Abstract
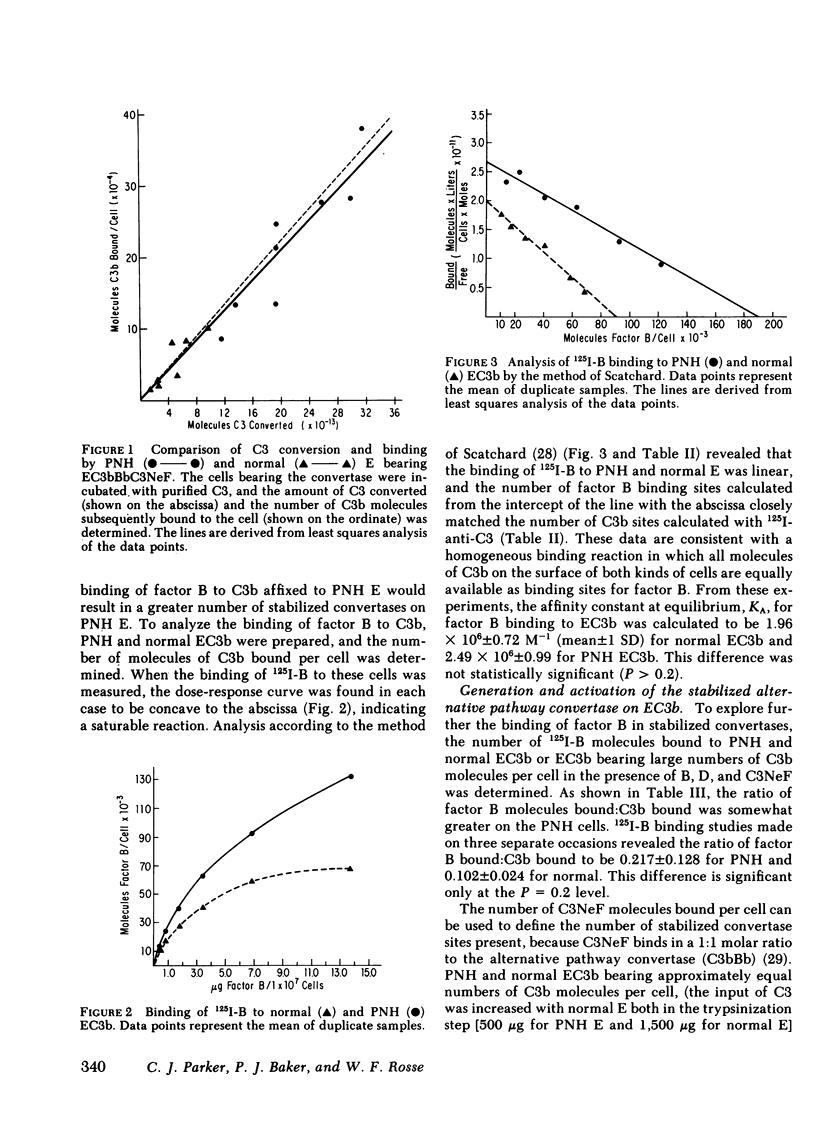
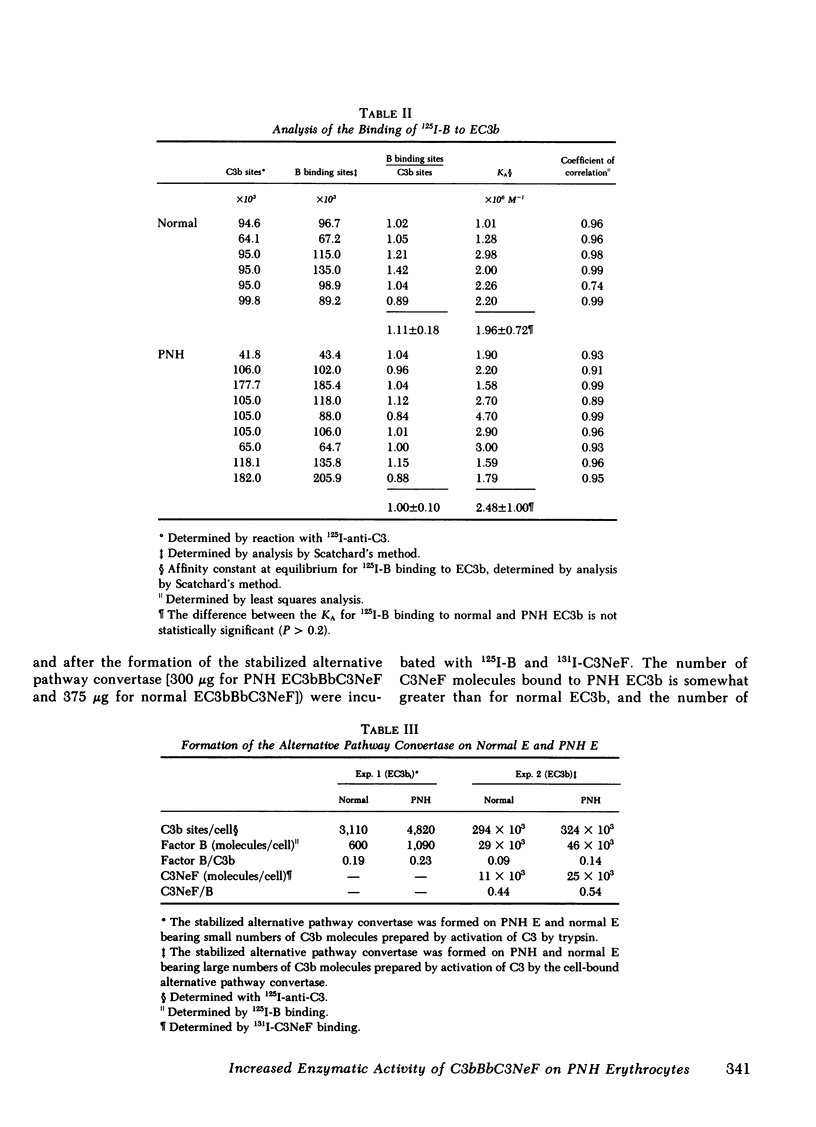
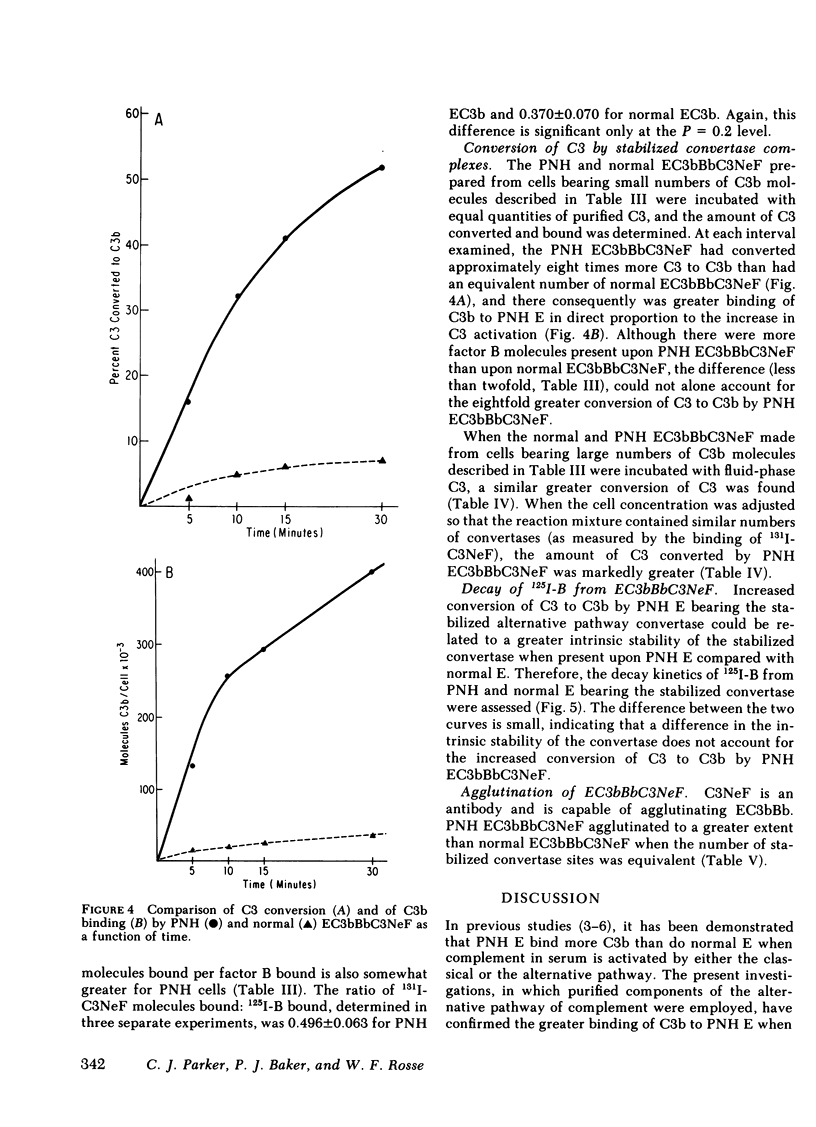
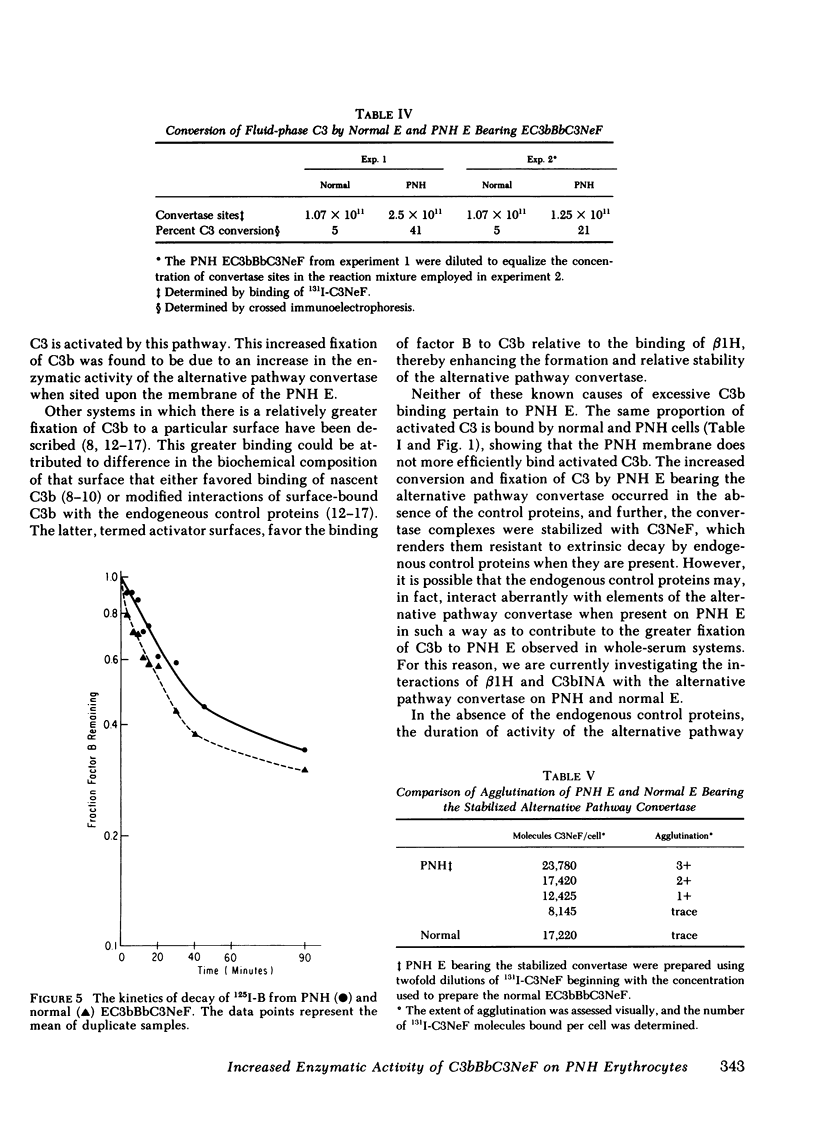
To investigate the greater fixation of C3 to the erythrocytes of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) upon activation of complement, we have examined the formation and the reaction of the C3 nephritic factor-stabilized alternative pathway convertase made with purified components on normal and PNH erythrocytes. Each convertase complex converts four to five times more fluid-phase C3 to C3b when affixed to a PNH cell than when affixed to a normal cell. The greater activity of the convertase on PNH cells is not due to differences in the intrinsic or extrinsic stability of the convertase complex. The excessive binding of C3 to PNH cell si due to this increased conversion of fluid-phase C3, because the efficiency of binding of nascent C3b was identical for the two cell types. This is the first instance in which the enzyme activity of a complement complex has been shown to be increased by being affixed to an abnormal surface.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUDITORE J. V., HARTMANN R. C. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. II. Erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase defect. Am J Med. 1959 Sep;27:401–410. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas S. J., Shapiro B., Green J. W. Surface properties of erythrocytes: normal, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and glutathione-treated cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):194–206. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capel P. J., Groeneboer O., Grosveld G., Pondman K. W. The binding of activated C3 to polysaccharides and immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2566–2572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua C., Hoffmann E. M., Adams J. P., Rosse W. F. Inhibitors of complement derived from the erythrocyte membrane in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):772–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Austen K. F., Fearon D. T. Heterogeneity, polypeptide chain composition and antigenic reactivity of C3 nephritic factor. