Figures 3 and 4 are currently in reverse order. Their legends are in the correct order.
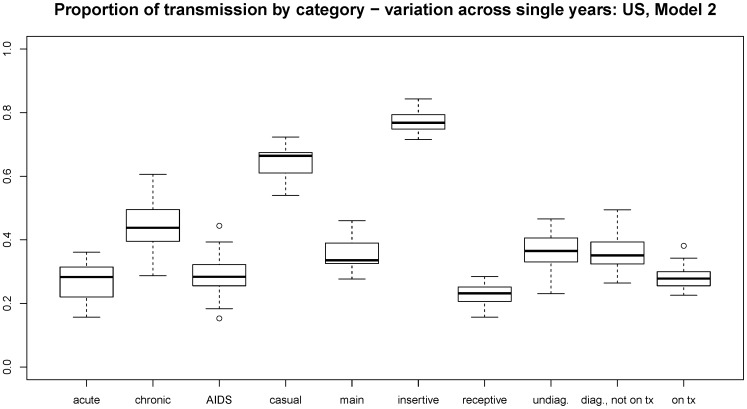
Figure 3. Range of variation from year to year for outcome metrics.
Each boxplot covers the values for a given outcome metric measured for each of the 25 years in a single run. We show US Model 1 here as demonstration; comparable plots for the other three country/model combinations are in the online technical supplement.
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050522.g003
Please see figure 3 at the following link:
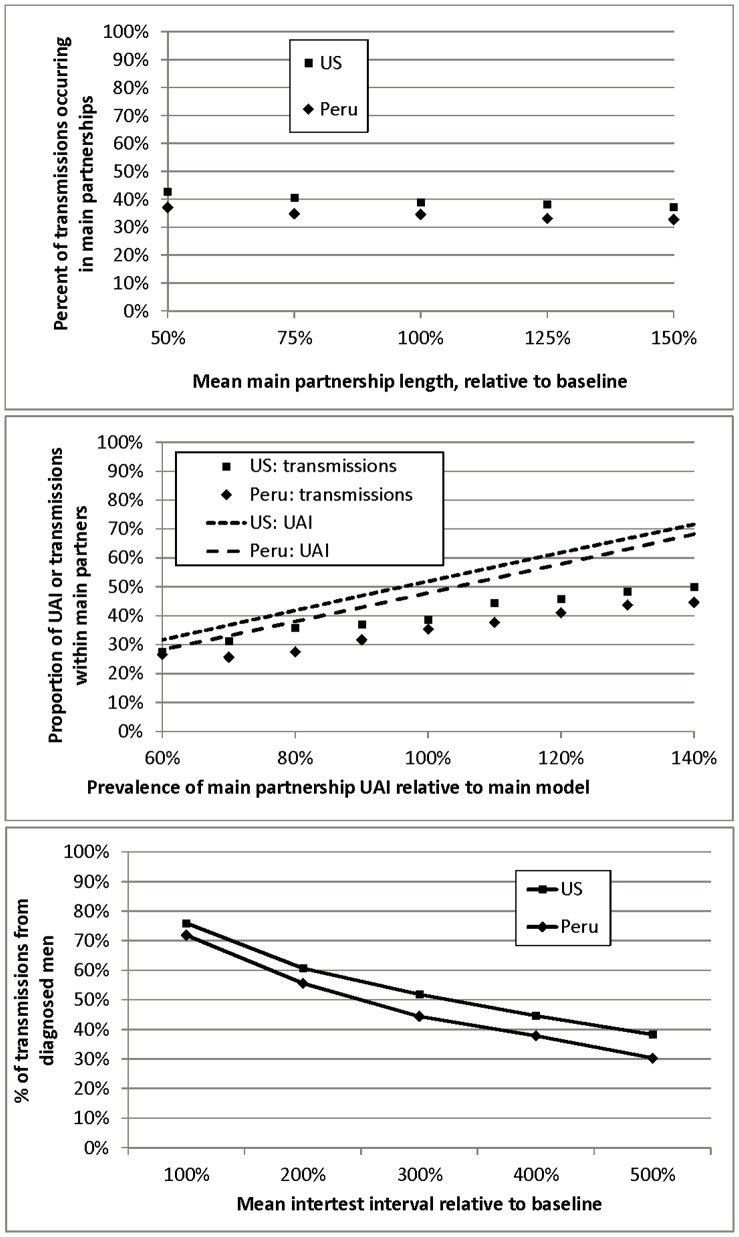
Figure 4. Sensitivity analyses.
a) Changes in main partnership duration relative to base model (100%). b) Changes in main and casual UAI relative to base model (100%). c) Changes in testing frequency relative to base model (100%).
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050522.g004
Please see Figure 4 at the following link:
Footnotes
Competing Interests: No competing interests declared.