Abstract
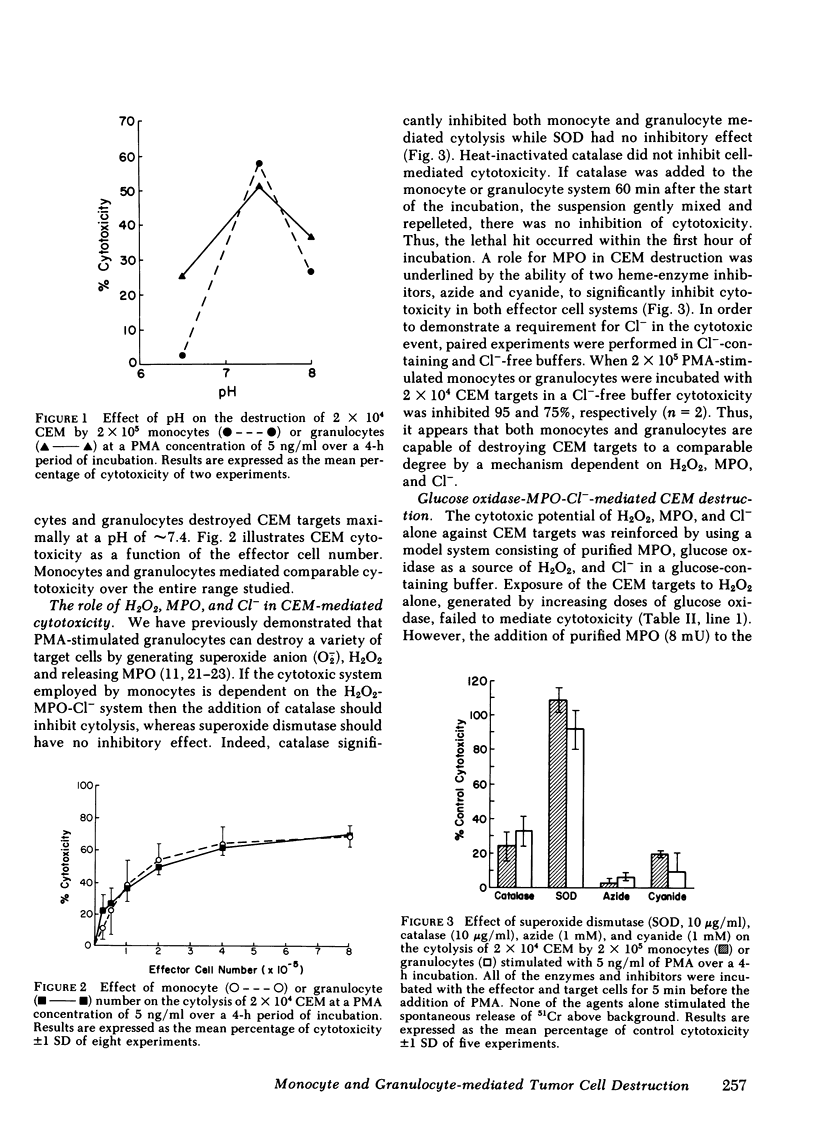
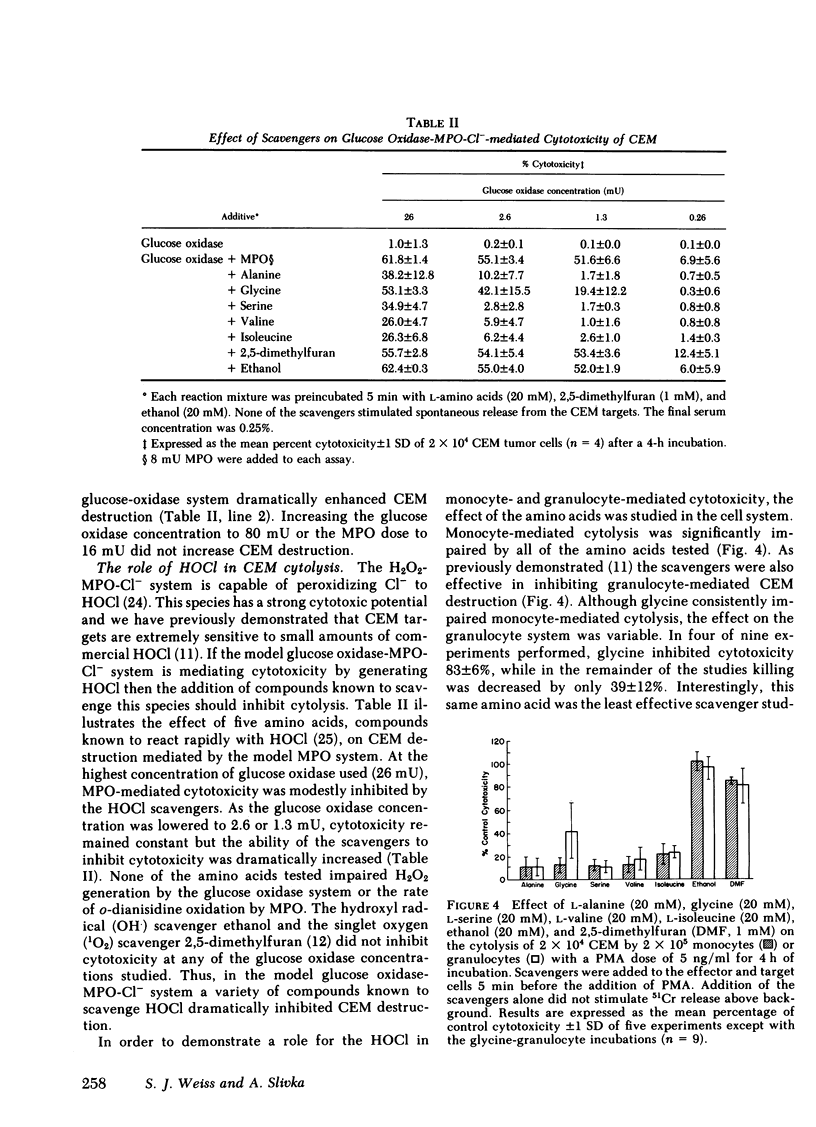
Human monocytes stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate were able to destroy a T lymphoblast cell target (CEM). Stimulated human granulocytes were also capable of mediating CEM cytotoxicity to a comparable degree as the monocyte. CEM destruction was dependent on the pH and the effector cell number. Both monocyte or granulocyte mediated cytotoxicity were inhibited by the addition of catalase, whereas superoxide dismutase had no inhibitory effect. In addition, CEM were protected from cytolysis by the effector cells by the myeloperoxidase inhibitors, azide and cyanide, or by performing the experiment under halide-free conditions. Glucose oxidase, an enzyme system capable of generating hydrogen peroxide, did not mediate CEM cytotoxicity, while the addition of purified myeloperoxidase dramatically enhanced cytolysis. Hypochlorous acid scavengers prevented CEM destruction by the glucose oxidase-myeloperoxidase-chloride system but neither hydroxyl radical nor singlet oxygen scavengers had any protective effect. These hypochlorous acid scavengers were also successful in inhibiting monocyte or granulocyte-mediated CEM cytotoxicity. Based on these observations we propose that human monocytes or granulocytes can utilize the hydrogen peroxide-myeloperoxidase-chloride system to generate hypochlorous acid or species of similar reactivity as a potential mediator of CEM destruction.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrich J. M., McCarthy C. A., Hurst J. K. Biological reactivity of hypochlorous acid: implications for microbicidal mechanisms of leukocyte myeloperoxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C. Halide dependence of the myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial system of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte in the phenomenon of electronic excitation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):675–683. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80437-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borregaard N., Kragballe K. Role of oxygen in antibody-dependent cytotoxicity mediated by monocytes and neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):676–683. doi: 10.1172/JCI109904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Neutrophil-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity: role of the peroxidase system. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1442–1447. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Neutrophil-platelet interaction mediated by myeloperoxidase and hydrogen peroxide. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):399–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Role of the myeloperoxidase-H2O2-halide system in concanavalin A-induced tumor cell killing by human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2605–2610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Szot S. The myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-halide system as effector of neutrophil-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1295–1301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S., Johnston R. B., Jr Effect of phorbol myristate acetate on the oxidative metabolism of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1976 Apr;47(4):545–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Haudenschild C. C. Monocyte-mediated serum-independent damage to hyphal and pseudohyphal forms of Candida albicans in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):173–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI110010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleer A., Roos D., von dem Borne A. E., Engelfriet C. P. Cytotoxic activity of human monocytes towards sensitized red cells is not dependent on the generation of reactive oxygen species. Blood. 