Abstract
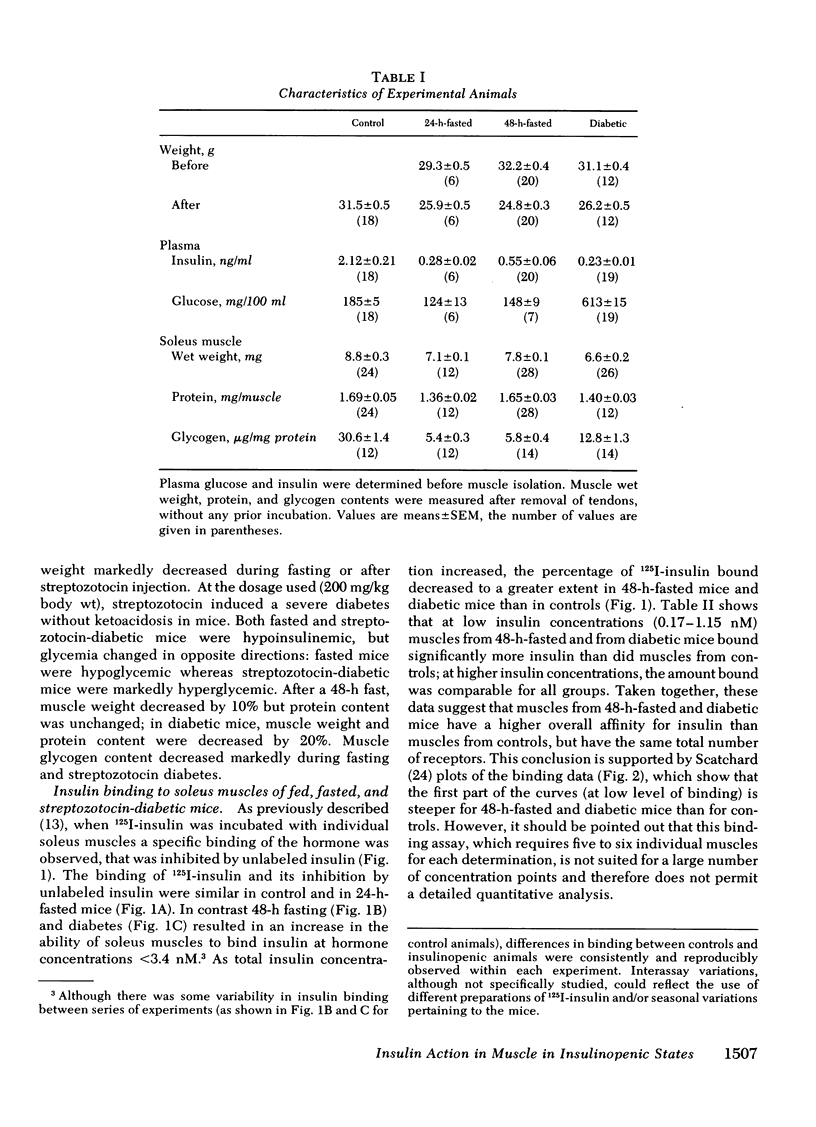
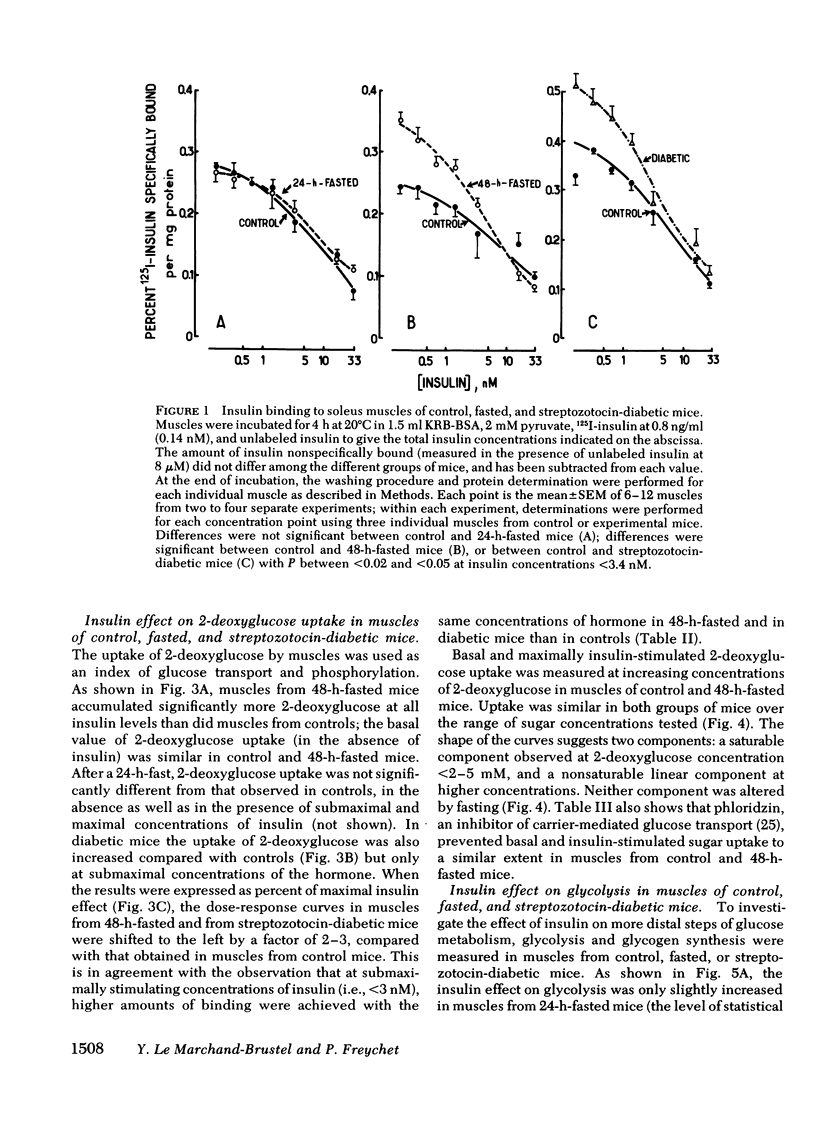
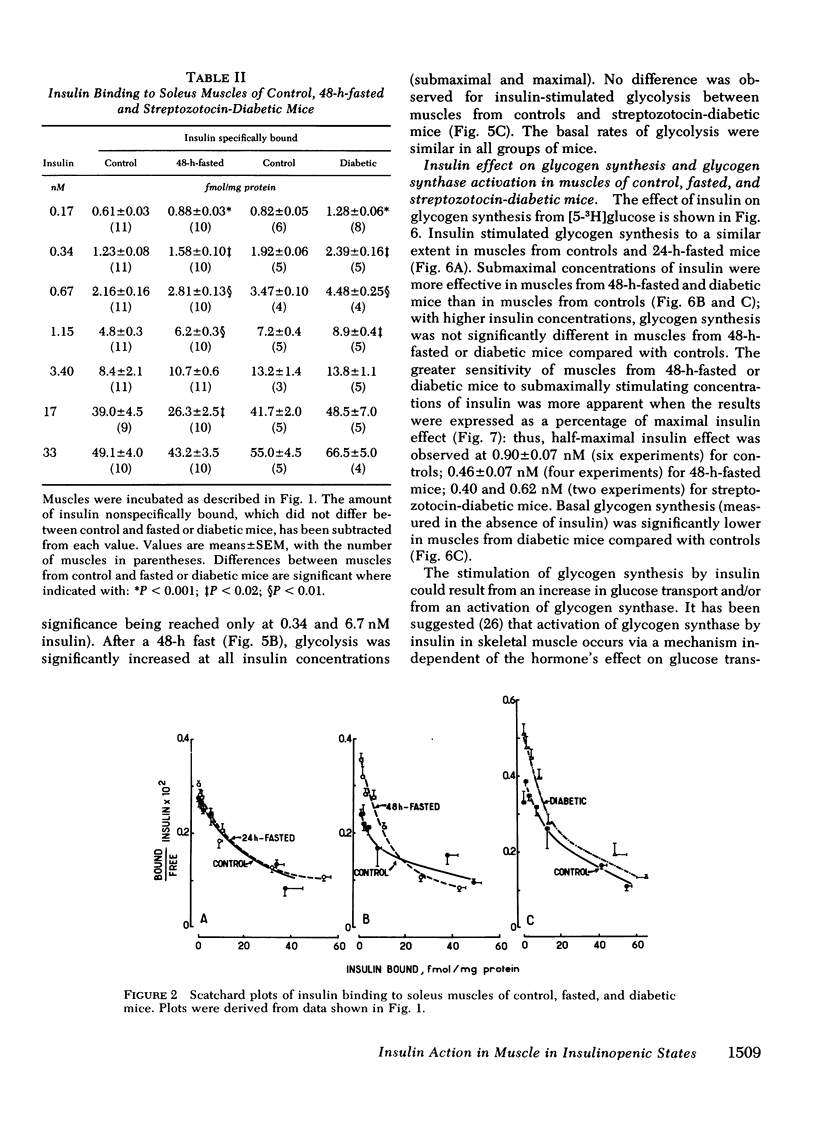
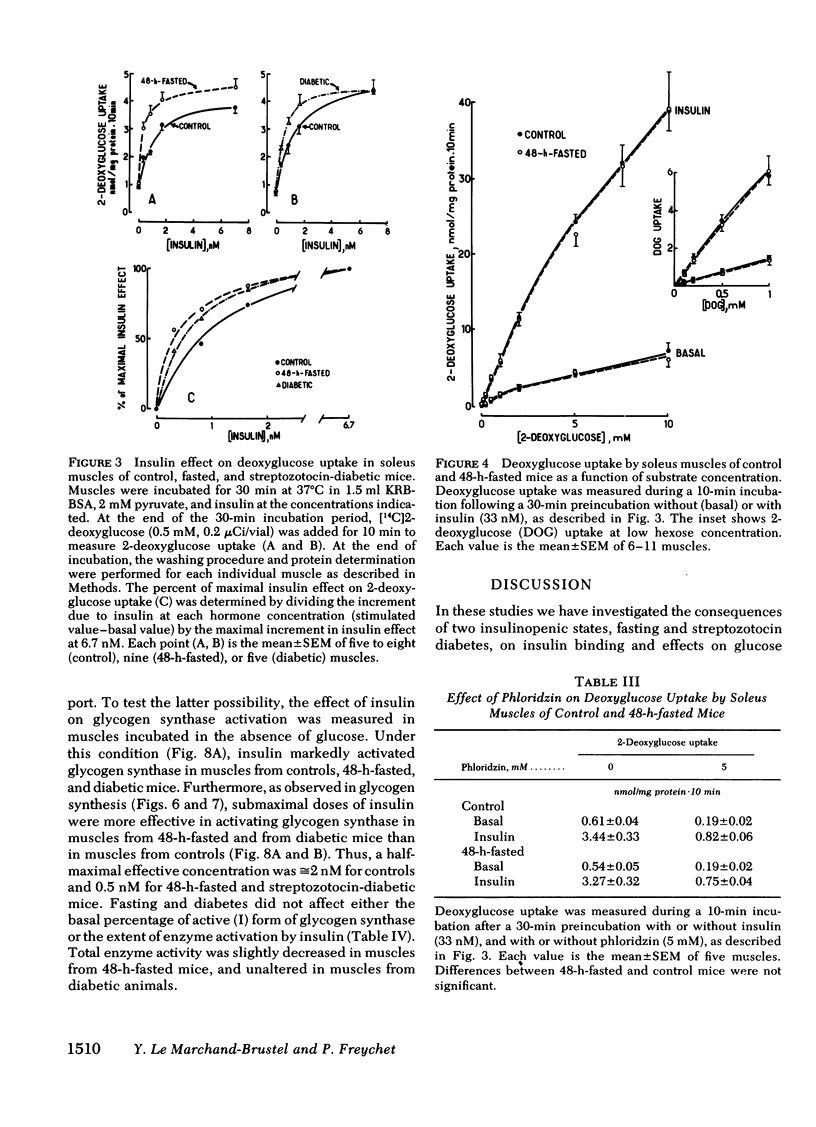
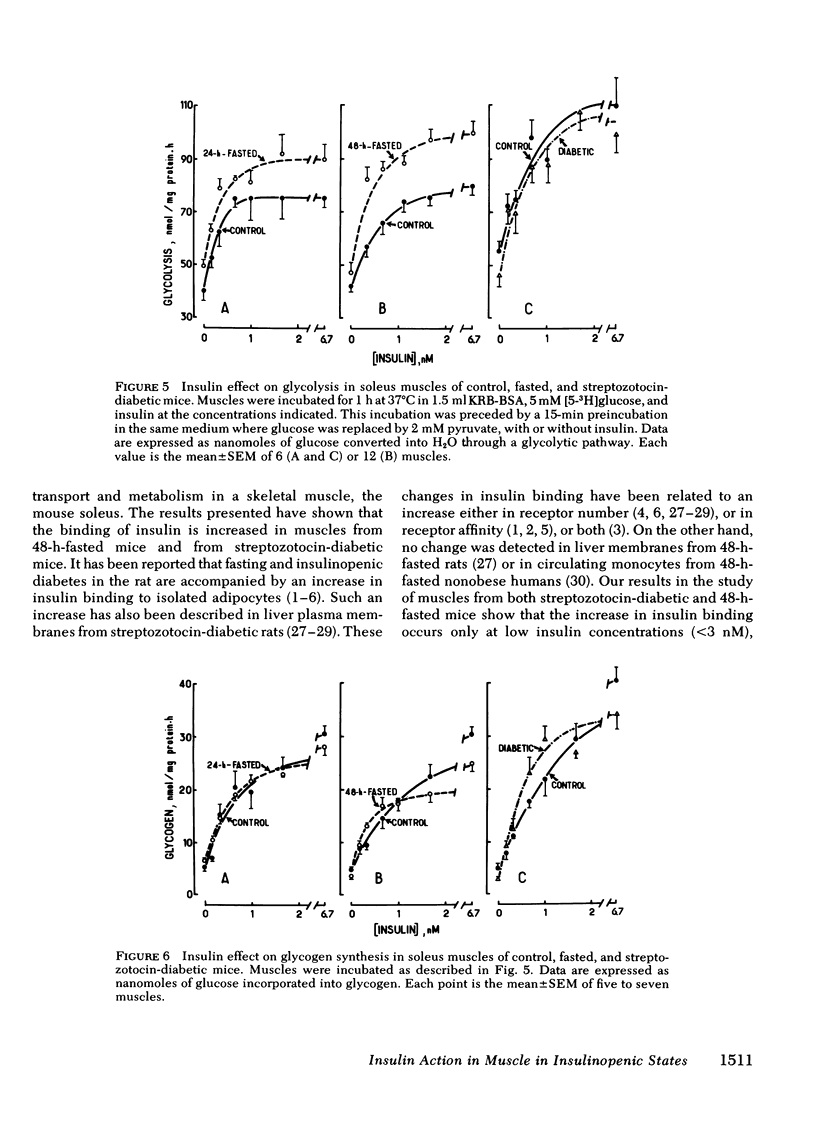
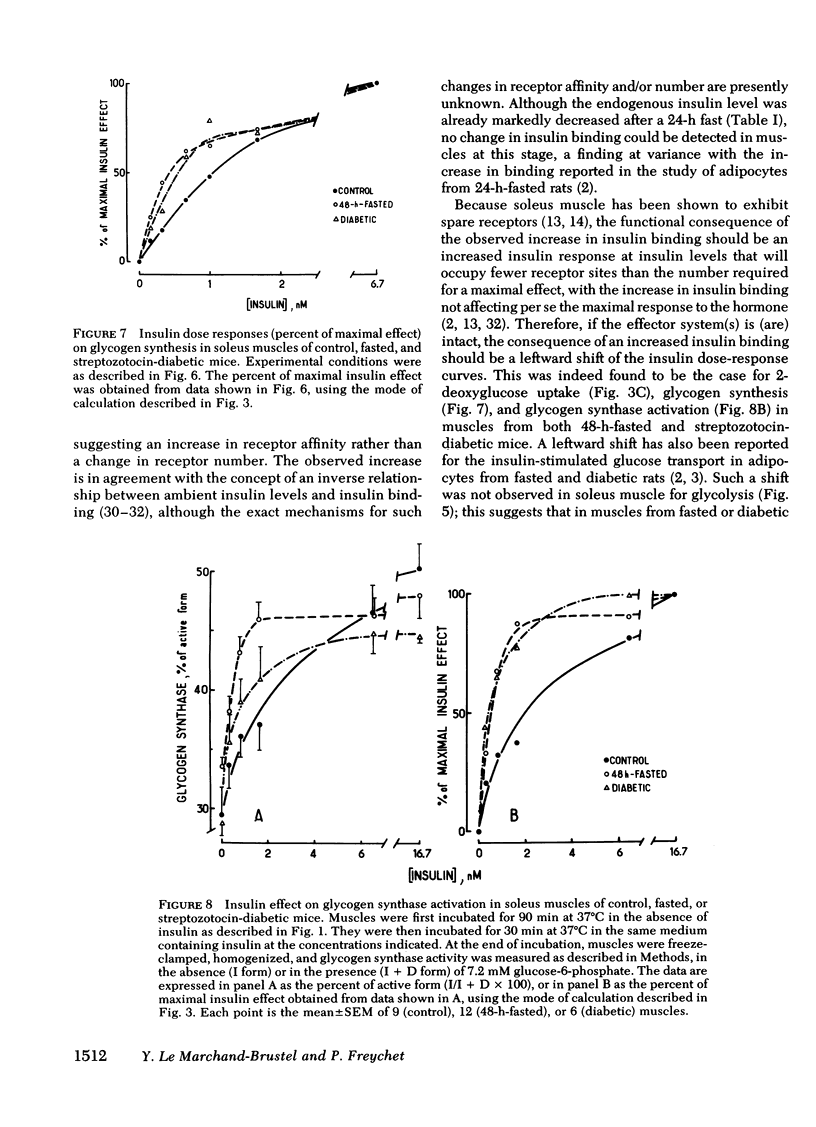
To investigate whether skeletal muscle is resistant to insulin in insulinopenic states, insulin binding and biological effects on glucose utilization were studied in isolated soleus muscles from 24- or 48-h-fasted mice and from streptozotocin-diabetic mice. Both 48-h fasting and diabetes led to an increase in insulin binding at insulin concentrations <3.4 nM. In both states, submaximal concentrations of insulin were also more effective in stimulating muscle 2-deoxyglucose uptake and glycogen synthesis, and in activating glycogen synthase. This resulted in a two- to fourfold leftward shift in the insulin dose-response curves in muscles from both groups compared with control. No change in insulin binding or biological effects was detected in muscles from 24-h-fasted mice. Maximal insulin effectiveness on 2-deoxyglucose uptake and glycolysis was either unchanged or only slightly enhanced in 48-h-fasted mice and in diabetic animals, compared with controls. Maximal insulin effects on glycogen synthesis and glycogen synthase activation were unaltered by fasting or diabetes. Basal glucose uptake and glycolysis were similar in all groups of mice. In conclusion, when soleus muscles from 48-h-fasted mice and from diabetic mice are compared with controls it can be observed that, (a) at low insulin concentrations insulin binding is increased and insulin effectiveness in stimulating glucose transport and metabolism is enhanced; (b) biological responses to maximally effective insulin concentrations are either unaltered or slightly increased; (c) basal rates of glucose transport and metabolism are essentially unaltered. These results indicate that in insulinopenic states soleus muscle is not insulin resistant in vitro but is hypersensitive to low concentrations of insulin, and normally responsive to maximally effective doses of the hormone.