Abstract
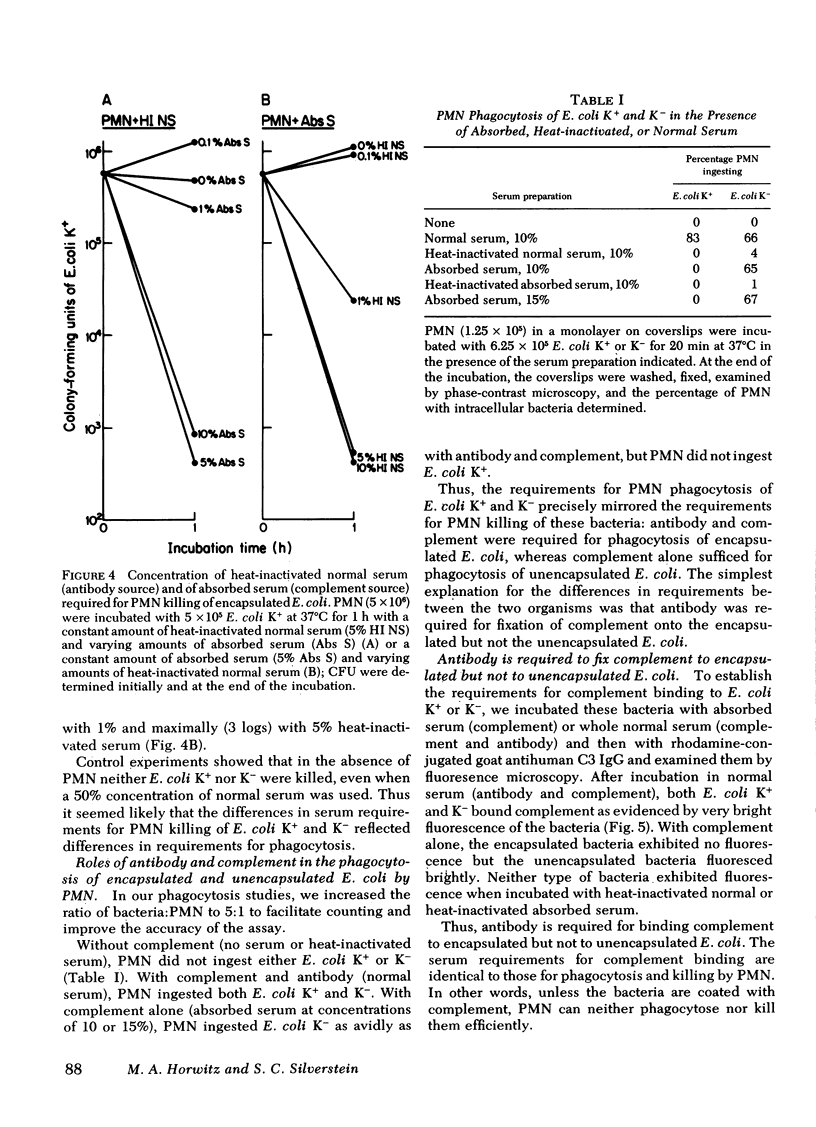
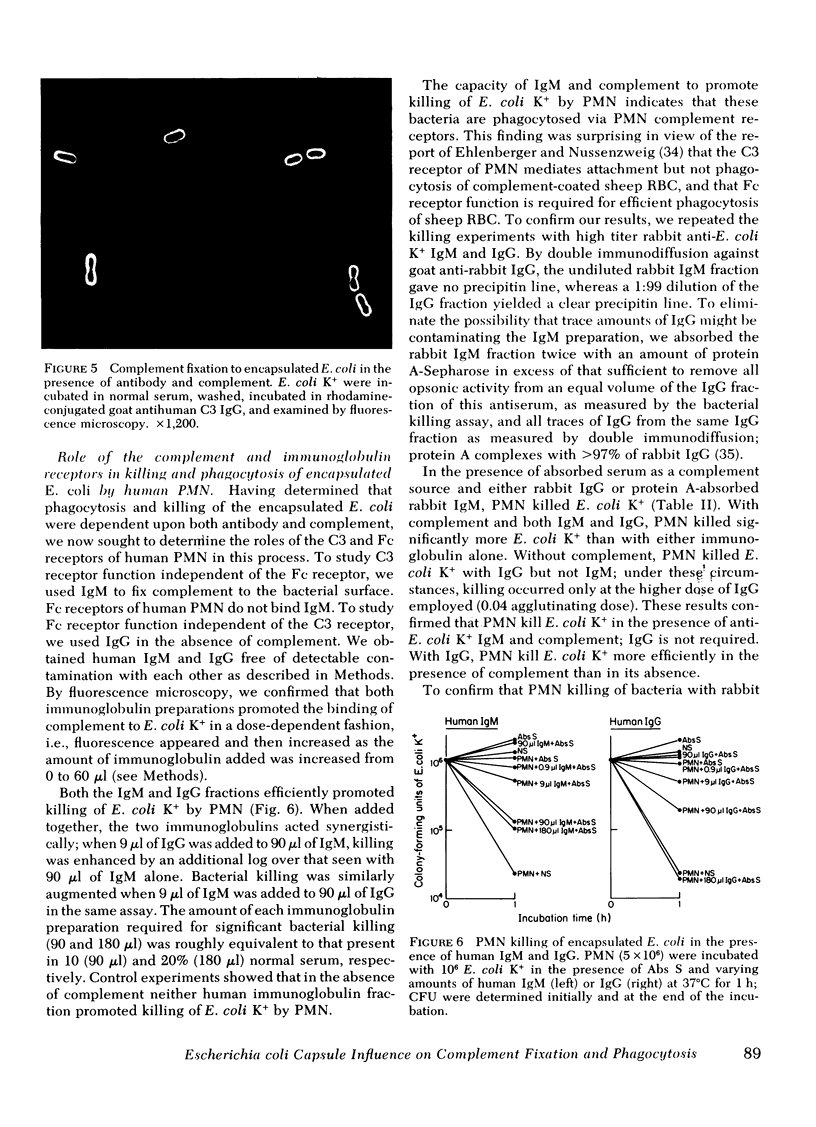
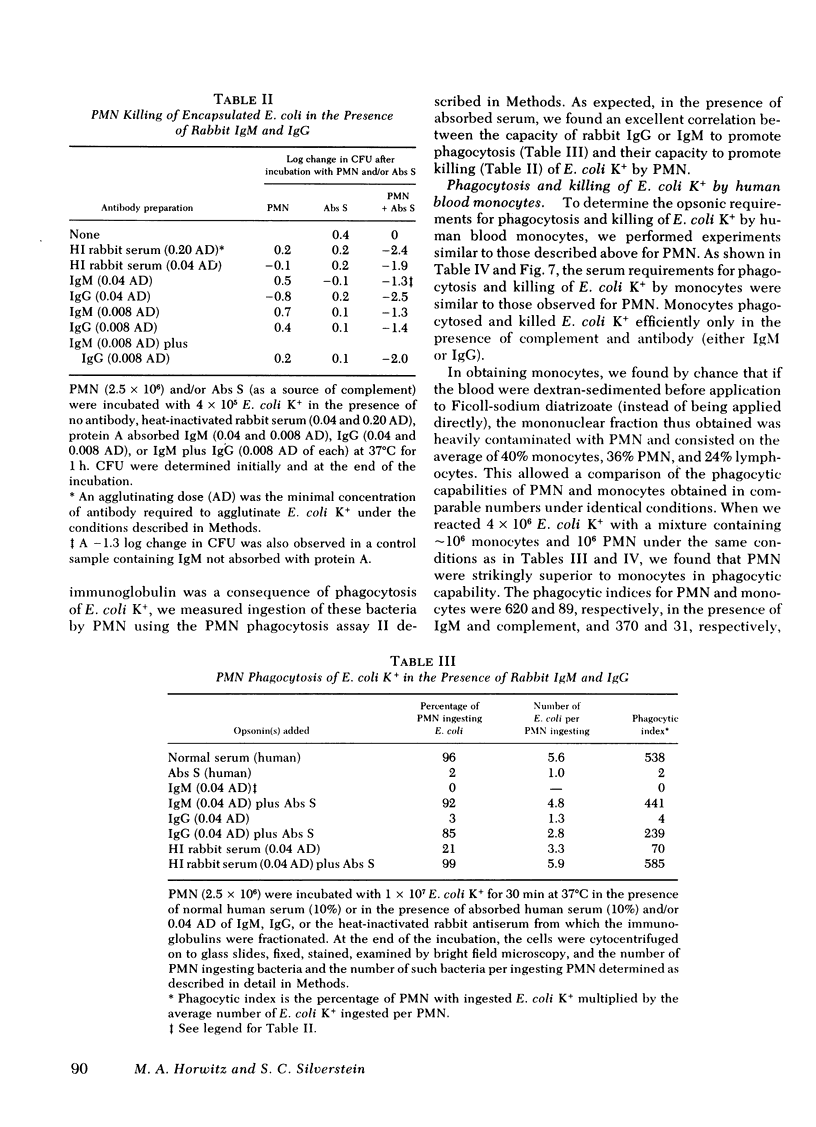
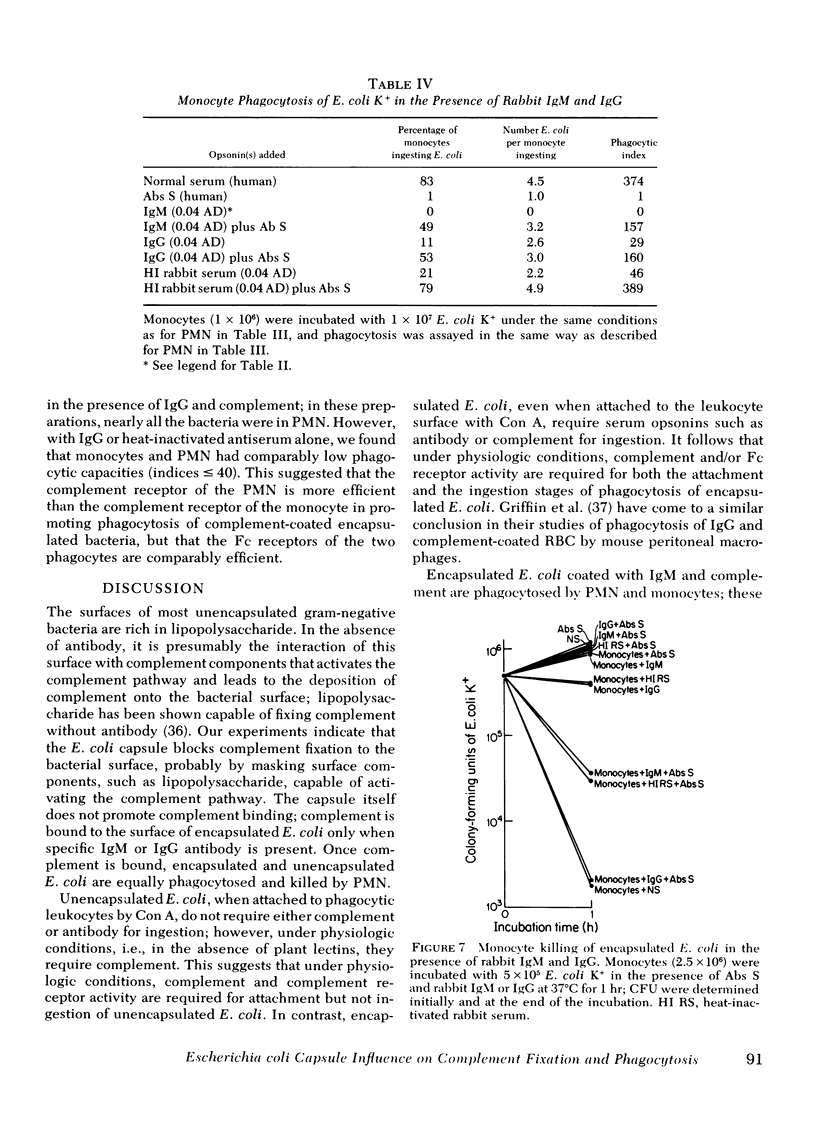
To define mechanisms by which polysaccharide capsules confer enhanced virulence on gram-negative bacteria, we examined the effect of the Escherichia coli capsule on complement fixation to the bacterial surface and on phagocytosis and killing of these bacteria by mouse macrophages and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) and monocytes. When E. coli were attached to mouse macrophages with concanavalin A, the macrophages readily phagocytosed unencapsulated but not encapsulated bacteria even in the presence of fresh mouse serum; macrophages did not phagocytose encapsulated E. coli unless antibacterial or anti-Con A antibody was added. Similarly, when these bacteria were attached to human PMN with Con A, PMN ingested unencapsulated but not encapsulated E. coli. PMN phagocytosed and killed encapsulated serum-resistant E. coli only in the presence of both complement and antibacterial antibody; PMN phagocytosed and killed unencapsulated E. coli of the same strain in the presence of complement alone. Fluorescence microscopy showed that antibody had to be present for encapsulated but not unencapsulated E. coli to fix complement to its surface. To examine the role of the complement receptors of human PMN and monocytes in phagocytosis and killing of encapsulated E. coli, we used human and rabbit antibacterial immunoglobulin (Ig)M to fix complement to the bacteria. PMN and monocytes phagocytosed and killed encapsulated E. coli in the presence of both IgM and complement, but not in the presence of either serum opsonin alone. In the presence of antibacterial IgG, PMN and monocytes required complement to effectively phagocytose and kill the E. coli. We conclude that (a) attachment by itself results in ingestion of unencapsulated but not encapsulated E. coli; (b) under physiologic conditions, E. coli are not phagocytosed or killed the absence of antibody, the E. coli capsule blocks complement