Abstract
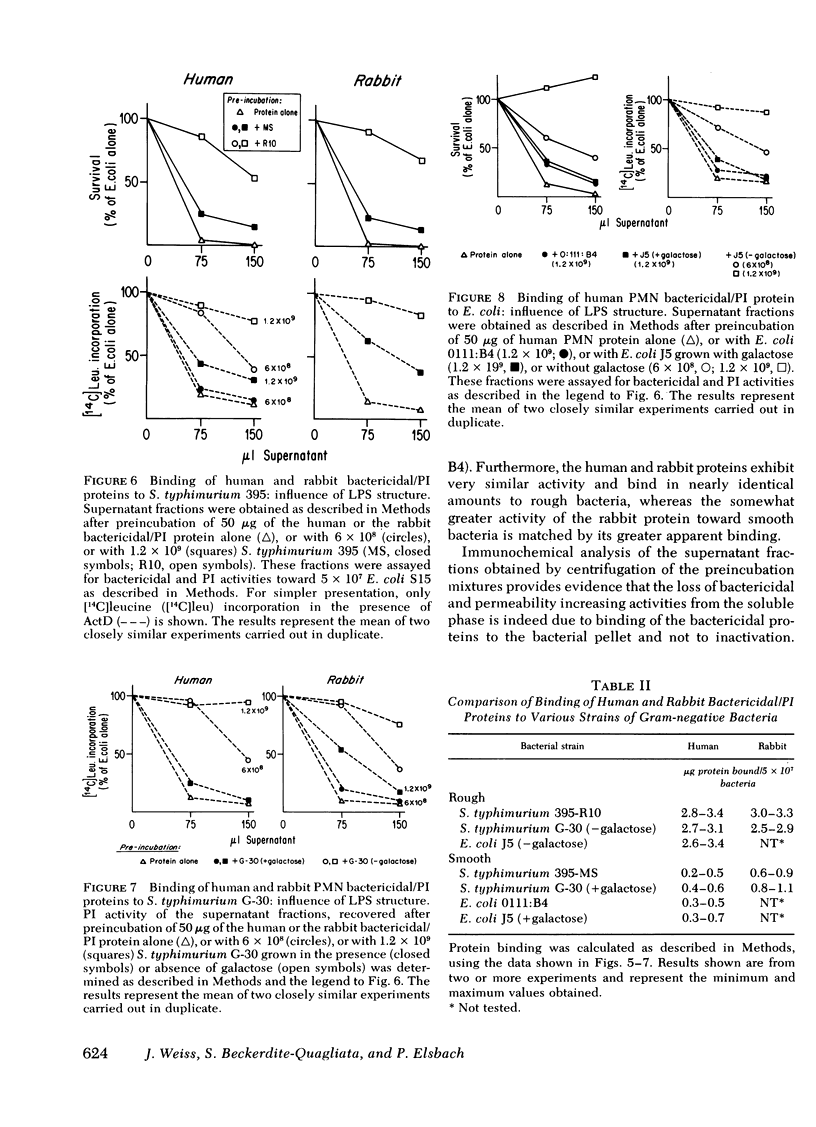
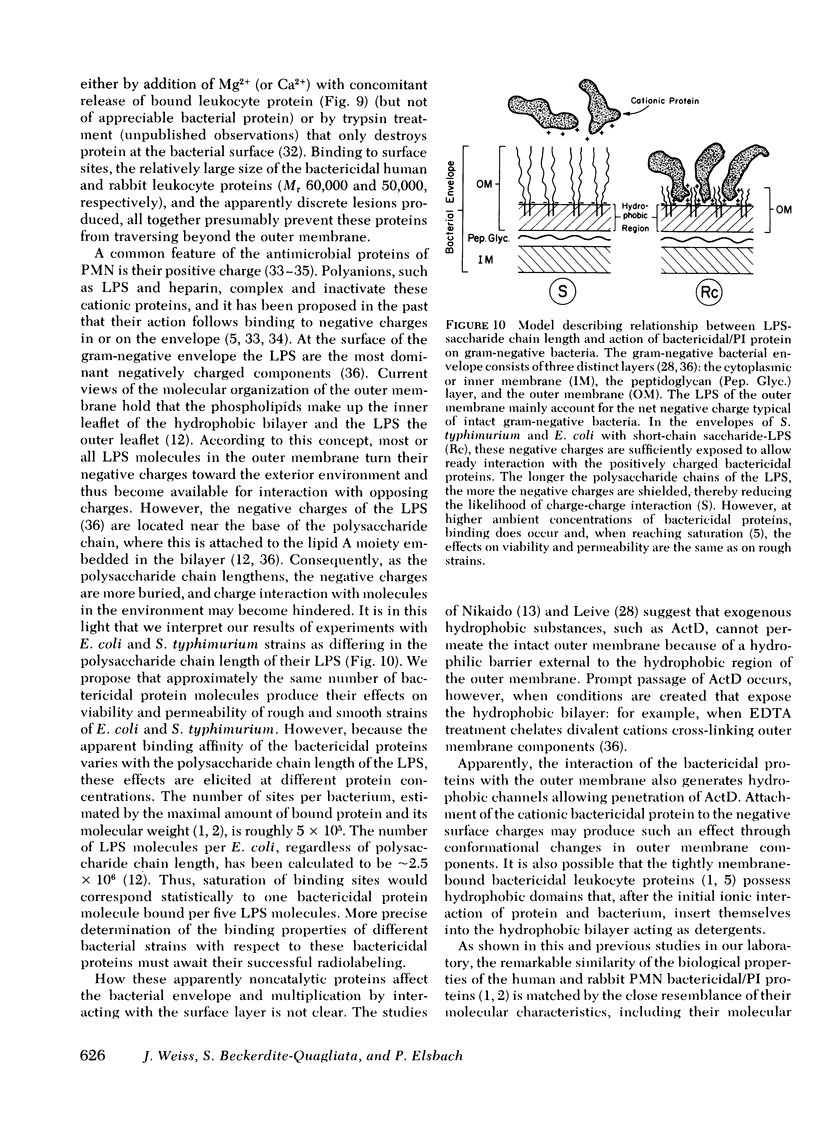
The sensitivity or resistance of gram-negative bacteria to antibacterial systems appears to be related to the length of the saccharide chain of the bacterial envelope lipopolysaccharides (LPS). To explore this relationship further, we made use of two bactericidal, membrane-active cationic proteins, recently purified to near homogeneity, one from human and one from rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN). We have studied the effects of these two closely similar proteins on strains of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli, each separate strain differing in the saccharide chain length of its outer membrane LPS. Binding of these proteins to the bacterial outer membrane is required for killing, and is accompanied by an almost immediate increase in outer membrane permeability to normally impermeant actinomycin D. Sensitivity to the bactericidal and permeability-increasing activities of the human and rabbit proteins increases with decreasing LPS-saccharide chain length (chemotype: [S < Ra < Rb3 < Rc < Rd1]). S. typhimurium G-30 and E. coli J5, mutant strains lacking UDP-galactose-4-epimerase, synthesize incomplete LPS (chemotype Rc) when grown without galactose, and are then as sensitive to both PMN proteins as the S. typhimurium strains 395 R10 (Rd1) and R5 (Rb3). However, when these mutants are grown with galactose, they synthesize complete LPS (chemotype S) and exhibit nearly the same relative insensitivity as the smooth strains S. typhimurium 395 MS and E. coli 0111:B4.
The differences among strains in sensitivity to the effects of the proteins on bacterial viability and permeability correspond to differences in bacterial binding of these PMN proteins. Thus, at protein concentrations that produce maximal antibacterial activity toward the rough bacteria, but little or no activity toward the smooth strains, rough bacteria bind from 3- to 10-fold more protein (S. typhimurium 395 R10; S. typhimurium G-30, and E. coli J5 [grown without galactose]) than do the smooth bacteria (S. typhimurium 395 MS; E. coli 0111:B4; S. typhimurium G-30 and E. coli J5 [grown with galactose]). These findings suggest that bacterial sensitivity or resistance to these purified bactericidal PMN proteins is determined by the binding properties of the outer membrane, which in turn depends upon the LPS-saccharide chain length.
