Abstract
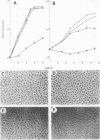
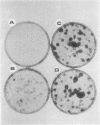
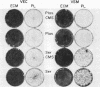
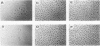
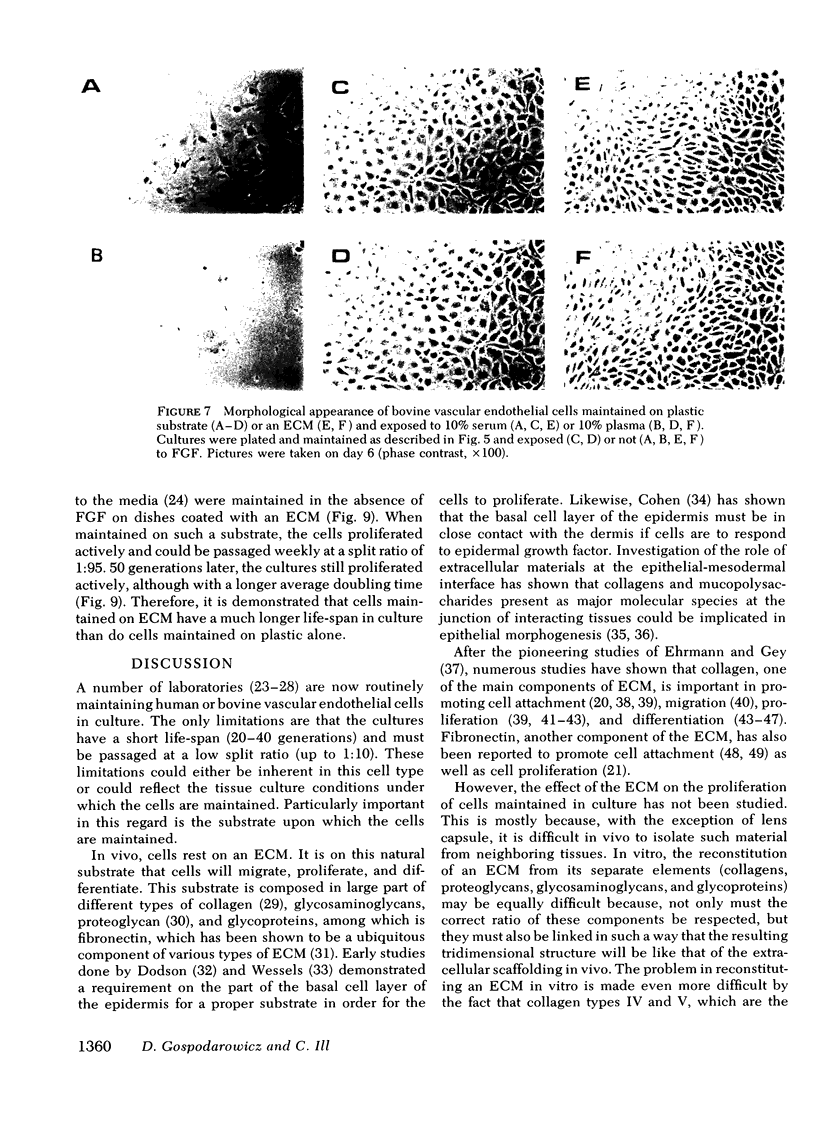
Bovine vascular endothelial cells plated at low cell density in the presence of high (10%) concentrations of serum and maintained on plastic tissue culture dishes proliferate slowly. If the cultures were exposed to fibroblast growth factors (FGF), the cells proliferated actively and, after a week, a monolayer composed of closely apposed and highly contact-inhibited mononucleated cells formed. In contrast to cultures maintained on plastic, cultures maintained on dishes coated with an extracellular matrix produced by corneal endothelial cells proliferated rapidly and no longer required FGF to reach confluence. Addition of FGF to such cultures did not decrease the mean doubling time, which was already at a minimum (18 h), nor did it result in a higher final cell density, which was already at a maximum (700-1,000 cells/mm2). Likewise, although human umbilical vein endothelial cells plated at low density on plastic did not proliferate, they proliferated rapidly when plated on dishes coated with an extracellular matrix. However, unlike bovine vascular endothelial cells, they still required FGF if the cultures were to become confluent.
