Abstract
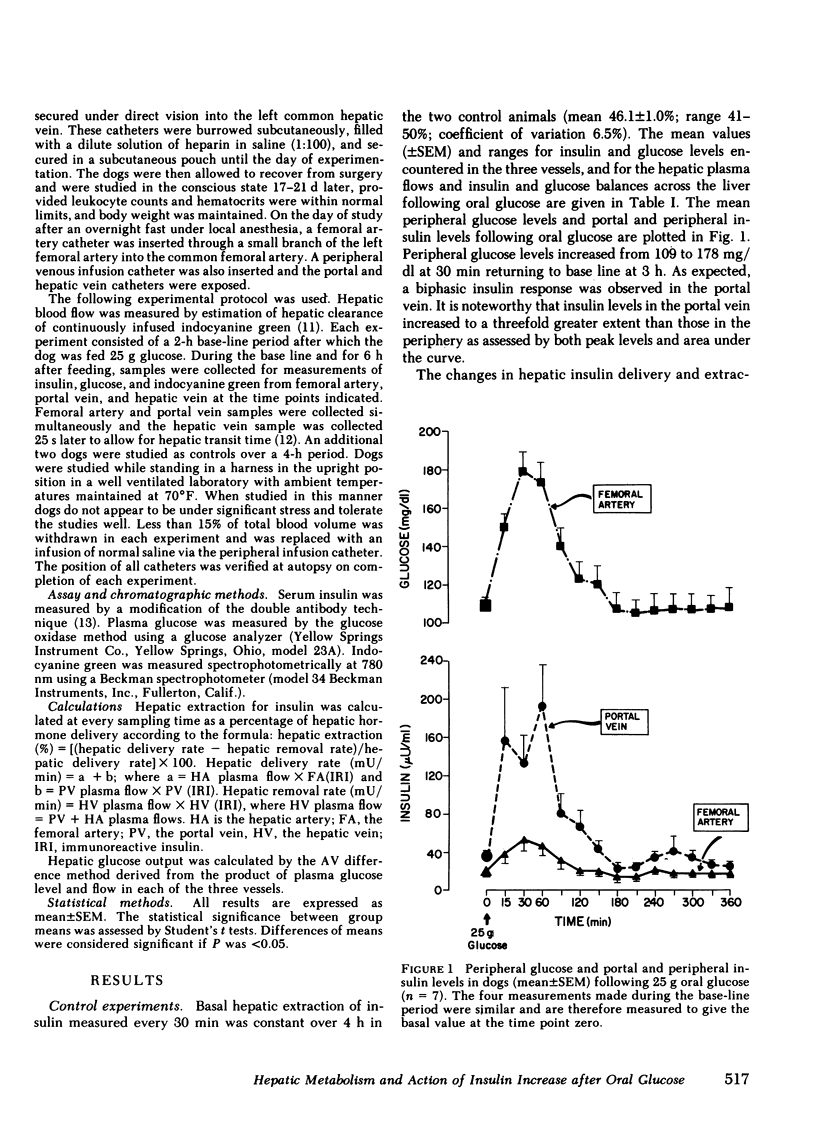
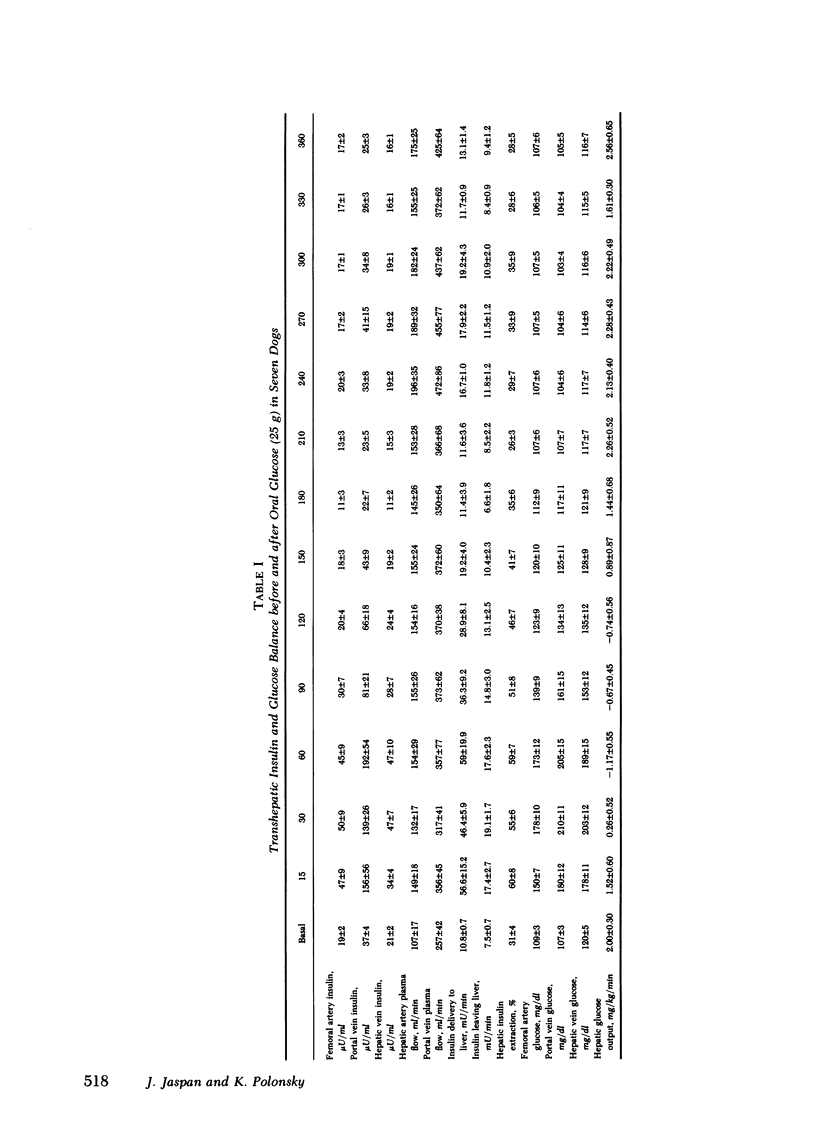
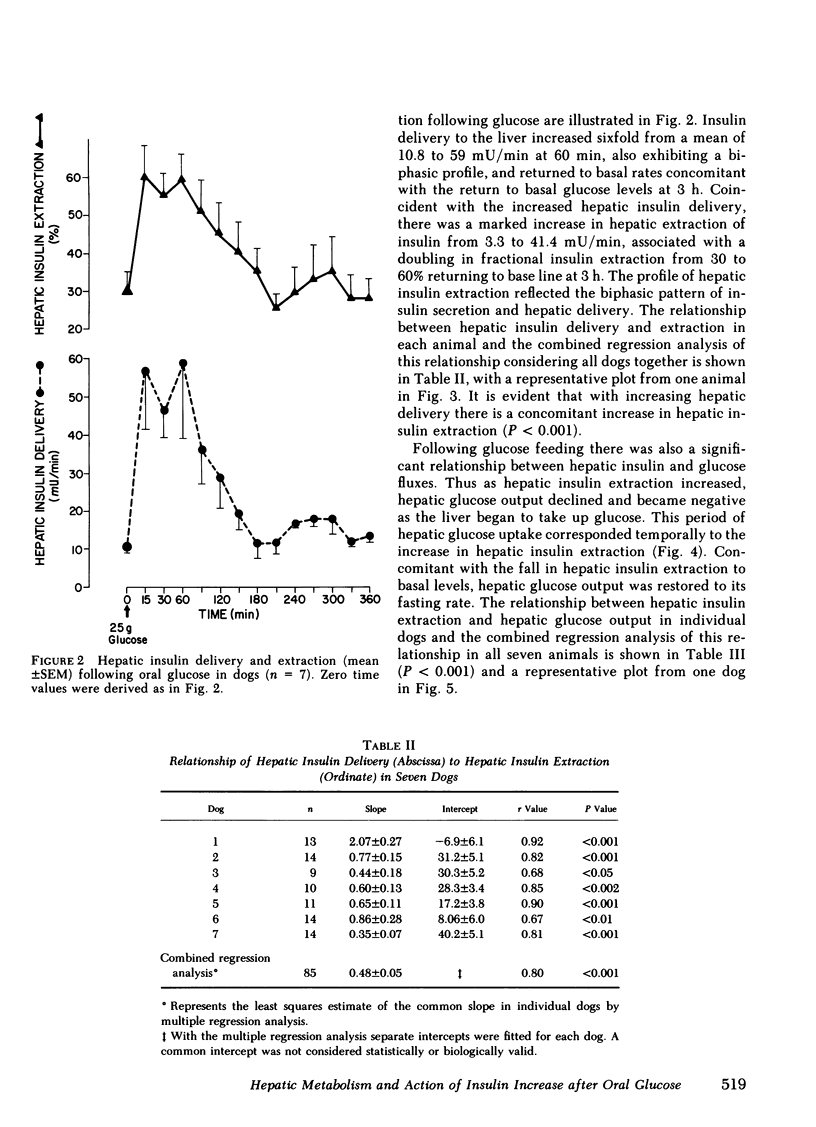
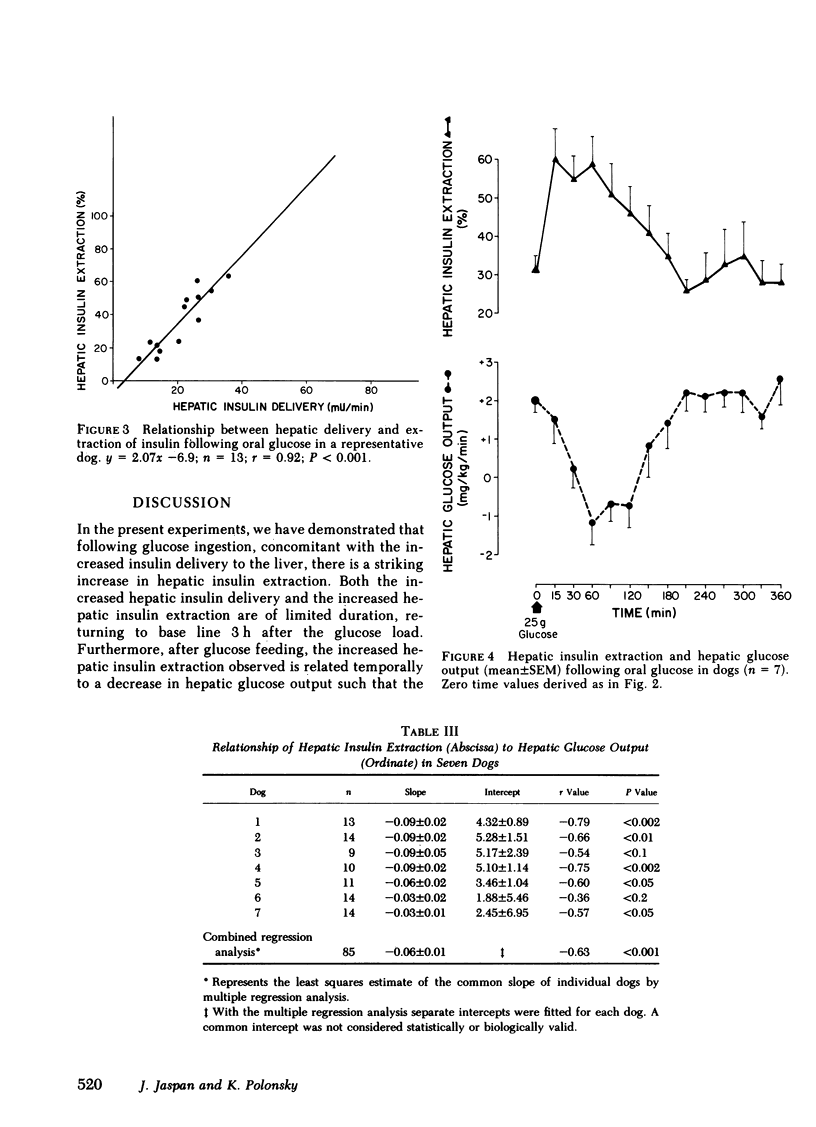
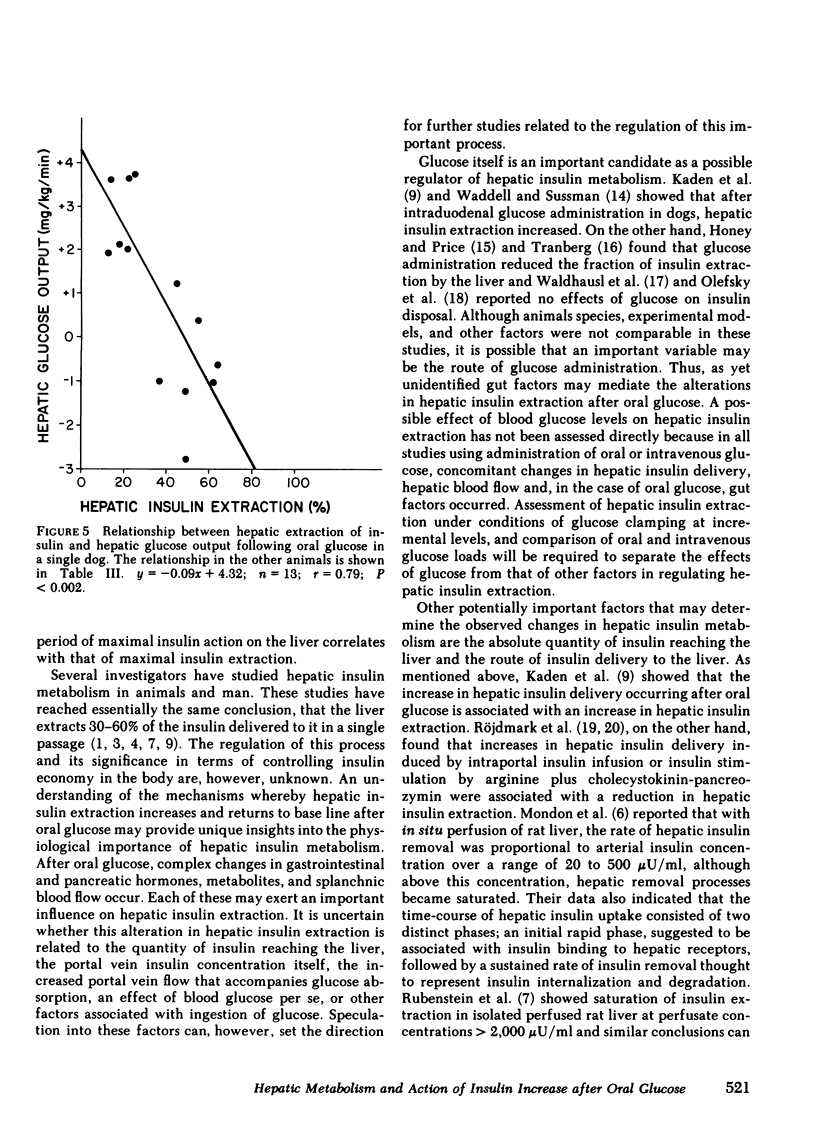
Oral glucose (25 g) fed to seven healthy, conscious dogs resulted in an increase in peripheral plasma glucose from 109 +/- 3 to 178 +/- 10 mg/dl. Concurrently serum insulin increased in the portal vein to levels approximately threefold greater than those in the periphery. Hepatic insulin delivery rose from 10.8 +/- 0.7 to 59.0 +/- 19.9 m U/min at 60 min. coincident with an increased hepatic insulin extraction from 3.3 to 41.4 mU/min (corresponding to an increase in hepatic extraction from 31 +/- 4 to 59 +/- 7%), both returning to basal at 3 h. In each animal there was a positive correlation between hepatic insulin delivery and extraction (r = 0.80, P less than 0.001 for the seven experiments combined). These changes in heptic insulin delivery and extraction after glucose metabolism associated with insulin action. As hepatic insulin extraction increased, hepatic glucose output declined, both parameters returning to basal levels by 3 h, indicating a negative correlation between hepatic insulin extraction and hepatic glucose output (r = 0.63, P less than 0.001; n = 7). The factors that mediate this marked and rapidly occurring increase in hepatic insulin extraction after oral glucose are unknown, and may include hepatic insulin delivery, glucose levels in the blood flow, and gut factors released by oral glucose intake. The association of changes in hepatic insulin extraction in vivo with an insulin effect on the liver as measured hepatic glucose output is consistent with in vitro observations relating insulin degradation to receptor binding.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., Gorden P., Roth J., Kahn C. R., De Meyts P. Fluctuations in the affinity and concentration of insulin receptors on circulating monocytes of obese patients: effects of starvation, refeeding, and dieting. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI108565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal and peripheral vein immunoreactive insulin concentrations before and after glucose infusion. Diabetes. 