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrouny G. A. Differential patterns of glycogen metabolism in cardiac and skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 1969 Sep;217(3):686–693. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.3.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Weerasinghe L. C., Bassett J. M., Randle P. J. The pentose cycle and insulin release in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1260525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Gorden P., Roth J., Kahn C. R., De Meyts P. Fluctuations in the affinity and concentration of insulin receptors on circulating monocytes of obese patients: effects of starvation, refeeding, and dieting. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI108565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Hagg S. A., Goodman M. N., Ruderman N. B. Glucose metabolism in perfused skeletal muscle. Effects of starvation, diabetes, fatty acids, acetoacetate, insulin and exercise on glucose uptake and disposition. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 15;158(2):191–202. doi: 10.1042/bj1580191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Hagg S., Ruderman N. B. Glucose metabolism in perfused skeletal muscle. Interaction of insulin and exercise on glucose uptake. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):231–238. doi: 10.1042/bj1460231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. M., Exton J. H. A rapid method for the determination of glycogen content and radioactivity in small quantities of tissue or isolated hepatocytes. Anal Biochem. 1976 Mar;71(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuendet G. S., Loten E. G., Jeanrenaud B., Renold A. E. Decreased basal, noninsulin-stimulated glucose uptake and metabolism by skeletal soleus muscle isolated from obese-hyperglycemic (ob/ob) mice. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1078–1088. doi: 10.1172/JCI108559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B., Kaplan S. A. Increased insulin binding by hepatic plasma membranes from diabetic rats: normalization by insulin therapy. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):22–30. doi: 10.1172/JCI108618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Soman V., Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., Felig P. Insulin binding to monocytes and insulin action in human obesity, starvation, and refeeding. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):204–213. doi: 10.1172/JCI109108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Feldman J. M., Lebovitz H. E. Effect of fasting on insulin secretion and action in mice. Endocrinology. 1970 Feb;86(2):313–321. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P. Interactions polypeptide hormones with cell membrane specific receptors: studies with insulin and glucagon. Diabetologia. 1976 May;12(2):83–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00428972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. N., Berger M., Ruderman N. B. Glucose metabolism in rat skeletal muscle at rest. Effect of starvation, diabetes, ketone bodies and free fatty acids. Diabetes. 1974 Nov;23(11):881–888. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.11.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepp K. D. Studies on the mechanism of insulin action: basic concepts and clinical implications. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):177–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01219697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., CORI C. F. Studies of tissue permeability. VI. The penetration and phosphorylation of 2-deoxyglucose in the diaphram of diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:3070–3075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Akanuma Y., Iwamoto Y., Kosaka K. Effects of fasting and refeeding of insulin receptors and glucose metabolism in rat adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1977 May;100(5):1384–1390. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-5-1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Akanuma Y., Iwamoto Y., Kosaka K. Insulin binding and glucose metabolism in adipocytes of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E175–E182. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal R. L., Zinman S. M., Zebrowski E. J. The effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes and of insulin supplementation on glycogen metabolism in rat liver. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1680541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Olefsky J. M. Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on insulin binding, glucose transport, and intracellular glucose metabolism in isolated rat adipocytes. Diabetes. 1979 Feb;28(2):87–95. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.2.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEFEVRE P. G. Sugar transport in the red blood cell: structure-activity relationships in substrates and antagonists. Pharmacol Rev. 1961 Mar;13:39–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Freychet P. Studies of insulin insensitivity in soleus muscles of obese mice. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):1982–1993. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Jeanrenaud B., Freychet P. Insulin binding and effects in isolated soleus muscle of lean and obese mice. Am J Physiol. 1978 Apr;234(4):E348–E358. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.4.E348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels E. Z., Ruderman N. B., Goodman M. N., Lau D. Effect of acetoacetate on glucose metabolism in the soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscles of the rat. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 15;162(3):557–568. doi: 10.1042/bj1620557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. I., Stocks A. E. Insulin sensitivity and vascular disease in insulin-dependent diabetics. Br Med J. 1968 Apr 13;2(5597):81–82. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5597.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. B., Jr A dual role for insulin in the regulation of cardiac glycogen synthase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5389–5394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Effects of fasting on insulin binding, glucose transport, and glucose oxidation in isolated rat adipocytes: relationships between insulin receptors and insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1450–1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI108601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Kobayashi M. Ability of circulating insulin to chronically regulate the cellular glucose transport system. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):1917–1929. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J., Garland P. B., Hales C. N., Newsholme E. A., Denton R. M., Pogson C. I. Interactions of metabolism and the physiological role of insulin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1966;22:1–48. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9825-5.50004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle P. J., Newsholme E. A., Garland P. B. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscle. 8. Effects of fatty acids, ketone bodies and pyruvate, and of alloxan-diabetes and starvation, on the uptake and metabolic fate of glucose in rat heart and diaphragm muscles. Biochem J. 1964 Dec;93(3):652–665. doi: 10.1042/bj0930652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Sageman W. S., Swenson R. S. Development of insulin resistance in normal dogs following alloxan-induced insulin deficiency. Diabetologia. 1977 Sep;13(5):459–462. doi: 10.1007/BF01234496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Goodman M. N., Conover C. A., Berger M. Substrate utilization in perfused skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 1979 Jan;28 (Suppl 1):13–17. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.1.s13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Effects of insulin and NSILA on adipocytes of normal and diabetic rats: receptor binding, glucose transport and glucose metabolism. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):243–249. doi: 10.1007/BF01219707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman V., Felig P. Glucagon binding and adenylate cyclase activity in liver membranes from untreated and insulin-treated diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):552–560. doi: 10.1172/JCI108966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Thomas J. A., Schlender K. K., Larner J. A rapid filter paper assay for UDPglucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase, including an improved biosynthesis of UDP-14C-glucose. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa T., Krans H. M. Reduced glucose transport and increased binding of insulin in adipocytes from diabetic and fasted rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 1;538(3):563–570. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



