Abstract
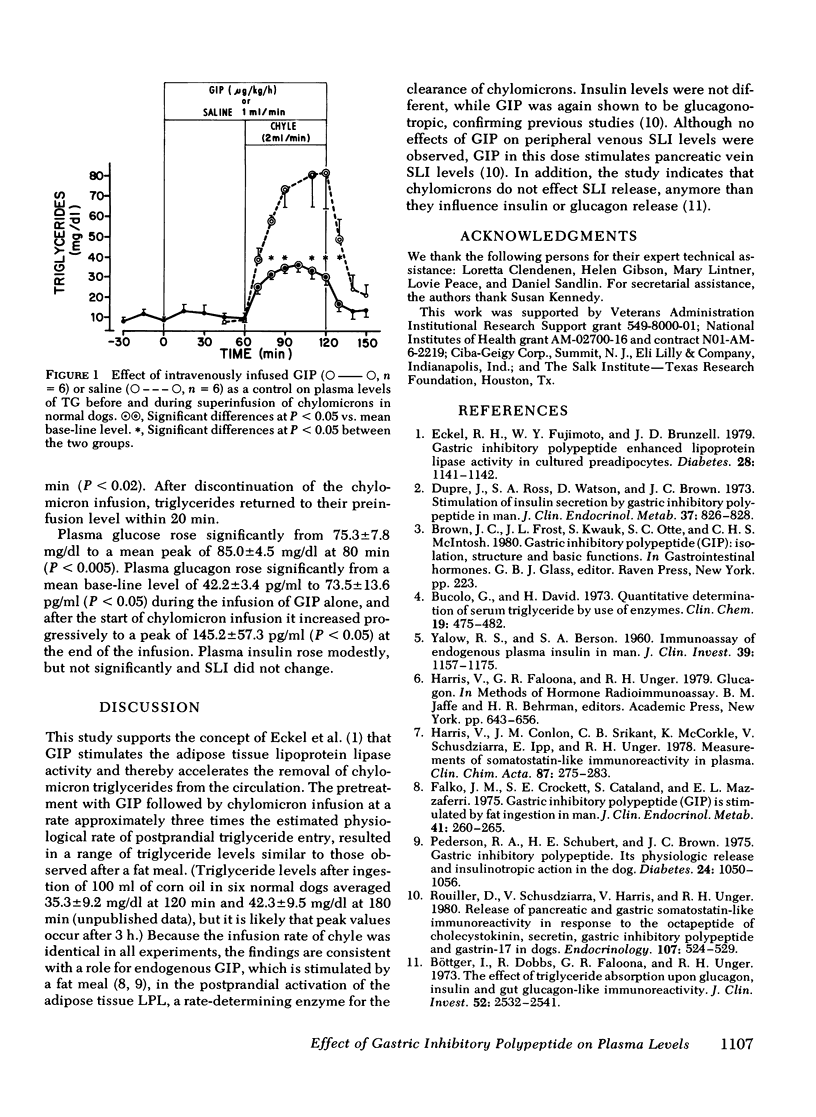
To determine whether gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) promotes the clearance of chylomicron triglycerides (TG) from the circulation in dogs, chyle collected from donor dogs via a thoracic duct fistula was infused at a rate of 2 ml/min i.v. into normal recipient dogs during an infusion of either porcine GIP (1 microgram/kg per h) or saline as a control. In the GIP-infused dogs the rise in plasma TG was significantly below that of the control animals [mean peak of 36 +/- 4 mg/dl vs. 82 +/- 18 mg/dl (P less than 0.05)]. It is concluded that GIP exerts an effect upon the removal of chylomicron TG from the blood. The results suggest that GIP may play a physiologic role in the disposition of ingested fat.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bucolo G., David H. Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clin Chem. 1973 May;19(5):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger I., Dobbs R., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. The effects of triglyceride absorption upon glucagon, insulin, and gut glucagon-like immunoreactivity. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2532–2541. doi: 10.1172/JCI107444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupre J., Ross S. A., Watson D., Brown J. C. Stimulation of insulin secretion by gastric inhibitory polypeptide in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Nov;37(5):826–828. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-5-826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H., Fujimoto W. Y., Brunzell J. D. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide enhanced lipoprotein lipase activity in cultured preadipocytes. Diabetes. 1979 Dec;28(12):1141–1142. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.12.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falko J. M., Crockett S. E., Cataland S., Mazzaferri E. L. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) stimulated by fat ingestion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Aug;41(2):260–265. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-2-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris V., Conlon J. M., Srikant C. B., McCorkle K., Schusdziarra V., Ipp E., Unger R. H. Measurements of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Jul 15;87(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90348-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson R. A., Schubert H. E., Brown J. C. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Its physiologic release and insulinotropic action in the dog. Diabetes. 1975 Dec;24(12):1050–1056. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.12.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouiller D., Schusdziarra V., Harris V., Unger R. H. Release of pancreatic and gastric somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in response to the octapeptide of cholecystokinin, secretin gastric inhibitory polypeptide, and gastrin-17 in dogs. Endocrinology. 1980 Aug;107(2):524–529. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-2-524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



