Abstract
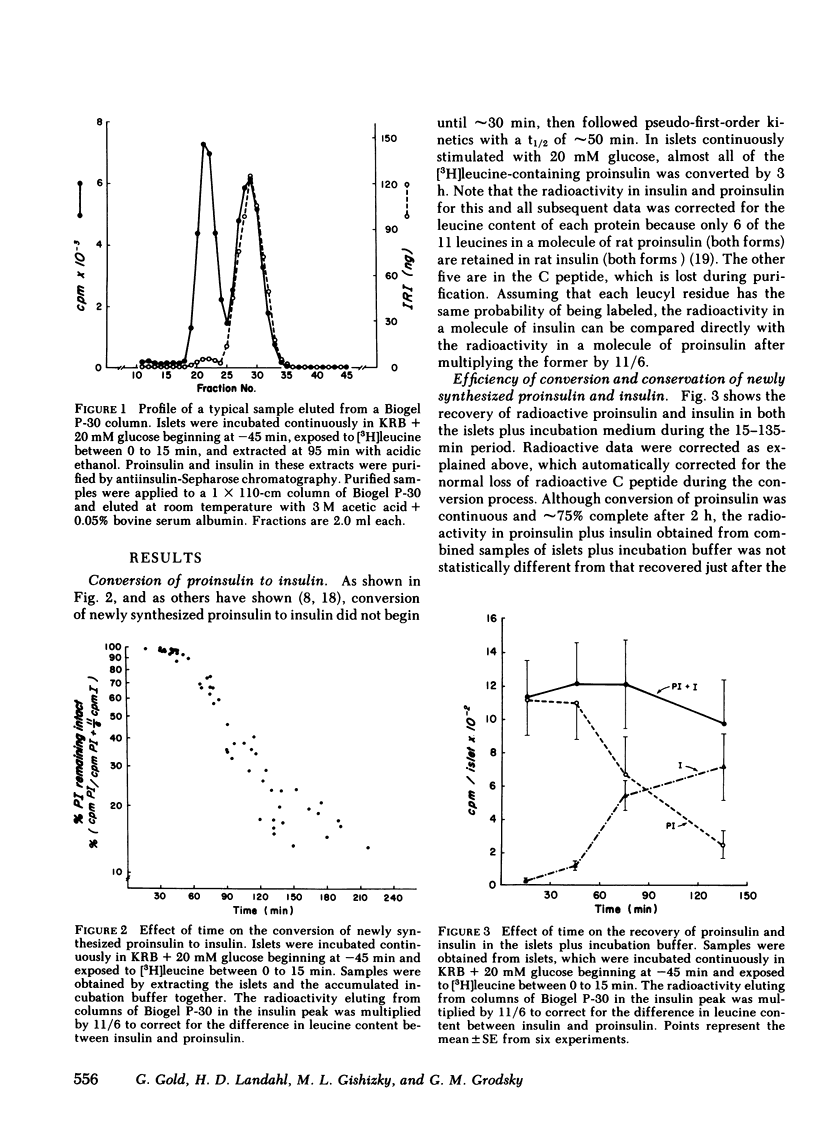
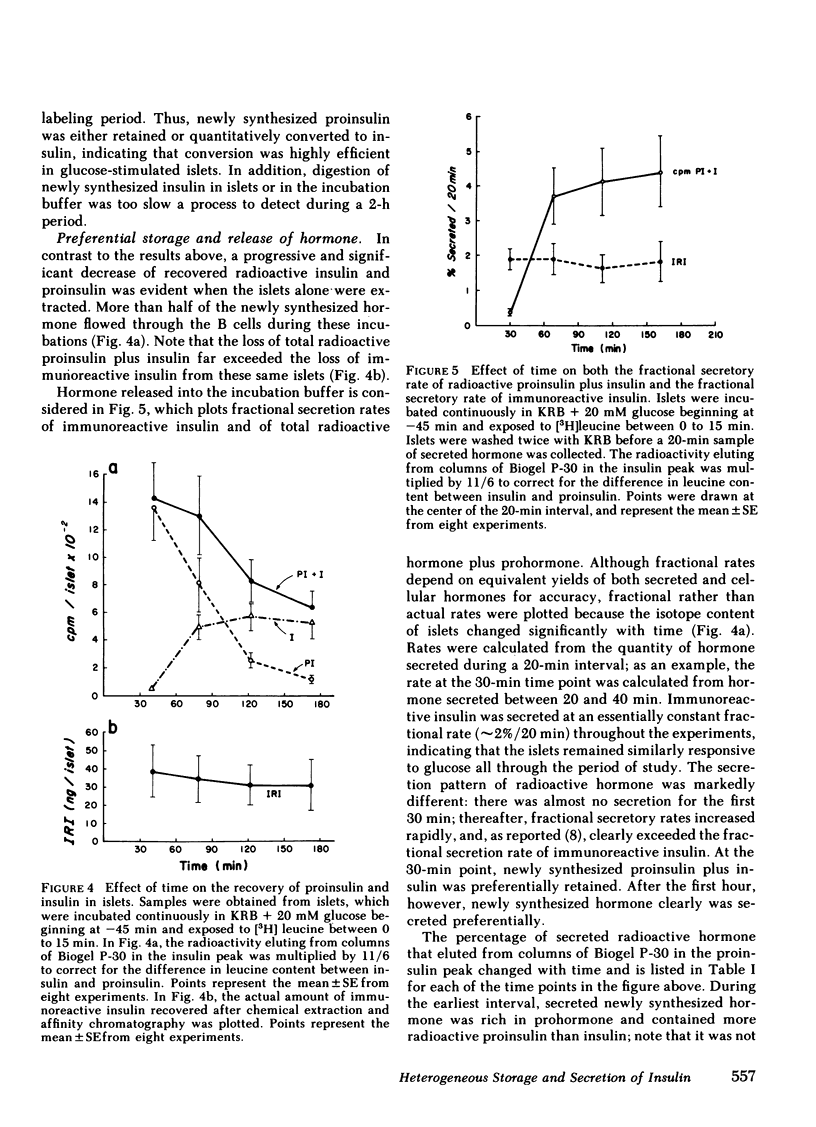
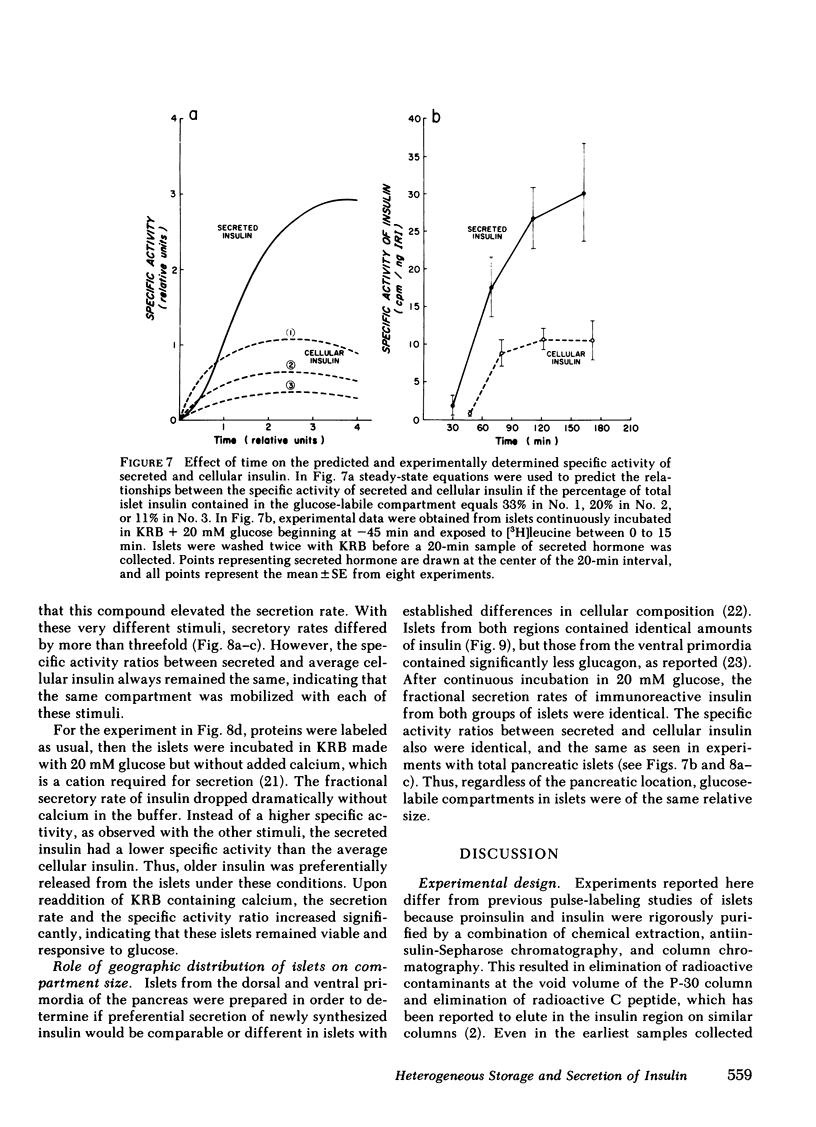
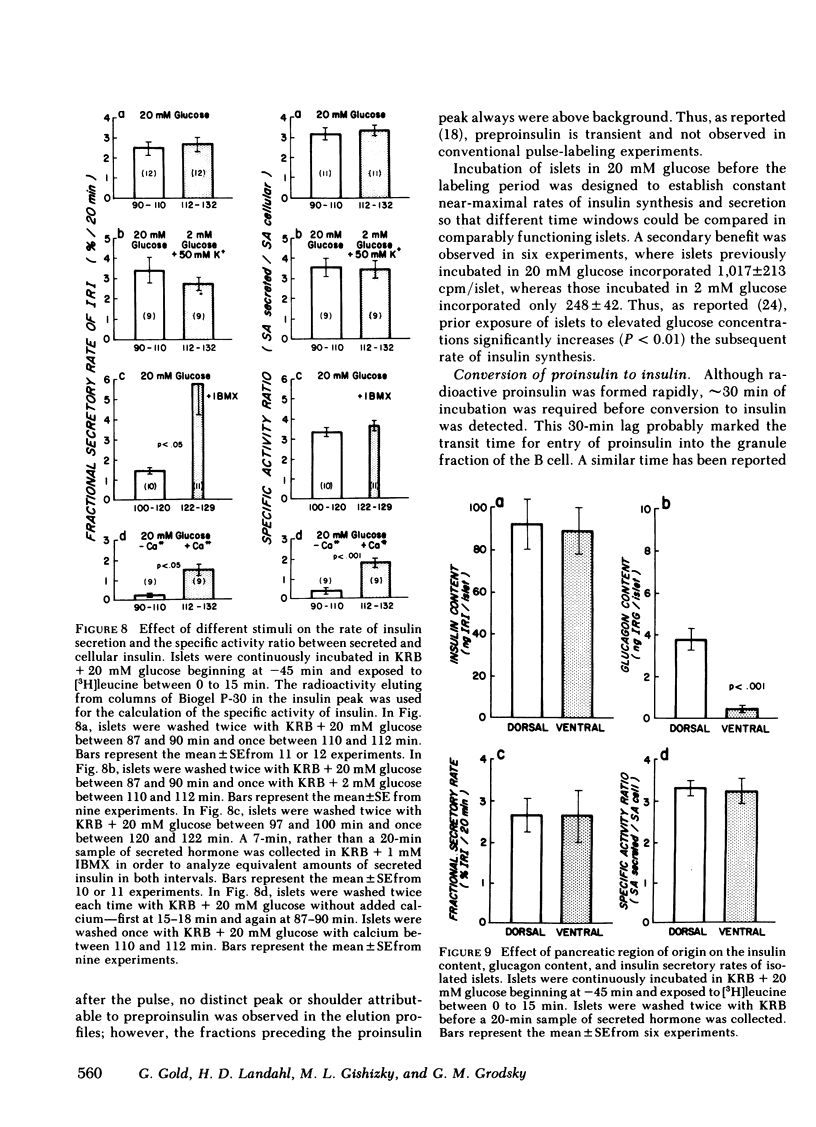
To investigate compartmental properties of insulin storage and secretion, isolated rat islets were used for pulse-labeling experiments, after which proinsulin and insulin were purified rigorously. Processing of proinsulin to insulin neared completion by 3 h without additional loss of either radioactive peptide by cellular or extracellular proteolysis. The amount of labeled hormone rapidly diminished in islets; it was secreted at a higher fractional rate than immunoreactive insulin, resulting in secreted insulin's having a higher specific activity than the average cellular insulin. Newly synthesized insulin, therefore, was secreted preferentially. Changes in the specific activity of secreted and cellular insulin with time were consistent with changes predicted for islets containing 33% of their total insulin in a glucose-labile compartment. Predictions were based on steady-state analysis of a simple storage-limited representation of B cell function. Islets from either the dorsal or ventral part of the pancreas also contained 33% of their total insulin in a glucose-labile compartment. The same compartment was mobilized by 20 mM glucose, 50 mM potassium + 2 mM glucose, or 20 MM glucose + 1 mM 3-isobutylmethylxanthine as indicated by the specific activity ratio of secreted vs. cellular insulin, even though average secretion rates with these stimuli differed by more than threefold. In the absence of calcium, the effectiveness of 20 mM glucose as a secretagogue declined markedly, and the older stored insulin was preferentially mobilized because secreted insulin had a lower rather than a higher specific activity than cellular insulin. Results provide insight into the mechanisms of nonrandom mobilization and secretion of insulin form the B cell.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson A., Westman J., Hellerström C. Effects of glucose on the ultrastructure and insulin biosynthesis of isolated mouse pancreatic islets maintained in tissue culture. Diabetologia. 1974 Dec;10(6):743–753. doi: 10.1007/BF01219536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetens D., Malaisse-Lagae F., Perrelet A., Orci L. Endocrine pancreas: three-dimensional reconstruction shows two types of islets of langerhans. