Abstract
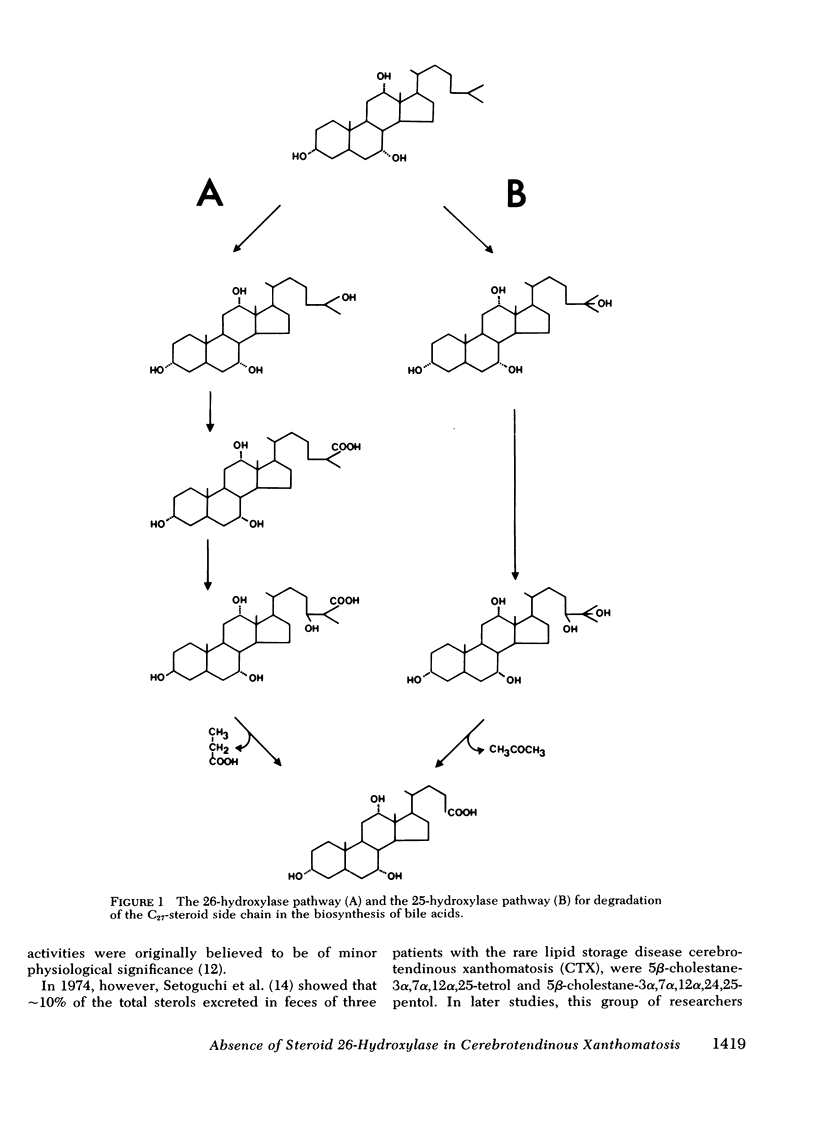
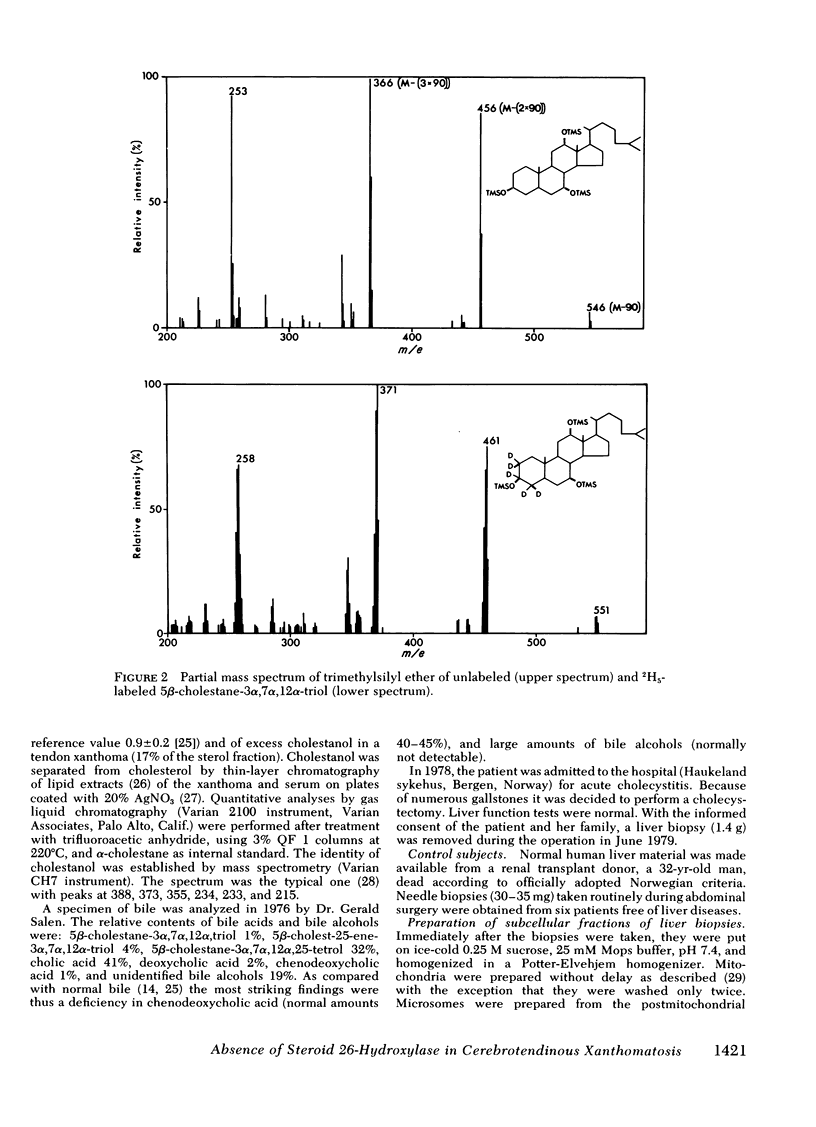
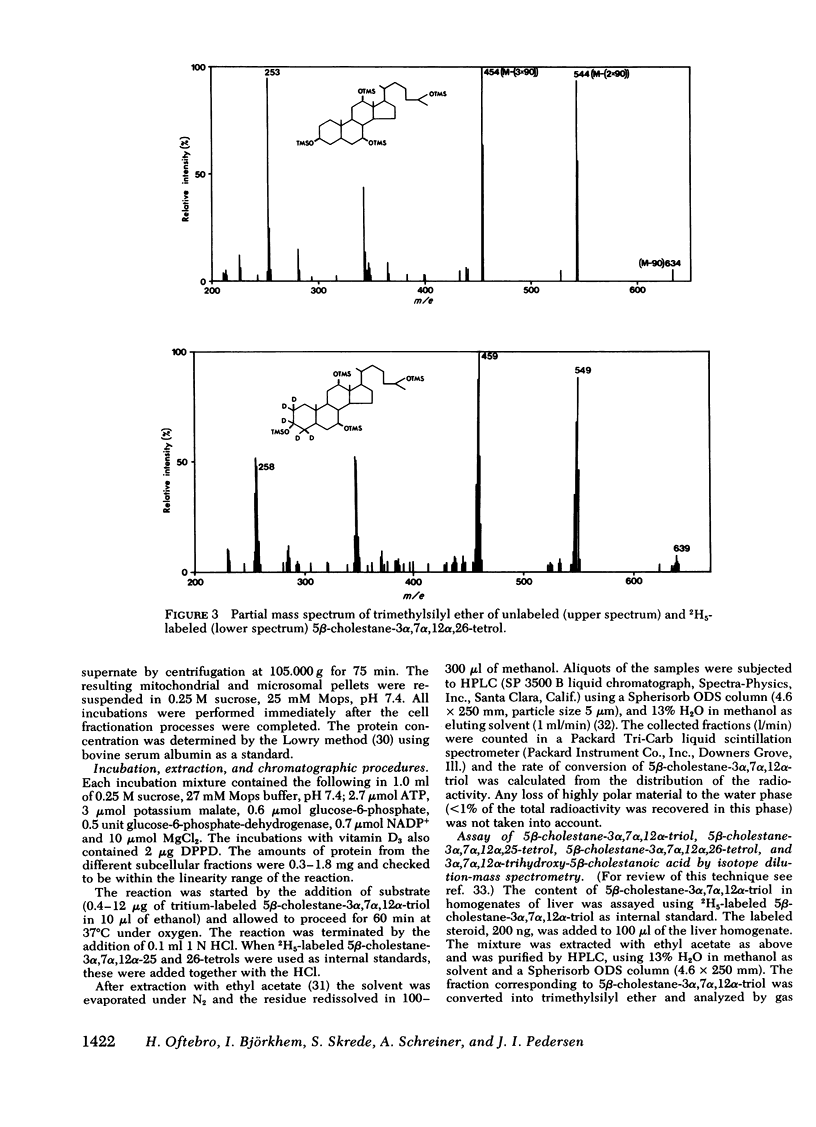
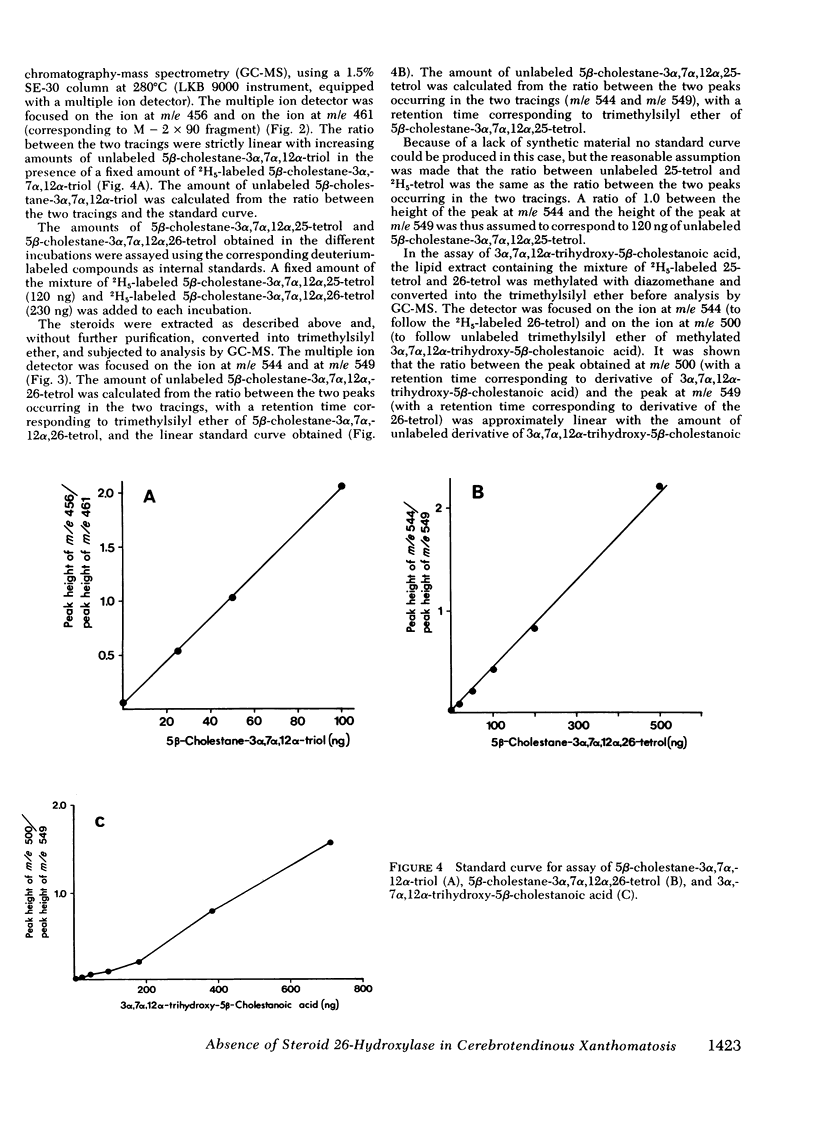
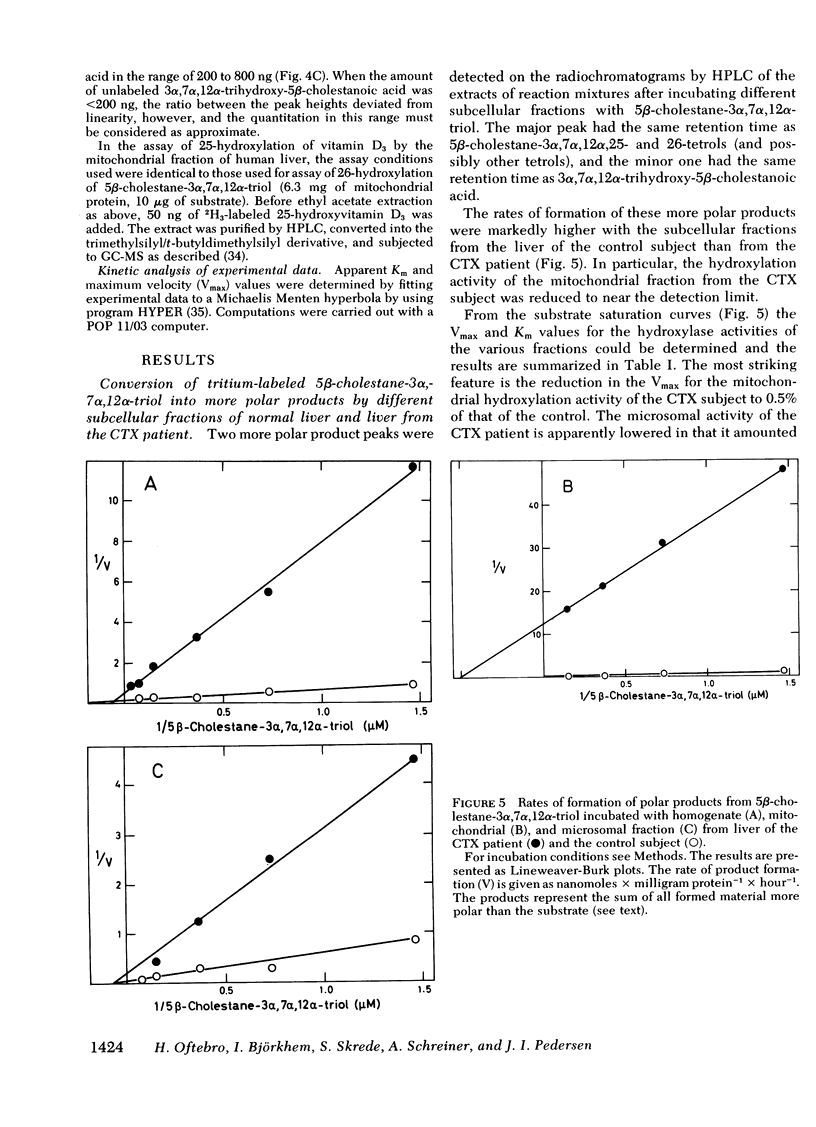
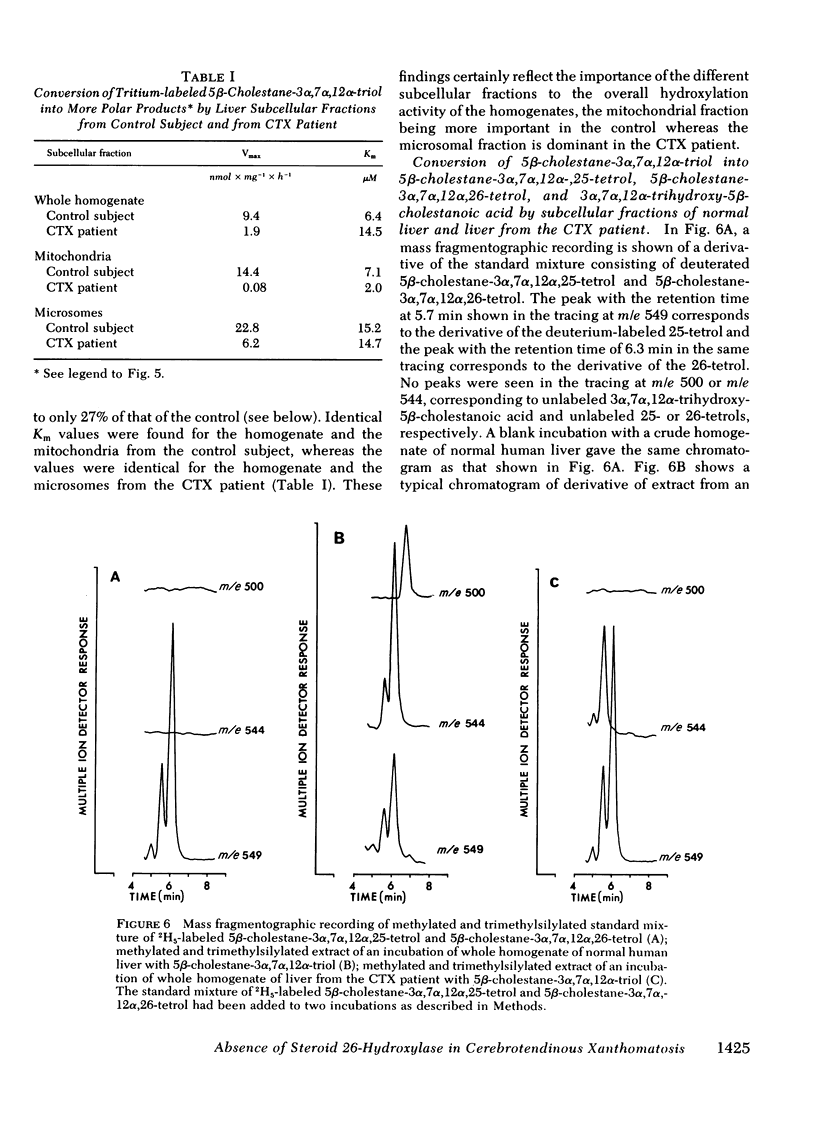
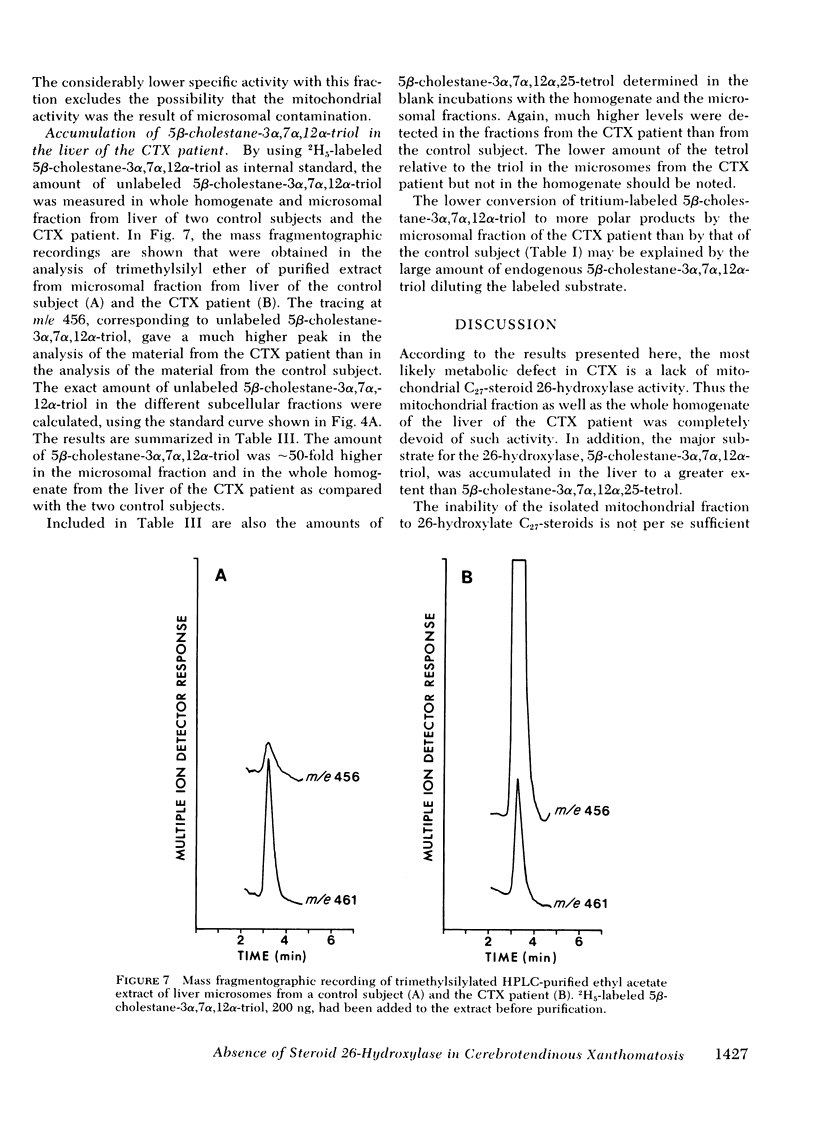
Oxidation of side chain of 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-triol was studied in a patient with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX) and in control subjects, using various subcellular fractions of liver homogenate and a method based on isotope dilution-mass spectrometry. In the control, 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-triol was converted into 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha,26-tetrol and 3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-trihydroxy-5 beta-cholestanoic acid by the mitochondrial fraction, and into 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha,-25-tetrol by the microsomal fraction. In the CTX patient, liver mitochondria were completely devoid of 26-hydroxylase activity. The same mitochondrial fraction catalyzed 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D3. The microsomal fraction of liver of the subject with CTX contained more than 50-fold the normal amount of 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-triol. The basic metabolid defect in CTX appears to be a lack of the mitochondrial 26-hydroxylase. The excretion in the bile of 