1970 May;19(5):302–306. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.5.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Jennings A. S., Keller U., Lacy W. W. The role of insulin and glucagon in the regulation of basal glucose production in the postabsorptive dog. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1407–1418. doi: 10.1172/JCI108596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Willeput J., Huet de Froberville A. Receptor-mediated internalisation of insulin in intact rat liver. A biochemical study. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 15;106(2):338–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P. The interactions of proinsulin with insulin receptors on the plasma membrane of the liver. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1020–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI107845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goriya Y., Bahoric A., Marliss E. B., Zinman B., Albisser A. M. Blood glucose control and insulin clearance in unrestrained diabetic dogs portally infused with a portable insulin delivery system. Diabetologia. 1980 Nov;19(5):452–457. doi: 10.1007/BF00281825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding P. E., Bloom G., Field J. B. Effect of infusion of insulin into portal vein on hepatic extraction of insulin in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1975 May;228(5):1580–1588. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.5.1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honey R. N., Price S. The determinants of insulin extraction in the isolated perfused rat liver. Horm Metab Res. 1979 Feb;11(2):111–117. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1092691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska K. A., Blondin J., Bass R., Santiago J., Thomas L., Altsheler P., Martin K., Klahr S. Effect of intact parathyroid hormone on hepatic glucose release in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):1016–1023. doi: 10.1172/JCI109538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel J. R., Kolterman O. G., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Short-term regulation of insulin receptor affinity in man. Diabetes. 