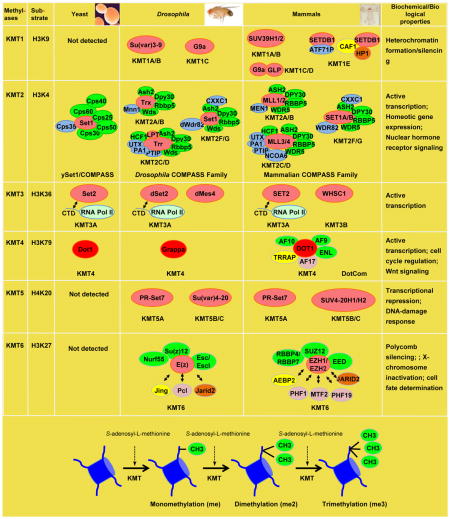
Lysine Methyl Transferases (KMTs) catalyze the transfer of one, two, or three methyl groups from S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) to the ε-amino group of a lysine residue on a histone to generate mono-, di-, and tri-methylated histone. KMTs exist either singly or within complexes, where the members of each complex modulate the activity of the enzymes. KMTs have been implicated in diverse roles in DNA-templated processes, and their mutations, deletions or translocations have been linked with various human diseases. Known KMTs contain a SET domain [named after Drosophila Su(var)3-9, Enhancer of zeste [E(z)], and trithorax (trx)], with an exception- Dot1, which harbors a unique catalytic domain. All the SET domain containing enzymes are shown in peach, and Dot1 is in red.
KMT1 family
The KMT1 family is found in S. pombe (Clr4) and metazoans, which includes Su(var)3-9 and G9a in Drosophila, and at least four enzymes in mammals - SUV39H1/2, G9a, GLP and SETDB1. SUV39H1/2 are responsible for generating the majority of H3K9 trimethylation at pericentric heterochromatin, where as G9a and GLP form functional heteromeric dimers in vivo to mono- and di-methylate H3K9 at euchromatic sites. SETDB1, which contains a methyl-CpG binding domain, exists in a complex with HP1 and CAF1 and this complex is believed to monomethylate histone H3. SETDB1, when in association with activating transcription factor 7 interacting protein (ATF71P), becomes capable of H3K9 trimethylation, and is associated with transcriptional repression. For further reading regarding the KMT1 family, please see Fodor, B.D., Shukeir, N., Reuter, G., and Jenuwein, T. (2010). Mammalian Su(var) genes in chromatin control. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 26, 471–501.
KMT2 family
The KMT2 family can mono-, di- and trimethylates histone H3K4. This family of enzymes is found within a macromolecular complex known as the COMPASS family and are highly conserved from yeast to human. The Set1/COMPASS in yeast was the first H3K4 methylase identified, with 7 members in the complex, and is responsible for all mono-, di-, and trimethylation of H3K4 in yeast. In Drosophila, there are three COMPASS family members containing dSet1, Trx, and Trr. dSet1 is the major di- and tri-methylase. Mammalian cells bear six COMPASS family members: dSet1 is represented by SET1A and SET1B, Trx is represented by MLL1 and MLL2 (MLL2 with GeneID 9757), and Trr is represented by MLL3 and MLL4 (MLL4 with GeneID 8085, also known as ALR). All the mammalian complexes share ASH2L, RBBP5, DPY30, HCF1 and WDR5 as common components. In addition to shared subunits, each COMPASS family member consist of complex specific subunits. SET1A and SET1B complexes uniquely associate with WDR82 and CXXC1, MLL1/MLL2 complexes associate with Menin, and MLL3/4 complexes contain PTIP, PA-1, UTX, and NCOA6. For further reading regarding the KMT2 family, please see Mohan, M., Lin, C., Guest, E., and Shilatifard, A. (2010). Licensed to elongate: a molecular mechanism for MLL-based leukaemogenesis. Nature Reviews Cancer 10, 721–728.
KMT3 family
The KMT3 family methylates histone H3K36 and mainly consists of a single enzyme Set2, which is conserved from yeast to human. Set2 is known to associate with RNA PolII during the elongation phase of transcription through interactions with Pol II CTD. Mammals also employ another conserved enzyme WHSC1 (homologous to Drosophila Mes4) functioning in H3K36 methylation. Mutations in this enzyme are known to associate with multiple cancers. For further reading regarding the KMT3 family, please see Buratowski, S., and Kim, T. (2010). The role of cotranscriptional histone methylations. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 75, 95–102.
