Abstract
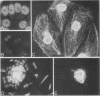
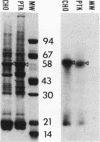
Serum from a patient with the CREST Syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus contained an IgM antibody that reacted at dilutions up to 1:800 with a fibrous cytoplasmic network in several epithelioid and fibroblastic cell lines. The antibody was shown by immunofluorescence microscopy to label a specific subset of cytoskeletal polymers, the intermediate filaments. The reactive antigen from this biochemically heterogeneous group of filaments was established as the 58,000-mol wt protein, vimentin: (a) the patient's serum reacts with a range of cell lines that contain intermediate filaments composed of vimentin, but not with cells whose intermediate filaments are composed of different protein subunits; (b) in PTK2 epithelioid cells the serum reacts with the class of filaments that coils around the nucleus after colchicine treatment (vimentin) and not with the filaments that remain dispersed after colchicine (prekeratin); and (c) the component of reactive cells that combines with the serum is shown by immunoelectrophoresis to be a 58,000-mol wt protein antigen. A similar antibody that binds intermediate filaments of PTK2 cells was encountered at lower titer in some sera from other patients with connective tissue diseases and in control sera. Previous routine antinuclear antibody assays using mouse liver or commercially prepared HEp-2 cells have failed to reveal anticytoskeletal antibodies in patient sera, perhaps due to inadequate presentation or preservation of cytoplasmic antigens.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubin J. E., Osborn M., Franke W. W., Weber K. Intermediate filaments of the vimentin-type and the cytokeratin-type are distributed differently during mitosis. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Sep;129(1):149–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90340-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. S., Tapscott S. J., Kleinbart F. A., Antin P. B., Holtzer H. Different proteins associated with 10-nanometer filaments in cultured chick neurons and nonneuronal cells. Science. 1981 May 1;212(4494):567–569. doi: 10.1126/science.6163217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin R. D., Oliver J. M. Analogous ultrastructure and surface properties during capping and phagocytosis in leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):789–804. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretherton L., Toh B. H. IgM autoantibody to intermediate filaments in infectious mononucleosis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1981 Jan;5(1):7–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral F., Gottesman M. M., Zimmerman S. B., Steinert P. M. Intermediate filaments from Chinese hamster ovary cells contain a single protein. Comparison with more complex systems from baby hamster kidney and mouse epidermal cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1428–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral F., Willingham M. C., Gottesman M. M. Ultrastructural localization to 10 nm filaments of an insoluble 58K protein in cultured fibroblasts. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Jul;28(7):653–662. doi: 10.1177/28.7.7391554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Breitkreutz D., Lüder M., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Osborn M., Weber K. Simultaneous expression of two different types of intermediate sized filaments in mouse keratinocytes proliferating in vitro. Differentiation. 1979;14(1-2):35–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Milsted A., Schloss J. A., Starger J., Yerna M. J. Cytoplasmic fibers in mammalian cells: cytoskeletal and contractile elements. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:703–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.003415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D., Weber K. Immuno-electron microscopical identification of the two types of intermediate filaments in established epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Apr;132(2):297–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Destree A. T. 10 nm filaments in normal and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Virtanen I., Stenman S., Linder E. Characterization of human smooth muscle autoantibodies reacting with cytoplasmic intermediate filaments. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Dec;11(4):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments--chemical heterogeneity in differentiation. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):649–650. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidman K., Biberfeld G., Fagraeus A., Norberg R., Torstensson R., Utter G., Carlsson L., Luca J., Lindberg U. Anti-actin specificity of human smooth muscle antibodies in chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):266–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty G. A., Valencia D. W., Fritzler M. J., Barada F. A. A unique antinuclear antibody staining only the mitotic-spindle apparatus. N Engl J Med. 1981 Sep 17;305(12):703–703. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198109173051223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. L., Delamere J. P., Jones L. J., Walton K. W. Significance of laminar antikeratin antibodies to rat oesophagus in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Jun;40(3):267–271. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo J., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Autoantibodies against axonal neurofilaments in patients with Kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):190–193. doi: 10.1126/science.6997994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Cantieri J. S., Teller D. C., Lonsdale-Eccles J. D., Dale B. A. Characterization of a class of cationic proteins that specifically interact with intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4097–4101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Yildiz A., Sotelo J., Osung O., Holborow E. J., Kanakoudi F., Small J. V. Viral infections and IgM autoantibodies to cytoplasmic intermediate filaments. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):76–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse J. M., Ferguson N., Currie G. A. Autoantibody to microtubules in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jun;17(2):227–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]