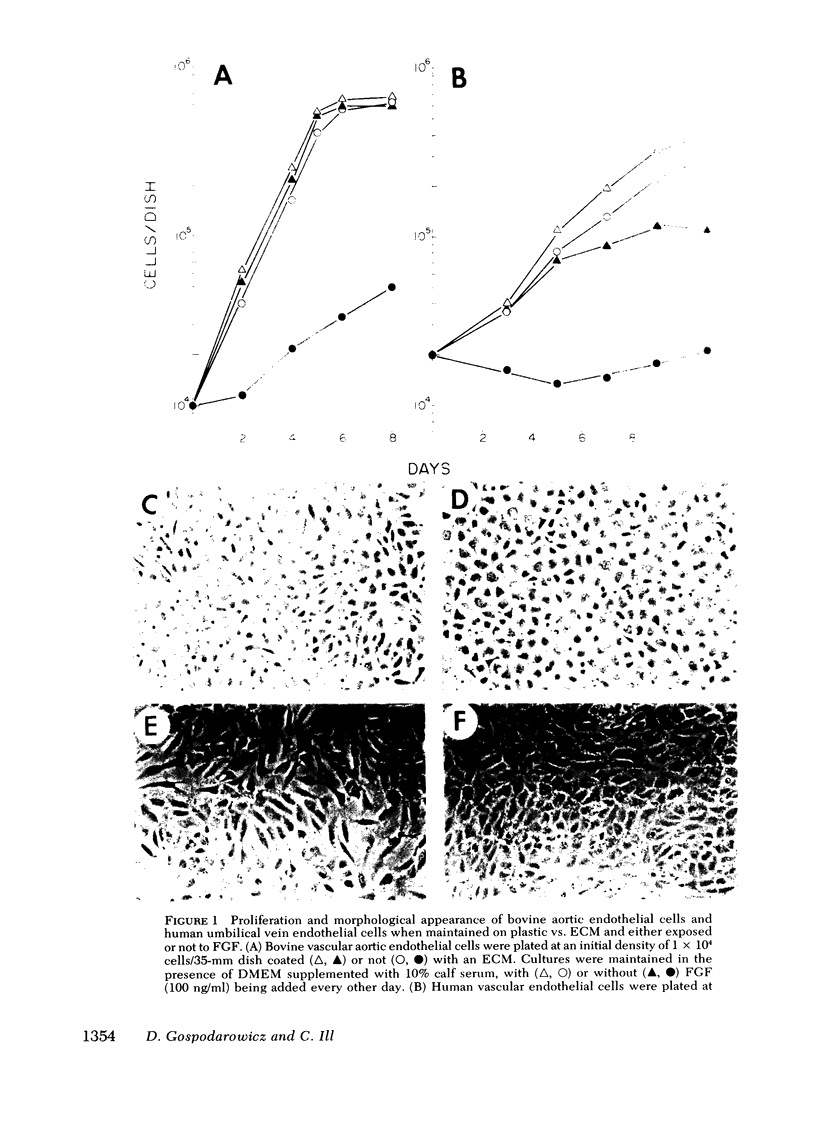
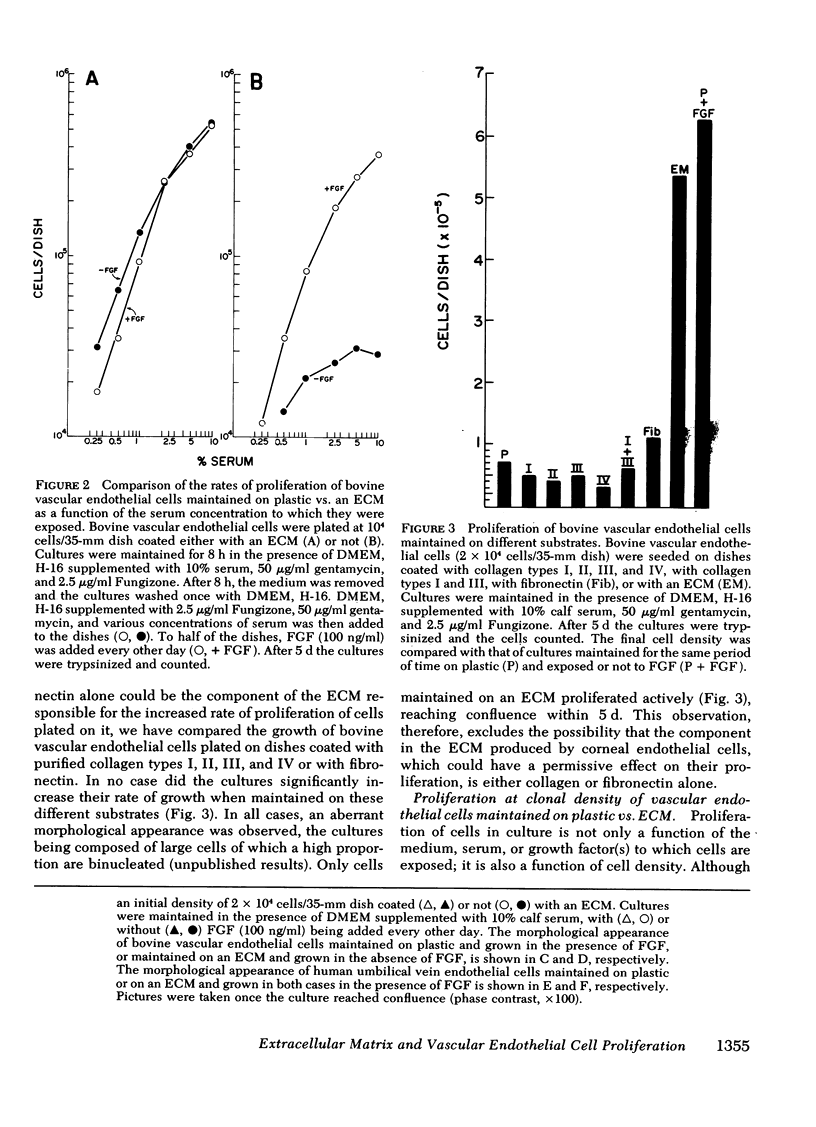
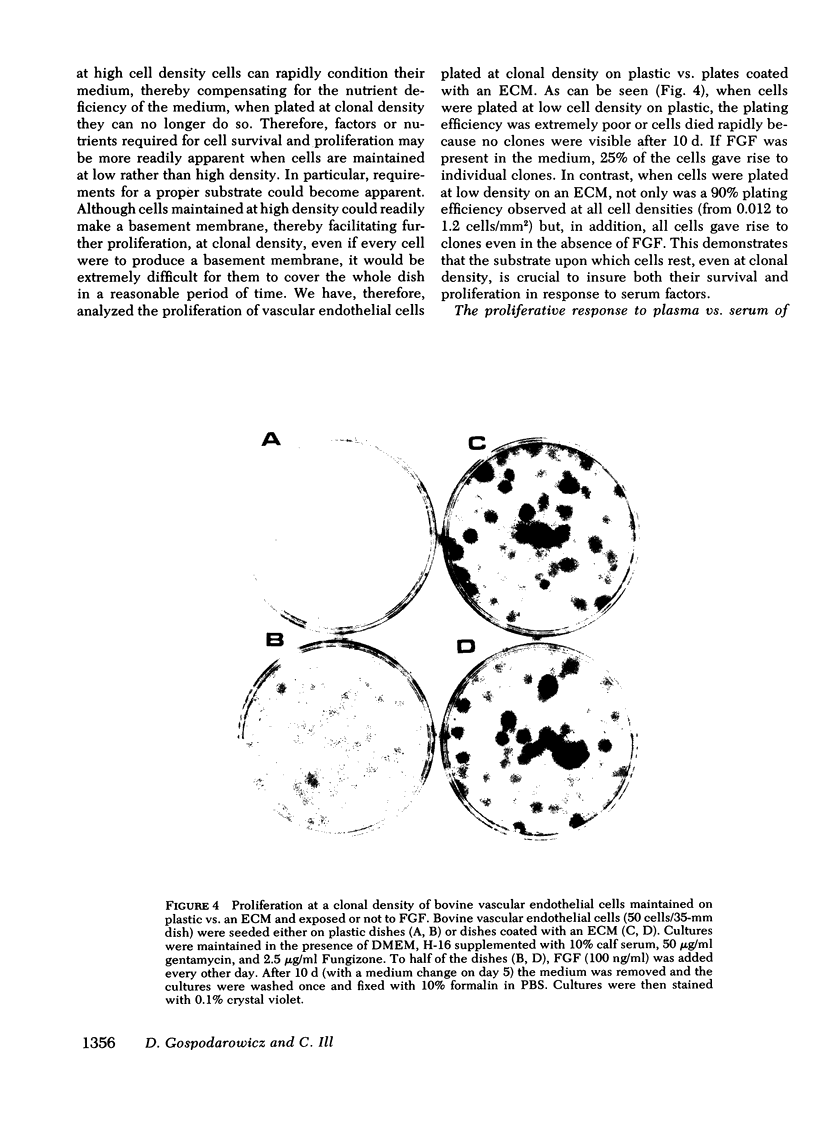
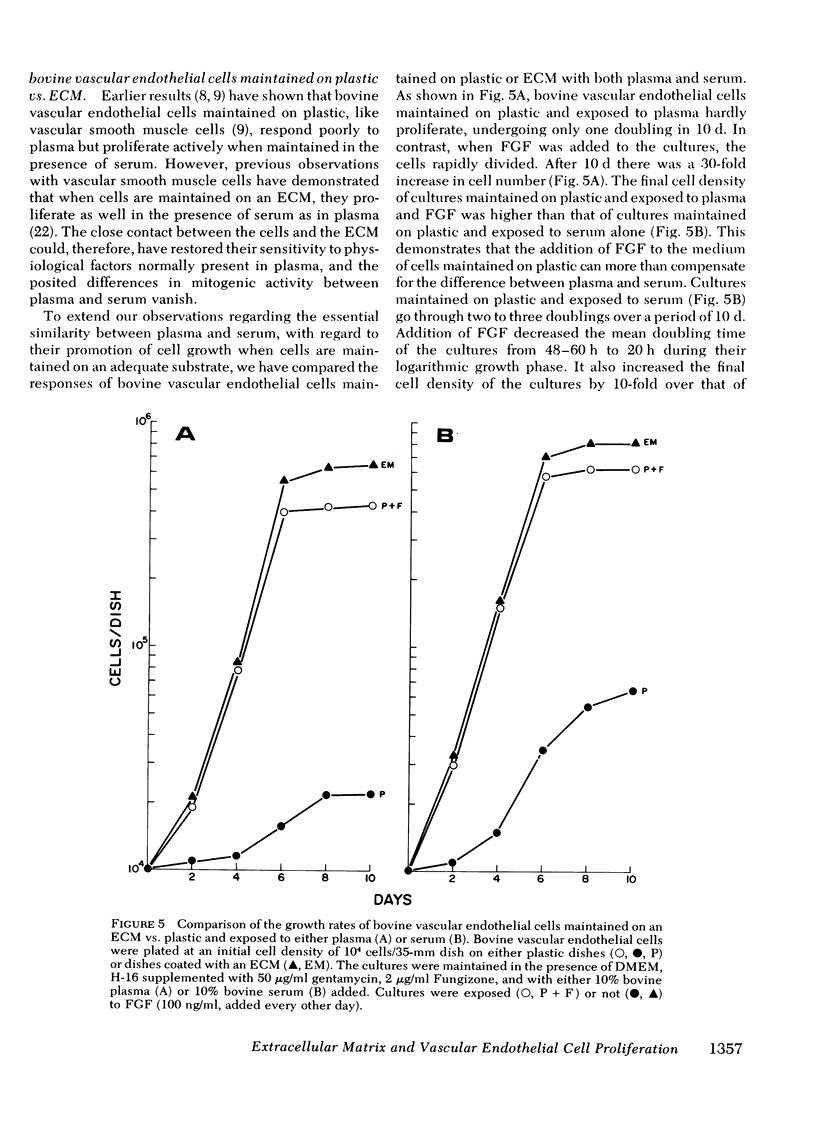
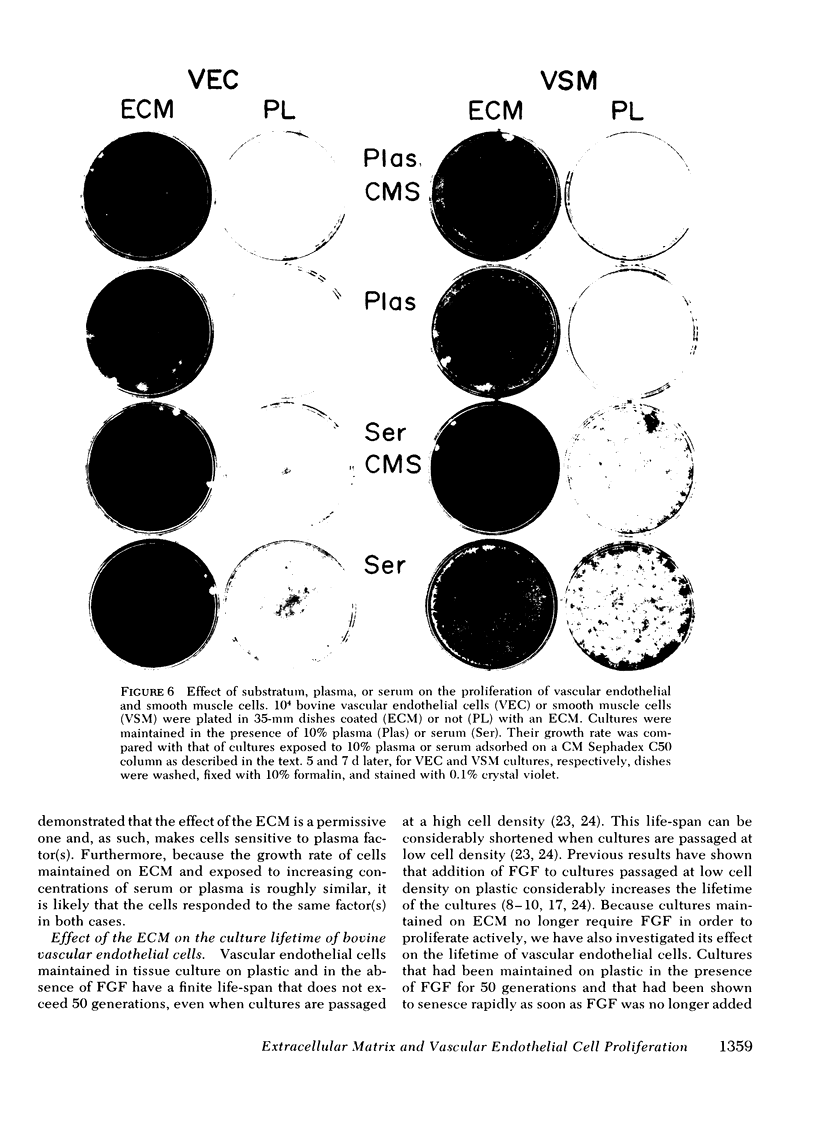
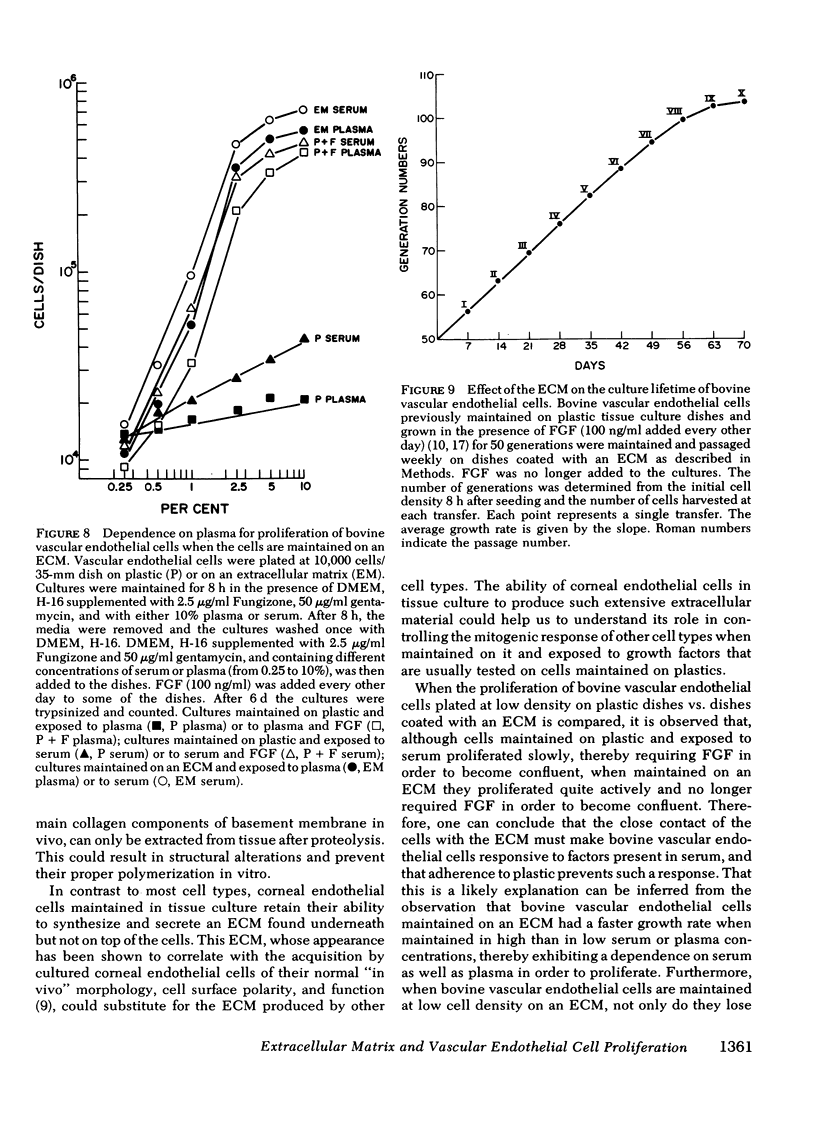
The ability of plasma vs. serum to sustain cell proliferation was analyzed using low density bovine-vascular endothelial cell cultures maintained either on plastic or on dishes coated with an extracellular matrix. Cells plated on plastic had a lower growth rate when exposed to plasma than to serum. In both cases, FGF was required for the cultures to become confluent. In contrast, when cells were plated on an extracellular matrix, they proliferated equally well, regardless of whether they were exposed to plasma or serum, and no longer required FGF to become confluent. Because the growth rate of the cultures maintained on an extracellular matrix was a direct function of the serum or plasma concentrations to which they were exposed, it is likely that the extracellular matrix had a permissive rather than a direct mitogenic effect on the cells. Therefore, one can conclude that the simple change of substrate from plastic to extracellular matrix will restore the sensitivity of vascular endothelial cells to physiological agents present in plasma or serum.
