Abstract
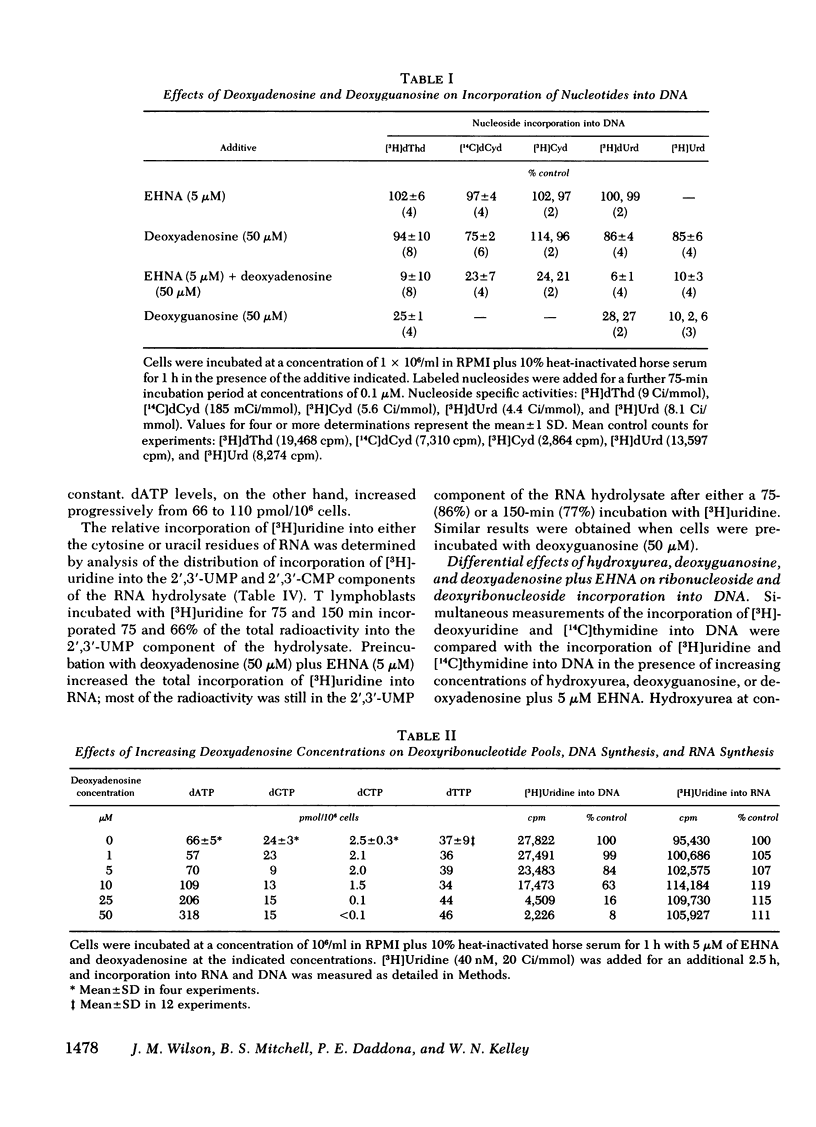
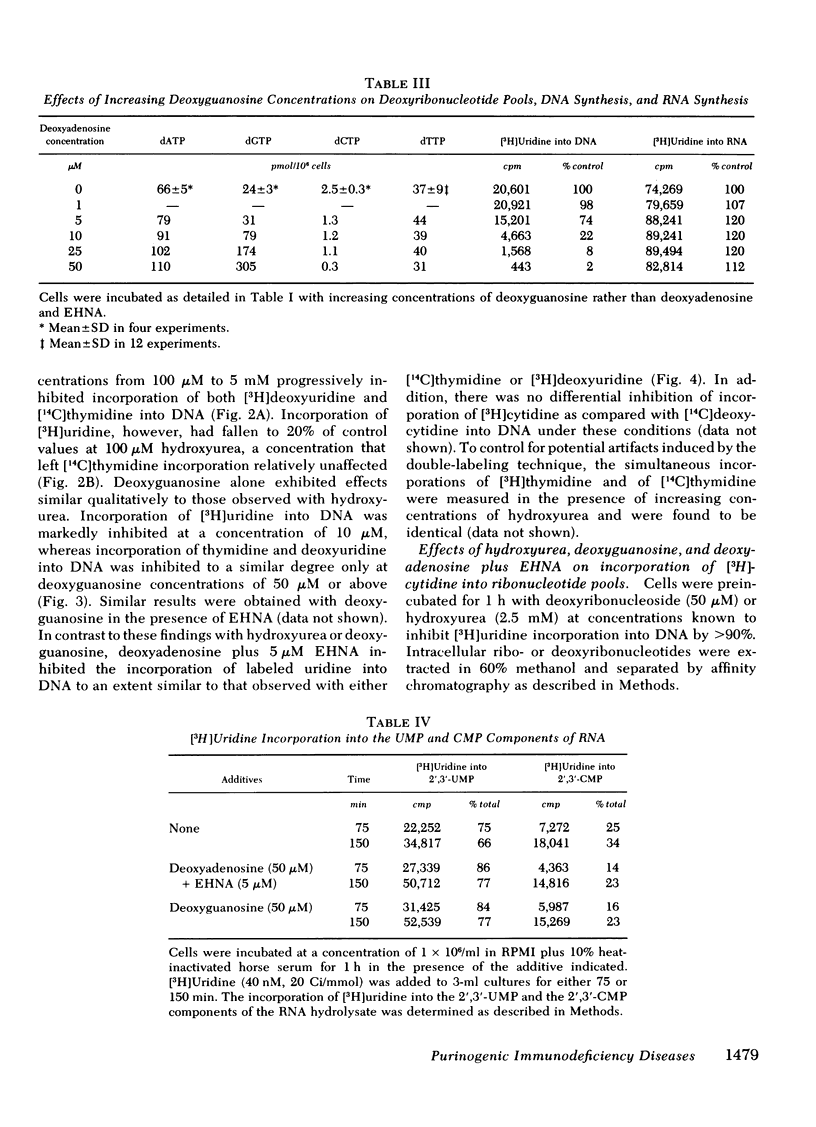
Deoxyadenosine and deoxyguanosine are toxic to human lymphoid cells in culture and have been implicated in the pathogenesis of the immunodeficiency states associated with adenosine deaminase and purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency, respectively. We have studied the relative incorporation of several labeled nucleosides into DNA and into nucleotide pools to further elucidate the mechanism of deoxyribonucleoside toxicity. In the presence of an inhibitor of adenosine deaminase [erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)adenine [EHNA], 5 μM], deoxyadenosine (1-50 μM) progressively decreased the incorporation of thymidine, uridine, and deoxyuridine into DNA, but did not affect uridine incorporation into RNA. This decrease in DNA synthesis was associated with increasing dATP and decreasing dCTP pools. Likewise, incubation of cells with deoxyguanosine caused an elevation of dGTP, depletion of dCTP, and inhibition of DNA synthesis.
