Abstract
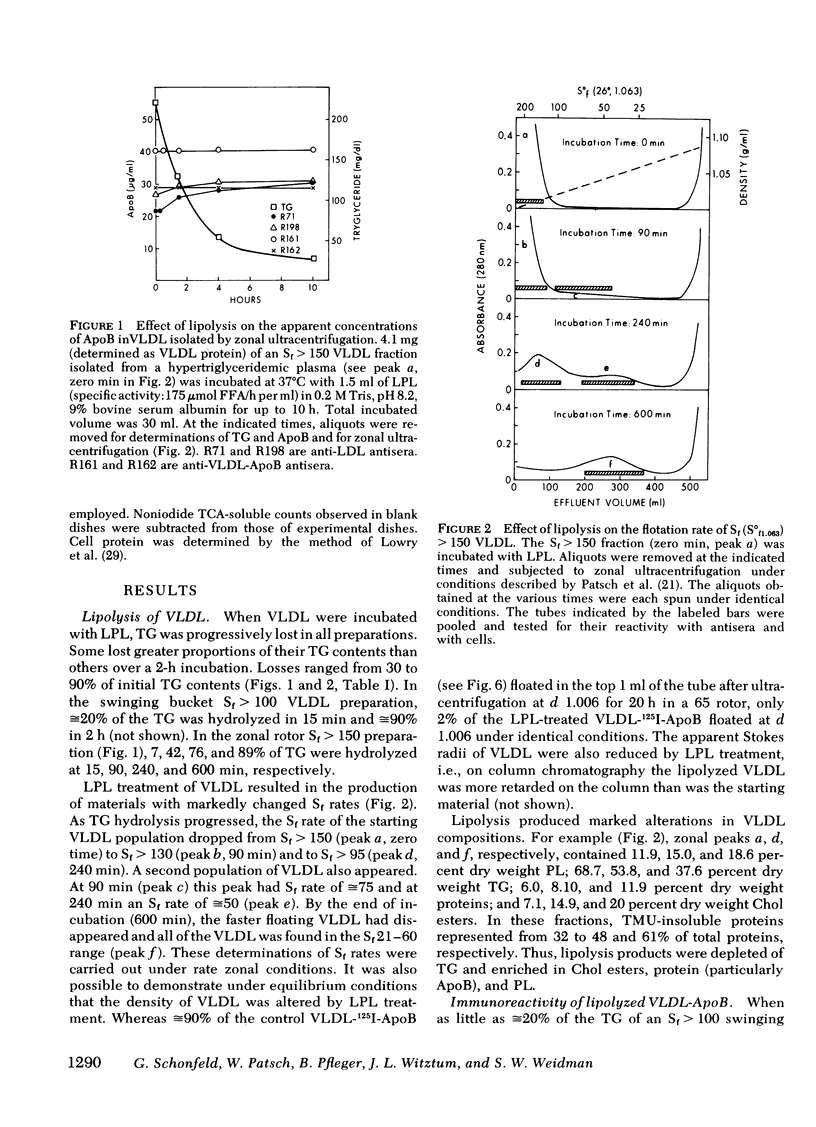
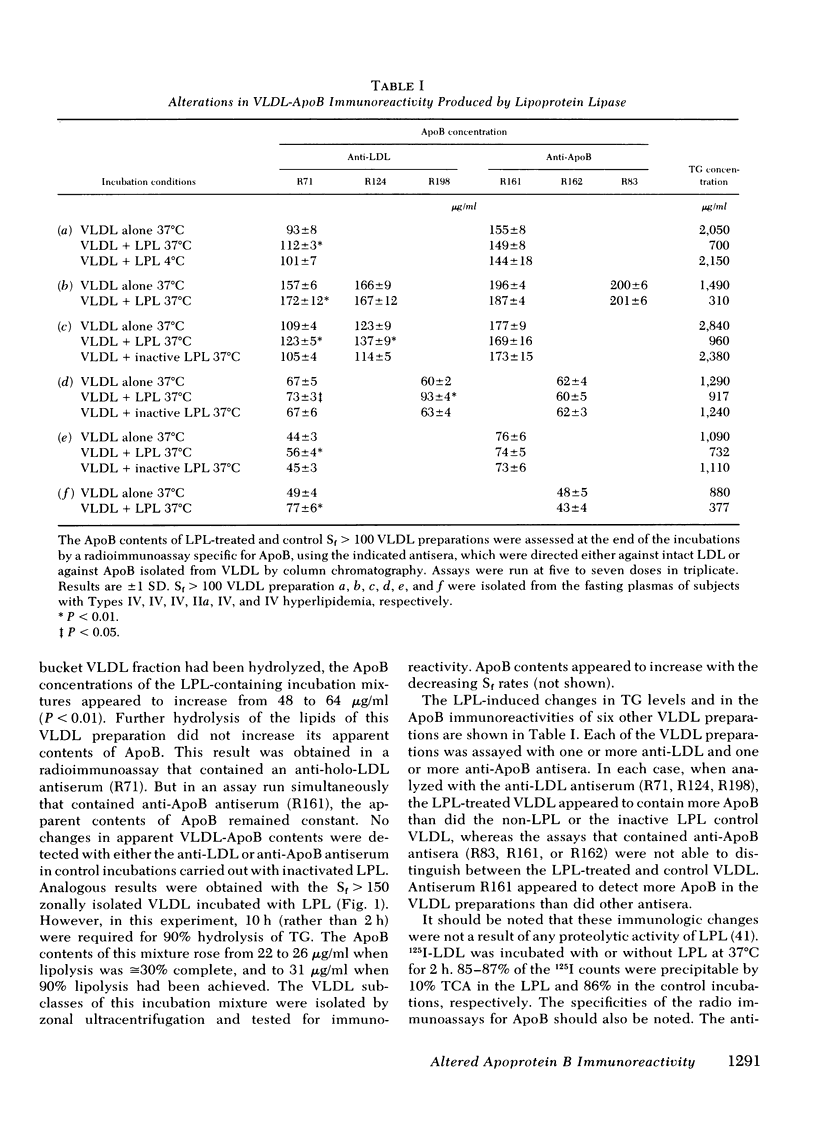
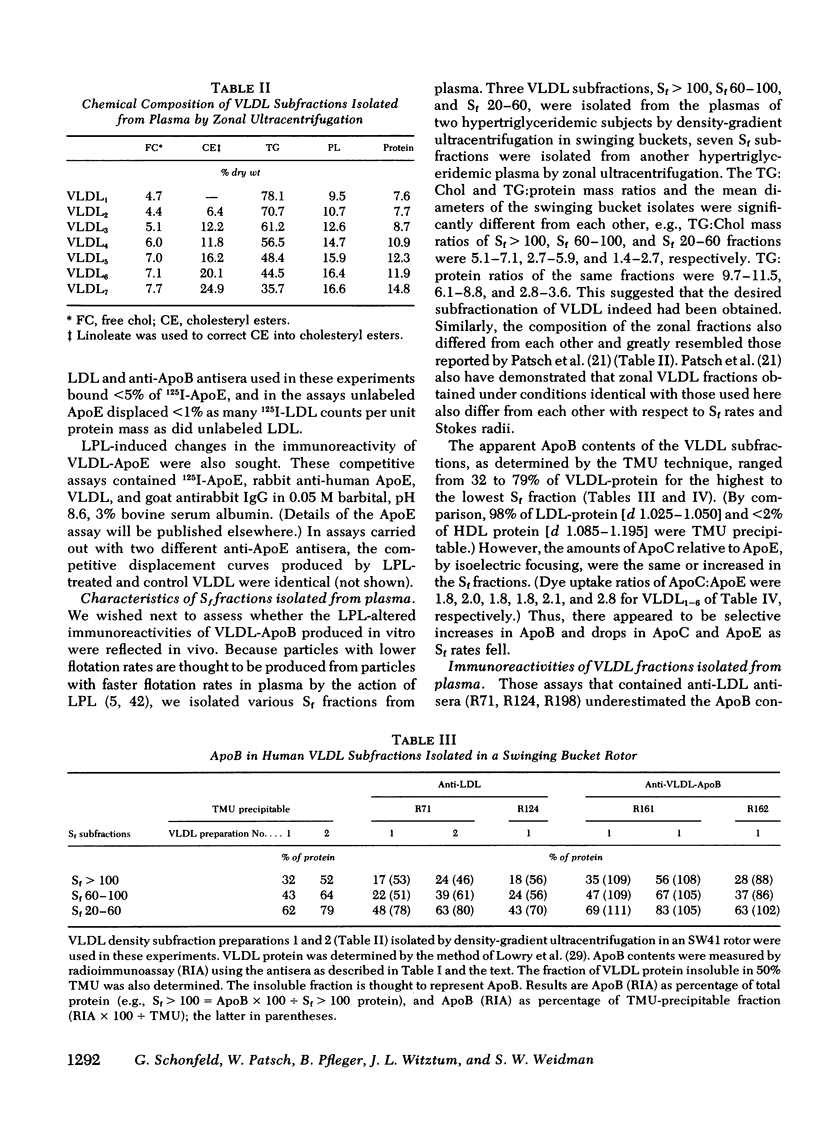
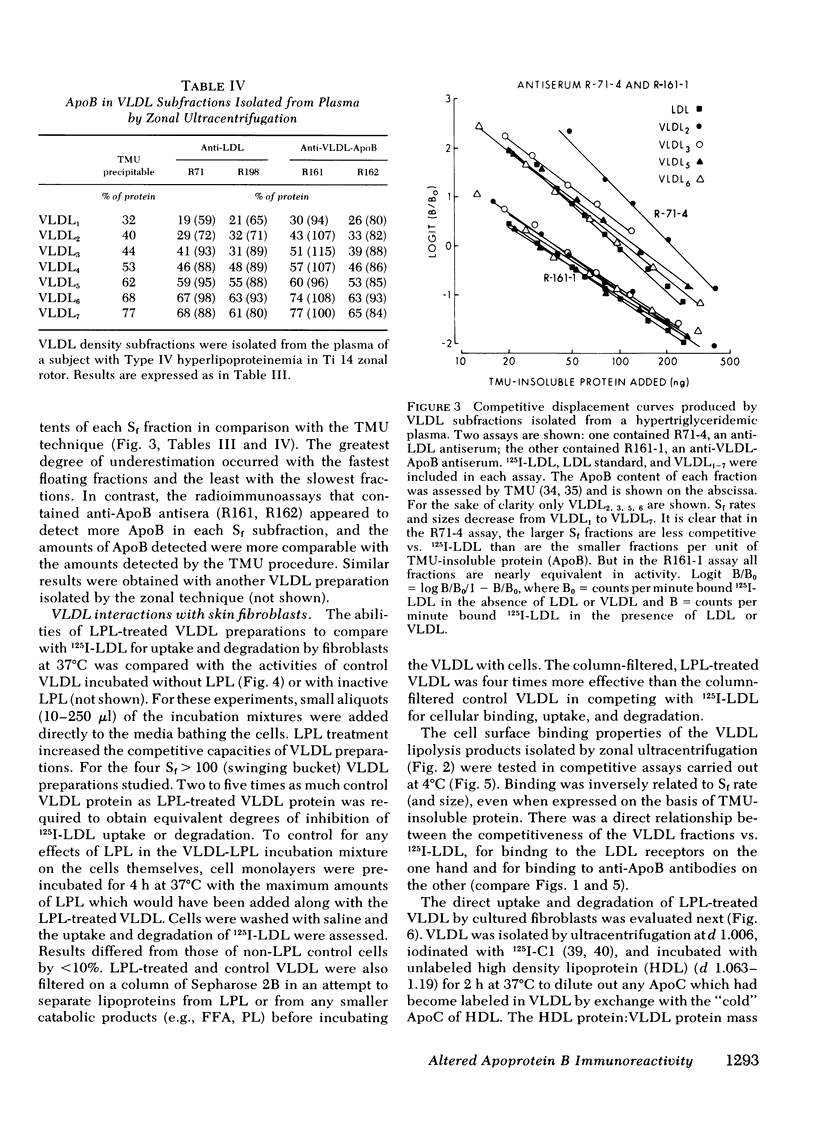
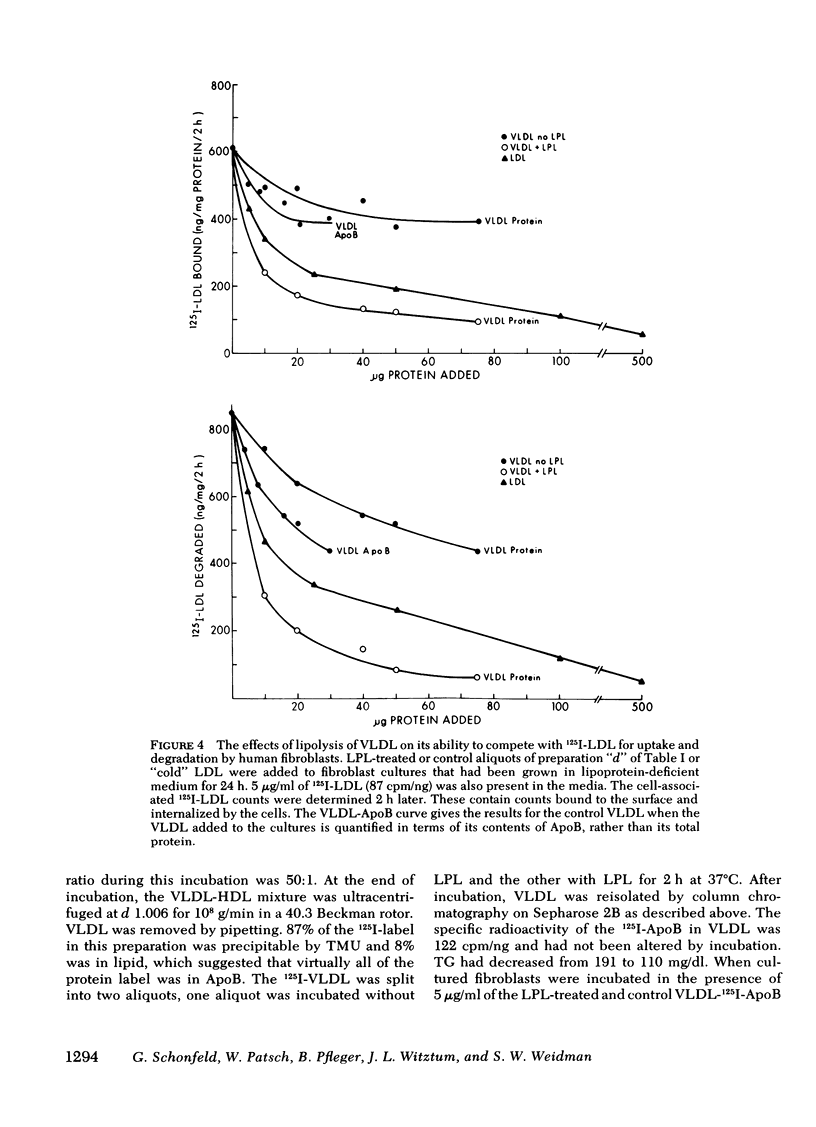
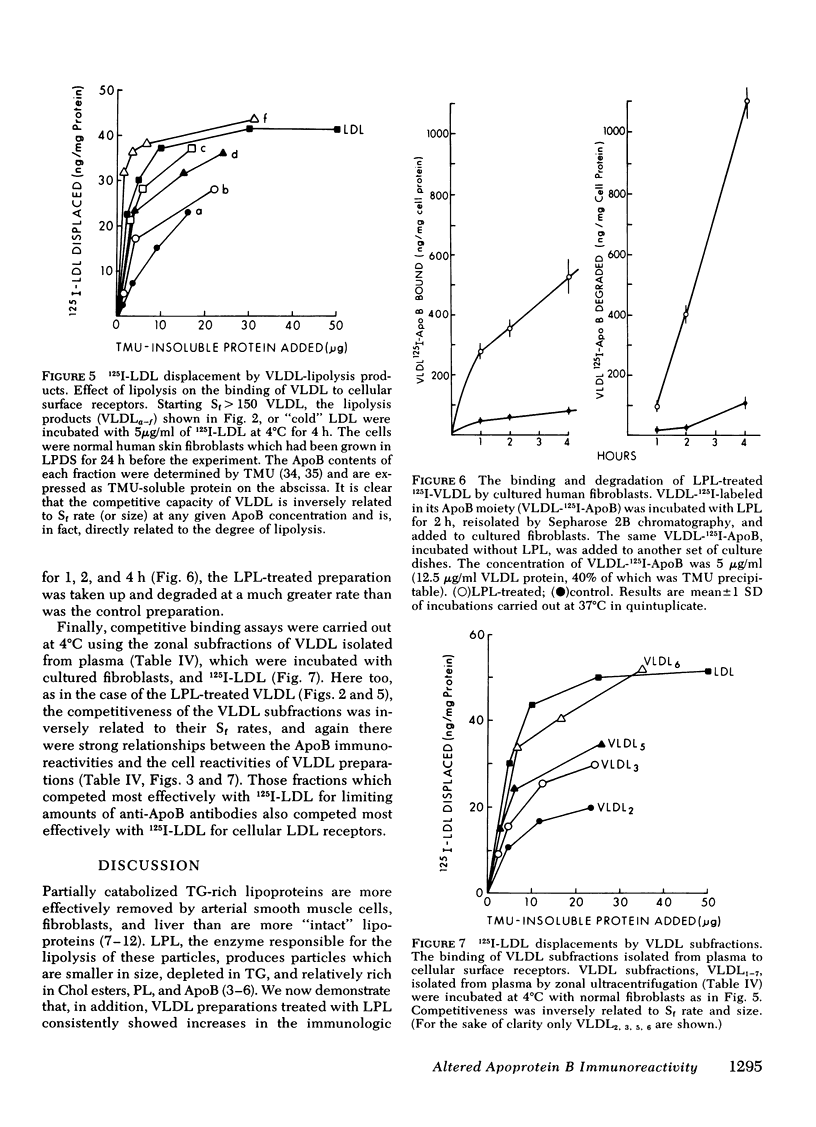
Smaller very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) remnants interact more readily with tissues than do larger “intact” VLDL. This may be related to changes in the availability of VLDL apoproteins on the surface of the lipoproteins. To test this hypothesis VLDL were incubated at 37°C with bovine milk lipase (LPL), and the abilities of LPL-treated VLDL preparations to compete with 125I-low density lipoproteins (LDL) for interaction with cultured normal human fibroblasts were measured. At the same time, the immunologic activities of these preparations were also tested by double antibody radioimmunoassay. Triglyceride (TG) contents of VLDL fell by 30-90% during incubation with LPL and, on zonal ultracentrifugation, VLDL of faster Svedberg unit of flotation (Sf1.063) rates (>150) were gradually converted to smaller VLDL with lower Sf rates (21-60). LPL-treated VLDL competed two to five times more effectively with 125I-LDL for binding to cellular receptors than did control VLDL. Control VLDL incubated with heat-inactivated LPL at 37°C, or with active LPL at 4°C had unaltered cell reactivities and TG contents compared with VLDL incubated without any enzyme. The direct uptake and degradation of LPL-treated VLDL was also assessed by using VLDL 125I-labeled in apoprotein (Apo)B. LPL-treated VLDL-125I-ApoB were taken up and degraded by fibroblast at greater rates than were control VLDL-125I-ApoB. Thus, hydrolysis of VLDL lipids was accompanied by an increased ability of VLDL to interact with fibroblasts. The immunoreactivity of ApoB in the same VLDL preparations, expressed as the “apparent ApoB contents” of LPL-treated