Abstract
Fructans and raffinose family oligosaccharides (RFOs) are the two most important classes of water-soluble carbohydrates in plants. Recent progress is summarized on their metabolism (and regulation) and on their functions in plants and in food (prebiotics, antioxidants). Interest has shifted from the classic inulin-type fructans to more complex fructans. Similarly, alternative RFOs were discovered next to the classic RFOs. Considerable progress has been made in the understanding of structure–function relationships among different kinds of plant fructan metabolizing enzymes. This helps to understand their evolution from (invertase) ancestors, and the evolution and role of so-called “defective invertases.” Both fructans and RFOs can act as reserve carbohydrates, membrane stabilizers and stress tolerance mediators. Fructan metabolism can also play a role in osmoregulation (e.g., flower opening) and source–sink relationships. Here, two novel emerging roles are highlighted. First, fructans and RFOs may contribute to overall cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis by specific ROS scavenging processes in the vicinity of organellar membranes (e.g., vacuole, chloroplasts). Second, it is hypothesized that small fructans and RFOs act as phloem-mobile signaling compounds under stress. It is speculated that such underlying antioxidant and oligosaccharide signaling mechanisms contribute to disease prevention in plants as well as in animals and in humans.
Keywords: antioxidant, fructan, immunity, oligosaccharide, raffinose, signaling, stress, sucrose
INTRODUCTION
Sucrose (Suc; Glcα1,2βFru) takes a central position in plant metabolism as the first free sugar formed during photosynthesis and the major transport compound to bring carbon skeletons from source to sink tissues (Koch, 2004). Suc is the substrate for the synthesis of different types of Suc-derived oligosaccharides (Keller and Pharr, 1996). Among those, fructans and raffinose family oligosaccharides (RFOs) are the most important two classes of water-soluble carbohydrates in the plant kingdom. Fructans are fructose (Fru)-based oligo- and polysaccharides, representing the major reserve carbohydrates in about 15% of flowering plant species (Hendry, 1993). Fructans can be linear or branched and their degree of polymerization (DP) ranges from three up to a few hundred, depending on the species, developmental stage and environmental conditions (Van den Ende et al., 2002a). Fructans are classified according to differences in glycosidic linkages [β(2,1), β(2,6) or both]. The best studied fructans are the linear inulin-type fructans (occurring in Asterales such as Jerusalem artichoke and chicory) consisting of β(2,1)-linked Fru units attached to the Suc starter unit. The trisaccharide 1-kestotriose (older nomenclature 1-kestose:Glcα1,2βFru1,2βFru) is the essential building block in this case. However, Fru-only versions of these fructans, lacking a terminal glucose (Glc), and termed inulo-n-oses, can also be found under some conditions (Van den Ende et al., 1996). The smallest representatives of these series are inulobiose (Fru1,2βFru) and inulotriose (Fru1,2βFru1,2βFru). The building block for the linear levan-type fructans (also termed phleins in plants) is 6-kestotriose (older nomenclature 6-kestose: Glcα1,2βFru6,2βFru) which is further elongated to polymers with β(2,6)-linkages. They typically occur in forage grasses such as Dactylis glomerata, Phleum pratense, and Poa secunda (Chatterton et al., 1993; Chatterton and Harrison, 1997; Tamura et al., 2009). Graminan-type fructans contain both β(2,1) and β(2,6) linkages. They occur in cereals such as wheat and barley (Van den Ende et al., 2003). Even more complex fructans, based on the 6G-kestotriose backbone (older nomenclature neokestose: Fru2,6Glcα1,2βFru), with further Fru elongations on both sides, occur for instance in oat, Asparagus, Agave, and in Lolium sp. (Pavis et al., 2001). These are termed neo-inulin [predominant β(2,1) linkages] and neo-levan-type [predominant β (2,6) linkages] fructans, respectively. The longstanding view that graminan- and levan-type fructans only occur in monocots has been overruled, since both types have been recently found in Pachysandra terminalis, an evergreen, frost-hardy basal eudicot species (Van den Ende et al., 2011a). Although some suggestions were made to link fructan structure to functionality in stress tolerance responses (Valluru and Van den Ende, 2008; Lasseur et al., 2011; Van den Ende et al., 2011a), these relationships are unclear and require further experimental verification. Fructans are believed to accumulate in vacuoles (Wiemken et al., 1986) but it was proposed that, under stress, tonoplast-derived vesicles may transport fructans from the vacuole to the apoplast (Livingston and Henson, 1998; Valluru et al., 2008).
The “classic” RFOs are soluble, non-reducing α(1,6) galactosyl (Gal) extensions of Suc. The trisaccharide raffinose (Raf; Galα1,6Glcα1,2βFru) is the smallest RFO and ubiquitous in the plant kingdom (Keller and Pharr, 1996). Further elongation with Gal residues leads to the DP4 stachyose (Sta; Galα1,6Galα1,6Glcα1,2βFru), verbascose (DP5), ajugose (DP6), etc. Classic RFOs with a DP up to 15 have been found after cold treatment in Ajuga reptans L. (Bachmann et al., 1994), a typical RFO accumulator belonging to the Lamiaceae. While Raf and Sta occur in all plant parts in genuine RFO accumulators, the higher homologous are usually restricted to the storage organs. Often Sta is the quantitatively dominating carbohydrate in such storage organs (Kandler and Hopf, 1984). Raf and Sta are also important transport compounds in the orders Lamiales, Cucurbitales, Cornales, and in one family of the Celastrales (Zimmermann and Ziegler, 1975; Haritatos et al., 1996; Hoffmann-Thoma et al., 1996; Turgeon et al., 2001). Recently, research has been devoted to so-called “alternative” RFOs in plants. These novel plant Gal oligosaccharides did not derive much attention in the past. Among these, the Sta derivative manninotriose (Galα1,6Galα1,6Glc) was found to be the predominant carbohydrate in cold-induced early spring red deadnettle (dos Santos et al., 2013), a unique feature since this compound was never observed before in any RFO accumulator (dos Santos et al., 2013). Intriguingly, Sta does not occur within the Caryophyllaceae. Instead, Raf is elongated to the DP4 lychnose (Galα1,6Glcα1,2βFru1,1Gal) and the DP5 stellariose ([6Galα1,6&Galα1,4]Glcα1,2βFru1,1Gal) in cold-treated Stellaria media (Vanhaecke et al., 2006, 2008, 2010).
METABOLISM AND ITS REGULATION
Sucrose is not only needed as a substrate for fructan biosynthetic enzymes (termed fructosyltransferases: FTs), organ-specific Suc thresholds trigger the expression of genes encoding FTs (Lu et al., 2002; Maleux and Van den Ende, 2007) and RFO biosynthesis genes (Nägele and Heyer, 2013). Similar to the induction of anthocyanins in Arabidopsis (a non-fructan accumulator), it is well-known that fructan synthesis is controlled by a Suc-specific pathway (Bolouri Moghaddam and Van den Ende, 2013a and references therein), which means that the same effects cannot be obtained by using a mixture of Glc and Fru. Calcium, protein kinases and phosphatases are also involved in this inductive process (Martínez-Noël et al., 2009, 2010). Recently, the transcription factor TaMYB13 was found to be an important player in the process leading to FT induction and fructan synthesis in wheat (Xue et al., 2011) but further research into this pathway is needed to fully understand where this transcription factor is situated in the pathway. Even less is known about the pathway leading to RFO synthesis. However, it seems that heat shock transcription factors (HSFs), C-repeat binding factor/drought response element binding factor 1 (CBF/DREB1) type transcription factors and WRKY type of transcription factors (Panikulangara et al., 2004; Ogawa et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2009). Recently, it was reported that target of rapamycin kinase complexes stimulate the pathway leading to RFO synthesis in Arabidopsis (Dobrenel et al., 2013 and references therein).