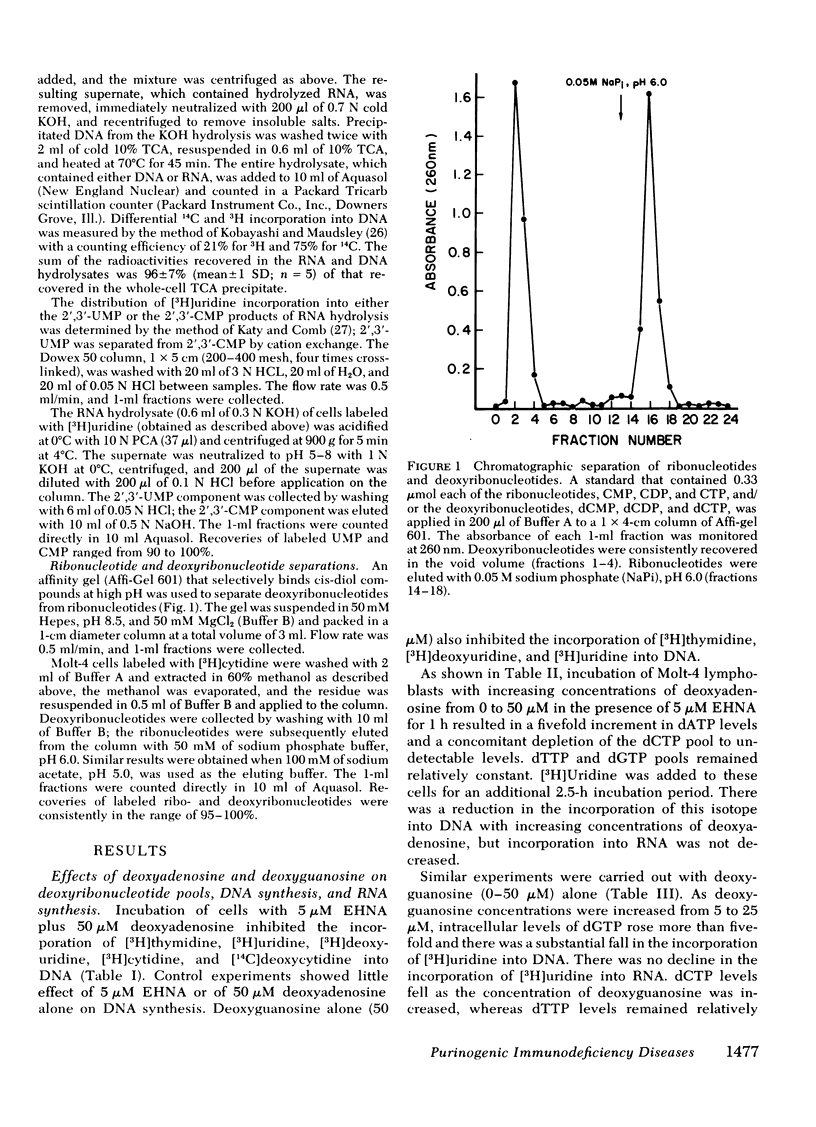
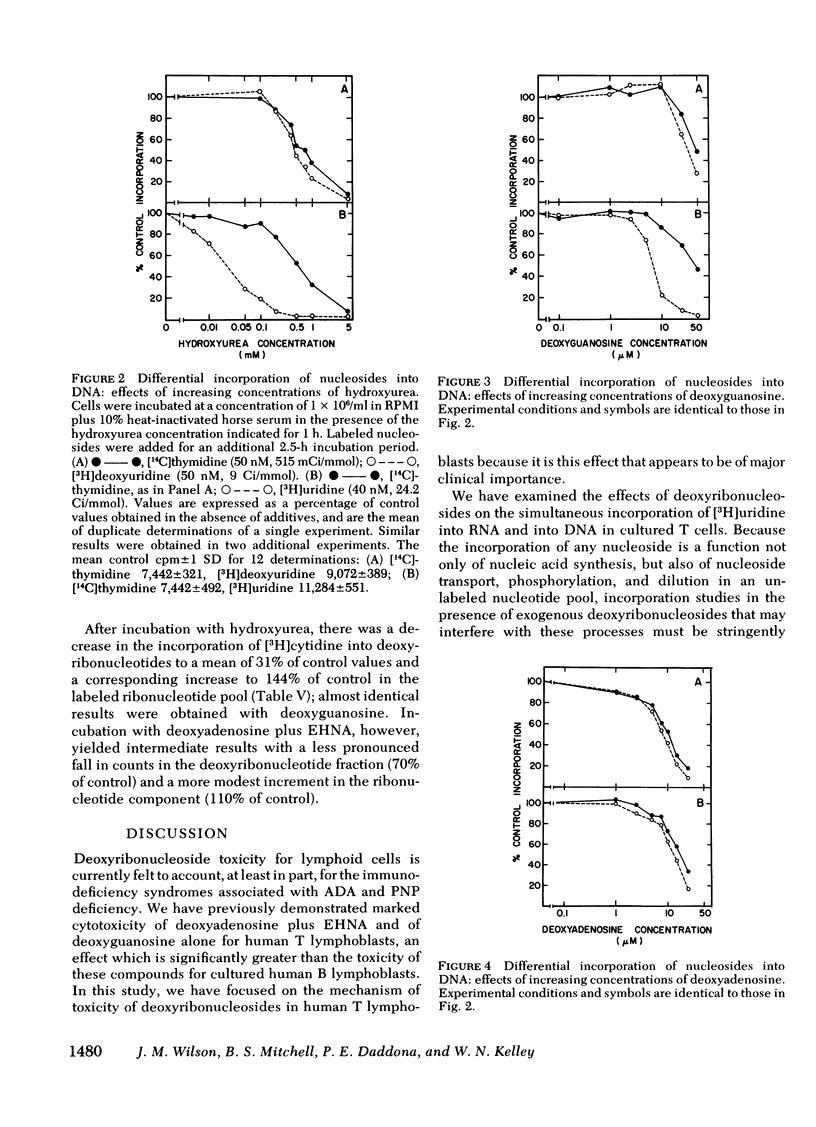
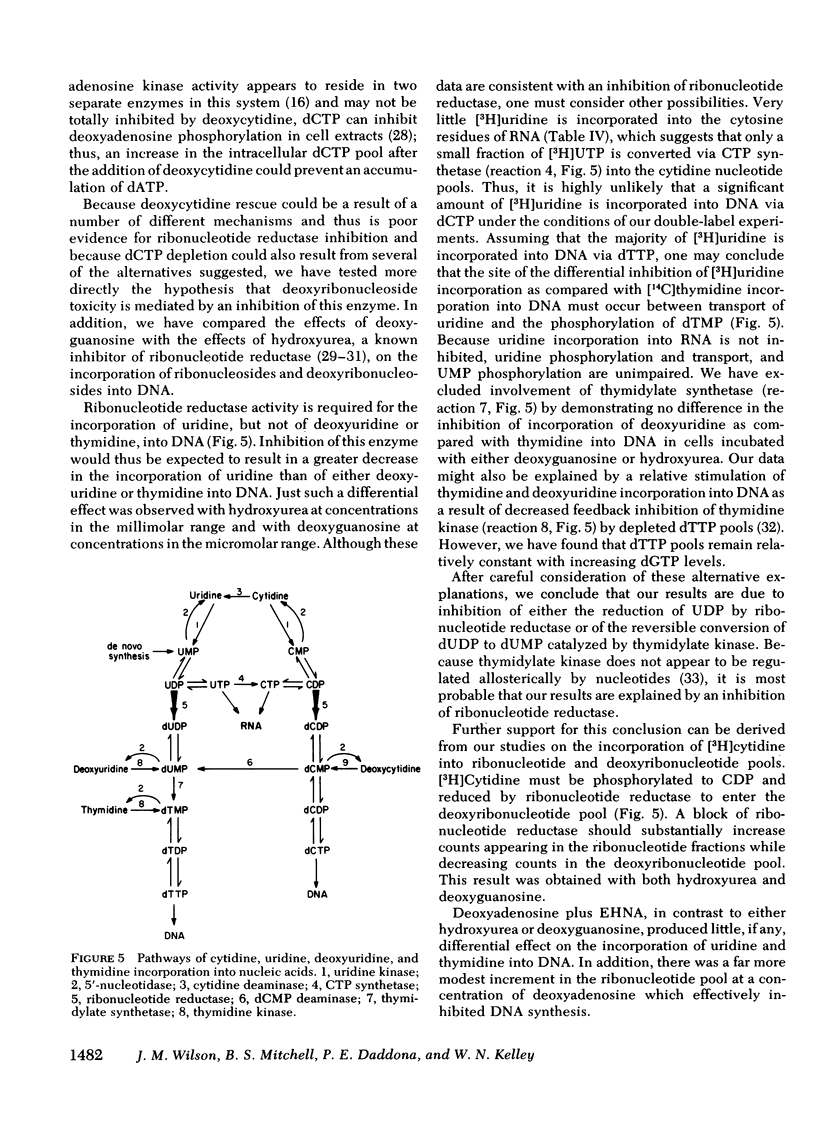
To test the hypothesis that dATP and dGTP accumulation inhibit DNA synthesis by inhibiting the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase, simultaneous rates of incorporation of [3H]uridine and [14C]thymidine into DNA were measured in the presence of deoxyadenosine plus EHNA or deoxyguanosine, and in the presence of hydroxyurea, a known inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase. Hydroxyurea (100 μM) and deoxyguanosine (10 μM) decreased the incorporation of [3H]uridine but not of [14C]thymidine into DNA; both compounds also substantially increased [3H]cytidine incorporation into the ribonucleotide pool while reducing incorporation into the deoxyribonucleotide pool. In contrast, deoxyadenosine plus EHNA did not show this differential inhibition of [3H]uridine incorporation into DNA, and the alteration in [3H]cytidine incorporation into nucleotide pools was less impressive.
These data show an association between accumulation of dATP or dGTP and a primary inhibition of DNA synthesis, and they provide support for ribonucleotide reductase inhibition as the mechanism responsible for deoxyguanosine toxicity. Deoxyadenosine toxicity, however, appears to result from another, or perhaps a combination of, molecular event(s).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. L., Lindsay J. G. Hydroxyurea reversal of inhibition and use as a cell-synchronizing agent. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 25;242(6):1314–1317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjursell G., Reichard P. Effects of thymidine on deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pools and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3904–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E., Thompson U. B. Properties of deoxythymidine kinase partially purified from animal tumors. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3967–3974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carapella-de Luca E., Aiuti F., Lucarelli P., Bruni L., Baroni C. D., Imperato C., Roos D., Astaldi A. A patient with nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency, selective t-cell deficiency, and autoimmune hemolytic anemia. J Pediatr. 1978 Dec;93(6):1000–1003. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81237-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Kaye J., Seegmiller J. E. Differential sensitivity of human leukemic T cell lines and B cell lines to growth inhibition by deoxyadenosine. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1726–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Kaye J., Seegmiller J. E. Lymphospecific toxicity in adenosine deaminase deficiency and purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency: possible role of nucleoside kinase(s). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5677–5681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. S. Deoxyguanosine toxicity on lymphoid cells as a cause for immunosuppression in purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Doyle D., Martin D. W., Jr, Ammann A. J. Abnormal purine metabolism and purine overproduction in a patient deficient in purine nucleoside phosphorylase. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 23;295(26):1449–1454. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612232952603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Gudas L. J., Ammann A. J., Staal G. E., Martin D. W., Jr Deoxyguanosine triphosphate as a possible toxic metabolite in the immunodeficiency associated with purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1405–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI109058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Hirschhorn R., Horowitz S. D., Rubinstein A., Polmar S. H., Hong R., Martin D. W., Jr Deoxyadenosine triphosphate as a potentially toxic metabolite in adenosine deaminase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):472–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M. S., Donofrio J., Hutton J. J., Hahn L., Daoud A., Lampkin B., Dyminski J. Identification and quantitation of adenine deoxynucleotides in erythrocytes of a patient with adenosine deaminase deficiency and severe combined immunodeficiency. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1619–1626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donofrio J., Coleman M. S., Hutton J. J., Daoud A., Lampkin B., Dyminski J. Overproduction of adenine deoxynucleosides and deoxynucletides in adenosine deaminase deficiency with severe combined immunodeficiency disease. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):884–887. doi: 10.1172/JCI109201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards N. L., Gelfand E. W., Biggar D., Fox I. H. Partial deficiency of purine nucleoside phosphorylase: studies of purine and pyrimidine metabolism. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 May;91(5):736–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Ammann A. J., Wara D. W., Sandman R., Diamond L. K. Nucleoside-phosphorylase deficiency in a child with severely defective T-cell immunity and normal B-cell immunity. Lancet. 1975 May 3;1(7914):1010–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91950-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Cohen F., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Ullman B., Cohen A., Martin D. W., Jr Deoxyguanosine toxicity in a mouse T lymphoma: relationship to purine nucleoside phosphorylase-associated immune dysfunction. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S. Apparent suicide inactivation of human lymphoblast S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase by 2'-deoxyadenosine and adenine arabinoside. A basis for direct toxic effects of analogs of adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):22–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ S., COMB D. G. A NEW METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF THE BASE COMPOSITION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3065–3067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krygier V., Momparler R. L. Mammalian deoxynucleoside kinases. 3. Deoxyadenosine kinase: inhibition by nucleotides and kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2752–2757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis W. H., Wright J. A. Isolation of hydroxyurea-resistant CHO cells with altered levels of ribonucleotide reductase. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Jan;5(1):83–96. doi: 10.1007/BF01538788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J. K., Gowans B., Brox L. Deoxyadenosine metabolism and toxicity in cultured L5178Y cells. Cancer Res. 1977 Sep;37(9):3013–3017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., Castellot J. J., Jr, Pardee A. B. A permeable animal cell preparation for studying macromolecular synthesis. DNA synthesis and the role of deoxyribonucleotides in S phase initiation. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):1073–1080. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell B. S., Mejias E., Daddona P. E., Kelley W. N. Purinogenic immunodeficiency diseases: selective toxicity of deoxyribonucleosides for T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5011–5014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. C., Hurlbert R. B. Regulation of mammalian deoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis by nucleotides as activators and inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 25;241(20):4802–4809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Nucleotide pools of Novikoff rat hepatoma cells growing in suspension culture. I. Kinetics of incorporation of nucleosides into nucleotide pools and pool sizes during growth cycle. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Apr;77(2):213–240. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich K. C., Arnold W. J., Palella T., Fox I. H. Cellular immune deficiency with autoimmune hemolytic anemia in purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. Am J Med. 1979 Jul;67(1):172–176. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds H. A., Panayi G. S., Corrigall V. A role for purine metabolism in the immune response: Adenosine-deaminase activity and deoxyadenosine catabolism. Lancet. 1978 Jan 14;1(8055):60–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoop J. W., Eijsvoogel V. P., Zegers B. J., Blok-Schut B., van Bekkum D. W., Ballieux R. E. Selective severe cellular immunodeficiency. Effect of thymus transplantation and transfer factor administration. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Nov;6(3):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoop J. W., Zegers B. J., Hendrickx G. F., van Heukelom L. H., Staal G. E., de Bree P. K., Wadman S. K., Ballieux R. E. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency associated with selective cellular immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1977 Mar 24;296(12):651–655. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197703242961203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman B., Gudas L. J., Clift S. M., Martin D. W., Jr Isolation and characterization of purine-nucleoside phosphorylase-deficient T-lymphoma cells and secondary mutants with altered ribonucleotide reductase: genetic model for immunodeficiency disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman B., Gudas L. J., Cohen A., Martin D. W., Jr Deoxyadenosine metabolism and cytotoxicity in cultured mouse T lymphoma cells: a model for immunodeficiency disease. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virelizier J. L., Hamet M., Ballet J. J., Reinert P., Griscelli C. Impaired defense against vaccinia in a child with T-lymphocyte deficiency associated with inosine phosphorylase defect. J Pediatr. 1978 Mar;92(3):358–362. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


