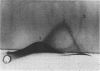
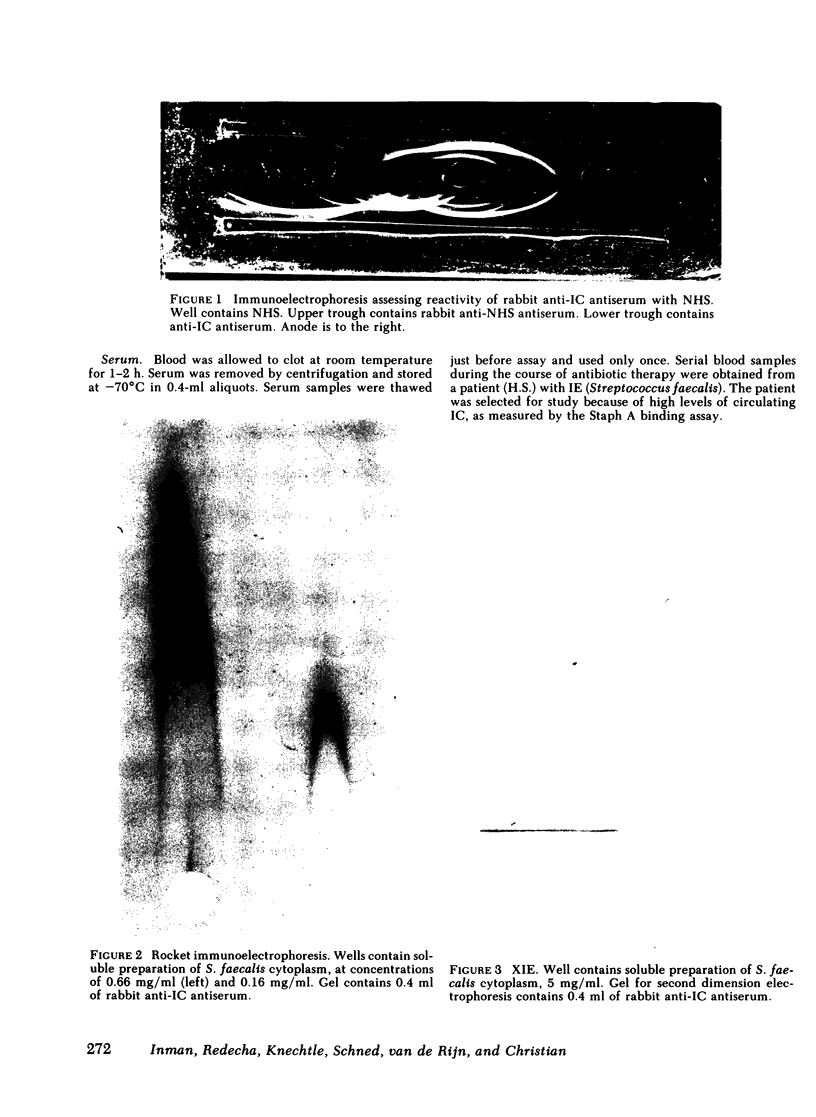
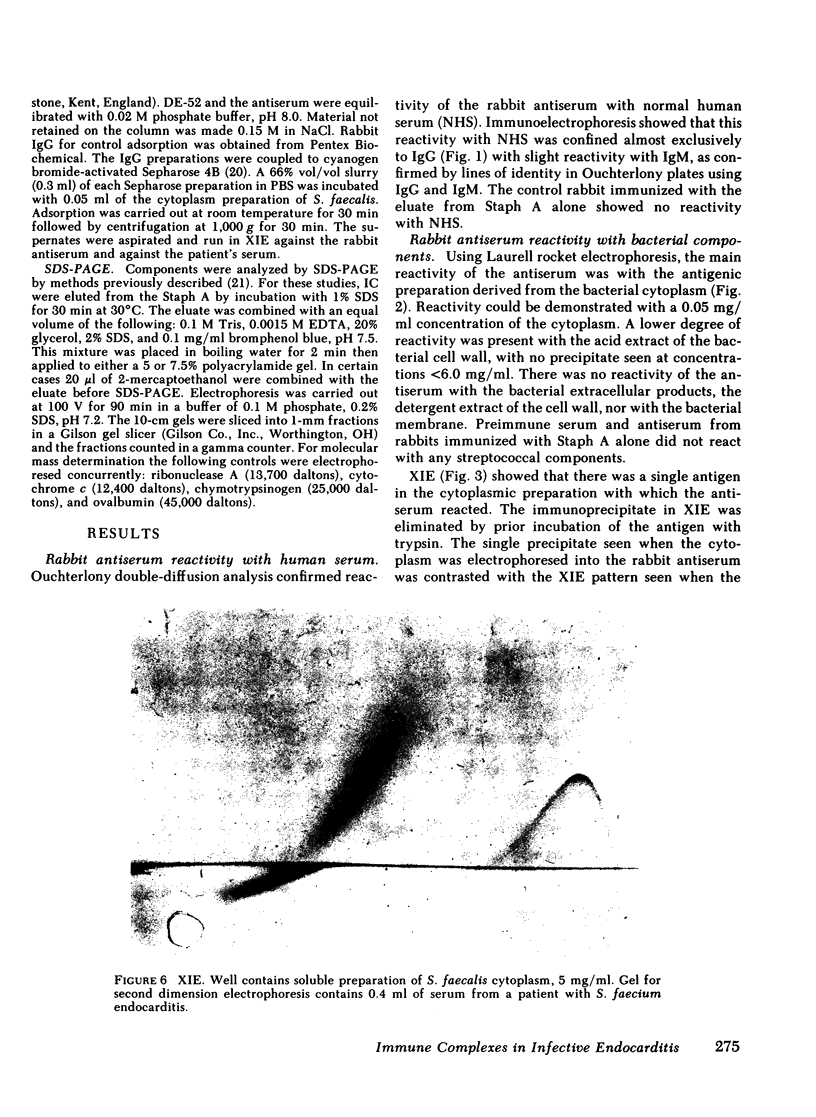
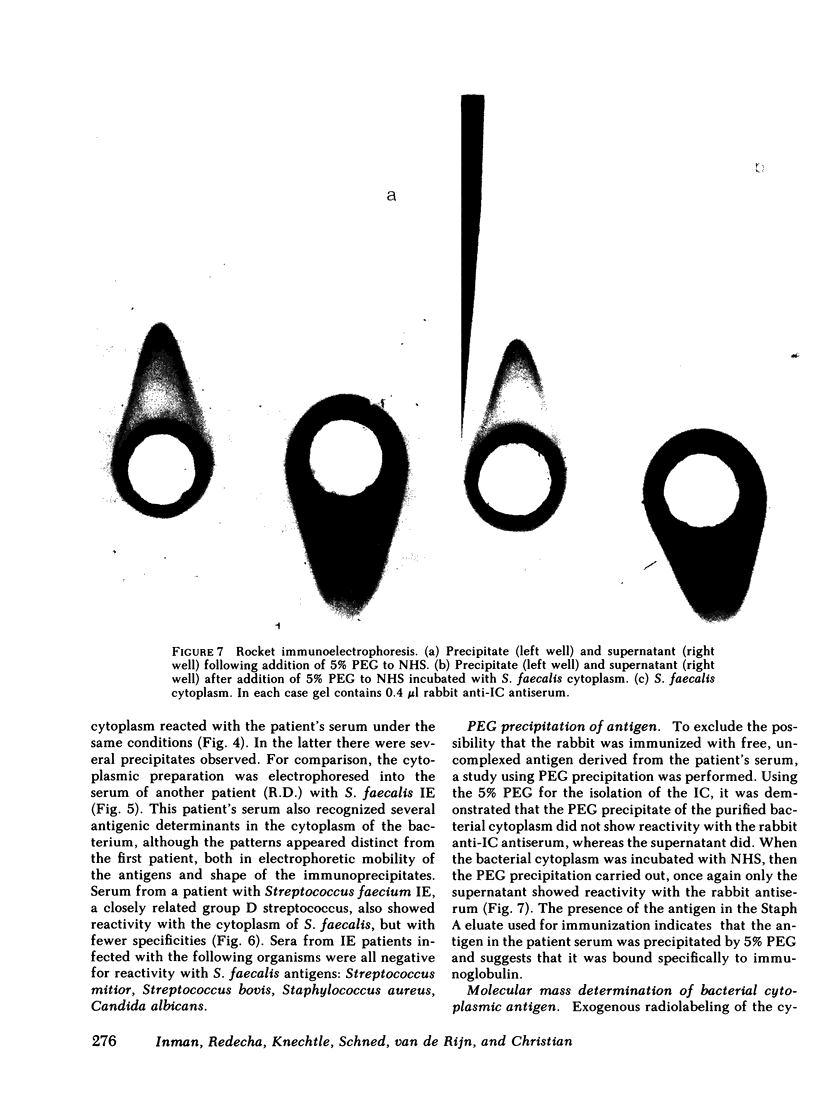
Abstract
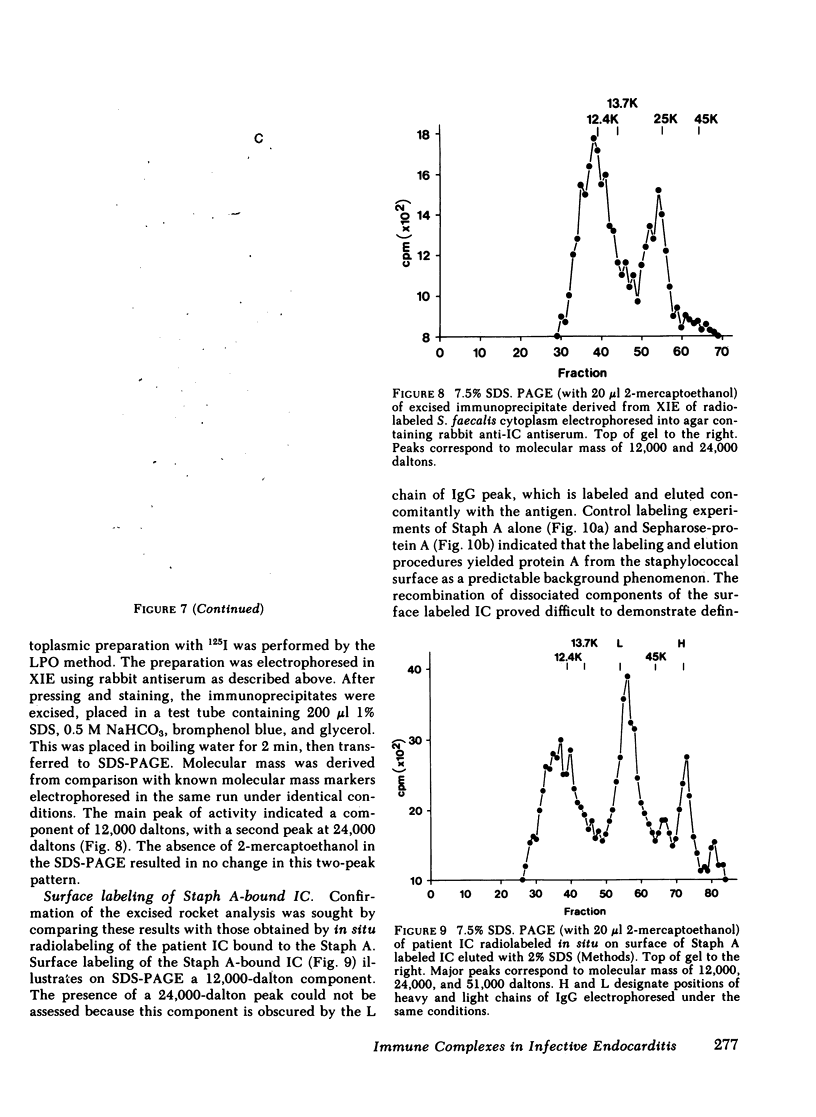
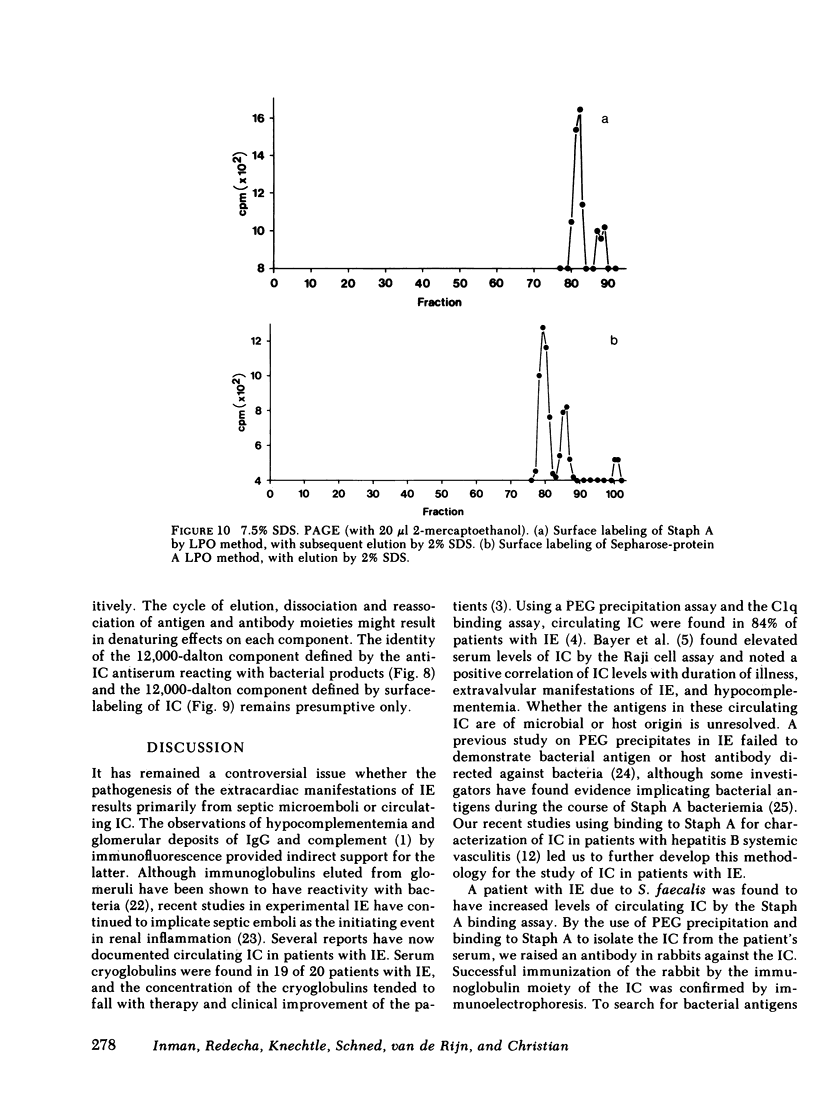
The presence of circulating immune complexes (IC) in patients with infective endocarditis has been well documented but the contributions of host and bacterial components to these IC have not been defined. To study this question, IC were isolated from serum of a patient with Streptococcus faecalis endocarditis by differential polyethylene glycol precipitation and competitive binding to staphylococcal protein A. A rabbit antiserum raised against the purified IC had reactivity by crossed immunoelectrophoresis primarily with an antigen derived from the cytoplasm of the infective organism. The antigen was a protein with a 12,000-dalton molecular mass. In situ radiolabeling of the IC bound to the protein A demonstrated a component of the same molecular mass as the bacterial antigen recognized by the antiserum. The patient serum had multiple antibody specificities reactive with bacterial antigens, including the antigen recognized by the rabbit anti-IC antiserum. These techniques for isolation and characterization of circulating IC may have value in the study of IC diseases in which the inciting antigens are not known.