Inulin-type fructans are biosynthesized from Suc by two FTs. First, 1-kestotriose is produced by the activity of a sucrose:sucrose 1-fructosyl transferase (1-SST) which transfers a fructosyl residue from a donor to an acceptor Suc. Then, a fructan:fructan 1-fructosyl transferase (1-FFT) polymerizes 1-kestotriose into higher DP inulin-type fructans (Edelman and Jefford, 1968; Van Laere and Van den Ende, 2002). Sucrose:fructan 6-fructosyl transferases (6-SFTs) are able to introduce branching. They preferentially transfer a fructosyl group from Suc as a donor substrate to 1-kestotriose as acceptor substrate, producing 1&6-kestotetraose (also termed bifurcose), the smallest graminan-type of fructan with mixed-type of linkages. Bifurcose can be further elongated by 6-SFT and 1-FFT, leading to branched, higher DP graminan-type of fructans (Yoshida et al., 2007). However, some of these 6-SFT enzymes might use Suc and/or 6-kestotriose as preferential acceptors, producing levan-type fructans (Tamura et al., 2009). Such 6-SST/6-SFT is also involved in fructan synthesis in Pachysandra terminalis, although this particular enzyme also shows extensive hydrolytic activities as well (Van den Ende et al., 2011a; Lammens et al., 2012), and it can be considered as a “premature” FT [preliminary fructosyl transferase (pFT); see also below]. Finally, the enzyme fructan:fructan 6G-fructosyl transferase (6G-FFT) synthesizes 6G-kestotriose (neokestose) from 1-kestotriose as donor substrate and Suc as acceptor substrate. Further elongation by 1-FFT and 6-SFT leads to the formation of inulin- and levan neoseries, respectively (Vijn and Smeekens, 1999). Plants use an array of different fructan exohydrolases (FEHs) to degrade their fructans (Van den Ende et al., 2004; Yoshida et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2008), including 1-FEHs [preferentially attacking β(2,1) Fru linkages], 6-FEHs [preferentially attacking β (2,6) Fru linkages] and 6&1-FEHs (attacking both types of linkages). These enzymes remove, one by one, terminal Fru units from fructan chains. In contrast to invertases, FEHs cannot use Suc as a substrate. Instead, many FEHs are directly inhibited by Suc at the enzyme level (Verhaest et al., 2007), which represents one of the most important ways of regulation, next to the control of FEH gene expression at the transcriptional level (Van den Ende et al., 2002a). Remarkably, some of the apoplastic localized FEHs show an extreme specificity for single fructan kestotrioses, and these are termed kestotriose exohydrolases (Van den Ende et al., 2005), indicating that these forms might play a role in fructan signaling events (Van den Ende et al., 2004). It is known since long that FEHs also occur in non-fructan accumulators. However, they are probably better considered as “defective invertases” with possible (artificial) FEH side activities. The role of these proteins remained enigmatic for a very long period. However, a recent breakthrough paper (Le Roy et al., 2013) shows that Nin88, an apoplastic defective invertase from tobacco lacking FEH side activities, acts as indirect activator of active cell wall invertases (CWIs) which are crucial players in overall plant development, especially seed and fruit setting (Ruan et al., 2012). Although the exact underlying regulatory mechanisms require further research, data indicate that Nin88 interacts with cell walls in such a way that active CWIs bind to the cell wall in a more productive way (Le Roy et al., 2013). This fits nicely within the emerging concept that dead enzymes are very common in all kingdoms of life and that many of them fulfil crucial biological roles, as reviewed in a recent Science paper (Leslie, 2013).
The first committed step in RFO biosynthesis is the production of galactinol (Gol) from myo-inositol and UDP-Gal, a reaction catalyzed by galactinol synthase (GolS; Keller and Pharr, 1996). Next, Gol is used as a donor to deliver Gal to Suc, creating Raf. This is catalyzed by raffinose synthase (RafS). Stachyose synthase uses Gol as donor and Raf as acceptor to synthesize Sta (Keller and Pharr, 1996). GolS, RafS, and StaS are believed to localize in the cytosol, although the RFOs they produce might also enter the vacuole and the chloroplasts (Nägele and Heyer, 2013). In some species, higher DP RFOs are produced by the action of galactan:galactan galactosyl transferases (GGTs; Bachmann et al., 1994), using RFOs as donor and acceptor substrates. Although the exact origin of manninotriose type of RFO in red deadnettle is not known, it was suggested that this compound results from invertase (β-fructosidase) activity on Sta (dos Santos et al., 2013). Lychnose synthase and stellariose synthase are the enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of lychnose and stellariose (Vanhaecke et al., 2010). RFO catabolism involves the activity of acid and alkaline α-galactosidases which sequentially remove the terminal Gal residues (Keller and Pharr, 1996), while β-fructosidases may produce melibiose (Galα1,6Glc) from Raf and manninotriose from Sta (dos Santos et al., 2013). The so-called seed imbibition proteins resemble the enzymes involved in RFO catabolism, but only a few forms have been functionally characterized (Peters et al., 2010). Similar to defective invertases, it can be speculated that some of these forms may represent catalytically inactive forms, acting as regulatory proteins. Some forms may be involved in the degradation of RFOs acting as cellular signals (see below).
ENZYMES: STRUCTURE–FUNCTION RELATIONSHIPS
The overall classification into families of carbohydrate active enzymes1 is based on amino acid sequence similarities (Cantarel et al., 2009). This classification (i) reflects the structural features of these enzymes better than their sole substrate specificity, (ii) helps to reveal the evolutionary relationship between these enzymes, and (iii) provides a convenient framework to understand mechanistic properties (Henrissat and Romeu, 1995).
Plant acid invertases (β-fructosidases), including vacuolar invertases (VIs) and CWIs, split Suc into Fru and Glc by hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond. FEHs hydrolyze a terminal Fru from a fructan chain, while FTs elongate a Suc or fructan molecule with an extra Fru moiety. Taken together, all these enzymes transfer a Fru unit either to water (hydrolysis), to Suc or fructan (Van den Ende et al., 2009). They only differ in their specificity for donor and acceptor substrates. Accordingly, the 3D structure determinations of a FEH from chicory (Verhaest et al., 2005), a CWI from Arabidopsis (Lammens et al., 2008) and a pFT from Pachysandra terminalis (Lammens et al., 2012) showed that all these enzymes (or proteins: defective invertases) have a common fold. Hence, they are grouped together with microbial β-fructosidases (degrading both Suc and fructans) in the family 32 of glycoside hydrolases (GH32). Family GH32 is combined with family GH68 in the clan GH-J. GH68 harbors bacterial invertases, levansucrases and inulosucrases. All these proteins consist of an N-terminal five-bladed β-propeller domain (GH32 and GH68) followed by a C-terminal domain formed by two β-sheets (only in GH32). The active site is present within the β-propeller domain and characterized by the presence of three highly conserved acidic groups (present in the WMNDPNG, RDP, and EC motifs). The Asp from the first motif is acting as nucleophile, the Asp from the second motif is believed to be a transition state stabilizer and the Glu residue from the EC motif acts as acid/base catalyst playing a crucial role in the catalytic mechanism (Van den Ende et al., 2009). Some sugars can bind as substrates or as inhibitors in the active site of plant GH32 members (Verhaest et al., 2007) and this depends on subtle amino acid variations in the active site area. Recent pKa calculations suggest that most GH-J members show an acid–base catalyst that is not sufficiently protonated before ligand entrance, while the acid–base can be fully protonated when a substrate, but not an inhibitor, enters the catalytic pocket (Yuan et al., 2012). Moreover, the conserved arginine in the RDP motif, rather than a previously proposed Tyr in the FYASK motif, is proposed to play a key role to increase the pKa of the acid–base catalyst (Yuan et al., 2012).
Intriguingly, defective invertases are never affected in their catalytic triad, but rather in a neighboring “Asp/Lys” or “Asp/Arg couple” (present in a flexible loop in the proximity of the acid/base catalyst) and in some Trp residues (Le Roy et al., 2007, 2013). These residues are essential to stabilize the Glc part of Suc in the active site of GH32 Suc splitting enzymes (CWINV, VI, 1-SST, 6-SFT; Van den Ende et al., 2009), and they are absent in enzymes that use fructans as donor substrates (FEH, 1-FFT, 6G-FFT). This was confirmed by site directed mutagenesis experiments on invertase, defective invertase, FEH and 6G-FFT (Le Roy et al., 2007, 2008, 2013; Lasseur et al., 2009). However, the presence of an Asp/Lys or Asp/Arg is not sufficient; this couple needs to be in the right 3D configuration as well (Schroeven et al., 2009). The recent 3D structure of Pachysandra terminalis with its acceptor substrate 6-kestotriose strongly suggested that the couple (Asp/Gln in this case) plays a prominent role in acceptor substrate specificity as well (Lammens et al., 2012).
All RFO metabolizing enzymes discussed in the previous section, with the exception of GolS, belong to GH27 and GH36 in clan D. The acid α-galactosidases and GGTs are grouped into GH27, where some 3D structures have been determined, including the acid α-galactosidase from rice (Fujimoto et al., 2003). Their active sites are well-conserved and formed by residues in the loops at the ends of the β-strands in a (β/α)8 barrel. Two Asp residues are required for catalysis, which are positioned on opposite sides of the labile glycosidic bond (Fujimoto et al., 2003). RafS, StaS, and alkaline α-galactosidases belong to the related GH36, but no structural information is yet available on plant members within this family (Vanhaecke, 2010), although a few microbial structures became available (Fredslund et al., 2011; Merceron et al., 2012). To our knowledge, no in depth structure–function research has been performed toward donor and acceptor substrate specificities within plant members of GH27 and GH36. Clearly, such studies would be very informative as well. Such insights greatly contribute to rational enzyme design contributing to the production of tailor-made fructans and RFOs.