Full text
PDF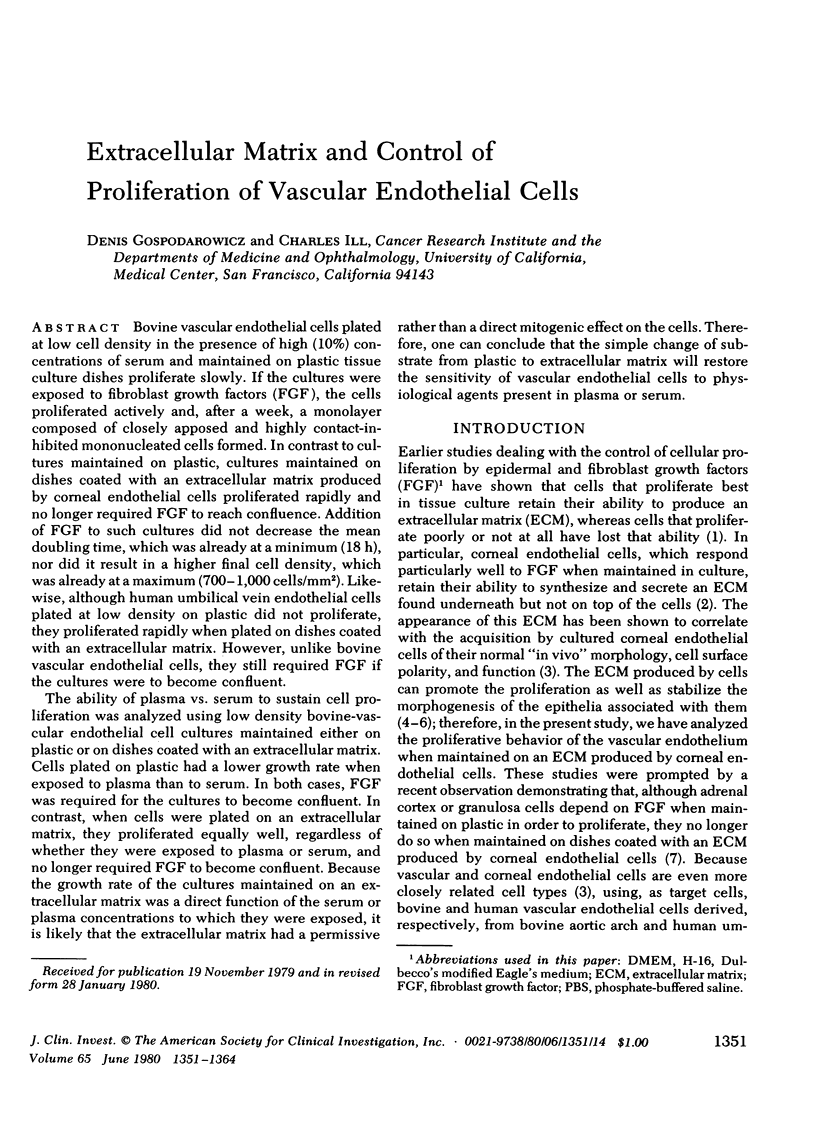






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali I. U., Mautner V., Lanza R., Hynes R. O. Restoration of normal morphology, adhesion and cytoskeleton in transformed cells by addition of a transformation-sensitive surface protein. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90322-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Sedlak B. J., Rafelson M. E., Jr Culture of arterial endothelial cells: characterization and growth of bovine aortic cells. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):825–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. The stimulation of epidermal proliferation by a specific protein (EGF). Dev Biol. 1965 Dec;12(3):394–407. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(65)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRMANN R. L., GEY G. O. The growth of cells on a transparent gel of reconstituted rat-tail collagen. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1956 Jun;16(6):1375–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M., Solursh M. The influence of the substratum on mesenchyme spreading in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90416-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gey G. O., Svotelis M., Foard M., Bang F. B. Long-term growth of chicken fibroblasts on a collagen substrate. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 15;84(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90380-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr Culture of vascular endothelium. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Bialecki H., Greenburg G. Purification of the fibroblast growth factor activity from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3736–3743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Brown K. D., Birdwell C. R., Zetter B. R. Control of proliferation of human vascular endothelial cells. Characterization of the response of human umbilical vein endothelial cells to fibroblast growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and thrombin. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):774–788. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Greenburg G., Bialecki H., Zetter B. R. Factors involved in the modulation of cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro: the role of fibroblast and epidermal growth factors in the proliferative response of mammalian cells. In Vitro. 1978 Jan;14(1):85–118. doi: 10.1007/BF02618177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Greenburg G., Birdwell C. R. Determination of cellular shape by the extracellular matrix and its correlation with the control of cellular growth. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4155–4171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Greenburg G. The coating of bovine and rabbit corneas denuded of their endothelium with bovine corneal endothelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 1979 Mar;28(3):249–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(79)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Greenburg G., Vlodavsky I., Alvarado J., Johnson L. K. The identification and localization of fibronectin in cultured corneal endothelial cells: cell surface polarity and physiological implications. Exp Eye Res. 1979 Nov;29(5):485–509. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(79)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Mescher A. L., Birdwell C. R. Control of cellular proliferation by the fibroblast and epidermal growth factors. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1978 May;(48):109–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Mescher A. L., Birdwell C. R. Stimulation of corneal endothelial cell proliferations in vitro by fibroblast and epidermal growth factors. Exp Eye Res. 1977 Jul;25(1):75–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(77)90248-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J. S., Braun D. L. Control of proliferation of bovine vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):377–385. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J., Braun D., Birdwell C. Clonal growth of bovine vascular endothelial cells: fibroblast growth factor as a survival agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Weseman J., Moran J. Presence in brain of a mitogenic agent promoting proliferation of myoblasts in low density culture. Nature. 1975 Jul 17;256(5514):216–219. doi: 10.1038/256216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grobstein C. Mechanisms of organogenetic tissue interaction. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1967 Sep;26:279–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosher R. A., Church R. L. Stimulation of in vitro somite chondrogenesis by procollagen and collagen. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):327–330. doi: 10.1038/258327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Vembu D., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Boone C. Collagen required for proliferation of cultured connective tissue cells but not their transformed counterparts. Nature. 1978 Apr 13;272(5654):622–624. doi: 10.1038/272622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Karasek M. Isolation and growth of adult human epidermal keratinocytes in cell culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Aug;71(2):157–162. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12546943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macarak E. J., Kirby E., Kirk T., Kefalides N. A. Synthesis of cold-insoluble globulin by cultured calf endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2621–2625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Cerundolo J., Ilsley S., Kelley P. R., Forand R. An endothelial cell growth factor from bovine hypothalamus: identification and partial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5674–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier L., Hay E. D. Stimulation of corneal differentiation by interaction between cell surface and extracellular matrix. I. Morphometric analysis of transfilter "induction". J Cell Biol. 1975 Aug;66(2):275–291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Stingl G., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R., Katz S. I. Epidermal cells adhere preferentially to type IV (basement membrane) collagen. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jan;80(1):197–202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Sato G. Fibronectin mediates cytokinesis and growth of rat follicular cells in serum-free medium. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Nist C., Kariya B., Rivest M. J., Raines E., Callis J. Physiological quiescence in plasma-derived serum: influence of platelet-derived growth factor on cell growth in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Dec;97(3 Pt 2 Suppl 1):497–508. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor S. L., Court J. Different mechanisms in the attachment of cells to native and denatured collagen. J Cell Sci. 1979 Aug;38:267–281. doi: 10.1242/jcs.38.1.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M. Selection and characterization of bovine aortic endothelial cells. In Vitro. 1978 Dec;14(12):966–980. doi: 10.1007/BF02616210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavkin H. C., Trump G. N., Brownell A., Sorgente N. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions: mesenchymal specificity. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1977;32:29–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman S., Vaheri A. Distribution of a major connective tissue protein, fibronectin, in normal human tissues. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1054–1064. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Johnson L. K., Greenburg G., Gospodarowicz D. Vascular endothelial cells maintained in the absence of fibroblast growth factor undergo structural and functional alterations that are incompatible with their in vivo differentiated properties. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):468–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Lui G. M., Gospodarowicz D. Morphological appearance, growth behavior and migratory activity of human tumor cells maintained on extracellular matrix versus plastic. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):607–616. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESSELLS N. K. SUBSTRATE AND NUTRIENT EFFECTS UPON EPIDERMAL BASAL CELL ORIENTATION AND PROLIFERATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:252–259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Marcus A. J., Jaffe E. A. Synthesis of prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) by cultured human and bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3922–3926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicha M. S., Liotta L. A., Garbisa S., Kidwell W. R. Basement membrane collagen requirements for attachment and growth of mammary epithelium. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Nov;124(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. Cell surface protein partially restores morphology, adhesiveness, and contact inhibition of movement to transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Richards J., Bowman P., Guzman R., Enami J., McCormick K., Hamamoto S., Pitelka D., Nandi S. Sustained growth and three-dimensional organization of primary mammary tumor epithelial cells embedded in collagen gels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3401–3405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]