1980 Feb;29(2):132–139. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.2.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KETTERER S. G., WIEGAND B. D., RAPAPORT E. Hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of indocyanine green and its use in estimation of hepatic blood flow in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1960 Sep;199:481–484. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaden M., Harding P., Field J. B. Effect of intraduodenal glucose administration on hepatic extraction of insulin in the anesthetized dog. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):2016–2028. doi: 10.1172/JCI107386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakash C., Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Jeanrenaud B. An anomaly of insulin removal in perfused livers of obese-hyperglycemic (ob/ob) mice. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1117–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Akanuma Y., Iwamoto Y., Kosaka K. Effects of fasting and refeeding of insulin receptors and glucose metabolism in rat adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1977 May;100(5):1384–1390. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-5-1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. I., Rubenstein A. H. Metabolism of proinsulin, insulin, and C-peptide in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1113–1121. doi: 10.1172/JCI107277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Peptide hormone-induced receptor mobility, aggregation, and internalization. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 9;305(2):77–88. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107093050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabchi A. E. Proinsulin and C-peptide: a review. Metabolism. 1977 May;26(5):547–587. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Greenfield M., Reaven G. M., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Effect of a high carbohydrate diet on insulin binding to adipocytes and on insulin action in vivo in man. Diabetes. 1979 Aug;28(8):731–736. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.8.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. The effects of acute and chronic starvation on insulin binding to isolated human adipocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 May;48(5):836–842. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-5-836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M., Lane M. D. On the mechanism of ligand-induced down-regulation of insulin receptor level in the liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1689–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E., TIETZE F., STETTEN D., Jr Metabolism of insulin-I 131; studies in isolated, perfused rat liver and hindlimb preparations. Diabetes. 1959 Jul-Aug;8(4):307–314. doi: 10.2337/diab.8.4.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison L. L. Role of insulin in the hepatic handling of glucose. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):284–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misbin R. I., Merimee T. J., Lowenstein J. M. Insulin removal by isolated perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jan;230(1):171–177. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondon C. E., Olefsky J. M., Dolkas C. B., Reaven G. M. Removal of insulin by perfused rat liver: effect of concentration. Metabolism. 1975 Feb;24(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggeo M., Bar R. S., Roth J. Change in affinity of insulin receptors following oral glucose in normal adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jun;44(6):1206–1209. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-6-1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Batchelder T., Colome S., Reaven G. M. Effect of intravenous glucose infusion on plasma insulin removal rate. Metabolism. 1974 Jun;23(6):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Effects of fasting on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation in isolated rat adipocytes: relationships between insulin receptors and insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1450–1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI108601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Johnson J., Liu F., Edwards P., Baur S. Comparison of 125-I-insulin binding and degradation to isolated rat hepatocytes and liver membranes. Diabetes. 