developing into adipocytes. J Lipid Res. 1978 Mar;19(3):316–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonassisi V., Root M. Enzymatic degradation of heparin-related mucopolysaccharides from the surface of endothelial cell cultures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 14;385(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonassisi V. Sulfated mucopolysaccharide synthesis and secretion in endothelial cell cultures. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Feb;76(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90388-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch C., Dawes J., Pepper D. S., Wasteson A. Binding of platelet factor 4 to cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Thromb Res. 1980 Jul 1;19(1-2):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90412-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Stein O., Stein Y. Lipoprotein lipase of cultured mesenchymal rat heart cells. I. Synthesis, secretion and releasability by heparin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 30;528(3):456–465. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Higgins J. M. Lipoprotein lipase: comparative properties of the membrane-supported and solubilized enzyme species. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4324–4330. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J. Inactivation of lipoprotein lipase in buffered saline solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 24;159(1):94–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. J., Adler J., Silbert C. K., Silbert J. E. Removal of glycosaminoglycans from cultures of human skin fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):299–307. doi: 10.1042/bj1940299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson L. C., Schotz M. C., Harary I. Lipoprotein lipase in cultured heart cells: characteristics and cellular location. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 26;487(1):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernell O., Egelrud T., Olivecrona T. Serum-stimulated lipases (lipoprotein lipases). Immunological crossreaction between the bovine and the human enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 13;381(2):233–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V. Uptake of very low density lipoprotein triglyceride by bovine aortic endothelial cells in culture. J Lipid Res. 1977 Sep;18(5):561–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H. Coupling of glycosaminoglycans to agarose beads (sepharose 4B). Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):677–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1240677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H., Lindahl U., Egelrud T., Olivecrona T. Effects of heparin on lipoprotein lipase from bovine milk. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6610–6616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H., Ostlund-Lindqvist A. M. Lipoprotein lipase from bovine milk. Isolation procedure, chemical characterization, and molecular weight analysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7791–7795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORN E. D. Clearing factor, a heparin-activated lipoprotein lipase. I. Isolation and characterization of the enzyme from normal rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jul;215(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén L., Oldberg A., Hök M. Cell-surface heparan sulfate. Mechanisms of proteoglycan-cell association. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10407–10413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer P. M. Heparin releases heparan sulfate from the cell surface. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 24;78(4):1334–1340. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91438-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Hök M. Glycosaminoglycans and their binding to biological macromolecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:385–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Lipolytic enzymes and plasma lipoprotein metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:667–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson-Ehle P., Schotz M. C. A stable, radioactive substrate emulsion for assay of lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res. 1976 Sep;17(5):536–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Bengtsson G., Marklund S. E., Lindahl U., Hök M. Heparin-lipoprotein lipase interactions. Fed Proc. 1977 Jan;36(1):60–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Egelrud T., Iverius P. H., Lindahl U. Evidence for an ionic binding of lipoprotein lipase to heparin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):524–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90645-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund-Lindqvist A. M. Properties of salt-resistant lipase and lipoprotein lipase purified from human post-heparin plasma. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):555–559. doi: 10.1042/bj1790555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polsky-Cynkin R., Fanburg B. L. Immunochemical comparison of angiotensin 1 converting enzymes from different rat organs. Int J Biochem. 1979;10(8):669–674. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(79)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Clements E., Habliston D., Ryan J. W. Isolation and culture of pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Tissue Cell. 1978;10(3):535–554. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(16)30347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Yamagata T., Suzuki S. Enzymatic methods for the determination of small quantities of isomeric chondroitin sulfates. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1536–1542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Smith L. C. Role of capillary endothelium in the clearance of chylomicrons. A model for lipid transport from blood by lateral diffusion in cell membranes. Circ Res. 1976 Aug;39(2):149–162. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A., Glimelius B., Busch C., Westermark H., Heldin C. H., Norling B. Effect of a platelet endoglycosidase on cell surface associated heparan sulphate of human culturei endothelial and glial cells. Thromb Res. 1977 Sep;11(3):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90184-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



