Abstract
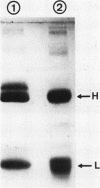
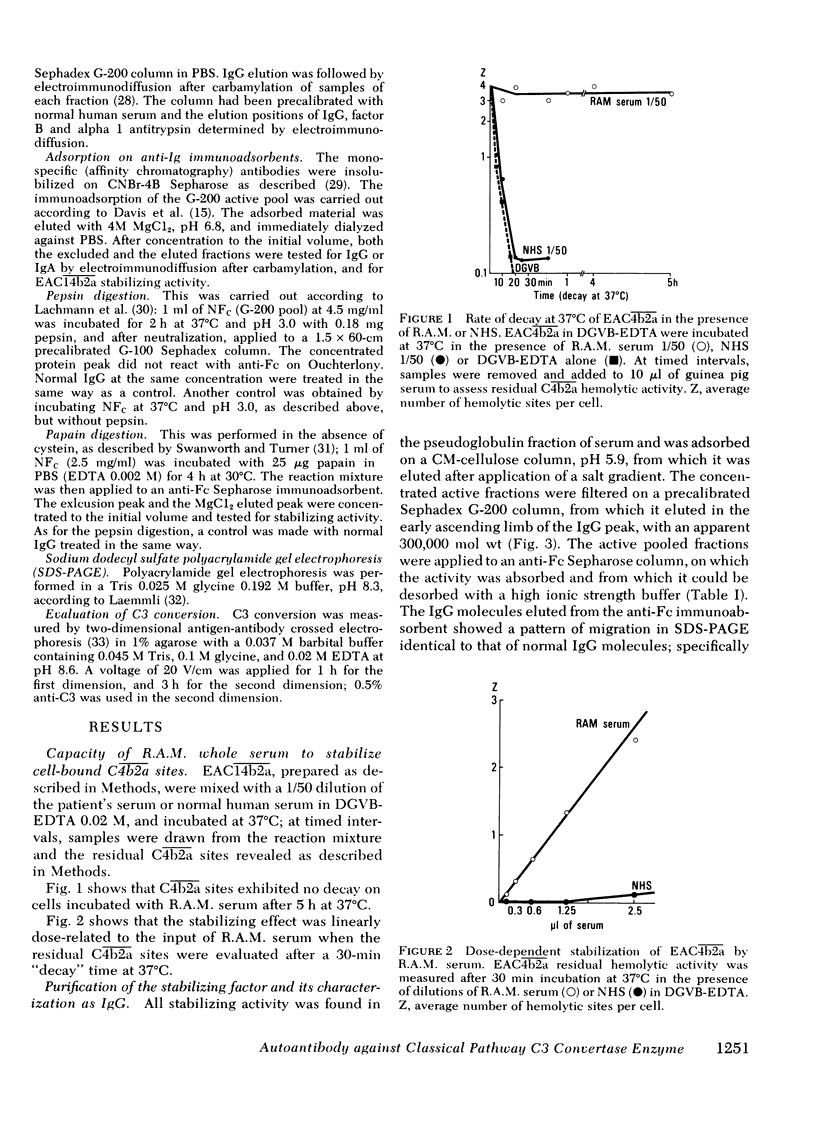
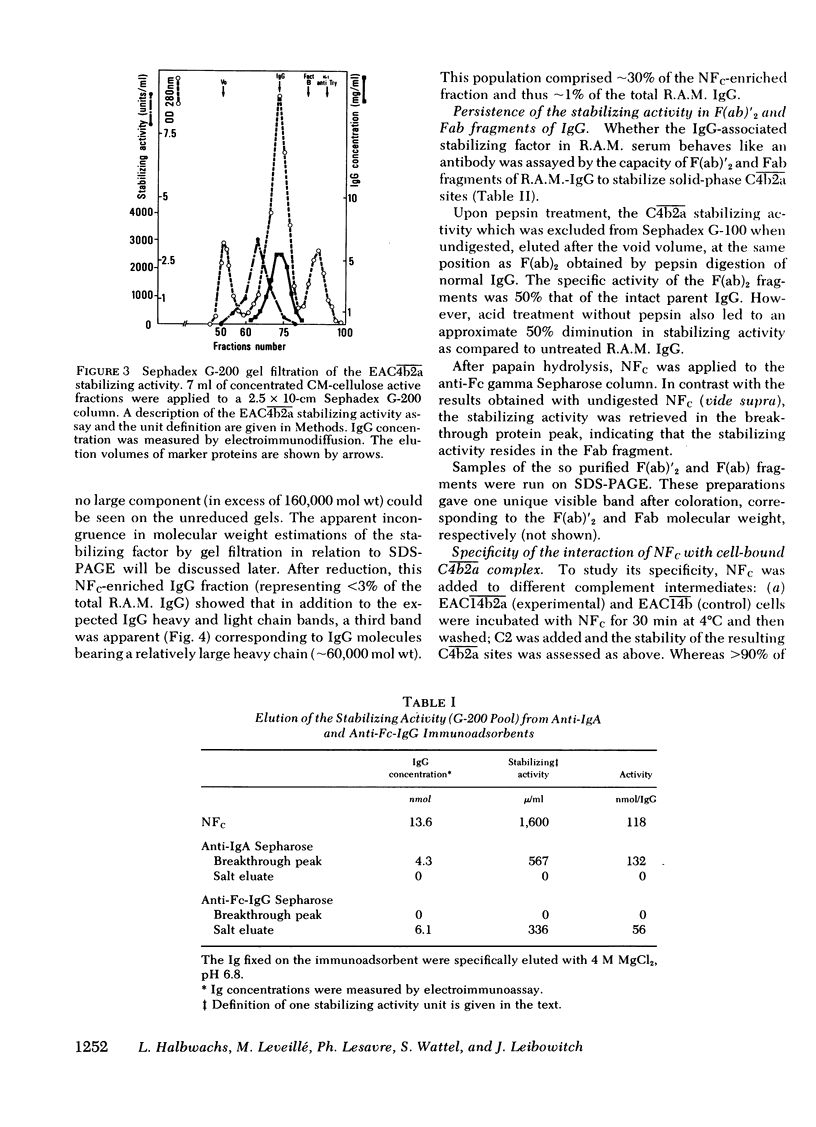
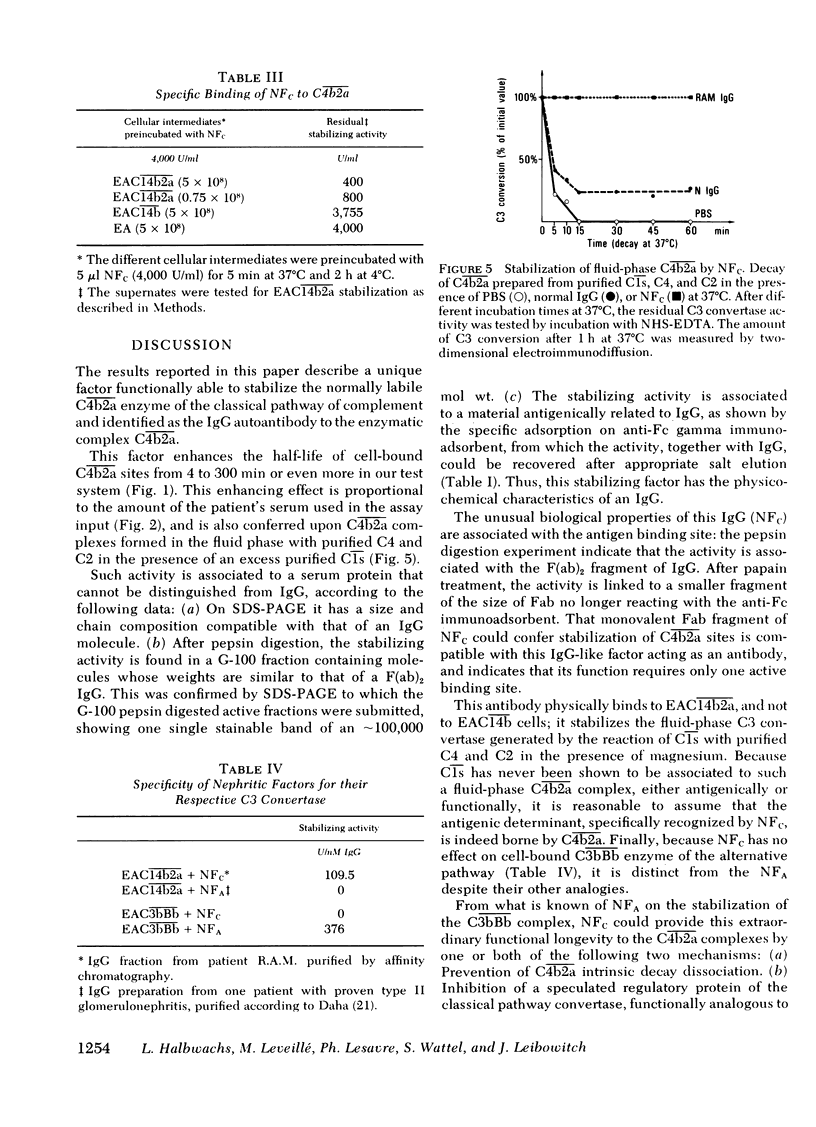
A factor, functionally characterized by its capacity to stabilize the normally labile classical pathway C3-converting complex of the classical pathway of complement, has been isolated from the serum of one patient with a case of acute glomerulonephritis, subsequent to a cutaneous infection. The factor confers long-lived stabilization of classical pathway C3 convertase complexes formed both in the solid (sensitized sheep erythrocytes bearing activated C̄1̄ and the classical pathway C3 convertase) and fluid phase. The half-life of such stabilized C3-cleaving enzymes extended beyond several hours at 37°C. The stabilizing activity was associated with a protein fraction immunochemically identified as immunoglobulin (Ig)G, a sizeable population of which exhibited a gamma chain of 60,000 daltons. The IgG-associated stabilizing activity was found to bind to the classical pathway C3 convertase enzyme via a fragment bearing the antigen-binding site of the molecule [F(ab)2 and F(ab)]. Such binding was demonstrable for classical pathway and not for alternative pathway C3 convertase. Thus, the stabilizing factor behaves like an autoantibody to the C3-converting complex of the classical pathway of complement. The binding of the antibody to the enzyme affords protection of the latter against decay-degradation. By analogy with the nephritic factor of the alternative pathway situation where IgG autoantibodies specifically bind to alternative pathway C3 convertase enzymes and protect them from degradation, the functionally unusual IgG in our patient was designated as the nephritic factor of the classical pathway. Indirect evidence suggests that nephritic factor of the classical pathway-IgG might be of the IgG3 subclass.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Bloch K. J., Rosen F. S. Increased susceptibility to infection in a patient with type II essential hypercatabolism of C3. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 22;288(12):601–606. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303222881204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R. Isolation and analysis of the mechanism of action of an inactivator of C4b in normal human serum. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):890–903. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M., Anfinsen C. B. Selective enzyme purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):636–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. C3 nephritic factor (C3NeF): stabilization of fluid phase and cell-bound alternative pathway convertase. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. C3 requirements for formation of alternative pathway C5 convertase. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):630–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd, Ziegler J. B., Gelfand E. W., Rosen F. S., Alper C. A. Heterogeneity of nephritic factor and its identification as an immunoglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3980–3983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. II. Role in proteolysis of C4b by C3b-inactivator. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1044–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Porter R. R. The purification and properties of the second component of human complement. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):99–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1710099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J. The purification of specific antibody as F(ab')2 by the pepsin digestion of antigen-antibody precipitates, and its application to immunoglobulin and complement antigens. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jan;8(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90423-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitch J., Leveille M., Halbwachs L. Description d'une activité enzymatique inhabituelle clivant le 3e composant du complément. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1979 Feb 5;288(5):567–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesavre P. H., Hugli T. E., Esser A. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The alternative pathway C3/C5 convertase: chemical basis of factor B activation. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):529–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak L. W., Lachmann P. J., Majewski J. The activation of the C3b feedback cycle with human complement components. I. Through the classical pathway. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Nov;30(2):200–210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Götze O. C3 proactivator convertase and its mode of action. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):1003–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Polley M. J., Calcott M. A. Formation and functional significance of a molecular complex derived from the second and the fourth component of human complement. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):359–380. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick C. C., Virella G. Isolation of normal human IgG3. Identical molecular weight for normal and monoclonal gamma-3 chains. Immunochemistry. 1978 Feb;15(2):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Medicus R. G., Gïtze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Properdin- and nephritic factor-dependent C3 convertases: requirement of native C3 for enzyme formation and the function of bound C3b as properdin receptor. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):760–772. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. M., Amos N., Sissons J. G., Lachmann P. J., Peters D. K. The immunogloblin nature of nephritic factor (NeF). Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Apr;32(1):12–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sissons J. G., West R. J., Fallows J., Williams D. G., Boucher B. J., Amos N., Peters D. K. The complement abnormalities of lipodystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 26;294(9):461–465. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602262940902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer R. E., Vallota E. H., Forristal J., Sudora E., Stitzel A., Davis N. C., West C. D. Serum C'3 lytic system in patients with glomerulonephritis. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):436–437. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Nagasawa S., Koyama J. The NH-2-terminal sequences of a subunit of the first component of human complement, C1s, and its activated form, C1s. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 15;50(3):330–333. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80521-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A. C3 inactivating factor in the serum of a patient with chronic hypocomplementaemic proliferative glomerulo-nephritis. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):147–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., Jr, KUNKEL H. G. Rheumatoid factor, complement, and conglutinin aberrations in patients with subacute bacterial endocarditis. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:666–675. doi: 10.1172/JCI104523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Quantitative estimation of human immunoglobulins following carbamylation by electrophoresis in antibody-containing agarose. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;22(2):107–111. doi: 10.3109/00365516809160953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]