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRUZZO J. L., CHRISTIAN C. L. The induction of a rheumatoid factor-like substance in rabbits. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:791–806. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon P. A., Davidson C., Smith B. Antibodies to candida and autoantibodies in sub-acute bacterial endocarditis. Q J Med. 1974 Oct;43(172):537–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Theofilopoulos A. N., Eisenberg R., Dixon F. J., Guze L. B. Circulating immune complexes in infective endocarditis. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 30;295(27):1500–1505. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612302952703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergquist N. R. The pulsed dye laser as a light source for the fluorescent antibody technique. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(1):37–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton-Kee J., Morgan-Capner P., Mowbray J. F. Nature of circulating immune complexes in infective endocarditis. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jul;33(7):653–659. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.7.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabane J., Godeau P., Herreman G., Acar J., Digeon M., Bach J. F. Fate of circulating immune complexes in infective endocarditis. Am J Med. 1979 Feb;66(2):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90545-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Bayer A. S., Eisenberg R. A., Lawrance S., Theofilopoulos A. IgG rheumatoid factor in subacute bacterial endocarditis: relationship to IgM rheumatoid factor and circulating immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jan;31(1):100–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman R. A., Striker G. E., Gilliland B. C., Cutler R. E. The immune complex glomerulonephritis of bacterial endocarditis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1972 Jan;51(1):1–25. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197201000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz D., Quismorio F. P., Friou G. J. Cryoglobulinaemia in patients with infectious endocarditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jan;19(1):131–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. D., McDougal J. S., Redecha P. B., Lockshin M. D., Stevens C. E., Christian C. L. Isolation and characterization of circulating immune complexes in patients with hepatitis B systemic vasculitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Dec;21(3):364–374. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. L., Hong R. The immune nature of subacute bacterial endocarditis (SBE) nephritis. Am J Med. 1973 May;54(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Redecha P. B., Inman R. D., Christian C. L. Binding of immunoglobulin G aggregates and immune complexes in human sera to Staphylococci containing protein A. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):627–636. doi: 10.1172/JCI109345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Laxdal T., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Rheumatoid factors in subacute bacterial endocarditis--bacterium, duration of disease or genetic predisposition? Ann Intern Med. 1968 Apr;68(4):746–756. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-4-746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabbarah Z. A., Wheat L. J., Kohler R. B., White A. Thermodissociation of staphylococcal immune complexes and detection of staphylococcal antigen in serum from patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):703–709. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.703-709.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thörig L., Daha M. R., Eulderink F., Kooy-Bauer W. C., Thompson J. Experimental Streptococcus sanguis endocarditis: immune complexes and renal involvement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jun;40(3):469–477. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal H., Jr, Fischetti V. A., van de Rijn I., Zabriskie J. B. The occurrence of a protein in the extracellular products of streptococci isolated from patients with acute glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):459–472. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., Jr, KUNKEL H. G. Rheumatoid factor, complement, and conglutinin aberrations in patients with subacute bacterial endocarditis. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:666–675. doi: 10.1172/JCI104523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yum M., Wheat L. J., Maxwell D., Edwards J. L. Immunofluorescent localization of Staphylococcos aureus antigen in acute bacterial endocarditis nephritis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Nov;70(5):832–835. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/70.5.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Kessler R. E. Growth characteristics of group A streptococci in a new chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.444-448.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Rijn I., Zabriskie J. B., McCarty M. Group A streptococcal antigens cross-reactive with myocardium. Purification of heart-reactive antibody and isolation and characterization of the streptococcal antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):579–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]