VLDL, increased by 10-50% (P < 0.02) in those assays that contained anti-LDL antisera, but the ApoB of control VLDL remained constant. However, assays that contained antisera directed against ApoB isolated from VLDL did not distinguish between LPL-treated and control VLDL. Thus, VLDL lipid hydrolysis was accompanied by changes in the immunoreactivity of VLDL-ApoB, which probably reflect changes in the disposition of ApoB on the surface of VLDL. The altered disposition of ApoB on VLDL “remnants” may be related to their enhanced interaction with cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierman E. L., Eisenberg S., Stein O., Stein Y. Very low density lipoprotein "remnant" particles: uptake by aortic smooth muscle cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 2;329(1):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Studies of the proteins in human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5687–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSON L. A. DETERMINATION OF SERUM TRIGLYCERIDES. J Atheroscler Res. 1963 Jul-Aug;3:334–336. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(63)80012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catapano A. L., Gianturco S. H., Kinnunen P. K., Eisenberg S., Gotto A. M., Jr, Smith L. C. Suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase by low density lipoproteins produced in vitro by lipoprotein lipase action on nonsuppressive very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1007–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek T., Eisenberg S. Very low density lipoprotein. Metabolism of phospholipids, cholesterol, and apolipoprotein C in the isolated perfused rat heart. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1654–1665. doi: 10.1172/JCI109086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D. The metabolism of chylomicron remnants by isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):464–474. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faergeman O., Havel R. J. Metabolism of cholesteryl esters of rat very low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1210–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI108039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faergeman O., Sata T., Kane J. P., Havel R. J. Metabolism of apoprotein B of plasma very low density lipoproteins in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1396–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI108220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Nilsson A. Binding, interiorization and degradation of cholesteryl ester-labelled chylomicron-remmant particles by rat hepatocyte monolayers. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):483–494. doi: 10.1042/bj1680483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Nilsson A. Degradation of chylomicron remnant cholesteryl ester by rat hepatocyte monolayers. Inhibition by chloroquine and colchicine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):520–528. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangl A., Ockner R. K. Intestinal metabolism of lipids and lipoproteins. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):167–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco S. H., Gotto A. M., Jr, Jackson R. L., Patsch J. R., Sybers H. D., Taunton O. D., Yeshurun D. L., Smith L. C. Control of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase activity in cultured human fibroblasts by very low density lipoproteins of subjects with hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):320–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI108942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaumann H., Bergstrand A., Ericsson J. L. Studies on the synthesis and intracellular transport of lipoprotein particles in rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):356–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S., Chapman M. J. Radioimmunological study of the surface protein of the human serum low-density lipoprotein: comparison of the native particle and the products obtained by tryptic treatment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91655-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Birnbaumer M. E., Fredrickson D. S. Evidence for the identity of the major apoprotein in low density and very low density lipoproteins in normal subjects and patients with familial hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1486–1494. doi: 10.1172/JCI106945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert P. N., Shulman R. S., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Fractionation of the C-apoproteins from human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4941–4946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. M., Fielding C. J. Lipoprotein lipase. Mechanism of formation of triglyceride-rich remnant particles from very low density lipoproteins and chylomicrons. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2288–2293. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Enhanced binding by cultured human fibroblasts of apo-E-containing lipoproteins as compared with low density lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1440–1447. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverius P. H., Ostlund-Lindqvist A. M. Lipoprotein lipase from bovine milk. Isolation procedure, chemical characterization, and molecular weight analysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7791–7795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. A rapid electrophoretic technique for identification of subunit species of apoproteins in serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):350–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Sata T., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Apoprotein composition of very low density lipoproteins of human serum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1622–1634. doi: 10.1172/JCI108245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Strober W., Levy R. I. The metabolism of low density lipoprotein in familial type II hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1528–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI106949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. I., Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S. The structure and metabolism of chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins (VLDL). Biochem Soc Symp. 1971;(33):3–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFARLANE A. S. Labelling of plasma proteins with radioactive iodine. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):135–143. doi: 10.1042/bj0620135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund R. E., Jr, Pfleger B., Schonfeld G. Role of microtubules in low density lipoprotein processing by cultured cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):75–84. doi: 10.1172/JCI109281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch W., Patsch J. R., Kostner G. M., Sailer S., Braunsteiner H. Isolation of subfractions of human very low density lipoproteins by zonal ultracentrifugation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4911–4915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch W., Sailer S., Braunsteiner H. An enzymatic method for the determination of the initial rate of cholesterol esterification in human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1976 Mar;17(2):182–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röschlau P., Bernt E., Gruber W. Enzymatische Bestimmung des Gesamt-Cholesterins im Serum. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1974 Sep;12(9):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Bradshaw R. A., Chen J. Structure of high density lipoprotein. The immunologic reactivities of the COOH- and NH2-terminal regions of apolipoprotein A-I. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3921–3926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Chen J. S., Roy R. G. Use of antibody specificity to study the surface disposition of apoprotein A-I on human high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6655–6659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Lees R. S., George P. K., Pfleger B. Assay of total plasma apolipoprotein B concentration in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1458–1467. doi: 10.1172/JCI107694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Lees R. S., George P. K., Pfleger B. Assay of total plasma apolipoprotein B concentration in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1458–1467. doi: 10.1172/JCI107694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shireman R., Kilgore L. L., Fisher W. R. Solubilization of apolipoprotein B and its specific binding by the cellular receptor for low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5150–5154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Nestel P. J., Weinstein D. B., Remaut-Desmeth M., Chang C. M. Interactions of native and modified human low density lipoproteins with human skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 27;528(2):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidman S. W., Suarez B., Falko J. M., Witztum J. L., Kolar J., Raben M., Schonfeld G. Type III hyperlipoproteinemia: development of a VLDL ApoE gel isoelectric focusing technique and application in family studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Apr;93(4):549–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