KMT4 family
Dot1, which is the sole member of the family, is the only known non-SET domain-containing KMT, is conserved from yeast to humans, and methylates histone H3K79. Mammalian Dot1 exists in a large macromolecular complex, known as DotCom, containing MLL-fusion proteins (AF10, ENL, AF9 and AF17), and is known to have role in Wnt and JAK-STAT signaling, and transcription. For further reading regarding the KMT4 family please see Nguyen, A.T., and Zhang, Y. (2011). The diverse functions of Dot1 and H3K79 methylation. Genes Dev 25, 1345–1358.
KMT5 family
The KMT5 family methylates histone H4K20 and is thought to be metazoan specific. Monomethylation is performed by a conserved enzyme, Pr-Set7, and is associated with various chromatin processes, including transcriptional activation and repression, DNA repair, cell cycle progression and DNA replication. Su(var)4-20, and its mammalian homologs, SUV4-20H1/2 mediate di- and tri-methylation of H4K20, and play a critical role in the maintenance of pericentric and telomeric hetrochromatin. For further reading please see Balakrishnan, L., and Milavetz, B. (2010). Decoding the histone H4 lysine 20 methylation mark. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 45, 440–452.
KMT6 family
The KMT6 family methylates histone H3K27, and is conserved from Drosophila to humans, but does not exist in yeast. The KMT6 family is required to maintain transcriptional repression of many developmentally regulated genes, including homeotic genes, thereby promoting cell identity. Deregulation of certain members of the KMT6 complex has been linked to various forms of cancer. In Drosophila, the catalytic subunit E(z) implements all mono-, di- and tri-methylation of H3K27. The two mammalian homologs of Drosophila E(z) – EZH1 and EZH2 – function redundantly to some degree and in many cases work in concert to achieve mono-, di- and tri-methylation of H3K27. Other core components of the complex are Su(z)12, Esc/Escl and Nurf55 in Drosophila and SUZ12, EED, and RBBP4/7 in mammals. Accessory factors are also conserved between Drosophila (Jing, Pcl and Jarid2) and mammals (AEBP2, PHF1, MTF2, PHF19 and JARID2). They either alter the enzymatic activity of the complex and/or are involved in recruitment of the core complex to certain KMT6 target genes. For further reading please see Margueron, R., and Reinberg, D. (2011). The Polycomb complex PRC2 and its mark in life. Nature 469, 343–349.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Edwin Smith for his critical reading and valuable comments. Studies in the Shilatifard laboratory on chromatin modifying machineries and childhood leukemia are supported by the National Institutes of Health grants R01CA150265, R01GM069905, and R01CA89455.
Abbreviations
- Trx
Trithorax
- Mnn1
Menin1
- Trr
Trithorax-related
- Wds
Will die slowly
- Dpy30
Dumpy-like 30
- E(z)
Enhancer of zeste
- Wdr5
WD repeat domain 5
- PHF1/19
PHD finger protein 1/19
- EZH1/2
Enhancer of zeste homolog 1/2
- EED
Embryonic ectoderm development
- Su(var)3-9
Suppressor of variegation 3-9
- Jarid2
Jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 2
- WHSC1
Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1
- Rbbp4/5/7
Retinoblastoma binding protein 4/5/7
- AF17
ALL1-fused gene from chromosome 17
- Pcl
Polycomb-like
- Esc
Extra sexcombs
- HCF1
Host Cell factor1
- Escl
Extra sexcombs-like
- AEBP2
AE binding protein 2
- PA1
PTIP associated factor 1
- Su(z)12
Suppressor of zeste 12
- Dot1
Disruptor of Telomeric silencing 1
- NURF55
nucleosome remodeling factor 55
- SUV39H1/2
Suppressor of variegation 3-9 homolog 1/2
- MTF2
Metal response element binding transcription factor 2
- TRRAP
Transformation/transcription domain-associated protein
- Cps25
30, 35, 40 and 60, Compass subunit 25, 30, 40, 40 and 60
- UTX
Ubiquitously-transcribed TPR protein on the X chromosome
- PTIP
PAX interacting (with transcription-activation domain) protein 1
- CXXC1
CXXC finger protein 1
- dWdr82
dWD repeat domain 82
- HP1
Heterochromatin protein 1
- SETDB1
SET domain, bifurcated 1
- CAF1
chromatin assembly factor 1
- Ash2
absent, small, or homeotic discs 2
- NCOA6
Nuclear receptor coactivator 6
- MLL1/2/3/4
Mixed-lineage Leukemia 1/2/3/4
- COMPASS
Complex proteins associated with Set1
- KMT
Lysine Methyl Transferase