fixation to the bacterial surface probably by masking surface components, such as lipopolysaccharide, capable of activating the complement pathway; (d) the E. coli capsule imposes a requirement for specific antibacterial antibody for complement fixation; and (e) the complement receptor of human PMN and monocytes mediates phagocytoses of complement-coated encapsulated bacteria and is the primary mediator of phagocytosis and killing of these bacteria.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy Y. M., Fehmel F., Frank N., Stirm S. Escherichia coli capsule bacteriophages. IV. Primary structure of the bacteriophage 29 receptor, the E. coli serotype 29 capsular polysaccharide. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):581–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.581-590.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P. The demonstration of bacterial capsules and slime. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;63(4):673–685. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlenberger A. G., Nussenzweig V. The role of membrane receptors for C3b and C3d in phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):357–371. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Andersen B. R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Opsonic activity in human serum chelated with ethylene glycoltetra-acetic acid. Immunology. 1974 Jun;26(6):1251–1256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Griffin J. A., Leider J. E., Silverstein S. C. Studies on the mechanism of phagocytosis. I. Requirements for circumferential attachment of particle-bound ligands to specific receptors on the macrophage plasma membrane. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1263–1282. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Glynn A. A. The virulence for mice of strains of Escherichia coli related to the effects of K antigens on their resistance to phagocytosis and killing by complement. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):767–777. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E. Human heat labile opsonins: evidence for their mediation via the alternate pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):26–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B., Hanson L. A., Jodal U., Lidin-Janson G., Robbins J. B. Frequency of E. coli K antigens in urinary-tract infections in children. Lancet. 1977 Mar 26;1(8013):663–666. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B., Holmgren J., Hanson L. A. The protective effect against E. coli of O and K antibodies of different immunoglobulin classes. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(1):27–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb03732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B. Immunology of Escherichia coli: K antigen and its relation to urinary-tract infection. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jun;127(6):670–677. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.6.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B., Olling S. Experimental hematogenous pyelonephritis due to Escherichia coli in rabbits: the antibody response and its protective capacity. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):41–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H. Bactericidal activity of normal serum against bacterial cultures. II. Activity against Eschericha coli strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Mar;103:632–636. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabeck C. E., Orskov F., Orskov I. Escherichia coli serotypes and renal involvement in urinary-tract infection. Lancet. 1971 Jun 26;1(7713):1312–1314. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91884-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Carling P. C., Bruins S., Greely A. The relation of K-antigen to virulence of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jan;131(1):6–10. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michl J., Ohlbaum D. J., Silverstein S. C. 2-Deoxyglucose selectively inhibits Fc and complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Description of the inhibitory effect. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1465–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Kline L. F. Activation of the classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platts-Mills T. A., Ishizaka K. Activation of the alternate pathway of human complements by rabbit cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):348–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P., Jann B., Jann K. The O9 antigen of Escherichia coli. Structure of the polysaccharide chain. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):53–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repine J. E., Clawson C. C., Friend P. S. Influence of a deficiency of the second component of complement on the bactericidal activity of neutrophils in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):802–809. doi: 10.1172/JCI108702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins: cell-agglutinating and sugar-specific proteins. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):949–959. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G., Michael A. F. Activation of complement by cell surface components of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):388–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.388-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Cryptic peptidoglycan and the antiphagocytic effect of the Staphylococcus aureus capsule: model for the antiphagocytic effect of bacterial cell surface polymers. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):502–508. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.502-508.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein J. A., Tomasz A. Activation of the alternative pathway by pneumococcal cell walls. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):451–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg G., DeWitt C. W. Mouse virulence of K(L) antigen-containing strains of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):730–737. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.730-737.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]