Full text
PDF

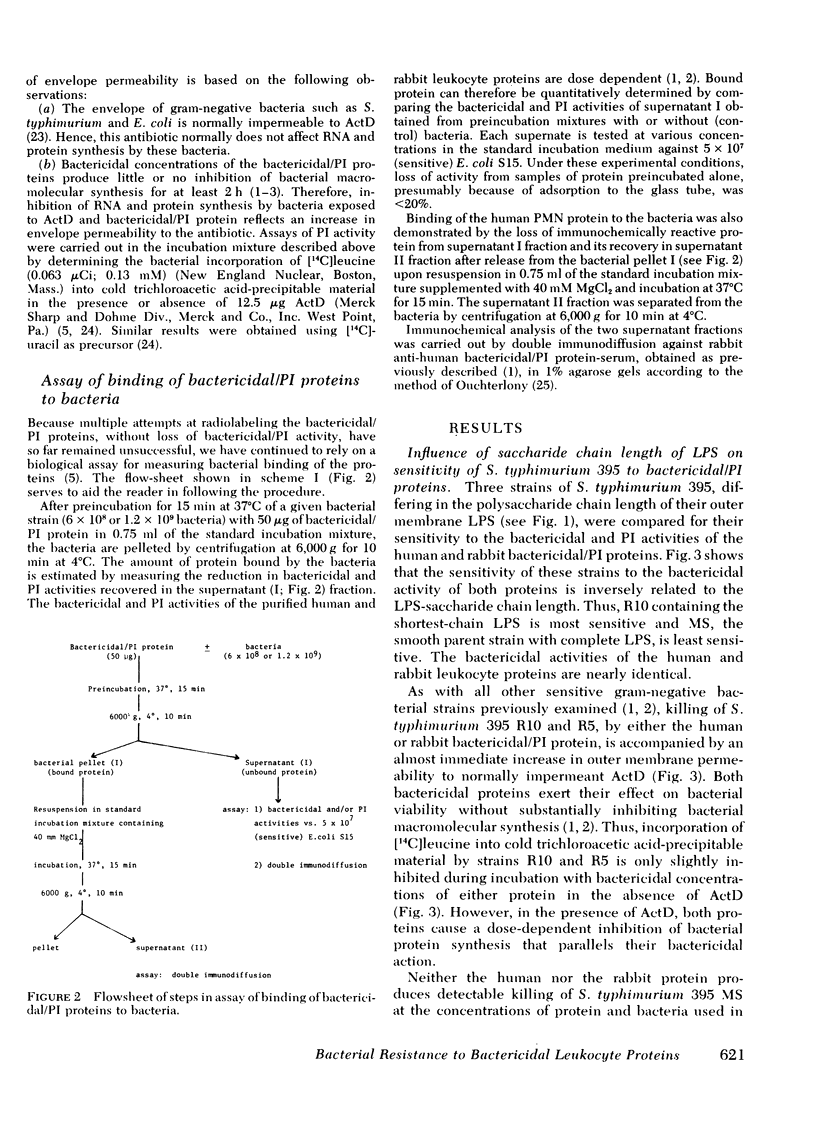
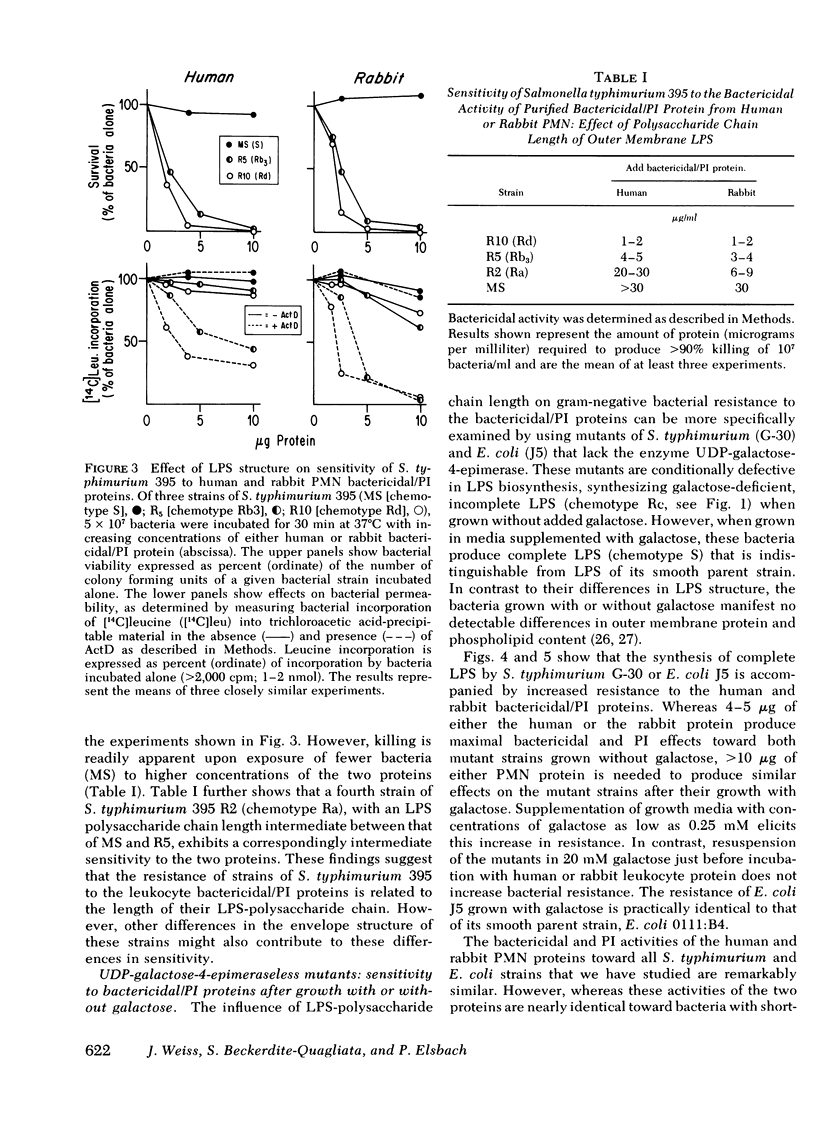
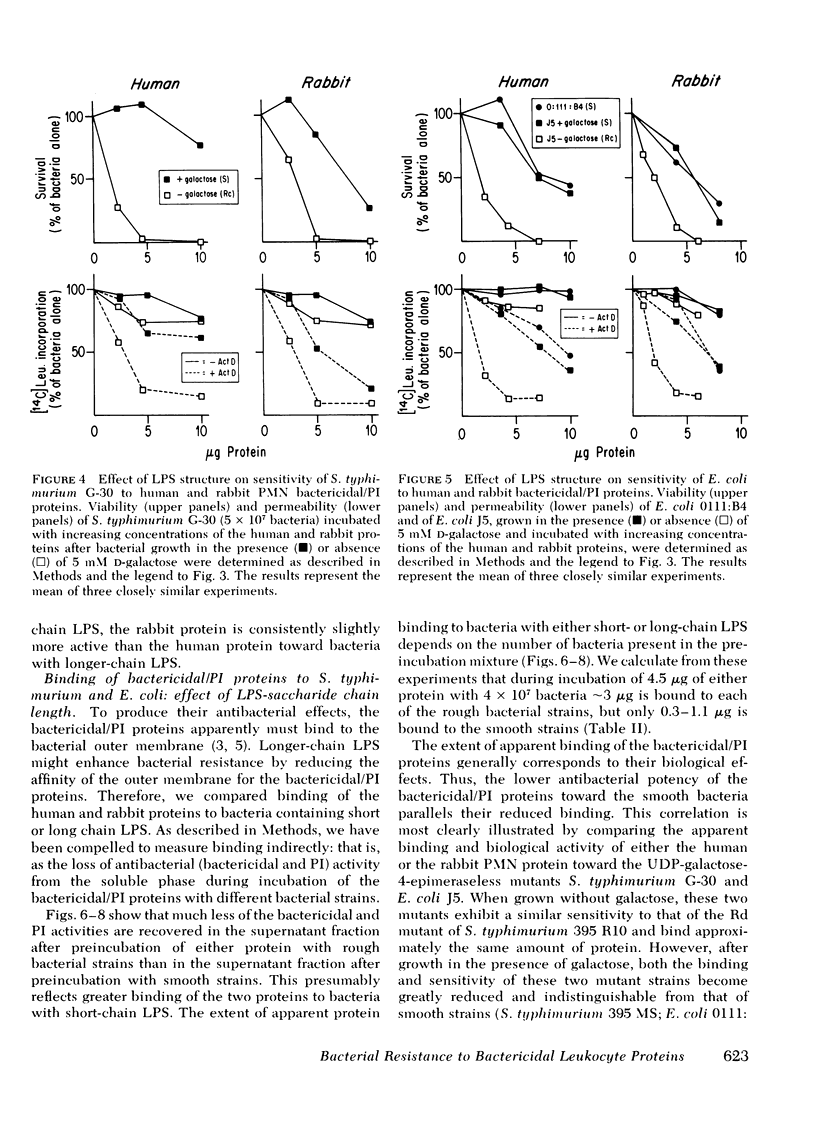



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckerdite S., Mooney C., Weiss J., Franson R., Elsbach P. Early and discrete changes in permeability of Escherichia coli and certain other gram-negative bacteria during killing by granulocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):396–409. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M., Mavis R. D., Osborn M. J., Vagelos P. R. Enzymes of phospholipid metabolism: localization in the cytoplasmic and outer membrane of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):628–635. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. K., Söderström T. O., Gillman C. F., van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. V. Contact angles and phagocytosis of rough and smooth strains of Salmonella typhimurium, and the influence of specific antiserum. Immunol Commun. 1975;4(5):429–442. doi: 10.3109/08820137509057331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBEIN A. D., HEATH E. C. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF CELL WALL LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. THE BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF A URIDINE DIPHOSPHATE GALACTOSE 4-EPIMERASELESS MUTANT. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1919–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J., Franson R. C., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Schneider A., Harris L. Separation and purification of a potent bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and a closely associated phospholipase A2 from rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Observations on their relationship. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11000–11009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg D., Friedberg I., Shilo M. Interaction of Gram-Negative Bacteria with the Lysosomal Fraction of Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes II. Changes in the Cell Envelope of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):311–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.311-318.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G. Further studies on preparation and properties of phagocytin. J Exp Med. 1960 Mar 1;111:323–337. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo L., Johansson G. The tendency of smooth and rough Salmonella typhimurium bacteria and lipopolysaccharide to hydrophobic and ionic interaction, as studied in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Jun;85(3):212–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Camitta B. M., Heath E. C. Cell wall composition and virulence in Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrzakowski M. C., Cooney M. H., Martin L. E., Spitznagel J. K. Bactericidal activity of fractionated granule contents from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):587–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.587-591.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Transmembrane diffusion of some hydrophobic substances. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):118–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J., ROSEN S. M., ROTHFIELD L., HORECKER B. L. Biosynthesis of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. I. Enzymatic incorporation of galactose in a mutant strain of Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Oct 15;48:1831–1838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.10.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odeberg H., Olsson I. Antibacterial activity of cationic proteins from human granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1118–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds B. L., Pruul H. Protective role of smooth lipopolysaccharide in the serum bactericidal reaction. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):764–771. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.764-771.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON E. J., VANPRAAG D. INHIBITION OF RNA SYNTHESIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI BY LEVORPHANOL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:877–883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., MacAlister T., Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J. Permeability of lipopolysaccharide-deficient (rough) mutants of Salmonella typhimurium to antibiotics, lysozyme, and other agents. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Aug;20(8):1135–1145. doi: 10.1139/m74-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stendahl O., Edebo L. Phagocytosis of mutants of Salmonella typhimurium by rabbit polymorphonuclear cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss C. J., Gillman C. F. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Contact angles and phagocytosis of non-opsonized bacteria. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Sep;12(3):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos M. M., op den Kamp J. A., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Elsbach P. Acylation of monoacylglycerophosphoethanolamine in the inner and outer membranes of the envelope of an Escherichia coli K12 strain and its phospholipase A-deficient mutant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 21;508(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P., Olsson I., Odeberg H. Purification and characterization of a potent bactericidal and membrane active protein from the granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2664–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Elsbach P. The use of a phospholipase A-less Escherichia coli mutant to establish the action of granulocyte phospholipase A on bacterial phospholipids during killing by a highly purified granulocyte fraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 1;466(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Franson C., Schmeidler K., Elsbach P. Reversible envelope effects during and after killing of Escherichia coli w by a highly-purified rabbit polymorpho-nuclear leukocyte fraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 4;436(1):154–169. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Franson R. C., Beckerdite S., Schmeidler K., Elsbach P. Partial characterization and purification of a rabbit granulocyte factor that increases permeability of Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):33–42. doi: 10.1172/JCI107915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. A., Albright F. R., Lennarz W. J., Schnaitman C. A. Distribution of phospholipid-synthesizing enzymes in the wall and membrane subfractions of the envelope of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):636–642. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeya H. I., Spitznagel J. K. Cationic proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysosomes. II. Composition, properties, and mechanism of antibacterial action. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):755–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.755-762.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]