Abstract
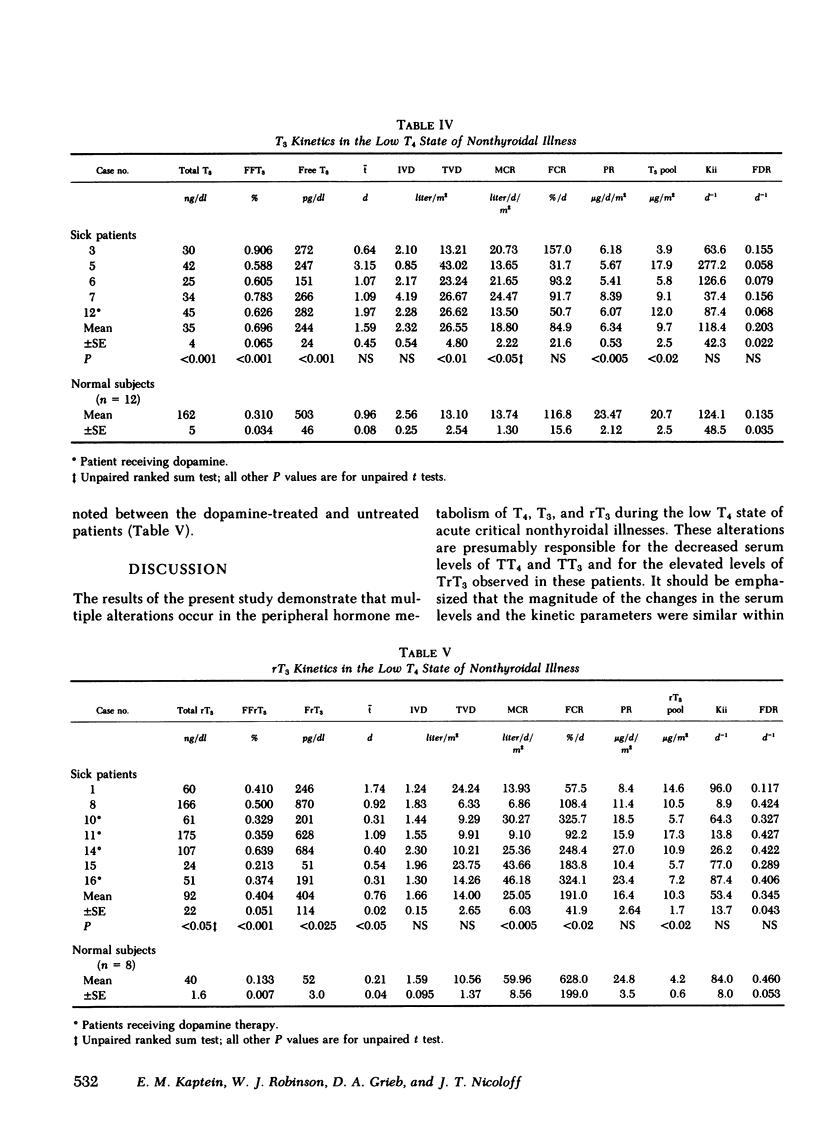
The low thyroxine (T4) state of acute critical nonthyroidal illnesses is characterized by marked decreases in serum total T4 and triiodothyronine (T3) with elevated reverse T3 (rT3) values. To better define the mechanisms responsible for these alterations, serum kinetic disappearance studies of labeled T4, T3, or rT3 were determined in 16 patients with the low T4 state and compared with 27 euthyroid controls and a single subject with near absence of thyroxine-binding globulin. Marked increases in the serum free fractions of T4 (0.070±0.007%, normal [nl] 0.0315±0.0014, P < 0.001), T3 (0.696±0.065%, nl 0.310±0.034, P < 0.001), and rT3 (0.404±0.051%, nl 0.133±0.007, P < 0.001) by equilibrium dialysis were observed indicating impaired serum binding. Noncompartmental analysis of the kinetic data revealed an increased metabolic clearance rate (MCR) of T4 (1.69±0.22 liter/d per m2, nl 0.73±0.05, P < 0.001) and fractional catabolic rate (FCR) (32.8±2.6%, nl 12.0±0.8, P < 0.001), analogous to the euthyroid subject with low thyroxine-binding globulin. However, the reduced rate of T4 exit from the serum (Kii) (15.2±4.6 d−1, nl 28.4±3.9, P < 0.001) indicated an impairment of extravascular T4 binding that exceeded the serum binding defect. This defect did not apparently reduce the availability of T4 to sites of disposal as reflected by the increased fractional disposal rate of T4 (0.101±0.018 d−1, nl 0.021±0.003, P < 0.001). The decreased serum T3 binding was associated with the expected increases in MCR (18.80±2.22 liter/d per m2, nl 13.74±1.30, P < 0.05) and total volume of distribution (26.55±4.80 liter/m2, nl 13.10±2.54, P < 0.01). However, the unaltered Kii suggested an extravascular binding impairment comparable to that found in serum. The decreased T3 production rate (6.34±0.53 μg/d per m2, nl 23.47±2.12, P < 0.005) appeared to result from reduced peripheral T4 to T3 conversion because of decreased 5′-deiodination rather than from a decreased T4 availability. This view was supported by the normality of the rT3 production rate. The normal Kii values for rT3 indicated a comparable defect in serum and extravascular rT3 binding. The reduced MCR (25.05±6.03 liter/d per m2, nl 59.96±8.56, P < 0.005) and FCR (191.0±41.19%, nl 628.0±199.0, P < 0.02) for rT3 are compatible with an impairment of the rT3 deiodination rate.