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1389–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd, Ziegler J. B., Gelfand E. W., Rosen F. S., Alper C. A. Heterogeneity of nephritic factor and its identification as an immunoglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3980–3983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Activation of the alternative complement pathway due to resistance of zymosan-bound amplification convertase to endogenous regulatory mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1683–1687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Activation of the alternative complement pathway with rabbit erythrocytes by circumvention of the regulatory action of endogenous control proteins. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):22–33. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Current concepts in immunology: the alternative pathway of complement--a system for host resistance to microbial infection. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 31;303(5):259–263. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007313030505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Identification of the membrane glycoprotein that is the C3b receptor of the human erythrocyte, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, B lymphocyte, and monocyte. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):20–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation by membrane sialic acid of beta1H-dependent decay-dissociation of amplification C3 convertase of the alternative complement pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1971–1975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation of the amplification C3 convertase of human complement by an inhibitory protein isolated from human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5867–5871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gockerman J. P. The lipids of the erythrocyte in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am J Hematol. 1978;5(4):323–333. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830050407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C3-activator system: an alternate pathway of complement activation. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):90s–108s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. A new activity of complement component C3: cell-bound C3b potentiates lysis of erythrocytes by C5b,6 and terminal components. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):830–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Human alternative complement pathway: membrane-associated sialic acid regulates the competition between B and beta1 H for cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Fearon D. T., Silbert J. E., Austen K. F. Surface-associated heparin inhibits zymosan-induced activation of the human alternative complement pathway by augmenting the regulatory action of the control proteins on particle-bound C3b. