Abstract
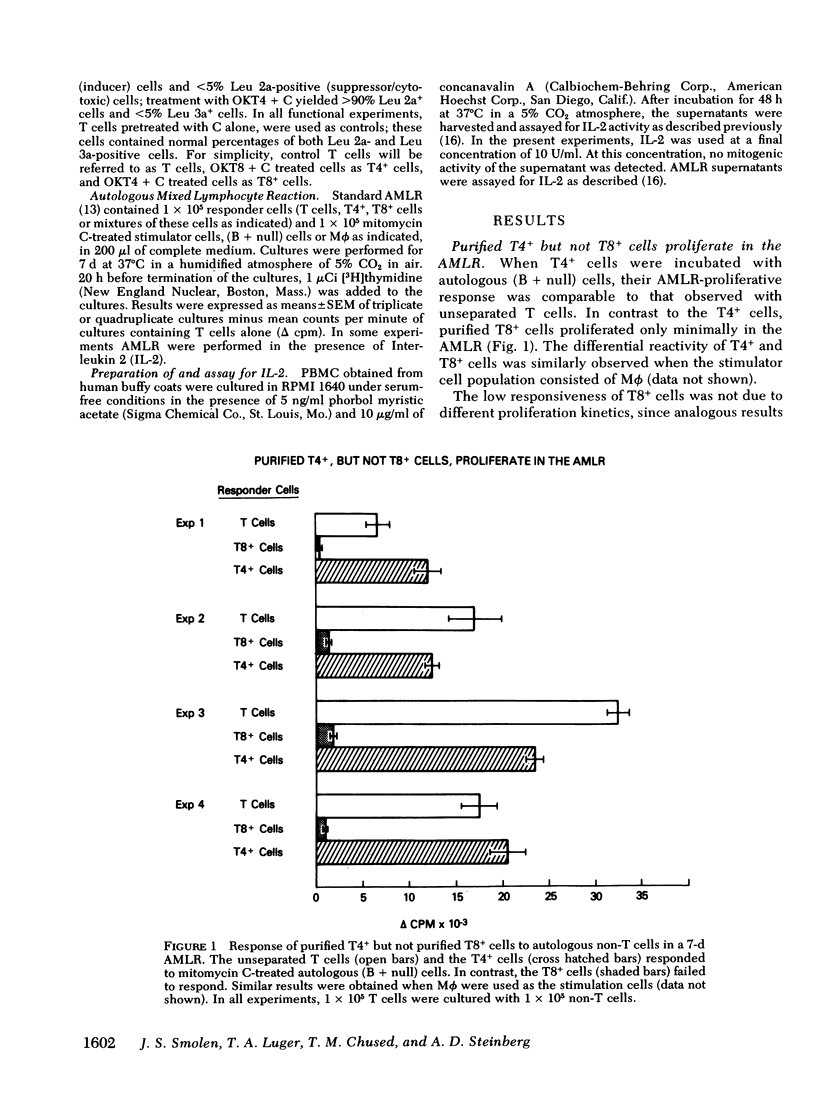
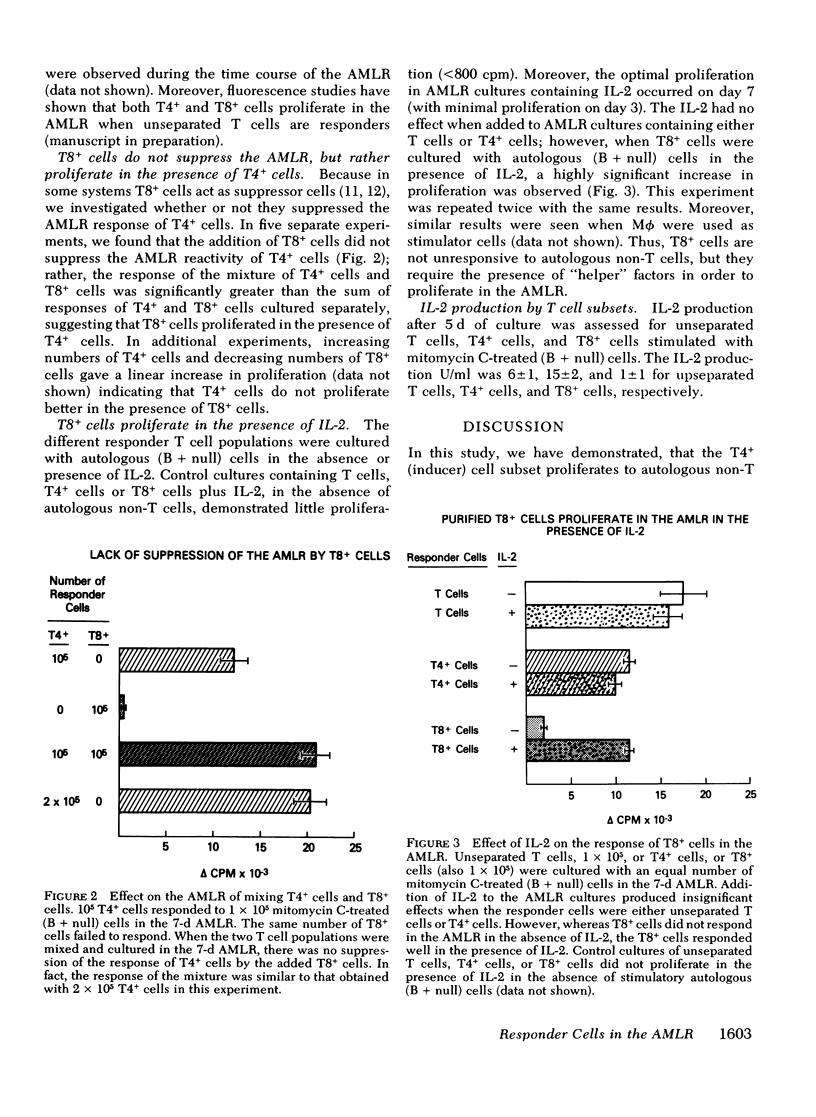
Isolated human T4+ cells proliferate in the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction (AMLR), whereas isolated T8+ cells do not. However, in the presence of Interleukin 2 or T4+ cells, the T8+ cells demonstrated substantial proliferation. These studies suggest that T8+ cells recognize signals from autologous non-T cells, but require an additional factor for the subsequent proliferative response. Since this stimulus can be provided by T4+ cells, the AMLR appears to constitute an inducer circuit. Different defects in this circuit may be responsible for the common abnormality of the AMLR in different diseases.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chiorazzi N., Fu S. M., Kunkel H. G. Induction of polyclonal antibody synthesis by human allogeneic and autologous helper factors. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1543–1548. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Benike C. J., Hoppe R. T., Kaplan H. S., Berberich F. R. Autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in patients with Hodgkin's disease. Evidence for a T cell defect. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):149–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI109828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman P. B., Stobo J. D. Specificity and function of a human autologous reactive T cell. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1537–1542. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz M. M., Innes J. B., Weksler M. E. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. IV. Human T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by autologous or allogeneic non-T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1042–1054. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Evans R. L., Lipinski M., Cunningham-Rundles C., Good R. A., Herzenberg L. A. Evolutionary conservation of surface molecules that distinguish T lymphocyte helper/inducer and cytotoxic/suppressor subpopulations in mouse and man. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):310–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger T. A., Stadler B. M., Katz S. I., Oppenheim J. J. Epidermal cell (keratinocyte)-derived thymocyte-activating factor (ETAF). J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1493–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka N., Sauvezie B., Pierce D. A., Daniels T. E., Talal N. Decreased autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):928–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI109960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opelz G., Kiuchi M., Takasugi M., Terasaki P. I. Autologous stimulation of human lymphocyte subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1327–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Separation of functional subsets of human T cells by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Specificity and suppressor function of human T cells responsive to autologous non-T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):584–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Failure of autologous mixed lymphocyte reactions between T and non-T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Knowlton R. P. Activation of suppressor T cells in human autologous mixed lymphocyte culture. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):419–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Ruscetti F. W. T-cell growth factor and the culture of cloned functional T cells. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:137–175. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60920-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Sharrow S. O., Reeves J. P., Boegel W. A., Steinberg A. D. The human autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. I. Suppression by macrophages and T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1987–1993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas Y., Sosman J., Irigoyen O., Friedman S. M., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Chess L. Functional analysis of human T cell subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies. I. Collaborative T-T interactions in the immunoregulation of B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2402–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler M. E., Kozak R. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells. V. Generation of immunologic memory and specificity during the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1833–1838. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


