Abstract
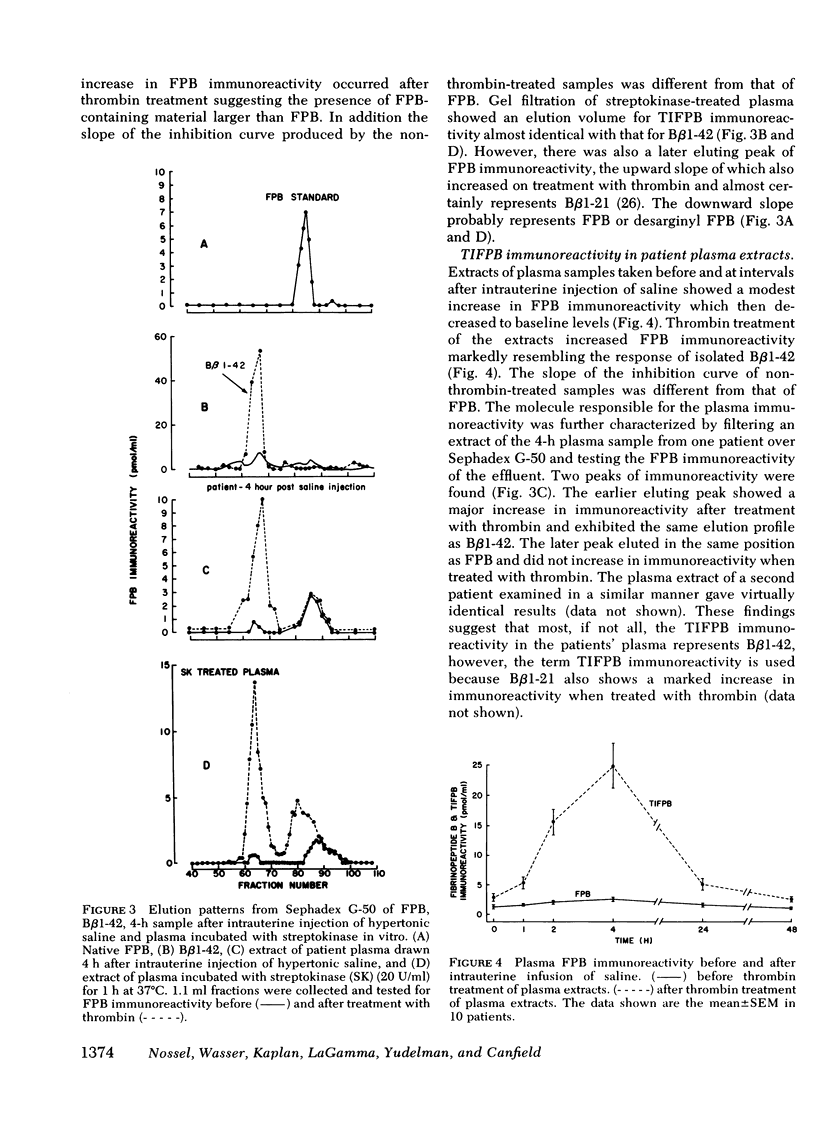
Plasma fibrinopeptide B (Bβ1-14 or FPB) immunoreactivity was studied by radioimmunoassay in patients who received intrauterine infusion of hypertonic saline to terminate pregnancy. FPB immunoreactivity increased with thrombin treatment (TIFPB) suggesting the presence of a larger FPB-containing peptide, since purified FPB is not altered by thrombin, whereas thrombin increases the immunoreactivity of Bβ1-42 (which includes FPB) 10-fold. TIFPB immunoreactivity in plasma, drawn 4 h after hypertonic saline infusion eluted from Sephadex G-50 similarly to isolated Bβ1-42. Streptokinase, incubated with normal plasma progressively generated TIFPB immunoreactivity, which showed a major component which eluted from Sephadex G-50 similarly to Bβ1-42. Streptokinase generated TIFPB much more rapidly in reptilase-treated plasma that contains fibrin I, (which still includes FPB), indicating that fibrin I is preferred over fibrinogen as a substrate for plasmin cleavage of arginine (Bβ42)-alanine (Bβ43). Serial studies were then made in 10 patients receiving intrauterine hypertonic saline. Fibrinopeptide A (FPA) levels rose immediately, reached a peak between 1 and 2 h, were declining at 4 h, and were normal at 24 and 48 h. TIFPB levels rose slightly in the 1st h, reached a peak at 4 h, and had returned to base-line values at 24 h. Serum fibrinogen degradation product levels were unchanged at 1 h, reached their highest level at 4 h, and were still markedly elevated at 24 and 48 h. Fibrinogen levels dropped slightly being lowest at 4 and 24 h. Platelet counts declined in parallel with the fibrinogen levels over the first 4 h, but continued to decrease through 48 h. Beta thromboglobulin (βTG) levels generally paralleled FPA levels whereas platelet factor 4 (PF4) levels showed only slight changes. The data indicate that immediately after intrauterine hypertonic saline infusion thrombin is formed that cleaves FPA from fibrinogen to produce fibrin I and releases βTG and PF4 from platelets. Later plasmin cleaves Bβ1-42 from fibrin I to produce fragment X, which is further degraded to form serum fibrinogen degradation products. This sequence of proteolysis indicates that plasmin action on fibrin I serves as a mechanism that regulates fibrin II formation by removing the Bβ chain cleavage site, which is required for thrombin action in converting fibrin I to fibrin II.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI103885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilezikian S. B., Nossel H. L., Butler V. P., Jr, Canfield R. E. Radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide B and kinetics of fibrinopeptide cleavage by different enzymes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):438–445. doi: 10.1172/JCI108110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilezikian S. B., Nossel H. L. Unique pattern of fibrinogen cleavage by human leukocyte proteases. Blood. 1977 Jul;50(1):21–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Edman P., Hessel B. Human fibrinopeptides. Isolation, characterization and structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):371–396. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Hessel B., Hogg D., Therkildsen L. A two-step fibrinogen--fibrin transition in blood coagulation. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):501–505. doi: 10.1038/275501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Ludlam C. A., Pepper D. S., Moore S., Cash J. D. A radioimmunoassay for platelet factor 4. Thromb Res. 1976 Jan;8(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzynski A. Z., Marder V. J., Shainoff J. R. Structure of plasmic degradation products of human fibrinogen. Fibrinopeptide and polypeptide chain analysis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2294–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIS B. C., STRANSKY A. A quick and accurate method for the determination of fibronogen in plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Sep;58:477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handin R. I., McDonough M., Lesch M. Elevation of platelet factor four in acute myocardial infarction: measurement by radioimmunoassay. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Feb;91(2):340–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Wallén P., Gröndahl N. J., Henschen A., Blombäck B. On the primary structure of human fibrinogen. Isolation and characterization of N-terminal fragments from plasmic digests. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(2):189–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. L., Nossel H. L., Drillings M., Lesznik G. Radioimmunoassay of platelet factor 4 and beta-thromboglobulin: development and application to studies of platelet release in relation to fibrinopeptide A generation. Br J Haematol. 1978 May;39(1):129–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb07135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlam C. A., Moore S., Bolton A. E., Pepper D. S., Cash J. D. The release of a human platelet specific protein measured by a radioimmunoassay. Thromb Res. 1975 Jun;6(6):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R., Carroll W. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. I. Physicochemical and immunological characterization. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2111–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Johnson A. J., Kleiner G. J., Wohl H. The defibrination syndrome: clinical features and laboratory diagnosis. Br J Haematol. 1967 Jul;13(4):528–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb00762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Lalezari P., Johnson A. J. A rapid, simple, sensitive method for measuring fibrinolytic split products in human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):871–875. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Umfleet R. A., Galanakis D. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. I. Structural and related studies of plasma fibrinogens which are high solubility catabolic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5210–5219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Thomas D. P. Platelet factor 4 and adenosine diphosphate release during human platelet aggregation. Nature. 1969 Jun 28;222(5200):1269–1270. doi: 10.1038/2221269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Ti M., Kaplan K. L., Spanondis K., Soland T., Butler V. P., Jr The generation of fibrinopeptide A in clinical blood samples: evidence for thrombin activity. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1136–1144. doi: 10.1172/JCI108566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Younger L. R., Wilner G. D., Procupez T., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr Radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2350–2353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr, Spanondis K., Wilner G. D., Qureshi G. D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):43–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R., Greston W., Kleiner G. J. Defibrination in saline abortion. Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Nov;40(5):728–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stander R. W., Flessa H. C., Glueck H. I., Kisker C. T. Changes in maternal coagulation factors after intra-amniotic injection of hypertonic saline. Obstet Gynecol. 1971 May;37(5):660–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequence studies on plasmin-derived fragments of human fibrinogen: amino-terminal sequences of intermediate and terminal fragments. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 11;14(5):940–946. doi: 10.1021/bi00676a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Royen E. A., Treffers P. E., Ten Cate J. W. Hypertonic saline induced abortion as pathophysiologic model of low grade intravascular coagulation. Scand J Haematol. 1974;13(3):166–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1974.tb00255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. E., Easterling W. E., Jr, Odom M. H., McMillan C. W., Johnson A. M., Talbert L. M. Defibrination syndrome after intra-amniotic infusion of hypertonic saline. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Aug 1;113(7):868–874. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90649-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. Molecular mechanism of physiological fibrinolysis. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):549–550. doi: 10.1038/272549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte L. D., Kaplan K. L., Nossel H. L., Lages B. A., Weiss H. J., Goodman D. S. Studies of the release from human platelets of the growth factor for cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1978 Mar;42(3):402–409. doi: 10.1161/01.res.42.3.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