EVOLUTION
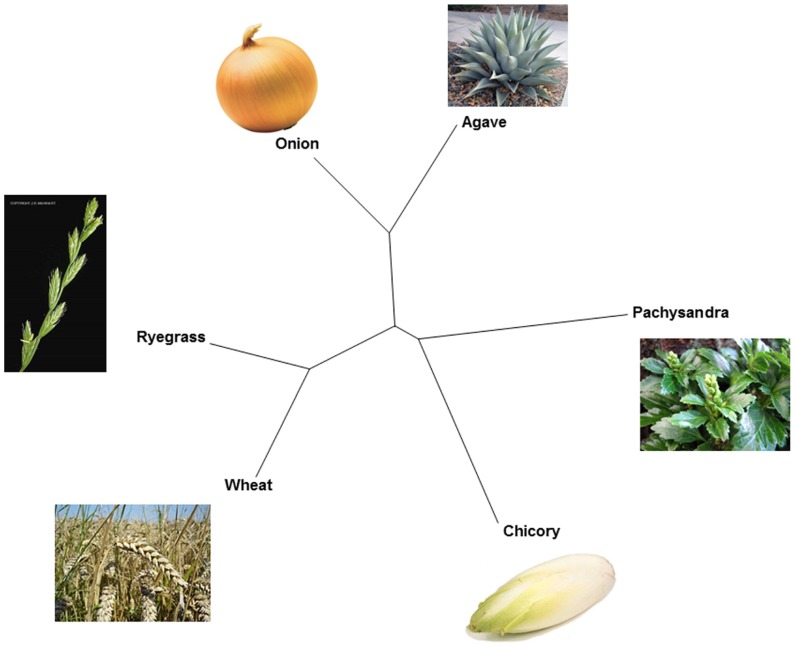
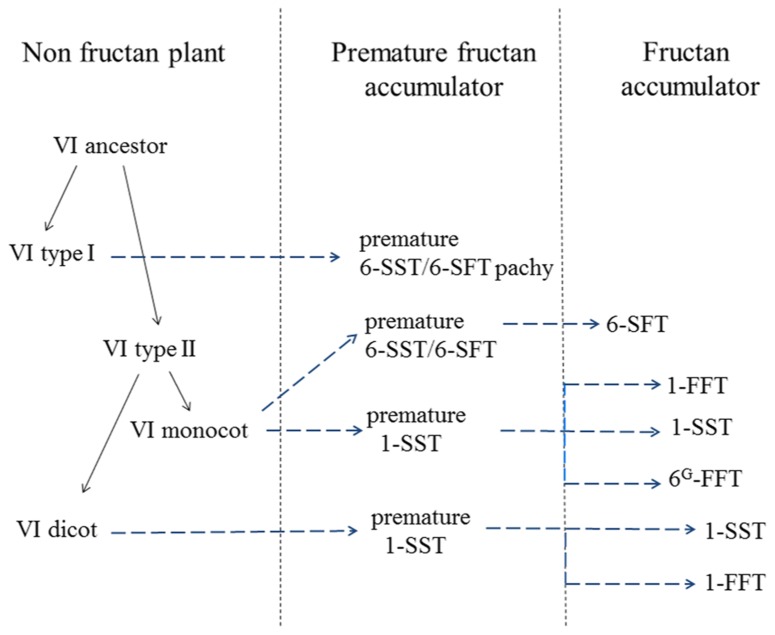
Within GH32, it became clear that plant FTs evolved from VIs (Wei and Chatterton, 2001; Altenbach et al., 2009), contributing to the observed diversity in fructan accumulators in the plant kingdom (Figure 1). Two types of VIs (I and II, Van den Ende et al., 2002b) can be discerned in plants and for a long time it was assumed that all plant FTs evolved from (different forms of) type II VIs. This occurred at least three times: (i) in the Asterales (inulin-type of fructans; e.g., chicory, (ii) in the Poales with further distinction between cool-season grasses (mainly levan and neokestose-derived fructans, e.g., ryegrass) and cereals (predominantly graminan-type fructans, e.g., wheat and barley) in the Poaceae and (iii) in the Asparagales further splitting into the Allioideae (e.g., onion) and Agavoideae (e.g., Agave) subfamilies that also mainly accumulate neokestose-based fructans (Figure 1). However, this view was changed by the unexpected discovery of both levan- and graminan-type fructans in the basal eudicot Pachysandra terminalis species, containing a pFT that, surprisingly, evolved from a type I VI (Figure 2) and not from a type II VI as observed for all other FTs (Figure 2). This further confirmed the polyphyletic origin of fructan biosynthesis (Altenbach et al., 2009; Van den Ende et al., 2011a) and suggests that the capacity for fructan biosynthesis arose at least four times during the plant diversification process (Figure 1). Such polyphyletic origin did not likely occur within GH27 and GH36, although more sequences should be generated to reach this conclusion (Vanhaecke, 2010). By combining alignments, 3D structure information and phylogenetic analyses (Schroeven et al., 2008; Altenbach et al., 2009; Lasseur et al., 2011; Lammens et al., 2012), the current view within GH32 is that an ancestral VI duplicated in two VI types (I and II, Figure 2) before the separation of monocots and dicots (Wei and Chatterton, 2001). Most probably, monocot and dicot type II VIs were than recruited to create preliminary 1-SSTs and 6-SFTs that later specialized into genuine 1-SSTs and 6-SFTs (Figure 2). Mutations in the “WMNDPNG” and “W(A/G)W” motifs are believed to play a key role in such processes (Schroeven et al., 2008, 2009; Altenbach et al., 2009). In evolutionary terms, it seems reasonable to assume that, in monocots as well as in dicots, 1-FFTs and 6G-FFTs evolved later, likely from (premature) 1-SST precursors (Figure 2). For instance, in wheat the identity between Ta1-SST and Ta1-FFT is much higher (84%) than between Ta1-SST and TaVI (67%) and between Ta1-FFT and TaVI (66%), strongly suggesting that Ta1-FFT evolved from Ta1-SST (Figure 2; Schroeven et al., 2009). A similar reasoning led to the hypothesis that the Lolium perenne Lp6G-FFT evolved from a (premature) Lp1-SST (Figure 2; Lasseur et al., 2009). In the same way, it can be speculated that the chicory Ci1-FFT evolved from a (premature) Ci1-SST (Figure 2; Schroeven et al., 2009). Within the basal eudicots, a type I VI developed into a pFT in Pachysandra terminalis (Figure 2) and this is considered as a rather “recent” evolutionary event (Van den Ende et al., 2011a). On the contrary, defective invertases and FEHs evolved from CWIs within GH32 (Le Roy et al., 2007, 2013). It can be speculated that the loss or alteration of the above-mentioned “couple” is an early evolutionary event that led to the formation of defective invertases with cell wall localization and a high iso-electric point (pI) for interaction with the cell wall. To further develop genuine FEHs in fructan plants, it can be further hypothesized that precursor defective invertases retrieved (i) a vacuolar targeting signal for sorting to the central vacuole, (ii) a low pI typical for vacuolar proteins, (iii) amino acid alterations that helped stabilization of higher DP fructans as donor substrates (Le Roy et al., 2008).
FIGURE 1.
Fructan diversity and polyphyletic origin of fructan biosynthesis in higher plants. An unrooted phylogenetic tree of fructan initiator enzymes (1-SSTs and a pFT) derived from six well-known fructan accumulators (chicory, wheat, ryegrass, onion, Agave, and Pachysandra) is drawn to illustrate the polyphyletic origin of fructan biosynthesis in higher plants.
FIGURE 2.
Model depicting the putative evolution of different higher plant fructosyl transferases. Likely, an ancestral VI duplicated in two VI types (I and II) in a non-fructan-accumulating plant, probably before the separation of monocots and dicots. Within the basal eudicots, a type I VI was recruited to create a preliminary FT (a 6-SST/6-SFT) in Pachysandra terminalis, a recent evolutionary event. During older evolutionary events, certain monocot and dicot type II VIs evolved into preliminary 1-SSTs and 6-SST/6-SFTs that later specialized into genuine, more specific 1-SSTs and 6-SFTs. Likely, 1-FFTs (dicots) and 6G-FFTs (monocots) evolved later, based on (preliminary) 1-SST precursors. See text for more details.