1975 Sep;24(9):801–810. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.9.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Roth J., Macchia V. Binding of hormone to tissue: the first step in polypeptide hormone action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1802–1809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Peptide hormone binding to receptors: a review of direct studies in vitro. Metabolism. 1973 Aug;22(8):1059–1073. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Pottenger L. A., Mako M., Getz G. S., Steiner D. F. The metabolism of proinsulin and insulin by the liver. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):912–921. doi: 10.1172/JCI106886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röjdmark S., Bloom G., Chou M. C., Field J. B. Hepatic extraction of exogenous insulin and glucagon in the dog. Endocrinology. 1978 Mar;102(3):806–813. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-3-806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röjdmark S., Bloom G., Chou M. C., Jaspan J. B., Field J. B. Hepatic insulin and glucagon extraction after their augmented secretion in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jul;235(1):E88–E96. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.1.E88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage P. J., Flock E. V., Mako M. E., Blix P. M., Rubenstein A. H., Bennett P. H. C-Peptide and insulin secretion in Pima Indians and Caucasians: constant fractional hepatic extraction over a wide range of insulin concentrations and in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Apr;48(4):594–598. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-4-594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvers A., Farquhar J. W., Lerner R. L., Reaven G. M. Evaluation of the dog as an experimental model for the study of insulin distribution and degradation in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Feb;75(2):175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman V. R., Koivisto V. A., Grantham P., Felig P. Increased insulin binding to monocytes after acute exercise in normal man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Jul;47(1):216–219. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-1-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll R. W., Touber J. L., Menahan L. A., Williams R. H. Clearance of porcine insulin, proinsulin, and connecting peptide by the isolated rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):894–896. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Hofmann C., Steiner D. F. Mode of uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated hepatocytes and H4 hepatoma cells. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):459–468. doi: 10.1139/o79-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Retention and degradation of 125I-insulin by perfused livers from diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):885–896. doi: 10.1172/JCI108365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranberg K. G., Thorell J. Variation in the disappearance of unlabeled insulin from plasma: studies with portal and peripheral infusions. Diabetes. 1979 Sep;28(9):846–851. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.9.846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. C., Grayburn J. A., Newman G. B., Nabarro J. D. Measurement of the insulin delivery rate in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):279–286. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. R., Sussman K. E. Plasma insulin after diversion of portal and pancreatic venous blood to vena cava. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Apr;22(4):808–812. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.4.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldhäusl W., Bratusch-Marrain P., Gasic S., Korn A., Nowotny P. Insulin production rate following glucose ingestion estimated by splanchnic C-peptide output in normal man. Diabetologia. 1979 Oct;17(4):221–227. doi: 10.1007/BF01235858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