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha,25-tetrol and 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha,24 alpha,25-pentol observed in CTX patients may be secondary to the accumulation of the major substrate for the 26-hydroxylase, i. e., 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha,7 alpha,12 alpha-triol, and exposure of this substrate to the normally less active microsomal 25-and 24-hydroxylases. It is concluded that the major pathway in the biosynthesis of cholic acid in human liver involves a mitochondrial C27-steroid 26-hydroxylation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidson G. A. Structural and metabolic heterogeneity of rat liver glycerophosphatides. Eur J Biochem. 1968 May;4(4):478–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSEUS O., DANIELSSON H., KALLNER A. SYNTHESIS AND METABOLISM OF CHOLEST-4-ENE-7-ALPHA,12-ALPHA-DIOL-3-ONE AND 5-BETA-CHOLESTANE-7-ALPHA,12-ALPHA-DIOL-3-ONE. BILE ACIDS AND STEROIDS 153. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2396–2401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSEUS O. ON THE STEREOSPECIFICITY OF 26-HYDROXYLATION OF CHOLESTEROL. BILE ACIDS AND STEROIDS. 155. Acta Chem Scand. 1965;19:325–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIDGWATER R. J. Partial synthesis of the two 3alpha:7alpha:12alpha-trihydroxycoprostanic acids and of similar bile acids with extended chains. Biochem J. 1956 Dec;64(4):593–599. doi: 10.1042/bj0640593a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkhem I., Holmberg I. A novel specific assay of 25-hydroxy vitamin D. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 May 3;68(3):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkheim I., Danielsson H., Einarsson K., Johansson G. Formation of bile acids in man: conversion of cholesterol into 5-beta-cholestane-3-alpha, 7-alpha, 12-alpha-triol in liver homogenates. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1573–1582. doi: 10.1172/JCI105849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Danielsson H. Biosynthesis and metabolism of bile acids in man. Prog Liver Dis. 1976;5:215–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Gustafsson J., Johansson G., Persson B. Biosynthesis of bile acids in man. Hydroxylation of the C27-steroid side chain. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):478–486. doi: 10.1172/JCI107954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Gustafsson J. Omega-hydroxylation of steriod side-chain in biosynthesis of bile acids. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):201–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Holmberg I. Assay and properties of a mitochondrial 25-hydroxylase active on vitamine D3. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):842–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Holmberg I. On the 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D3 in vitro studied with a mass fragmentographic technique. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9518–9524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I. Selective ion monitoring in clinical chemistry. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1979 Aug;11(1):53–105. doi: 10.3109/10408367909105854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAREY J. B., Jr CONVERSION OF CHOLESTEROL TO TRIHYDROXYCOPROSTANIC ACID AND CHOLIC ACID IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jul;43:1443–1448. doi: 10.1172/JCI105020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAREY J. B., Jr, HASLEWOOD G. A. Crystallization of trihydroxycoprostani acid from human bile. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:855–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. Computer programmes for processing enzyme kinetic data. Nature. 1963 May 4;198:463–465. doi: 10.1038/198463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronholm T., Johansson G. Oxidation of 5 beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha, 12alpha-triol by rat liver microsomes. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Oct;16(2):373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson H., Sjövall J. Bile acid metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:233–253. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson J., Sjöstedt S. On the stereospecificity of microsomal "26"-hydroxylation in bile acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):199–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASLEWOOD G. A. D. Comparative studies of bile salts. V. Bile salts of Crocodylidae. Biochem J. 1952 Dec;52(4):583–587. doi: 10.1042/bj0520583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. F., Staples A. B., Williams G. C. Metabolism of 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha, 7 alpha, 12 alpha, 26-tetrol and 5 beta-cholestane-3 alpha, 7 alpha, 12 alpha, 25-tetrol into cholic acid in normal human subjects. J Lipid Res. 1979 May;20(4):489–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. I., Björkhem I., Gustafsson J. 26-Hydroxylation of C27-steroids by soluble liver mitochondrial cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6464–6469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. I., Godager H. K. Purification of NADPH-ferredoxin reductase from rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 7;525(1):28–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. I., Holmberg I., Björkhem I. Reconstitution of vitamin D3 25-hydroxylase activity with a cytochrome P-450 preparation from rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 15;98(2):394–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popják G., Edmond J., Anet F. A., Easton N. R., Jr Carbon-13 NMR studies on cholesterol biosynthesized from [13C]mevalonates. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Feb 2;99(3):931–935. doi: 10.1021/ja00445a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAPLE E., RABINOWITZ J. L. Formation of trihydroxycoprostanic acid from cholesterol in man. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jun 4;59:735–736. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90663-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salen G. Cholestanol deposition in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. A possible mechanism. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Dec;75(6):843–851. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-6-843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salen G., Shefer S., Cheng F. W., Dayal B., Batta A. K., Tint G. S. Cholic acid biosynthesis: the enzymatic defect in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):38–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI109275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salen G., Shefer S., Setoguchi T., Mosbach E. H. Bile alcohol metabolism in man. Conversion of 5beta-cholestane-3alpha, 7alpha,12alpha, 25-tetrol to cholic acid. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):226–231. doi: 10.1172/JCI108071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner A., Hopen G., Skrede S. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (cholestanolosis). Investigations on two sisters and their family. Acta Neurol Scand. 1975 May;51(5):405–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. C., Cohen B. I., Vlahcevic Z. R., Gregory D. H., Halloran L. G., Kuramoto T., Mosbach E. H., Swell L. Quantitative aspects of the conversion of 5 beta-cholestane intermediates to bile acids in man. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6308–6314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoguchi T., Salen G., Tint G. S., Mosbach E. H. A biochemical abnormality in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Impairment of bile acid biosynthesis associated with incomplete degradation of the cholesterol side chain. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1393–1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI107688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Cheng F. W., Batta A. K., Dayal B., Tint G. S., Salen G. Biosynthesis of chenodeoxycholic acid in man: stereospecific side-chain hydroxylations of 5beta-cholestane-3alpha,7alpha-diol. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):539–545. doi: 10.1172/JCI109158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Cheng F. W., Dayal B., Hauser S., Tint G. S., Salen G., Mosbach E. H. A 25-hydroxylation pathway of cholic acid biosynthesis in man and rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):897–903. doi: 10.1172/JCI108366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi S., Hoshita N., Okuda K. Enzymatic characteristics of CO-sensitive 26-hydroxylase system for 5beta-cholestane-3 alpha, 7 alpha, 12 alpha-triol in rat-liver mitochondria and its intramitochondrial localization. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 17;40(2):607–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



