Abstract
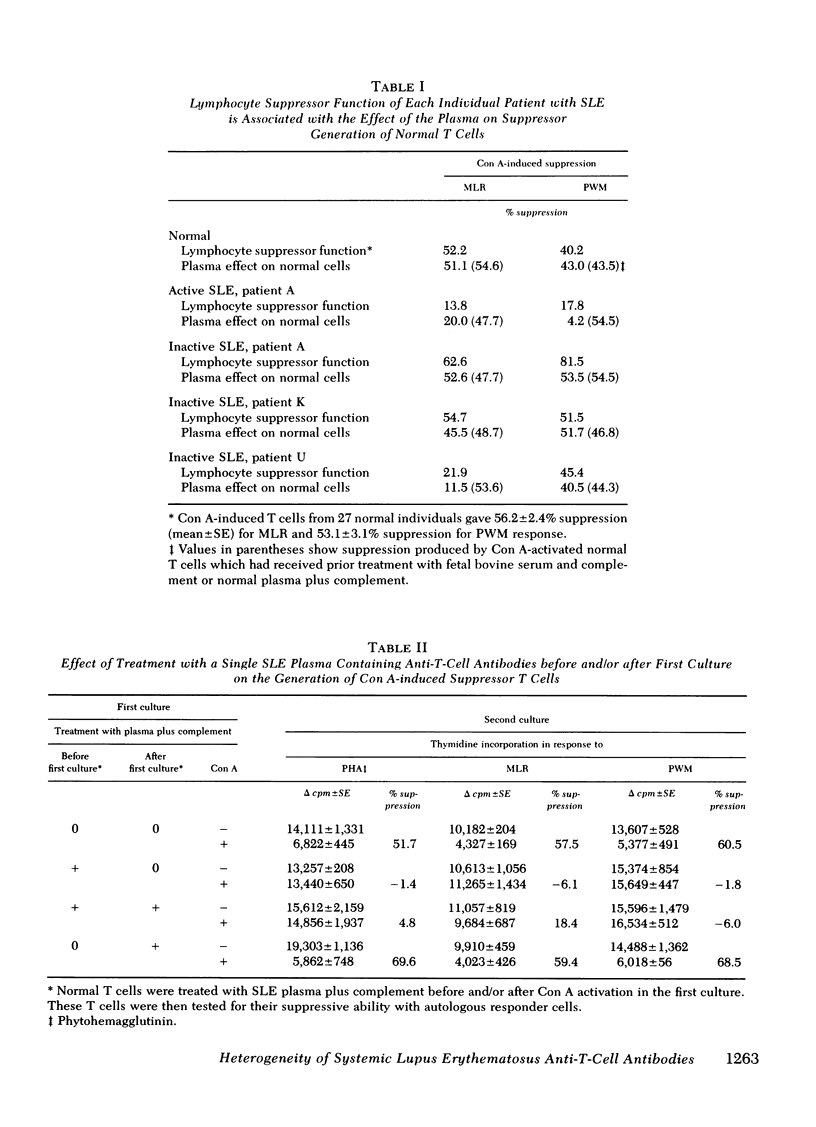
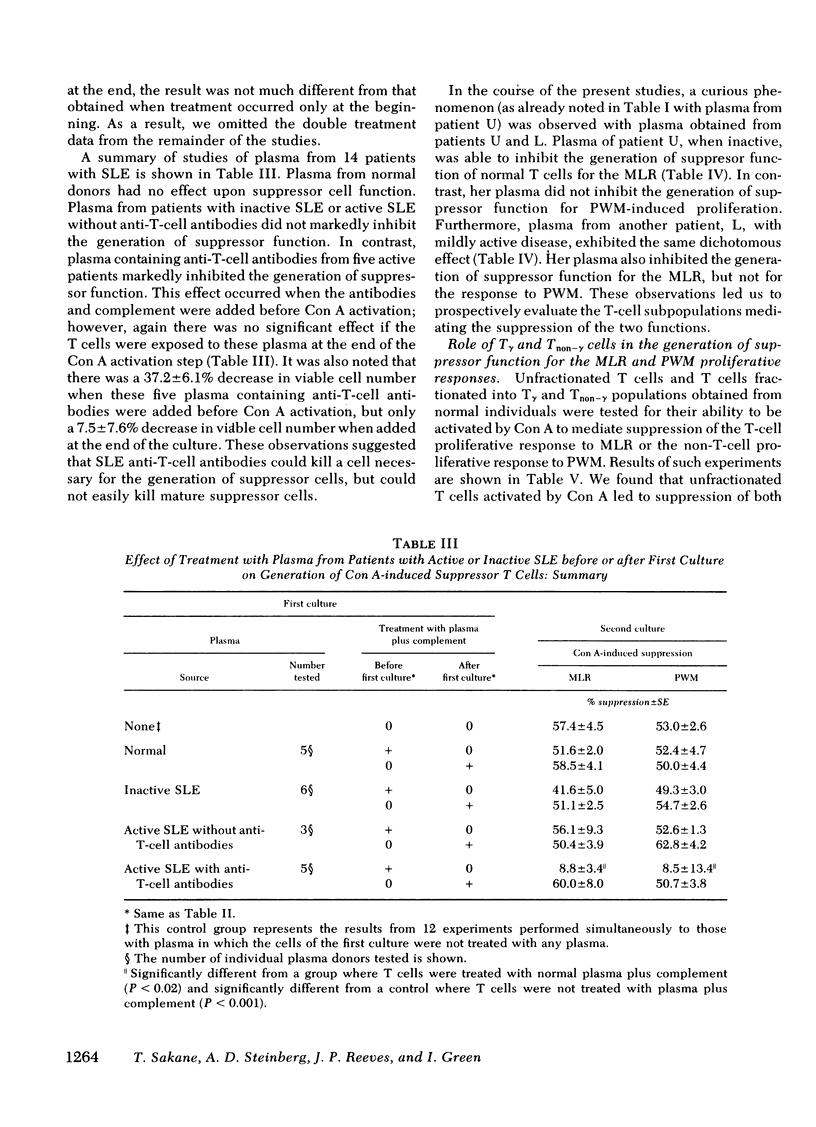
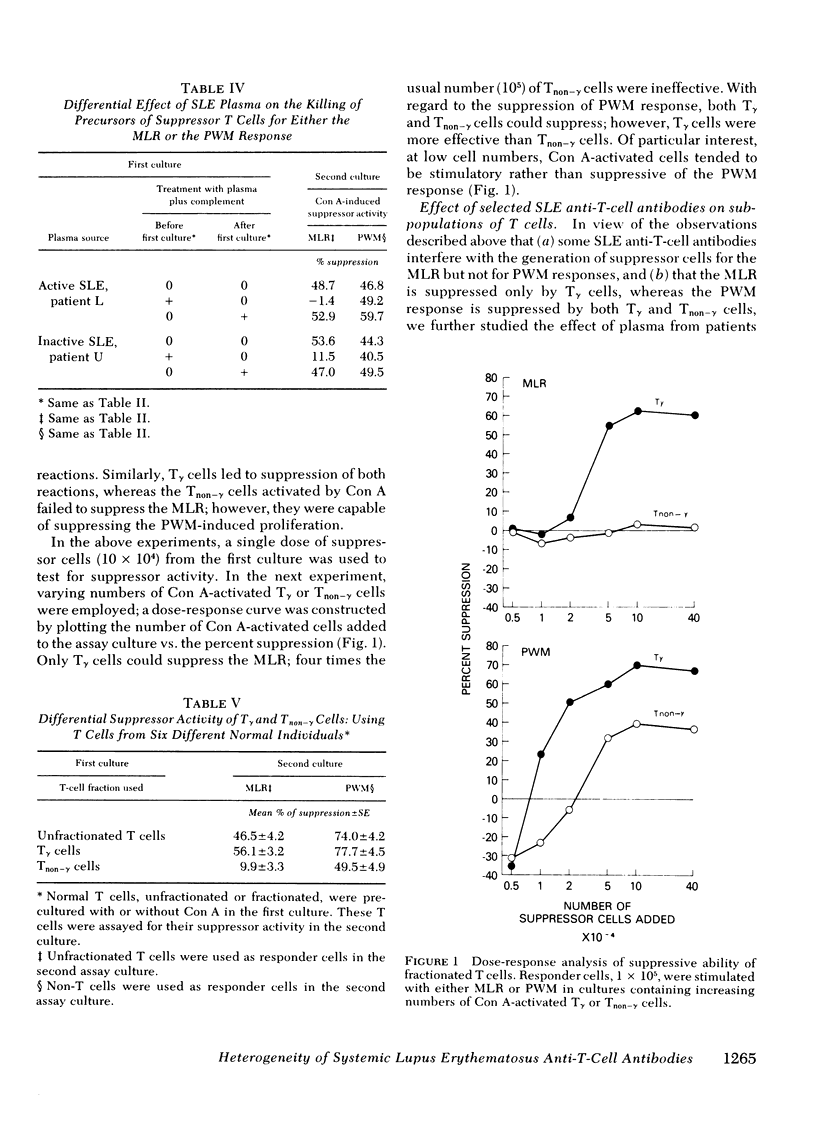
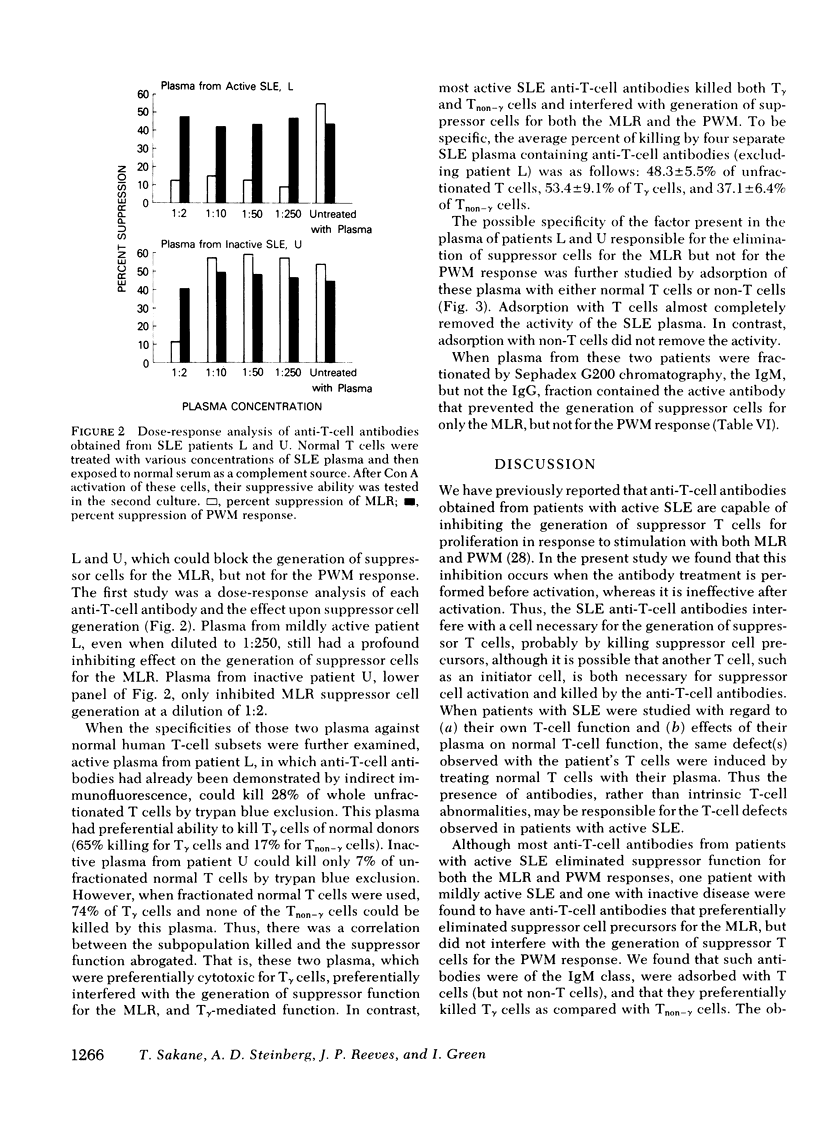
Antibodies to T cells present in the plasma of patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) plus complement are able to eliminate concanavalin A-induced suppressor function for the proliferative responses of T cells to allogeneic lymphocytes (MLR) and of B cells to pokeweed mitogen (PWM). Such antibodies were found to be effective in eliminating suppressor function only when T cells were treated before activation; there was no effect when treatment was performed after activation. These studies indicate that the antibodies preferentially interact with a T cell necessary for the generation of suppressor cells, rather than with mature, activated suppressor cells. Studies of individual SLE patients indicate that the same defects observed in SLE T cells were induced in normal T cells by plasma from that patient. Such observations suggest that many T-cell defects associated with active SLE may not be intrinsic T-cell abnormalities, but, rather, secondary effects of anti-T-cell antibodies. Studies of the T-cell subpopulations responsible for suppression of the MLR and PWM responses indicate that only T gamma cells (T cells bearing receptors for the Fc portion of immunoglobulin [Ig]G) acted as precursors of suppressor cells for the MLR, whereas both T gamma and T non-gamma cells (T cells not bearing receptors for the Fc portion of IgG) could be activated to suppress the PWM response. Consistent with this observation, SLE anti-T-cell antibodies that preferentially killed T gamma cells preferentially eliminated suppressor cells for the MLR.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell D. A., Clark C., Blomgren S. E., Vaughan J. H. Anti DNA antibody production by lymphoid cells of NZB-W mice and human systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Apr;1(3):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budman D. R., Merchant E. B., Steinberg A. D., Doft B., Gershwin M. E., Lizzio E., Reeves J. P. Increased spontaneous activity of antibody-forming cells in the peripheral blood of patients with active SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):829–833. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbarre F., Le Gô A., Kahan A. Hyperbasophilic immunoblasts in circulating blood in chronic inflammatory rheumatic and collagen diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Oct;34(5):422–430. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.5.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Steinberg A. D., Haynes B. F., Whalen G. Immunoregulatory aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1473–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershwin M. E., Chused T. M., Steinberg A. D. Cytotoxic activity of anti-theta antibody found in the gamma m fraction. Transplantation. 1974 Oct;18(4):377–380. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197410000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinski W., Gershwin M. E., Budman D. R., Steinberg A. D. Study of lymphocyte subpopulations in normal humans and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus by fractionation of peripheral blood lymphocytes on a discontinuous Ficoll gradient. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):228–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinski W., Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Fractionation of cells on a discontinuous Ficoll gradient. Study of subpopulations of human T cells using anti-T-cell antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):604–614. doi: 10.1172/JCI108316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Bagby K. K., Osterland C. K. Abnormalities of delayed hypersensitivity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1973 Jul;55(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbeck R. J., Bardana E. J., Kohler P. F., Carr R. I. DNA:anti-DNA complexes: their detection in systemic lupus erythematosus sera. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):789–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI107242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Fauci A. S. Activation of human B lymphocytes. X. Heterogeneity of concanavalin A-generated suppressor cells of the pokeweed mitogen-induced plaque-forming cell response of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):559–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Layward L., Lydyard P. M., Moretta L., Dagg M., Lawton A. R. Fc-receptor heterogeneity of human suppressor T cells. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Borcherding W., Moorthy A. V., Chesney R., Schulte-Wisserman H., Hong R. Induction of suppressor T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus by thymosin and cultured thymic epithelium. Science. 1977 Sep 2;197(4307):999–1001. doi: 10.1126/science.302032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. A. Impaired delayed hypersensitivity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):353–359. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lies R. B., Messner R. P., Williams R. C., Jr Relative T-cell specificity of lymphocytotoxins from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 May-Jun;16(3):369–375. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner R. P., Lindström F. D., Williams R. C., Jr Peripheral blood lymphocyte cell surface markers during the course of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3046–3056. doi: 10.1172/JCI107503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ferrarini M., Mingari M. C., Moretta A., Webb S. R. Subpopulations of human T cells identified by receptors for immunoglobulins and mitogen responsiveness. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2171–2174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Mingari M. C., Moretta A., Cooper M. D. Human T lymphocyte subpopulations: studies of the mechanism by which T cells bearing Fc receptors for IgG suppress T-dependent B cell differentiation induced by pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):984–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Webb S. R., Grossi C. E., Lydyard P. M., Cooper M. D. Functional analysis of two human T-cell subpopulations: help and suppression of B-cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):184–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Abe T., Hara M., Homma M. In vitro TNP-specific antibody formation by peripheral lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(6-7):575–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb02135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H. V., Cochrum K. C., Stobo J. D. Macrophage-T cell interactions in the Con A induction of human suppressive T cells. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2311–2315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Depression of cellular-mediated immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus. relation to disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):207–217. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagawa A., Abdou N. I. Suppressor-cell antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. Possible mechanism for suppressor-cell dysfunction. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):536–539. doi: 10.1172/JCI109333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagawa A., Abdou N. I. Suppressor-cell dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cells involved and in vitro correction. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):789–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI109190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Human suppressor T cells induced by concanavalin A: suppressor T cells belong to distinctive T cell subclasses. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Green I. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus-a mitogen for human T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes but not L lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):302–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Arnett F. C., Reinertsen J. L., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jul;22(7):770–776. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. I. Dysfunction of suppressor T-cell activity related to impaired generation of, rather than response to, suppressor cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jul-Aug;21(6):657–664. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Reeves J. P., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Complement-dependent immunoglobulin M anti-thymus-derived cell antibodies preferentially inactivate suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):954–965. doi: 10.1172/JCI109396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T. Studies on cell-mediated immune responses by human lymphocytes in vitro. III. Lymphocyte response to phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A in patients with auto-immune diseases. Nihon Ketsueki Gakkai Zasshi. 1976 Feb;39(1):29–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg M. A., Cathcart E. S. B cell and T cell lymphopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Immunol. 1974 May;12(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Ziff M. Antibodies against cell membrane constituents in systemic lupus erythematosus and related diseases. I. Cytotoxic effect of serum from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) for allogeneic and for autologous lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Apr;8(4):543–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Klassen L. W., Budman D. R., Williams G. W. Immunofluorescence studies of anti-T cell antibodies and T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Selective loss of brightly staining T cells in active disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Feb;22(2):114–122. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strelkauskas A. J., Callery R. T., McDowell J., Borel Y., Schlossman S. F. Direct evidence for loss of human suppressor cells during active autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5150–5154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strelkauskas A. J., Schauf V., Wilson B. S., Chess L., Schlossman S. F. Isolation and characterization of naturally occurring subclasses of human peripheral blood T cells with regulatory functions. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1278–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suciu-Foca N., Buda J. A., Thiem T., Reemtsma K. Impaired responsiveness of lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):295–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twomey J. J., Laughter A. H., Steinberg A. D. A serum inhibitor of immune regulation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):713–715. doi: 10.1172/JCI109180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Chihara T. Lymphocyte function in rheumatic disorders. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Oct;135(10):1324–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernet P., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to a specific surface antigen of T cells in human sera inhibiting mixed leukocyte culture reactions. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):1021–1026. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