CLASSIC FUNCTIONS OF FRUCTANS AND RFOs
The most widely accepted function of fructans is their role as a storage carbohydrate. Dicots typically store inulin-type fructans in underground reserve organs (roots, tubers) (Van Laere and Van den Ende, 2002) while monocots typically store fructans on a shorter term basis in above ground parts of the plant (Pollock and Cairns, 1991; Slewinski, 2012). To the best of our knowledge, fructans are the only neutral type of polysaccharides that accumulate in plant vacuoles. Fructans can accumulate to 20% on fresh weight basis and even up to 70% on a dry weight basis in some organs (Wiemken et al., 1995). Trying to solubilize such levels in vitro invariably leads to fructan precipitation, suggesting that fructans in vivo should be organized in a special way to keep them in a (semi)-soluble condition in the vacuole (Van den Ende, 1996). It is clear that starch is the most widespread reserve carbohydrate in the plant kingdom. On the one hand, insoluble starch granules represent a very elegant way of storing huge amounts of carbon in a very small volume. On the other hand, excessive amounts of water-insoluble starch would be physically destructive to the chloroplast, its site of synthesis and storage in leaves. Therefore, fructans may have some advantages as compared to starch. One of the arguments in favor of using fructans could be the fact that starch biosynthesis dramatically decreases when the temperature drops below 10°C, whereas fructan biosynthesis is much less sensitive to low temperatures (Pollock, 1986). Another difference between starch and fructans might include the speed of its breakdown and carbon remobilization. While a large array of different enzymes (dikinases, phosphatases, starch hydrolases) are necessary to release small sugars from a starch granule (Stitt and Zeeman, 2012), water-soluble fructans are expected to be degraded much quicker by the action of FEHs as a single enzyme type. In grasses fructans are mainly stored in the leaf bases and used for regrowth after defoliation (Morvan-Bertrand et al., 2001). In cereals, fructans temporarily accumulate in stems and early in seed development (Van den Ende et al., 2003; Van den Ende et al., 2011b; Joudi et al., 2012) as well as in reproductive organs (Ji et al., 2010). Contrary to the situation in dicots, where growth and fructan accumulation are usually separated in time, monocots are able to combine these processes. It could be argued that the activity of Suc splitting enzymes 1-SST and 6-SFT contribute to control and maintain sink strength and carbohydrate supplies (Ji et al., 2010), but then the obvious question can be raised why this is not simply accomplished by increasing the activity of invertases? This indicates that the accumulation of fructans as such should somehow be beneficial (see also below), especially under stress.
Fructans can also play a role during flower opening. Fructan contents are high in closed petals of Campanula rapunculoides and Hemerocallis while no fructan is present anymore in petals of opened flowers (Bieleski, 1993; Vergauwen et al., 2000). FEHs quickly release massive amounts of Fru, lowering the osmotic potential and contributing to water inflow and flower opening. Fructans appear to have additional functions in drought, salt, and freezing tolerance of plants (Valluru and Van den Ende, 2008; Livingston et al., 2009). This is further supported by the fact that fructan-accumulating plants are especially abundant in temperate and arid climate zones with seasonal frost or drought periods, and are almost absent in tropical regions (Hendry, 1993). In fructan species, fructan accumulation can be induced under drought (De Roover et al., 2000) and cold (Livingston and Henson, 1998; Yoshida et al., 2007). More direct evidence comes from the observation that fructan-accumulating transgenic plants show enhanced stress tolerance (Pilon-Smits et al., 1995, 1999; Konstantinova et al., 2002; Li et al., 2007; Kawakami et al., 2008; Bie et al., 2012). Transgenic perennial ryegrass expressing wheat 1-SST or 6-SFT genes accumulate more fructans and acquired higher tolerance for freezing at the cellular level (Hisano et al., 2004). Therefore, it would be interesting to introduce FT genes in a number of food and biomass crops, to make them more tolerant to abiotic stresses.
Next to fructans, RFOs are also used as “storage carbohydrates,” arbitrarily defined as those which occur at more than 1% of the dry weight of a given tissue. So, despite the fact that most plants synthesize RFOs (at least Raf) to some extent at some stage of their development, only some plants accumulate large amounts of them (Kandler and Hopf, 1984; Keller and Pharr, 1996). These RFO accumulators store RFOs in concentrations up to 25–80% of their dry weight in specialized storage organs such as tubers (e.g., Stachys sieboldii), seeds (e.g., soybean, lentil, chickpea), or in photosynthesizing leaves (e.g., Ajuga reptans; Bachmann et al., 1994; Tahir et al., 2012). Similar to fructans, and in contrast to starch, RFOs are osmotically flexible as their DP may easily change and so the osmotic pressure. Species that use Suc as reserve carbohydrate (sugar beet, sugar cane) can only double the osmotic pressure upon hydrolysis (Gilbert et al., 1997). Finally, RFOs are phloem-mobile, and are readily available for carbon translocation when required. This feature is less clear for fructans, since phloem mobility has only been documented in a single fructan accumulator (see below). Typically, strong RFO and fructan accumulation do not occur together in a single plant species, suggesting that RFOs and fructans might fulfill similar (or partially overlapping) physiological functions. To better understand subtle differences in their physiological functions, it would be interesting to seek for plants that are capable to store high levels of both RFOs and fructans. Similar to the introduction of FTs in non-fructan accumulators, the overexpression of GolS in Arabidopsis thaliana resulted in plants with increased Raf levels and increased stress tolerance (Taji et al., 2002; Nishizawa et al., 2008). This suggests that the presence of increased levels of fructans or RFOs (in plants that normally contain very low or undetectable levels of such components) helps plants to survive adverse climatic conditions.
MEMBRANE STABILIZATION AND ANTIOXIDANT PROPERTIES
What could be the underlying mechanisms to explain such increased stress tolerances? Since membranes (and critical membrane proteins) are one of the primary targets of freezing and desiccation injury in cells (Oliver et al., 2000), membrane protective effects have been dedicated to fructans as well as to RFOs. In vitro experiments provided evidence for this ability, demonstrating that both fructans and RFOs contribute to enhanced membrane stability during freezing and cellular dehydration by deep insertion between the headgroups of lipids, both in mono- and bilayers (Demel et al., 1998; Vereyken et al., 2001; Hincha et al., 2002, 2003; Valluru and Van den Ende, 2008; Valluru et al., 2008). As such, they are also well-positioned to scavenge hydroxyl radicals (·OH) which might originate from tonoplast-associated Class III peroxidase activities (Passardi et al., 2004; Van den Ende and Valluru, 2009). Among the biologically relevant reactive oxygen species (ROS: H2O2 and ·OH), hydroxyl radicals are the most reactive and dangerous species (Keunen et al., 2013). The ·OH is known to react with almost all biomolecules at rates as those occurring in diffusion-controlled reactions (Hernandez-Marin and Martínez, 2012). As a consequence there are no enzymatic systems known to neutralize them in any living beings (Gechev et al., 2006). The in vitro ·OH scavenging activity of Raf and fructans has recently been confirmed (Stoyanova et al., 2011, Peshev et al., 2013) and compared to an array of phenolic compounds, well-known superior antioxidants (Peshev et al., 2013). Based on these findings, a hypothetical model has been proposed explaining how vacuolar fructans and phenolic compounds may act in a synergistic way to contribute to vacuolar antioxidant mechanisms in vivo, and to overall cellular homeostasis (Peshev et al., 2013). While fructans are obvious candidates for tonoplast stabilization and protection, RFOs (Raf in cold-induced Arabidopsis leaves) that are synthesized in the cytosol are candidates to protect the plasma membrane. However, this seems not to be the target membrane in Arabidopsis (Nägele and Heyer, 2013). Instead, it was demonstrated that Raf specifically acts to protect the photosystems located in the thylakoid membranes of plastids from damage during freeze thaw cycles (Knaupp et al., 2011). It was recently demonstrated that Raf can be imported in chloroplasts (Schneider and Keller, 2009) and therefore it could function as a cryoprotectant. As explained above for fructans or other osmolytes, it can be speculated that the ·OH scavenging capacity of Raf counteracts membrane and protein damage, contributing to thylakoid membrane stability and chloroplast integrity under stress (Doltchinkova et al., 2013). Likewise, targeting the synthesis of mannitol, another well-known ·OH scavenger (Stoyanova et al., 2011), to chloroplasts resulted in increased resistance to oxidative stress (Shen et al., 1997a, b), similar to what is observed in GolS overexpressors with their increased Raf levels (Nishizawa et al., 2008).
SIGNALING?
Nowadays, Glc, Fru, and Suc-specific signaling pathways have been elucidated in plants (Rolland et al., 2006; Cho and Yoo, 2011; Li et al., 2011), already suggesting that a signaling role for other types of small endogenous sugars should not be simply neglected. It seems that (a) Suc-specific signaling pathway(s) contributes to plant defense responses (Bolouri Moghaddam and Van den Ende, 2013a, b). Increased Suc levels typically lead to increased levels of fructans, RFOs and/or anthocyanins (Teng et al., 2005; Martínez-Noël et al., 2009, 2010; Nägele and Heyer, 2013), perhaps controlled by (a single) Suc-specific signaling pathway(s) (Bolouri Moghaddam and Van den Ende, 2013a).
Gol and Raf are now recognized as signaling molecules during biotic stress responses (Kim et al., 2008) and a similar role during abiotic stress responses has been suggested for RFOs (Valluru and Van den Ende, 2011; Eyles et al., 2013) and for fructans (Van den Ende et al., 2004). This led to the hypothesis that both RFOs and small fructans might act as endogenous, phloem-mobile stress signals. Indeed, small fructans have been detected in the phloem sap of Agave (Wang and Nobel, 1998) and it was reported that the fructan 6-kestotriose is phloem-mobile when it is produced by yeast invertase expressed in companion cells (Zuther et al., 2004). According to this view, the small fructans 1-kestotriose2 and its derivative inulobiose3 have been recently detected at very low levels in Arabidopsis, widely known as a strict non-fructan accumulator. What could be the origin of these small fructans in healthy Arabidopsis tissues? The most straightforward explanation is that these fructans are produced by the activities of VIs (AtVI1 and AtVI2), since Arabidopsis is lacking genuine FTs. Arabidopsis VIs were isolated before and found to contain considerable FT activities when tested at high Suc levels (De Coninck et al., 2005). Thus, next to Suc signaling, RFO and fructan signaling concepts should not be neglected and become the subject of intensive investigations. Possibly, such signaling events form the basis of the so-called “sugar-based resistance” or “sweet immunity” concept (Gomez-Ariza et al., 2007; Bolouri Moghaddam and Van den Ende, 2012, 2013b) in plants, but perhaps also in animals (see below).