These alterations in thyroid hormones indices and kinetic parameters for T4, T3, and rT3 in the low T4 state of acute nonthyroidal illnesses can be accounted for by: (a) decreased binding of T4, T3, and rT3 to vascular and extravascular sites with a proportionately greater impairment of extravascular T4 binding, and (b) impaired 5′-deiodination activity affecting both T4 and rT3 metabolism.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balsam A., Ingbar S. H. The influence of fasting, diabetes, and several pharmacological agents on the pathways of thyroxine metabolism in rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):415–424. doi: 10.1172/JCI109143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi R., Zucchelli G. C., Giannessi D., Pilo A., Mariani G., Carpi A., Toni M. G. Evaluation of triiodothyronine (T3) kinetics in normal subjects, in hypothyroid, and hyperthyroid patients using specific antiserum for the determination of labeled T3 in plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Feb;46(2):203–214. doi: 10.1210/jcem-46-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H. G., Riegelman S., Elashoff R. M. Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1974 Apr;2(2):123–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgi H., Wimpfheimer C., Burger A., Zaunbauer W., Rösler H., Lemarchand-Béraud T. Changes of circulating thyroxine, triiodothyronine and reverse triiodothyronine after radiographic contrast agents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Dec;43(6):1203–1210. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-6-1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter J. N., Eastmen C. J., Corcoran J. M., Lazarus L. Inhibition of conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in patients with severe chronic illness. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1976 Nov;5(6):587–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1976.tb03861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. R., Searle G. L. The kinetics of distribution between plasma and liver of 131-I-labeled L-thyroxine in man: observations of subjects with normal and decreased serum thyroxine-binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):939–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI105409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. R., Steinberg M., Searle G. L. The distribution kinetics of triiodothyronine: studies of euthyroid subjects with decreased plasma thyroxine-binding globulin and patients with Graves' disease. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1172/JCI106320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challand G. S., Ratcliffe W. A., Ratcliffe J. G. Semi-automated radioimmunoassays for total serum thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Apr 2;60(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A radioimmunoassay for measurement of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3). J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):583–592. doi: 10.1172/JCI107795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. An assessment of daily production and significance of thyroidal secretion of 3, 3', 5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3) in man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):32–40. doi: 10.1172/JCI108456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Chopra U., Smith S. R., Reza M., Solomon D. H. Reciprocal changes in serum concentrations of 3,3',5-triiodothyronine (T3) in systemic illnesses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Dec;41(06):1043–1049. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-6-1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Hepner G. W., Morgenstein A. A. Misleadingly low free thyroxine index and usefulness of reverse triiodothyronine measurement in nonthyroidal illnesses. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jun;90(6):905–912. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-6-905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Teco G. N., Nguyen A. H., Solomon D. H. In search of an inhibitor of thyroid hormone binding to serum proteins in nonthyroid illnesses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jul;49(1):63–69. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felicetta J. V., Green W. L., Nelp W. B. Inhibition of hepatic binding of thyroxine by cholecystographic agents. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1032–1040. doi: 10.1172/JCI109755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamstedt A., Järnerot G., Kågedal B., Söderholm B. Corticosteroids and thyroid function. Different effects on plasma volume, thyroid hormones and thyroid hormone-binding proteins after oral and intravenous administration. Acta Med Scand. 1979;205(5):379–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. A., Flock E. V., Owen C. A., Jr, Paris J. Factors affecting exchange of thyroid hormones between liver and blood. Endocrinology. 1966 Aug;79(2):391–405. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurpide E., Mann J. Interpretation of isotopic data obtained from blood-borne compounds. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Jun;30(6):707–718. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-6-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillier A. P. The mechanism of thyroxine transfer from plasma to tissue binding sites. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(3):635–639. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings A. S., Ferguson D. C., Utiger R. D. Regulation of the conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in the perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1614–1623. doi: 10.1172/JCI109623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang N. S., Tue K. A. Determination of free thyroxine in serum by radioimmunoassay. Clin Chem. 1977 Sep;23(9):1679–1683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaptein E. M., Grieb D. A., Spencer C. A., Wheeler W. S., Nicoloff J. T. Thyroxine metabolism in the low thyroxine state of critical nonthyroidal illnesses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Oct;53(4):764–771. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-4-764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaptein E. M., MacIntyre S. S., Weiner J. M., Spencer C. A., Nicoloff J. T. Free thyroxine estimates in nonthyroidal illness: comparison of eight methods. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jun;52(6):1073–1077. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-6-1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochupillai N., Yalow R. S. Preparation, purification, and stability of high specific activity 125I-labeled thyronines. Endocrinology. 1978 Jan;102(1):128–135. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-1-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman L. G., Hershman J. M., Chopra I. J., Levine G. A., Pekary E., Geffner D. L., Chua Teco G. N. Patterns off recovery of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in patients taken of chronic thyroid therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Jul;41(1):70–80. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-1-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R., Atkinson A. J., Jr, Wellman H. N., Goldsmith R. E. The effect of diphenylhydantoin on thyroxine metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1266–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI106339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. R. Salicylate-induced increases in free triiodothyronine in human serum. Evidence of inhibition of triiodothyronine binding to thyroxine-binding globulin and thyroxine-binding prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1125–1134. doi: 10.1172/JCI106905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. P., Marshall J. S., Velayo N. L. Radioimmunoassay of human thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Mar;32(3):372–381. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-3-372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim V. S., Fang V. S., Katz A. I., Refetoff S. Thyroid dysfunction in chronic renal failure. A study of the pituitary-thyroid axis and peripheral turnover kinetics of thyroxine and triiodothyronine. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):522–534. doi: 10.1172/JCI108804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald L. J., Robin N. I., Siegel L. Free thyroxine in serum as estimated by polyacrylamide gel filtration. Clin Chem. 1978 Apr;24(4):652–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musa B. U., Kumar R. S., Dowling J. T. Effects of salicylates on the distribution and early plasma disappearance of thyroxine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Oct;28(10):1461–1464. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-10-1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoloff J. T., Fisher D. A., Appleman M. D., Jr The role of glucocorticoids in the regulation of thyroid function in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1922–1929. doi: 10.1172/JCI106411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoloff J. T., Low J. C., Dussault J. H., Fisher D. A. Simultaneous measurement of thyroxine and triiodothyronine peripheral turnover kinetics in man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):473–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI106835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Buck M. W., Shimizu T. Reduced peripheral conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):643–652. doi: 10.1172/JCI108134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Bernstein G., Hasen J. Estimation of rapidly exchangeable cellular thyroxine from the plasma disappearance curves of simultaneously administered thyroxine-131-I and albumin-125-I. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):762–777. doi: 10.1172/JCI105577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Fleischer A. S., Kutner M. H., Raggio J. F. Suprahypophyseal hypogonadism and hypothyroidism during prolonged coma after head trauma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Oct;45(4):747–754. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-4-747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. L., Sheppard R. H., Steiner G., Chandarlapaty C. S., de Veber G. A. Influence of heparin on serum free thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Aug;29(8):1015–1022. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-8-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Schadlow A. R., Faierman D., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Heparin administration appears to decrease cellular binding of thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Mar;36(3):598–600. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-3-598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slag M. F., Morley J. E., Elson M. K., Crowson T. W., Nuttall F. Q., Shafer R. B. Hypothyroxinemia in critically ill patients as a predictor of high mortality. JAMA. 1981 Jan 2;245(1):43–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A. Free thyroxine in human serum: simplified measurement with the aid of magnesium precipitation. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1172/JCI105320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda A. K., Pittman C. S., Shimizu T., Chambers J. B., Jr The production and metabolism of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine and 3,3',5-triiodothyronine in normal and fasting subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Dec;47(6):1311–1319. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-6-1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. G., Cyrus J., Samols E. Low T4 and low FT4I in seriously ill patients: concise communication. J Nucl Med. 1980 May;21(5):432–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Bennett L. R. Changes in circulating iodothyronines in euthyroid and hyperthyroid subjects given ipodate (Oragrafin), an agent for oral cholecystography. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Apr;46(4):691–697. doi: 10.1210/jcem-46-4-691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



