Abstract
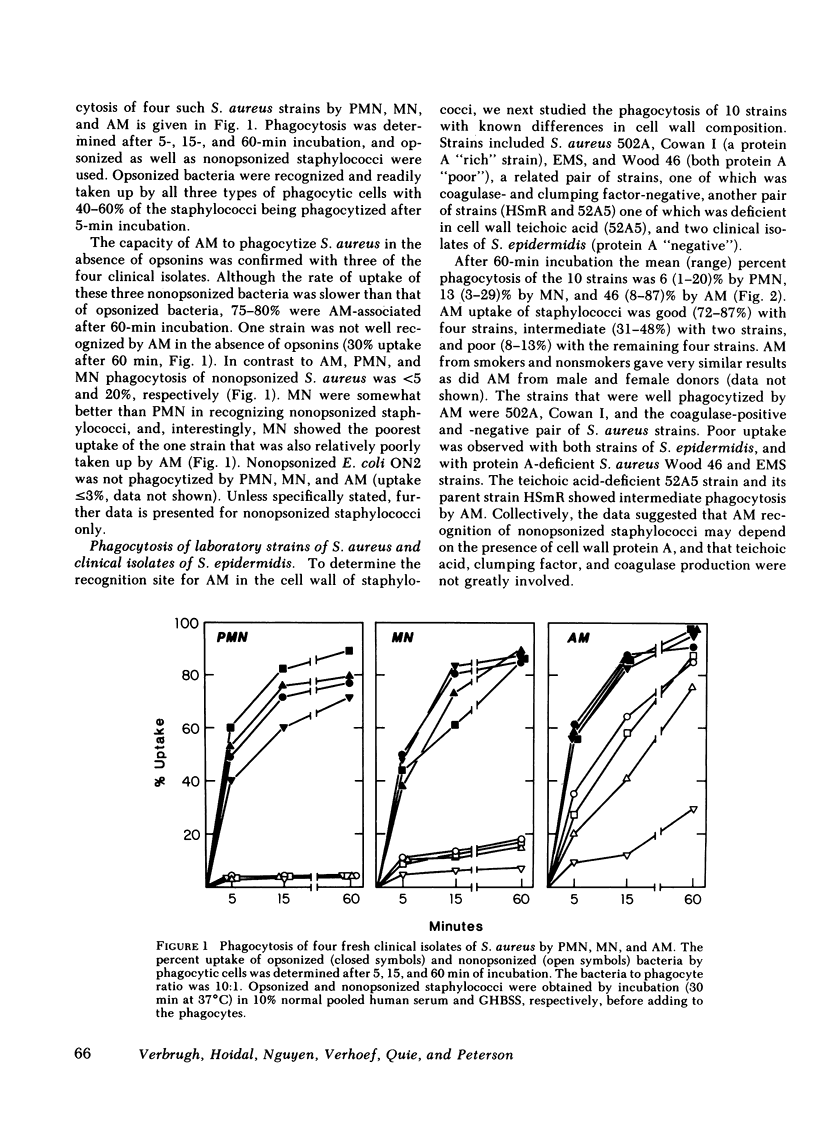
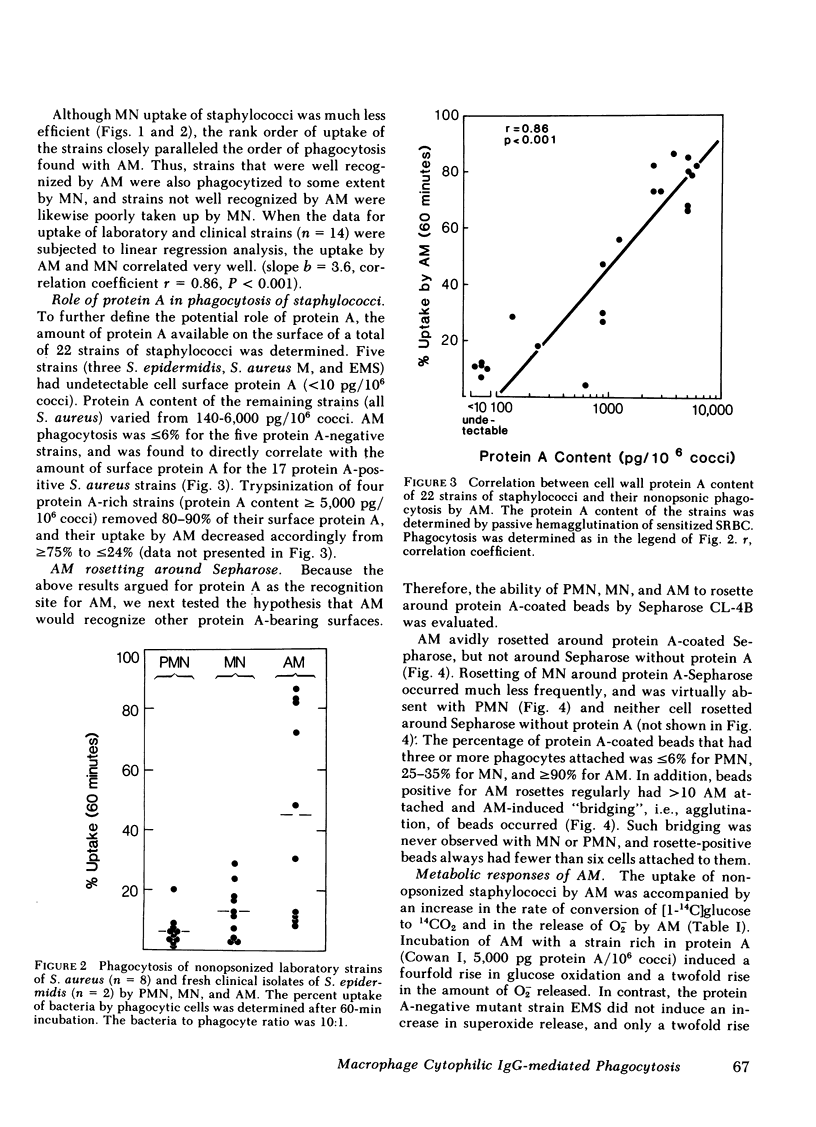
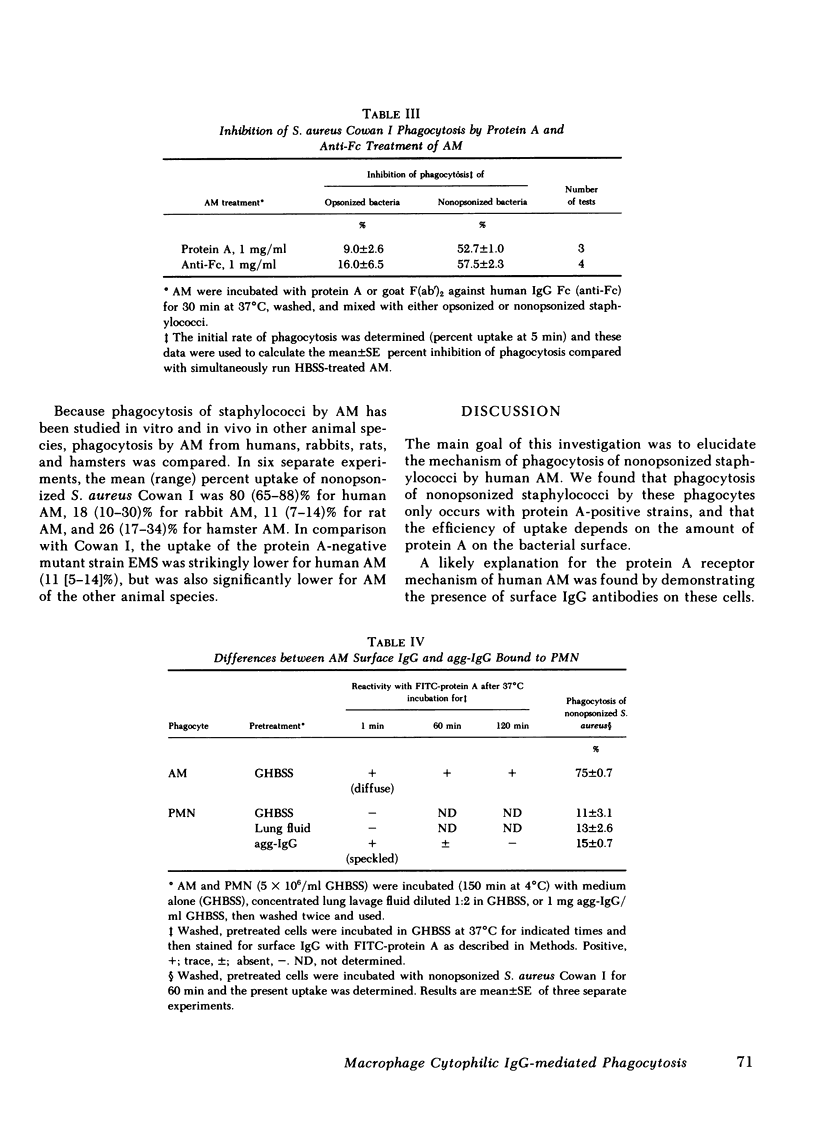
Human alveolar macrophages (AM) have recently been reported to ingest and kill a strain of Staphylococcus (502A) in the absence of opsonins. To further investigate the mechanism of non-opsonic recognition, we studied phagocytosis of 23 clinical and laboratory strains of S. aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis by AM, and by blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) and monocytes (MN). In the absence of opsonins, AM phagocytized 18 protein A-positive but not 5 protein A-negative strains of staphylococci, and the efficiency of phagocytosis directly correlated with the amount of protein A present in the bacterial cell wall (r = 0.86, P less than 0.001). Furthermore, AM rosetted around protein A-coated Sepharose beads, but not around beads without protein A. In contrast, PMN did not phagocytize nonopsonized staphylococci, and did not rosette around either type of Sepharose. MN phagocytized protein A-positive staphylococci, but much less efficiently than AM, and showed some rosetting around protein A-coated Sepharose. The nature of the AM receptor for protein A-positive staphylococci was studied. The surface of AM was positively stained with fluorescein-conjugated antibody to human IgG, but not with IgA- or IgM-specific conjugates. No such surface-immunoglobulins were detected on PMN, and MN were only weakly positive for surface IgG. Pretreatment of AM with F(ab')2 fragments specific for human IgG (anti-Fc) inhibited subsequent phagocytosis of protein A-positive staphylococci. There was no evidence that the AM surface IgG was aggregated or immunecomplexed. From these studies we conclude that human AM possess cytophilic IgG antibodies, which can function as receptors for phagocytosis of protein A-positive staphylococci.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. K., Douglas S. D. Purification of human monocytes on microexudate-coated surfaces. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1372–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander E. L., Titus J. A., Segal D. M. Human leukocyte Fc (IgG) receptors: quantitation and affinity with radiolabeled affinity cross-linked rabbit IgG. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V. CYTOPHILIC ANTIBODY IN GUINEA-PIGS WITH DELAYED-TYPE HYPERSENSITIVITY. Immunology. 1964 Jul;7:474–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V., SORKIN E. The adsorption of antigen by spleen cells previously treated with antiserum in vitro. Immunology. 1960 Jul;3:272–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berken A., Benacerraf B. Properties of antibodies cytophilic for macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):119–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Newcomb R. W., Ishizaka K. Proteolytic degradation of exocrine and serum immunoglobulins. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jul;49(7):1374–1380. doi: 10.1172/JCI106354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccimarra F., Rosen F. S., Merler E. Localization of the IgG effector site for monocyte receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2081–2083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Jones T. A., Huber R., Sjödahl J., Sjöquist J. Crystallization, crystal structure analysis and atomic model of the complex formed by a human Fc fragment and fragment B of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Aug;359(8):975–985. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Effects of staphylococcal protein A on heat labile opsonins. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1177–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Hansen J. A., Bloomfield C. D., Good R. A. B lymphocytes in untreated patients with malignant lymphoma and Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3064–3073. doi: 10.1172/JCI107505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. J., Kreier J. P. Demonstration of the role of cytophilic antibody in resistance to malaria parasites (Plasmodium berghei) in rats. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):138–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.138-145.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Bianco C., Silverstein S. C. Characterization of the macrophage receptro for complement and demonstration of its functional independence from the receptor for the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1269–1277. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Steckley S., Hammond D., Cheng C., Timmons S., Glick A. D., Des Prez R. M. Staphylococci-induced human platelet injury mediated by protein A and immunoglobulin G Fc fragment receptor. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):931–937. doi: 10.1172/JCI109559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking W. G., Golde D. W. The pulmonary-alveolar macrophage (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Sep 13;301(11):580–587. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197909133011104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hof D. G., Repine J. E., Peterson P. K., Hoidal J. R. Phagocytosis by human alveolar macrophages and neutrophils: qualitative differences in the opsonic requirements for uptake of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jan;121(1):65–71. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R., Beall G. D., Rasp F. L., Jr, Holmes B., White J. G., Repine J. E. Comparison of the metabolism of alveolar macrophages from humans, rats, and rabbits: phorbol myristate acetate. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Nov;92(5):787–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R., Repine J. E., Beall G. D., Rasp F. L., Jr, White J. G. The effect of phorbol myristate acetate on the metabolism and ultrastructure of human alveolar macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jun;91(3):469–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R., Schmeling D., Peterson P. K. Phagocytosis, bacterial killing, and metabolism by purified human lung phagocytes. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):61–71. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoidal J. R., White J. G., Repine J. E. Influence of cationic local anesthetics on the metabolism and ultrastructure of human alveolar macrophages. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 May;93(5):857–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Douglas S. D., Nusbacher J., Kochwa S., Rosenfield R. E. IgG subclass specificity of human monocyte receptor sites. Nature. 1971 Feb 5;229(5284):419–420. doi: 10.1038/229419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys D. W., Wheat L. J., White A. Staphylococcal heat-stable opsonins. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jul;84(1):122–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Tomioka H., Ishizaka T. Mechanisms of passive sensitization. I. Presence of IgE and IgG molecules on human leukocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1459–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juers J. A., Rogers R. M., McCurdy J. B., Cook W. W. Enhancement of bactericidal capacity of alveolar macrophages by human alveolar lining material. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):271–275. doi: 10.1172/JCI108468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A. Association and dissociation of aggregated IgG from rat peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1368–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Williams R. C., Jr Differences in anti-protein A activity among IgG subgroups. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):828–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI I. W., MUDD S. THE HEAT-LABILE SERUM FACTOR ASSOCIATED WITH INTRACELLULAR KILLING OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:852–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaForce F. M. Effect of alveolar lining material on phagocytic and bactericidal activity of lung macrophages against Staphylococcus aureau. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Nov;88(5):691–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaForce F. M., Kelly W. J., Huber G. L. Inactivation of staphylococci by alveolar macrophages with preliminary observations on the importance of alveolar lining material. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Oct;108(4):784–790. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.4.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancet D., Isenman D., Sjödahl J., Sjöquist J., Pecht I. Interactions between staphylococcal protein A and immunoglobulin domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 29;85(2):608–614. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J., Boyle M. D., Borsos T. Studies on the interaction between protein A and immunoglobulin G. I. Effect of protein A on the functional activity of IgG. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):327–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Weigle W. O., Spiegelberg H. L. Immunoglobulins cytophilic for human lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):368–376. doi: 10.1172/JCI107940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Receptors for complement of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):991–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. G. Macrophage handling of soluble immune complexes. Ingestion and digestion of surface-bound complexes at 4, 20 and 37 degrees C. Eur J Immunol. 1980 May;10(5):323–333. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R. Altered morphology and increased acid hydrolase content of pulmonary macrophages from cigarette smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Apr;107(4):596–601. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.4.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. H., Forsgren A., Björkstén B., Kim Y., Quie P. G., Michael A. F. Decreased serum factor B concentration associated with decreased opsonization of Escherichia coli in the idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Res. 1977 Aug;11(8):910–916. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197708000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphey S. A., Root R. K., Schreiber A. D. The role of antibody and complement in phagocytosis by rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):896–903. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kronvall G. Heterogeneity of nonimmune immunoglobulin Fc reactivity among gram-positive cocci: description of three major types of receptors for human immunoglobulin G. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):475–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.475-482.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okafor G. O., Turner M. W., Hay F. C. Localisation of monocyte binding site of human immunoglobulin G. Nature. 1974 Mar 15;248(445):228–230. doi: 10.1038/248228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Kim Y., Wilkinson B. J., Schmeling D., Michael A. F., Quie P. G. Dichotomy between opsonization and serum complement activation by encapsulated staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):770–775. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.770-775.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Kinetics of phagocytosis and bacterial killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1977 Oct;136(4):502–509. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.4.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Douglas S. D., Quie P. G., Verhoef J. The key role of peptidoglycan in the opsonization of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):597–609. doi: 10.1172/JCI108971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittard W. B., 3rd, Polmar S. H., Fanaroff A. A. The breastmilk macrophage: a potential vehicle for immunoglobulin transport. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1977 Dec;22(6):597–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., Messner R. P., Williams R. C., Jr Phagocytosis in subacute bacterial endocarditis. Localization of the primary opsonic site to Fc fragment. J Exp Med. 1968 Oct 1;128(4):553–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.4.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin S. B., Stossel T. P. Complement (C3)-activated phagocytosis by lung macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1305–1312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkebaum G., Arend W. P. Neutrophil-binding immunoglobulin G in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):902–912. doi: 10.1172/JCI109556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulica A., Medesan C., Laky M., Onică D., Sjöquist J., Ghetie V. Effect of protein A of Staphylococcus aureus on the binding of monomeric and polymeric IgG to Fc receptor-bearing cells. Immunology. 1979 Sep;38(1):173–179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I. R. Macrophage cytophilic antibody in mice. Differentiation between antigen adherence due to these antibodies and opsoni adherence. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;36(4):332–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I. R. Macrophage-cytophilic antibodies and the functions of macrophage-bound immunoglobulins. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Dec;35(4):365–378. doi: 10.1128/br.35.4.365-378.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underdown B. J., Dorrington K. J. Studies on the structural and conformational basis for the relative resistance of serum and secretory immunoglobulin A to proteolysis. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):949–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., van Dijk W. C., Peters R., van Erne M. E., Daha M. R., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Opsonic recognition of staphylococci mediated by cell wall peptidoglycan: antibody-independent activation of human complement and opsonic activity of peptidoglycan antibodies. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1167–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Human polymorphonuclear leucocyte receptors for staphylococcal opsonins. Immunology. 1977 Aug;33(2):231–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P., Kim Y., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Opsonic requirements for staphylococcal phagocytosis. Heterogeneity among strains. Immunology. 1977 Aug;33(2):191–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winblad S., Ericson C. Sensitized sheep red cells as a reactant for Staphylococcus aureus protein A. Methodology and epidemiology with special reference to weakly reacting methicillin-resistant strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasmeen D., Ellerson J. R., Dorrington K. J., Painter R. H. Evidence for the domain hypothesis: location of the site of cytophilic activity toward guinea pig macrophages in the C H 3 homology region of human immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1706–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