UNIVERSAL IMMUNOSTIMULATORS?
Interest in fructans and RFOs increased during the last decade due to their health-promoting effects, selectively stimulating beneficial bacteria, acting as prebiotics (Shoaf et al., 2006; Kolida et al., 2007). These effects may be indirectly mediated through their fermentation products, but direct effects should not be neglected (Van den Ende et al., 2011b; Di Bartolomeo et al., 2013). Inulin-type fructans and fructo-oligosaccharides are the most studied and widely applied prebiotics isolated from chicory roots, and added to a variety of food products (Roberfroid et al., 2010). However, attention is shifting to longer DP and branched-type fructans (e.g., wheat graminans and Agave fructans) and RFOs as superior prebiotics (Urias-Silvas et al., 2008; Vanhaecke, 2010; Casiraghi et al., 2011; Jenkins et al., 2011), since these may provide a better “protection” (lowered colon cancer risk) over the whole length of the colon (Di Bartolomeo et al., 2013). Besides their prebiotic characteristics, fructans and RFOs are also emerging as important immunostimulators in animals and humans (Hoentjen et al., 2005; Seifert and Watzl, 2007; Vos, 2008; Delgado et al., 2012; Lee et al., 2012), as they likely do in plants (Bolouri Moghaddam and Van den Ende, 2012, 2013b). Taken all together, it can be speculated that these oligosaccharides may be involved in universal antioxidant and immunostimulatory mechanisms in plants, animals, humans, and perhaps in all eukaryotic organisms, but this requires further investigations. Needless to say, understanding the underlying mechanisms could greatly contribute to disease prevention strategies, both in plants and in mammals (Van den Ende et al., 2011b; Bolouri Moghaddam and Van den Ende, 2012, 2013b; Di Bartolomeo et al., 2013).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Wim Van den Ende is supported by grants from FWO Vlaanderen.
ABBREVIATIONS
- 1-FFT
fructan:fructan 1-fructosyl transferase
- 1-SST
sucrose:sucrose 1-fructosyl transferase
- 6G-FFT
fructan:fructan 6G-fructosyl transferase
- 6-SFT
sucrose:fructan 6-fructosyl transferase
- CWIs
cell wall invertases
- DP
degree of polymerization
- FEH
sucrose:fructan 6-fructosyl transferase
- Fru
fructose
- FTs
fructosyltransferases
- Gal
galactose
- GGTs
galactan:galactan galactosyl transferases
- GHXX
family XX of glycoside hydrolases
- Glc
glucose
- Gol
galactinol
- GolS
galactinol synthase
- pFT
preliminary fructosyl transferase
- pI
iso-electric point
- Raf
raffinose
- RafS
raffinose synthase
- RFOs
Raffinose Family Oligosaccharides
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- Sta
stachyose
- StaS
stachyose synthase
- Suc
sucrose
- VIs
vacuolar invertases
Footnotes
REFERENCES
- Altenbach D., Rudino-Pinera E., Olvera C., Boller T., Wiemken A., Ritsema T. (2009) An acceptor-substrate binding site determining glycosyl transfer emerges from mutant analysis of a plant vacuolar invertase and a fructosyltransferase. Plant Mol. Biol. 69 47–56 10.1007/s11103-008-9404-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Matile P., Keller F. (1994) Metabolism of the raffinose family oligosaccharides in leaves of Ajuga reptans L.Cold acclimation, translocation and sink to source transition – discovery of chain elongation enzyme . Plant Physiol. 105 1335–1345 10.1104/pp.105.4.1335 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieleski R. L. (1993) Fructan hydrolysis drives petal expansion in the ephemeral daylily flower. Plant Physiol. 103 213–219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bie X., Wang K., She M., Du L., Zhang S., Li J. et al. (2012) Combinational transformation of three wheat genes encoding fructan biosynthesis enzymes confers increased fructan content and tolerance to abiotic stresses in tobacco. Plant Cell Rep. 31 2229–2238 10.1007/s00299-012-1332-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolouri Moghaddam M., Van den Ende W. (2012) Sugars and plant innate immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 63 3989–3998 10.1093/jxb/ers129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolouri Moghaddam M., Van den Ende W. (2013a) Sugars, the clock and transition to flowering. Front. Plant Sci. 4:22. 10.3389/fpls.2013.00022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolouri Moghaddam M., Van den Ende W. (2013b) Sweet immunity in the plant circadian regulatory network. J. Exp. Bot. 64 1439–1449 10.1093/jxb/ert046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantarel B. L., Coutinho P. M., Rancurel C., Bernard T., Lombard V., Henrissat B. (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 37 D233–D238 10.1093/nar/gkn663 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casiraghi M. C., Zanchi R., Canzi E., Pagani M. A., Viaro T., Benini L. et al. (2011) Prebiotic potential and gastrointestinal effects of immature wheat grain (IWG) biscuits. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 99 795–805 10.1007/s10482-011-9553-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterton N. J., Harrison P. A. (1997) Fructan oligomers in Poa ampla. New Phytol. 136 3–10 10.1046/j.1469-8137.1997.00716.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterton N. J., Harrison P. A., Thornley W. R., Bennett J. H. (1993) Structures of fructan oligomers in orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.). J. Plant Physiol. 142 552–556 10.1016/S0176-1617(11)80397-4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cho Y. H., Yoo S. D. (2011) Signaling role of fructose mediated by FINS1/FBP in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plos Genetics 7: e1001263 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001263 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Coninck B., Le Roy K., Francis I., Clerens S., Vergauwen R., Halliday A., et al. (2005) Arabidopsis AtcwINV3 and 6 are not invertases but are fructan exohydrolases (FEHs) with different substrate specificities. Plant Cell Environ. 28 432–443 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01281.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Delgado G. T. C., Thome R., Gabriel D. L., Tamashiro W., Pastore G. M. (2012) Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius)-derived fructooligosaccharides improves the immune parameters in the mouse. Nutr. Res. 32 884–892 10.1016/j.nutres.2012.09.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Dorrepaal E., Ebskamp M. J. M., Smeekens J. C. M, de Kruijff B. (1998) Fructans interact strongly with model membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1375 36–42 10.1016/S0005-2736(98)00138-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Roover L., Vandenbranden K., Van Laere A., Van den Ende W. (2000) Drought induces fructan synthesis and 1-SST (sucrose:sucrose fructosyltransferase) in roots and leaves of Cichorium seedlings (Cichorium intybus L.). Planta 210 808–814 10.1007/s004250050683 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Bartolomeo F., Startek J., Van den Ende W. (2013) Prebiotics to fight diseases: reality or fiction? Phytother.Res. 10.1002/ptr.4901[Epubaheadofprint] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrenel T., Marchive C., Azzopardi M., Clément G., Moreau M., Sormani R., et al. (2013) Sugar metabolism and the plant target of rapamycin kinase: a sweet operaTOR? Front. Plant Sci. 4 : 93 10.3389/fpls.2013.00093 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doltchinkova V., Angelova P., Ivanova E., Djilianov D., Moyankova D. (2013) Surface electric charge of thylakoid membranes from genetically modified tobacco plants under freezing stress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 119 22–30 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2012.12.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos R., Vergauwen R., Pacolet P., Lescrinier E., Van den Ende W. (2013) Manninotriose is a major carbohydrate in red deadnettle (Lamium purpureum, Lamiaceae). Ann. Bot. 111 385–393 10.1093/aob/mcs288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman J., Jefford T. G. (1968) The mechanism of fructosan metabolism in higher plants as exemplified in Helianthus tuberosus. New Phytol. 67 517–531 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1968.tb05480.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Eyles A., Pinkard E. A., Noel W., Davies N. W., Corkrey R., Churchill K., et al. (2013) Whole-plant- versus leaf-level regulation of photosynthetic responses after partial defoliation in Eucalyptus globulus saplings. J.Exp. Bot. 64 1625–1636 10.1093/jxb/ert017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredslund F., Hachem M. A., Larsen R. J., Sørensen P. G., Coutinho P. M., Lo Leggio L., et al. (2011) Crystal structure of α-galactosidase from Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM: insight into tetramer formation and substrate binding. J. Mol. Biol. 412 466–480 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.07.057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto Z., Kaneko S., Momma M., Kobayashi H., Mizuno H. (2003) Crystal structure of rice α-galactosidase complexed with D-galactose. J. Biol. Chem. 278 20313–20318 10.1074/jbc.M302292200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gechev T. S., Van Breusegem F., Stone J. M., Denev I., Laloi C. (2006) Reactive oxygen species as signals that modulate plant stress responses and programmed cell death. Bioessays 28 1091–1101 10.1002/bies.20493 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert G. A., Wilson C., Madore M. A. (1997) Root-zone salinity alters raffinose oligosaccharide metabolism and transport in Coleus. Plant Physiol. 115 1267–1276 10.1104/pp.115.3.1267 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Ariza J., Campo S., Rufat M., Estopa M., Messeguer J., San Segundo B., et al. (2007) Sucrose-mediated priming of plant defense responses and broad-spectrum disease resistance by overexpression of the maize pathogenesis-related PRms protein in rice plants. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 20 832–842 10.1094/MPMI-20-7-0832 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritatos E., Keller F., Turgeon R. (1996) Raffinose oligosaccharide concentrations measured in individual cells and tissue types in Cucumis melo L. leaves: implications for phloem loading. Planta 198 614–622 10.1007/BF00262649 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry G. A. F. (1993) Evolutionary origins and natural functions of fructans - a climatological, biogeographic and mechanistic appraisal. New Phytol. 123 3–14 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1993.tb04525.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Henrissat B., Romeu A. (1995) Families, superfamilies and subfamilies of glycosyl hydrolases. Biochem. J. 311 350–351 10.1186/1471-2164-6-112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Marin E., Martínez A. (2012) Carbohydrates and their free radical scavenging capability: a theoretical study. J. Phys. Chem. B. 116 9668–9675 10.1021/jp304814r [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hincha D. K., Zuther E., Hellwege E. M., Heyer A. G. (2002) Specific effects of fructo- and gluco-oligosaccharides in the preservation of liposomes during drying. Glycobiology 12 103–110 10.1093/glycob/12.2.103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hincha D. K., Zuther E., Heyer A. G. (2003) The preservation of liposomes by raffinose family oligosaccharides during drying is mediated by effects on fusion and lipid phase transitions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1612 172–177 10.1016/S0005-2736(03)00116-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisano H., Kanazawa A., Kawakami A., Yoshida M., Shimamoto Y., Yamada T. (2004) Transgenic perennial ryegrass plants expressing wheat fructosyltransferase genes accumulate increased amounts of fructan and acquired increased tolerance on a cellular level to freezing. Plant Sci. 167 861–868 10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.05.037 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hoentjen F., Welling G. W., Harmsen H. J., Zhang X., Snart J., Tannock G. W., et al. (2005) Reduction of colitis by prebiotics in HLA-B27 transgenic rats is associated with microflora changes and immunomodulation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 11 977–985 10.1097/01.MIB.0000183421.02316.d5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann-Thoma G., van Bel A. J. E., Ehlers K. (1996) Ultrastructure of minor-vein phloem and assimilate transport in summer and winter leaves of the symplasmically loading evergreens Ajuga reptans L., Aucuba japonica Thunb., and Hedera helix L. Planta 212 231–242 10.1007/s004250000382 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins C. L. D., Lewis D., Bushell R., Belobrajdic D. P., Bird A. R. (2011) Chain length of cereal fructans isolated from wheat stem and barley grain modulates in vitro fermentation. J. Cereal Sci. 53 188–191 10.1016/j.jcs.2010.12.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ji X., Shiran B., Wan J., Lewis D. C., Jenkins C. L. D., Condon A. G., et al. (2010) Importance of pre-anthesis anther sink strength for maintenance of grain number during reproductive stage water stress in wheat. Plant Cell Environ. 33 926–942 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02130.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joudi M., Ahmadi A., Mohamadi V., Abbasi A., Vergauwen R., Mohamadi H., et al. (2012) Comparison of fructan dynamics in two wheat cultivars with different capacities of accumulation and remobilizationunder terminal drought stress. Physiol. Plant. 144 1–12 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2011.01517.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandler O., Hopf H. (1984) “Biosynthesis of oligosaccharides in vascular plants,” in Storage Carbohydrates in Vascular Plants, ed. D. H. Lewis (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) 115–132 [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami A., Sato Y., Yoshida M. (2008) Genetic engineering of rice capable of synthesizing fructans and enhancing chilling tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 59 803–814 10.1093/jxb/erm367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller F., Pharr D. M. (1996) “Metabolism of carbohydrates in sinks and sources: galactosyl-sucrose oligosaccharides,” in Photoassimilate Distribution in Plants and Crops: Source–Sink Relationships edsZamski E., Schaffer A. A.(New York: Marcel Dekker; ) 157–183 [Google Scholar]
- Keunen E., Peshev D., Vangronsveld J., Van den Ende W., Cuypers A. (2013) Plant sugars are crucial players in the oxidative challenge during abiotic stress: extending the traditional concept. Plant Cell Environ. 10.1111/pce.12061 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. S., Cho S. M., Kang E. Y., Im Y. J., Hwangbo H., Kim Y. C., et al. (2008) Galactinol is a signaling component of the induced systemic resistance caused by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 root colonization. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 21 1643–1653 10.1094/MPMI-21-12-1643 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaupp M., Mishra K. B., Nedbal L., Heyer A. G. (2011) Evidence for a role of raffinose in stabilizing photosystem II during freeze-thaw cycles. Planta 234 477–486 10.1007/s00425-011-1413-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. (2004) Sucrose metabolism: regulatory mechanisms and pivotal roles in sugar sensing and plant development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 7 235–246 10.1016/j.pbi.2004.03.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolida S., Meyer D., Gibson G. R. (2007) A double-blind placebo-controlled study to establish the bifidogenic dose of inulin in healthy humans. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 61 1189–1195 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinova T., Parvanova D., Atanassov A., Djilianov D. (2002) Freezing tolerant tobacco, transformed to accumulate osmoprotectants. Plant Sci. 163 157–164 10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00090-0 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lammens W., Le Roy K., Van Laere A., Rabijns A., Van den Ende W. (2008) Crystal structures of Arabidopsis thaliana cell-wall invertase mutants in complex with sucrose. J. Mol. Biol. 377 378–385 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.12.074 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammens W., Le Roy K., Yuan S., Vergauwen R., Rabijns A., Van Laere A., et al. (2012) Crystal structure of 6-SST/6-SFT from Pachysandra terminalis, a plant fructan biosynthesizing enzyme in complex with its acceptor substrate 6-kestose. Plant J. 70 205–219 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04858.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasseur B., Lothier J., Wiemken A., Van Laere A., Morvan-Bertrand A., Van den Ende W., et al. (2011) Towards a better understanding of the generation of fructan structure diversity in plants: molecular and functional characterization of a sucrose:fructan 6-fructosyltransferase (6-SFT) cDNA from perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne). J. Exp. Bot. 62 1871–1885 10.1093/jxb/erq388 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasseur B., Schroeven L., Lammens W., Le Roy K., Spangenberg G., Manduzio H., et al. (2009) Transforming a fructan:fructan 6G-fructosyltransferase from perennial ryegrass into a sucrose:sucrose 1-fructosyltransferase. Plant Physiol. 149 327–339 10.1104/pp.108.125559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. B., Miyake S., Umetsu R., Hayashi K., Chijimatsu T., Hayashi T. (2012) Anti-influenza A virus effects of fructan from Welsh onion (Allium fistulosum L.) . Food Chem. 134 2164–2168 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.04.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Roy K., Lammens W., Van Laere A., Van den Ende W. (2008) Influencing the binding configuration of sucrose in the active sites of chicory fructan 1-exohydrolase and sugar beet fructan 6-exohydrolase. New Phytol. 178 572–580 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02386.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Roy K., Lammens W., Verhaest M., De Coninck B., Rabijns A., Van Laere A., et al. (2007) Unraveling the difference between invertases and fructan exohydrolases: a single amino acid (Asp-239) substitution transforms Arabidopsis cell wall invertase1 into a fructan 1-exohydrolase. Plant Physiol. 145 616–625 10.1104/pp.107.105049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Roy K., Vergauwen R., Struyf T., Yuan S., Lammens W., Matrai J., et al. (2013) Understanding the role of defective invertases in plants: tobacco Nin88 fails to degrade sucrose. Plant Physiol. 161 1670–1681 10.1104/pp.112.209460 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie M. (2013) ‘Dead’ enzymes show signs of life. Science 340 25–27 10.1126/science.340.6128.25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H.-J., Yang A.-F., Zhang X.-C., Gao F., Zhang J.-R. (2007) Improving freezing tolerance of transgenic tobacco expressing-sucrose: sucrose 1-fructosyl-transferase gene from Lactuca sativa. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 89 37–48 10.1007/s11240-007-9213-8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li P., Wind J. J., Shi X. L., Zhang H. L., Hanson J., Smeekens S. C., et al. (2011) Fructose sensitivity is suppressed in Arabidopsis by the transcription factor ANAC089 lacking the membrane-bound domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108 3436–3441 10.1073/pnas.1018665108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. P., III, Henson C. A. (1998) Apoplastic sugars, fructans, fructan exohydrolase, and invertase in winter oat: responses to second-phase cold hardening. Plant Physiol. 