1979 Aug;54(2):407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabig T. G., Bearman S. I., Babior B. M. Effects of oxygen tension and pH on the respiratory burst of human neutrophils. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1133–1139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Pabalan S., Schultz J. The subunit structure of crystalline canine myeloperoxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 23;493(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Schultz J. Studies on the chlorinating activity of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Watson B. D., Schultz J. Myeloperoxidase and singlet oxygen: a reappraisal. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80780-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held A. M., Hurst J. K. Ambiguity associated with use of singlet oxygen trapping agents in myeloperoxidase-catalyzed oxidations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):878–885. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr Oxygen metabolism and the microbicidal activity of macrophages. Fed Proc. 1978 Nov;37(13):2759–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Simone C. B., Henkart P. A., Fauci A. S. Mechanisms of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity: the use of effector cells from chronic granulomatous disease patients as investigative probes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):55–63. doi: 10.1172/JCI109660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Oxygen metabolism and the toxic properties of phagocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Sep;93(3):480–489. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-3-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson I. B., Etheridge R. D., Kratowich N. R., Lee J. The quenching of singlet oxygen by amino acids and proteins. Photochem Photobiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):165–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1975.tb06647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson R., Merkel P. B., Kearns D. R. Unambiguous evidence for the participation of singlet oxygen ( 1 ) in photodynamic oxidation of amino acids. Photochem Photobiol. 1972 Aug;16(2):117–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1972.tb07343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R. In vitro and in vivo investigations on antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;80:65–96. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66956-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinehart J. J., Lange P., Gormus B. J., Kaplan M. E. Human monocyte-induced tumor cell cytotoxicity. Blood. 1978 Jul;52(1):211–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Formation of singlet oxygen by the myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4803–4810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj R. J., Zgliczynski J. M., Paul B. B., Sbarra A. J. Chlorination or reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides by myeloperoxidase: a novel bactericidal mechanism. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Jan;27(1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Levy P. C., LoBuglio A. F. Human monocyte antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to tumor cells. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1172–1180. doi: 10.1172/JCI109236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sips H. J., Hamers M. N. Mechanism of the bactericidal action of myeloperoxidase: increased permeability of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):11–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.11-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka A., LoBuglio A. F., Weiss S. J. A potential role for hypochlorous acid in granulocyte-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Territo M. C., Cline M. J. Mononuclear phagocyte proliferation, maturation and function. Clin Haematol. 1975 Oct;4(3):685–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, chloride antimicrobial system: nitrogen-chlorine derivatives of bacterial components in bactericidal action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):522–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.522-531.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L. Myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride antimicrobial system: effect of exogenous amines on antibacterial action against Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):110–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.110-116.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurman R. G., Ley H. G., Scholz R. Hepatic microsomal ethanol oxidation. Hydrogen peroxide formation and the role of catalase. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb;25(3):420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsan M. F., Chen J. W. Oxidation of methionine by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1041–1050. doi: 10.1172/JCI109756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., LoBuglio A. F. An oxygen-dependent mechanism of neutrophil-mediated cytotoxicity. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):1020–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., LoBuglio A. F., Kessler H. B. Oxidative mechanisms of monocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):584–587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Rustagi P. K., LoBuglio A. F. Human granulocyte generation of hydroxyl radical. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):316–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. The role of superoxide in the destruction of erythrocyte targets by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9912–9917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Young J., LoBuglio A. F., Slivka A., Nimeh N. F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil-mediated destruction of cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgliczynski J. M., Selvaraj R. J., Paul B. B., Stelmaszynska T., Poskitt P. K., Sbarra A. J. Chlorination by the myeloperoxidase-H2O2-Cl- antimicrobial system at acid and neutral pH. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Mar;154(3):418–422. doi: 10.3181/00379727-154-39684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgliczyński J. M., Stelmaszyńska T., Domański J., Ostrowski W. Chloramines as intermediates of oxidation reaction of amino acids by myeloperoxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 16;235(3):419–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgliczyński J. M., Stelmaszyńska T., Ostrowiski W., Naskalski J., Sznajd J. Myeloperoxidase of human leukaemic leucocytes. Oxidation of amino acids in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Eur J Biochem. 1968 May;4(4):540–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