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1202–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunstling T. R., Rosse W. F. Erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase deficiency in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). A comparison of the complement-sensitive and insensitive populations. Blood. 1969 Apr;33(4):607–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Dobson N. J., Ross G. D. Release of endogenous C3b inactivator from lymphocytes in response to triggering membrane receptors for beta 1H globulin. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1625–1644. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Levine R. P. Interaction between the third complement protein and cell surface macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Evidence for an ester linkage between the labile binding site of C3b and receptive surfaces. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1388–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logue G. L., Rosse W. F., Adams J. P. Mechanisms of immune lysis of red blood cells in vitro. I. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1129–1137. doi: 10.1172/JCI107279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A., Brade V., Schorlemmer H. U., Burger R., Bitter-Suermann D., Hadding U. Interaction of C3b, B, and D in the alternative pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1108–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman C. H., Rosenfeld S. I., Jenkins D. E., Jr, Thiem P. A., Leddy J. P. Complement lysis of human erythrocytes. Differeing susceptibility of two types of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells to C5b-9. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):428–433. doi: 10.1172/JCI109479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Morrison D. C., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Activation of the alternative complement pathway: recognition of surface structures on activators by bound C3b. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):977–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement C3 convertase: cell surface restriction of beta1H control and generation of restriction on neuraminidase-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2416–2420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Adams J. P., Thorpe A. M. The population of cells in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria of intermediate sensitivity to complement lysis: significance and mechanism of increased immune lysis. Br J Haematol. 1974 Oct;28(2):181–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Dacie J. V. Immune lysis of normal human and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) red blood cells. I. The sensitivity of PNH red cells to lysis by complement and specific antibody. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):736–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI105388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Dacie J. V. Immune lysis of normal human and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) red blood cells. II. The role of complement components in the increased sensitivity of PNH red cells to immune lysis. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):749–757. doi: 10.1172/JCI105389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Logue G. L., Adams J., Crookston J. H. Mechanisms of immune lysis of the red cells in hereditary erythroblastic multinuclearity with a positive acidified serum test and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):31–43. doi: 10.1172/JCI107551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F. Variations in the red cells in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol. 1973 Mar;24(3):327–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Nephritic factor: its structure and function and its relationship to initiating factor of the alternative pathway. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(6-7):705–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siriwittayakorn J., Yuthavong Y. Relation between low erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase activity and membrane lipids in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol. 1979 Mar;41(3):383–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb05871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. D., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: purification from plasma and physicochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4513–4521. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Eisen H. N. Binding of monomeric immunoglobulins to Fc receptors of mouse macrophages. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1520–1533. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