116 403–408 10.1104/pp.116.1.403 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. P., III, Hincha D. K., Heyer A. G. (2009) Fructan and its relationship to abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66 2007–2023 10.1007/s00018-009-0002-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C., Koroleva O. A., Farrar J. F., Gallagher J., Pollock C. J., Tomos A. D. (2002) Rubisco small subunit, chlorophyll a/b-binding protein and sucrose:fructan-6-fructosyl transferase gene expression and sugar status in single barley leaf cells in situ. Cell type specificity and induction by light. Plant Physiol. 130 1335–1348 10.1104/pp.008979 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maleux K., Van den Ende W. (2007) Levans in excised leaves of Dactylis glomerata: effects of light, sugars, temperature and senescence. J. Plant Biol. 50 671–680 10.1007/BF03030612 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Noël G. A., Tognetti J. A., Salerno G. L., Pontis H. G. (2010) Sugar signaling of fructan metabolism: new insights on protein phosphatases in sucrose-fed wheat leaves. Plant Signal. Behav. 5 311–313 10.1007/s00425-009-1002-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Noël G. M. A., Tognetti J. A., Salerno G. L., Wiemken A., Pontis H. G. (2009) Protein phosphatase activity and sucrose–mediated induction of fructan synthesis in wheat. Planta 230 1071–1079 10.1007/s00425-009-1002-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merceron R., Foucault M., Haser R., Mattes R., Watzlawick H., Gouet P. (2012) The molecular mechanism of thermostable α-galactosidases AgaA and AgaB explained by X-ray crystallography and mutational studies. J. Biol. Chem. 287 39642–39652 10.1074/jbc.M112.394114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morvan-Bertrand A., Boucaud J., Le Saos J., Prud’homme M. P. (2001) Roles of the fructans from leaf sheaths and from the elongating leaf bases in the regrowth following defoliation of Lolium perenne L. Planta 213 109–120 10.1007/s004250000478 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nägele T., Heyer A. G. (2013) Approximating subcellular organisation of carbohydrate metabolism during cold acclimation in different natural accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 198 777–787 10.1111/nph.12201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa A., Yabuta Y., Shigeoka S. (2008) Galactinol and raffinose constitute a novel function to protect plants from oxidative damage. Plant Physiol. 147 1251–1263 10.1104/pp.108.122465 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa D., Yamaguchi K., Nishiuchi T. (2007) High-level over expression of the Arabidopsis HsfA2 gene confers not only increased thermo tolerance but also salt/osmotic stress tolerance and enhanced callus growth. J. Exp. Bot. 58 3373–3383 10.1093/jxb/erm184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver M. J., Tuba Z., Mishler B. D. (2000) The evolution of vegetative desiccation tolerance in land plants. Plant Ecol. 151 85–100 10.1023/A:1026550808557 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Panikulangara T. J., Eggers-Schumacher G., Wunderlich W., Stransky H., Schöffl F. (2004) Galactinol synthase1. A novel heat shock factor target gene responsible for heat-induced synthesis of raffinose family oligosaccharides in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 136 3148–3158 10.1104/pp.104.042606 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passardi F., Penel C., Dunand C. (2004) Performing the paradoxical: how plant peroxidases modify the cell wall. Trends Plant Sci. 9 534–540 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.09.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavis N., Chatterton N. J., Harrison P. A., Baumgartner S., Praznik W., Boucaud J., et al. (2001) Structure of fructans in roots and leaf tissues of Lolium perenne. New Phytol. 150 83–95 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00069.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Peshev D., Vergauwen R., Moglia A., Hideg E., Van den Ende W. (2013) Towards understanding vacuolar antioxidant mechanisms: a role for fructans? J.Exp. Bot. 64 1025–1038 10.1093/jxb/ers377 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S., Egert A., Stieger B., Keller F. (2010) Functional identification of Arabidopsis ATSIP2 (At3g57520) as an alkaline α-galactosidase with a substrate specificity for raffinose and an apparent sink-specific expression pattern. Plant Cell Physiol. 51 1815–1819 10.1093/pcp/pcq127 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilon-Smits E. A. H., Ebskamp M. J. M., Paul M. J., Jeuken M. J. W., Weisbeek P. J., Smeekens S. C. M. (1995) Improved performance of transgenic fructan-accumulating tobacco under drought stress. Plant Physiol. 107 125–130 10.1104/pp.107.1.125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilon-Smits E. A. H., Terry N., Sears T., van Dun K. (1999) Enhanced drought resistance in fructan-producing sugar beet. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 37 313–317 10.1016/S0981-9428(99)80030-8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock C. J. (1986) Fructans and the metabolism of sucrose in vascular plants. New Phytol. 104 1–24 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1986.tb00629.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock C. J., Cairns A. J. (1991) Fructan metabolism in grasses and cereals. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 42 77–101 10.1146/annurev.pp.42.060191.000453 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Roberfroid M., Gibson G. R., Hoyles L., McCartney A. L., Rastall R., Rowland I., et al. (2010) Prebiotic effects: metabolic and health benefits. Br. J. Nutr. 104 S1–S63 10.1017/S0007114510003363 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolland F., Baena-Gonzalez E., Sheen J. (2006) Sugar sensing and signaling in plants: conserved and novel mechanisms. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 57 675–709 10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105441 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan Y.-L., Patrick J. W., Bouzayen M., Osorio S., Fernie A. R. (2012) Molecular regulation of seed and fruit set. Trends Plant Sci. 17 656–665 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.06.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T., Keller F. (2009) Raffinose in chloroplasts is synthesized in the cytosol and transported across the chloroplast envelope. Plant Cell Physiol. 50 2174–2182 10.1093/pcp/pcp151 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeven L., Lammens W., Kawakami A., Yoshida M., Van Laere A., Van den Ende W. (2009) Creating S-type characteristics in the F-type enzyme fructan:fructan 1-fructosyl-transferase of Triticum aestivum L. J. Exp. Bot. 60 3687–3696 10.1093/jxb/erp208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeven L., Lammens W., Van Laere A., Van den Ende W. (2008) Transforming wheat vacuolar invertase into a high affinity sucrose: sucrose 1-fructosyltransferase. New Phytol. 180 822–831 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02603.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert S., Watzl B. (2007) Inulin and oligofructose: review of experimental data on immune modulation. J. Nutr. 137 2563S–2567S 10.1038/ejcn.2009.64 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B., Jensen R. C., Bohnert H. J. (1997a) Increased resistance to oxidative stress in transgenic plants by targeting mannitol biosynthesis to chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 113 1177–1183 10.1104/pp.113.4.1177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B., Jensen R. C., Bohnert H. J. (1997b) Mannitol protects against oxidation by hydroxyl radicals. Plant Physiol. 115 527–532 10.1104/pp.115.2.527 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoaf K., Mulvey G. L., Armstrong G. D., Hutkins R. W. (2006) Prebiotic galactooligosaccharides reduce adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to tissue culture cells. Infect. Immun. 74 6920–6928 10.1128/IAI.01030-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slewinski T. L. (2012) Non-structural carbohydrate partitioning in grass stems: a target to increase yield stability, stress tolerance, and biofuel production. J. Exp. Bot. 63 4647–4670 10.1093/jxb/ers124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Zeeman S. C. (2012) Starch turnover: pathways, regulation and role in growth. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 15 282–292 10.1016/j.pbi.2012.03.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoyanova S., Geuns J., Hideg E., Van den Ende W. (2011) The food additives inulin and stevioside counteract oxidative stress. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 62 207–214 10.3109/09637486.2010.523416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahir M., Baga M., Vandenberg A., Chibbar R. N. (2012) An assessment of raffinose family oligosaccharides and sucrose concentration in genus Lens. Crop Sci. 52 1713–1720 10.2135/cropsci2011.08.0447 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Taji T., Ohsumi C., Iuchi S., Seki M., Kasuga M., Kobayashi M., et al. (2002) Important roles of drought- and cold-inducible genes for galactinol synthase in stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 29 417–426 10.1046/j.0960-7412.2001.01227.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Kawakami A., Sanada Y., Tase K., Komatsu T., Yoshida M. (2009) Cloning and functional analysis of a fructosyltransferase cDNA for synthesis of highly polymerized levans in timothy (Phleum pratense L.) J. Exp. Bot. 60 893–905 10.1093/jxb/ern337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng S., Keurentjes J., Bentsink L., Koornneef M., Smeekens S. (2005) Sucrose-specific induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis requires the MYB75/PAP1 gene. Plant Physiol. 139 1840–1852 10.1104/pp.105.066688 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turgeon R., Medville R., Nixon K. C. (2001) The evolution of minor veinphloem and phloem loading. Am. J. Bot. 88 1331–1339 10.2307/3558441 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urias-Silvas J. E., Cani P. D., Delmee E., Neyrinck A., Lopez M. G., Delzenne N. M. (2008) Physiological effects of dietary fructans extracted from Agave tequilana Gto. and Dasylirion spp Br. J. Nutr. 99 254–261 10.1017/S0007114507795338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valluru R., Lammens W., Claupein W., Van den Ende W. (2008) Freezing tolerance by vesicle-mediated fructan transport. Trends Plant Sci. 13 409–414 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.05.