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1323–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.390711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berne C. Anti-insulin serum coupled to Sepharose 4B as a tool for the investigation of insulin biosynthesis in the B-cells of obese hyperglycemic mice. Endocrinology. 1975 Nov;97(5):1241–1247. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-5-1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier B. The preferential release of newly synthesized transmitter by a sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(2):341–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutzfeldt C., Track N. S., Creutzfeldt W. In vitro studies of the rate of proinsulin and insulin turnover in seven human insulinomas. Eur J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;3(5):371–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1973.tb02203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVOREN P. R. The isolation of insulin from a single cat pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Sep 10;63:150–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinck J. W., Shepard C., Dudl R. J., Williams R. H. Use of benzamidine as a proteolytic inhibitor in the radioimmunoassay of glucagon in plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Sep;35(3):463–467. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-3-463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein G., Fanska R., Grodsky G. M. The effect of potassium and valinomycin on insulin and glucagon secretion in the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1978 Dec;103(6):2207–2215. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-6-2207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Charles M. A., Grodsky G. M. Characterization of the effects of arginine and glucose on glucagon and insulin release from the perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):833–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI107823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold G., Reaven G. M., Reaven E. P. Effect of age on proinsulin and insulin secretory patterns in isolated rat islets. Diabetes. 1981 Jan;30(1):77–82. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Bennett L. L. Cation requirements for insulin secretion in the isolated perfused pancreas. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):910–913. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman R. A., Fink G., Shapiro J. R., Selawry H., Recant L. Proinsulin and insulin release with a human insulinoma and adjacent nonadenomatous pancreas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 May;36(5):978–987. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-5-978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B. Intracellular degradation of insulin stores by rat pancreatic islets in vitro. An alternative pathway for homeostasis of pancreatic insulin content. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6003–6006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff J. D., Lasley B. L., Wang C. F., Yen S. S. The two pools of pituitary gonadotropin: regulation during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Feb;44(2):302–312. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-2-302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Parry D. G., Taylor K. W. Secretion of newly synthesized insulin in vitro. Nature. 1965 Oct 30;208(5009):487–487. doi: 10.1038/208487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmler W., Steiner D. F., Borg J. Studies on the conversion of proinsulin to insulin. 3. Studies in vitro with a crude secretion granule fraction isolated from rat islets of Langerhans. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4544–4551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P., Rosenthal N., Efstratidadis A., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Tizard R. The structure and evolution of the two nonallelic rat preproinsulin genes. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist I., Fanska R., Grodsky G. M. Interaction of calcium and glucose on glucagon secretion. Endocrinology. 1976 Nov;99(5):1304–1312. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-5-1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. The by-pass of tissue hormone stores during the secretion of newly synthesized parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1975 Jul;97(1):178–188. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-1-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod R. M., Abad A. On the control of prolactin and growth hormone synthesis in rat pituitary glands. Endocrinology. 1968 Oct;83(4):799–806. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-4-799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J., Cohn D. V. Secretion and degradation of parathormone as a function of intracellular maturation of hormone pools. Modulation by calcium and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):521–528. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M. D., Landahl H., Grodsky G. M. Comparison of storage- and signal-limited models of pancreatic insulin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1980 May;238(5):R378–R389. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1980.238.5.R378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Lambert A. E., Kanazawa Y., Amherdt M., Rouiller C., Renold A. E. Morphological and biochemical studies of B cells of fetal rat endocrine pancreas in organ culture. Evidence for (pro) insulin biosynthesis. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):565–582. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Gold G., Reaven G. M. Effect of age on glucose-stimulated insulin release by the beta-cell of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):591–599. doi: 10.1172/JCI109498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H., Fawcett P., Takabatake Y., Portanova R. Biosynthesis and release of vasopressin and neurophysin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:447–491. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando H., Borg J., Steiner D. F. Studies on the secretion of newly synthesized proinsulin and insulin from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1476–1485. doi: 10.1172/JCI106944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando H., Grodsky G. M. Dynamic synthesis and release of insulin and proinsulin from perifused islets. Diabetes. 1973 May;22(5):354–360. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.5.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz H., Nierle C., Pfeiffer E. F. (Pro-) insulin biosynthesis and release of newly synthesized (pro-) insulin from isolated islets of rat pancreas in the presence of amino acids and sulphonylureas. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov 21;5(6):477–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharoni Y., Eimerl S., Schramm M. Secretion of old versus new exportable protein in rat parotid slics. Control by neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):107–122. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaby F., Bryan J. High uptake of myo-inositol by rat pancreatic tissue in vitro stimulates secretion. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):5078–5086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwa S., Friesen H. Biosynthesis of human placental proteins and human placental lactogen (HPL) in vitro. II. Dynamic studies of normal term placentas. Endocrinology. 1969 Dec;85(6):1037–1045. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-6-1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swearingen K. C. Heterogeneous turnover of adenohypophysial prolactin. Endocrinology. 1971 Dec;89(6):1380–1388. doi: 10.1210/endo-89-6-1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