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valluru R., Van den Ende W. (2008) Plant fructans in stress environments: emerging concepts and future prospects. J. Exp. Bot. 59 2905–2916 10.1093/jxb/ern164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valluru R., Van den Ende W. (2011) Myoinositol and beyond – emerging networks under stress. Plant Sci. 181 387–400 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.07.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W. (1996)Fructan Metabolism in Chicory Roots (Cichorium intybus L.). Ph.D. thesis KU Leuven; Belgium. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., Clerens S., Vergauwen R., Van Riet L., Van Laere A., Yoshida M., et al. (2003) Fructan 1-exohydrolases.β (2,1) trimmers during graminan biosynthesis in stems of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)? purification, characterization, mass mapping and cloning of two fructan 1-exohydrolase isoforms. Plant Physiol. 131 621–631 10.1104/pp.015305 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., Coopman M., Clerens S., Vergauwen R., Le Roy K., Lammens W., et al. (2011a) Unexpected presence of graminan- and levan-type fructans in the evergreen frost-hardy eudicot Pachysandra terminalis (Buxaceae). Purification, cloning and functional analysis of a 6-SST/6-SFT enzyme. Plant Physiol. 155 603–614 10.1104/pp.110.162222 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., Peshev D., De Gara L. (2011b) Disease prevention by natural antioxidants and prebiotics acting as ROS scavengers in the gastrointestinal tract. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 22 689–697 10.1016/j.tifs.2011.07.005 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., De Coninck B., Van Laere A. (2004) Plant fructan exohydrolases: a role in signaling and defense? Trends Plant Sci. 9 523–528 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.09.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., De Roover J., Van Laere A. (1996) In vitro synthesis of fructofuranosyl-onlyoligosaccharides from inulin and fructose by purified chicory root fructan:fructan fructosyl transferase. Physiol. Plant. 97 346–352 10.1034/j.1399-3054.1996.970219.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., Lammens W., Van Laere A., Schroeven L., Le Roy K. (2009) Donor and acceptor substrate selectivity among plant glycoside hydrolase family 32 enzymes. FEBS J. 276 5788–5798 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07316.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., Michiels A., De Roover J., Van Laere A. (2002a) Fructan biosynthetic and breakdown enzymes in dicots evolved from different invertases. Expression of fructan genes throughout chicory development. ScientificWorldJoural 2 1273–1287 10.1100/tsw.2002.288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., Michiels A., Le Roy K., Van Laere A. (2002b) Cloning of a vacuolar invertase from Belgian endive leaves (Cichorium intybus L.). Physiol. Plant. 115 504–512 10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1150404.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., Valluru R. (2009) Sucrose, sucrosyl oligosaccharides, and oxidative stress: scavenging and salvaging? J. Exp. Bot. 60 9–18 10.1093/jxb/ern297 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Ende W., Yoshida M., Clerens S., Vergauwen R., Kawakami A. (2005) Cloning, characterization and functional analysis of novel 6-kestose exohydrolases (6-KEHs) from wheat (Triticum aestivum). New Phytol. 166 917–932 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01394.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaecke M. (2010) Metabolism of Galactosyl-Oligosaccharides in Caryophyllaceae. Ph.D. thesis, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven; Belgium. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaecke M., Dyubankova N., Lescrinier E., Van den Ende W. (2010) Metabolism of galactosyl-oligosaccharides in Stellaria media - discovery of stellariose synthase, a novel type of galactosyltransferase. Phytochem. 71 1095–1103 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.04.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaecke M., Van den Ende W., Lescrinier E., Dyubankova N. (2008) Isolation and characterization of a pentasaccharide from Stellaria media. J. Nat. Prod. 71 1833–1836 10.1021/np800274k [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhaecke M., Van den Ende W., Van Laere A., Herdewijn P., Lescrinier E. (2006) Complete NMR characterization of lychnose from Stellaria media (L.) Vill. Carbohydr. Res. 341 2744–2750 10.1016/j.carres.2006.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Laere A., Van den Ende W. (2002) Inulin metabolism in dicots: chicory as a model system. Plant Cell Environ. 25 803–813 10.1046/j.1365-3040.2002.00865.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Vereyken I. J., Chupin V., Demel R. A., Smeekens S. C. M, De Kruijff B. (2001) Fructans insert between the headgroups of phospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomem. 1510 307–320 10.1016/S0005-2736(00)00363-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergauwen R., Van den Ende W., Van Laere A. (2000) The role of fructan in flowering of Campanula rapunculoides. J. Exp. Bot. 51 1261–1266 10.1093/jexbot/51.348.1261 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaest M., Lammens W., Le Roy K., De Ranter C., Van Laere A., Rabijns A., et al. (2007) Insights into the fine architecture of the active site of chicory fructan 1- exohydrolase: 1-kestose as substrate vs sucrose as inhibitor. New Phytol. 174 90–100 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.01988.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhaest M., Van den Ende W., Le Roy K., De Ranter C. A., Van Laere A., Rabijns A. (2005) X-Ray diffraction structure of a plant glycosyl hydrolase family 32 protein: fructan 1-exohydrolase IIa of Cichorium intybus. Plant J. 41 400–411 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02304.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijn I., Smeekens S. (1999) Fructan: more than a reserve carbohydrate? Plant Physiol. 120 351–359 10.1104/pp.120.2.351 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos A. J. (2008) Preclinical Studies on the Immune-Modulatory Effects of Dietary Oligosaccharides. Ph.D. thesis, Maastricht University; Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Nobel P. S. (1998) Phloem transport of fructans in the crassulacean acid metabolism species Agave deserti. Plant Physiol. 116 709–714 10.1104/pp.116.2.709 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Zhu Y., Wang L., Liu X., Liu Y., Phillips J., et al. (2009) A WRKY transcription factor participates in dehydration tolerance in Boea hygrometrica by binding to the W-box elements of the galactinol synthase (BhGolS1) promoter. Planta 230 1155–1166 10.1007/s00425-009-1014-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei J. Z., Chatterton N. J. (2001) Fructan biosynthesis and fructosyltransferase evolution: expression of the 6-SFT (sucrose: fructan 6-fructosyltransferase) gene in crested wheatgrass (Agropyron cristatum). J. Plant Physiol. 158 1203–1213 10.1078/0176-1617-00241 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemken A., Frehner M., Keller F., Wagner W. (1986) Fructan metabolism, enzymology and compartmentation. Curr. Top. Plant Biochem. Physiol. 5 17–37 10.1007/s00018-009-0002-x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemken A., Sprenger N., Boller T. (1995) “Fructan - an extension of sucrose by sucrose,” in Sucrose Metabolism, Biochemistry, Physiology, and Molecular Biology eds Pontis H.G, Salerno G. L., Echeverria E. S. (American Society of Plant Physiologists; Rockville: ) 179–189 10.1007/BF00200301 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Xue G. P., Kooiker M., Drenth J., McIntyre C. L. (2011) TaMYB13 is a transcriptional activator of fructosyltransferase genes involved in β-2,6-linked fructan synthesis in wheat. Plant J. 68 857–870 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04737.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Kawakami A., Van den Ende W. (2007) “Graminan metabolism in cereals: wheat as a model system. in recent advances,” in Fructooligosaccharides Research edsShiomi N., Benkeblia N., Onodera S. (Kerala,India: Research Signpost; ) 201–212 10.1104/pp.110.162222 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan S., Le Roy K., Venken T., Lammens W., Van den Ende W., De Maeyer M. (2012) pKa modulation of the acid/base catalyst within GH32 and GH68: a role in substrate/inhibitor specificity? PLoS One 7 : e37453 10.1371/journal.pone.0037453 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Dell B., Conocono E., Waters I., Setter T., Appels R. (2008) Water deficits in wheat: fructan exohydrolase (1-FEH) mRNA expression and relationship to soluble carbohydrate concentrations in two varieties. New Phytol. 181 843–850 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02713.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann M. H., Ziegler H. (1975) “List of sugars and sugar alcohols in sieve-tube exudates,” in Transport in Plants 1: Phloem Transport.Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology New Series, Vol. 1 edsZimmerman M. H., Milburn J. A.(New York: Springer; ) 480–503 10.1104/pp.108.134791 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zuther E., Kwart M., Willmitzer L., Heyer A. G. (2004) Expression of a yeast-derived invertase in companion cells results in long-distance transport of a trisaccharide in an apoplastic loader and influences sucrose transport. Planta 218 759–766 10.1007/s00425-003-1148-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]