Abstract
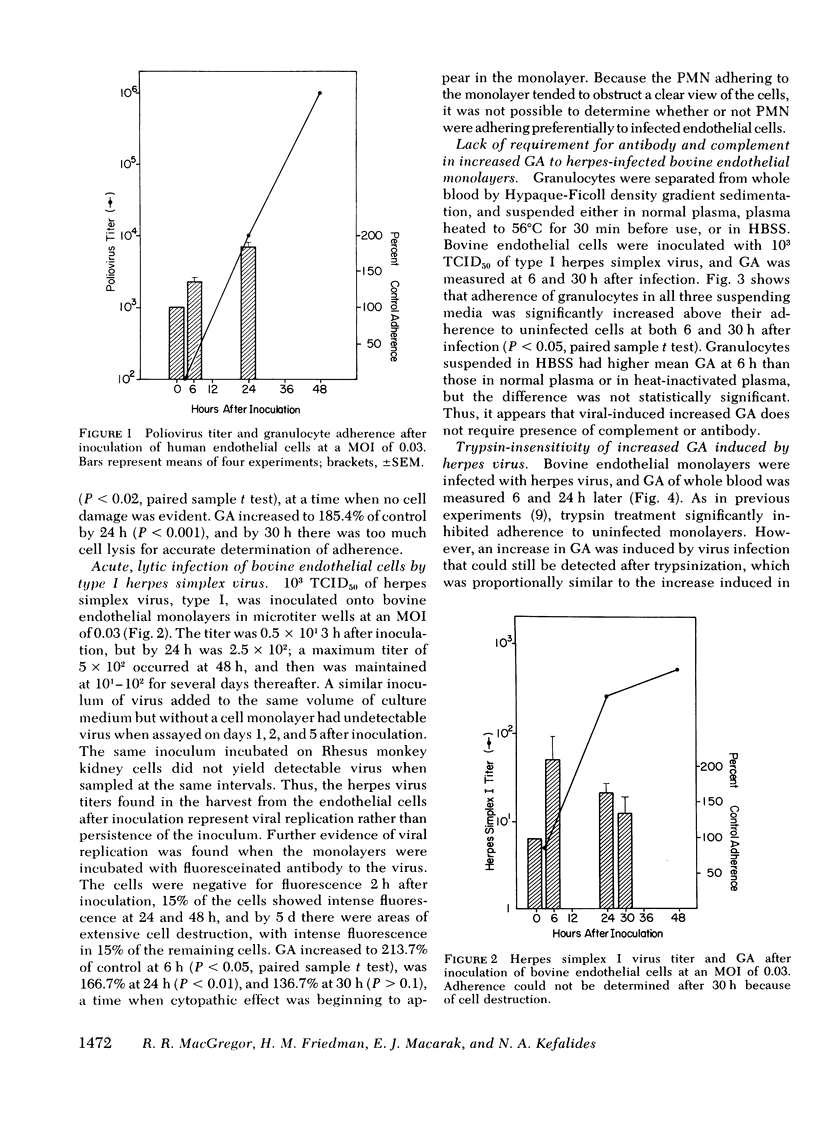
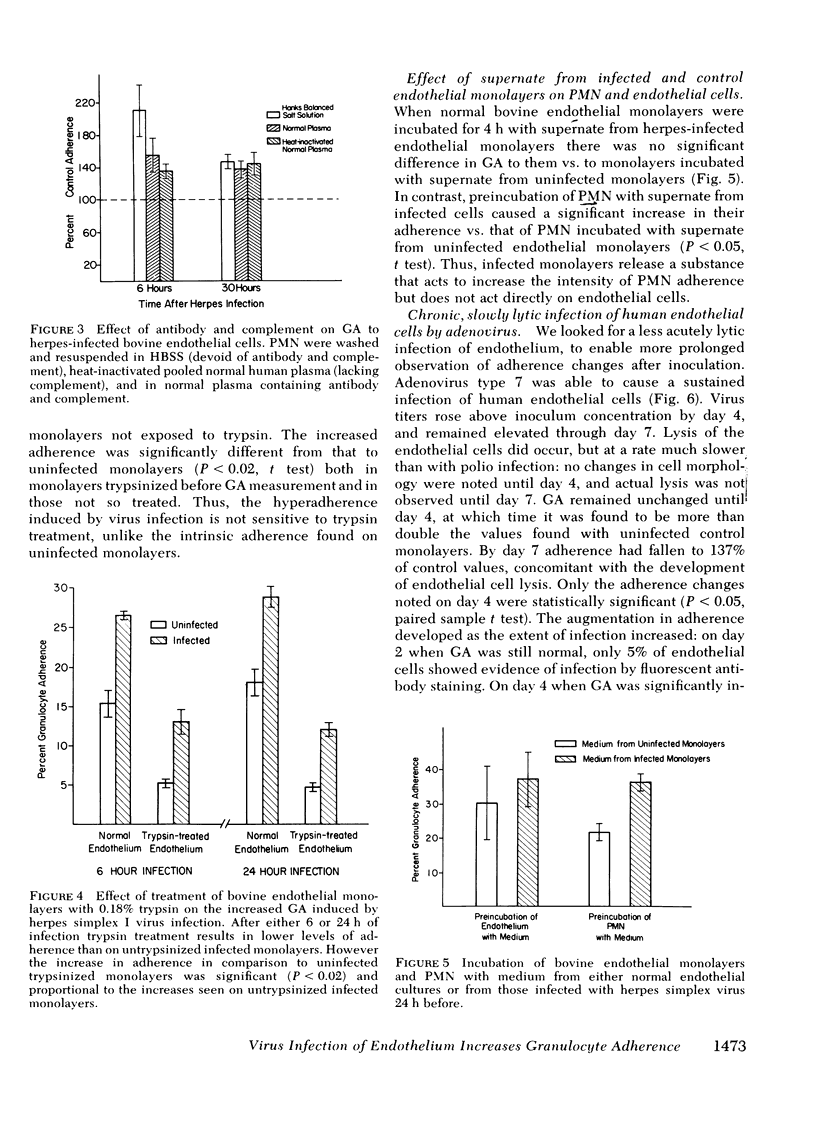
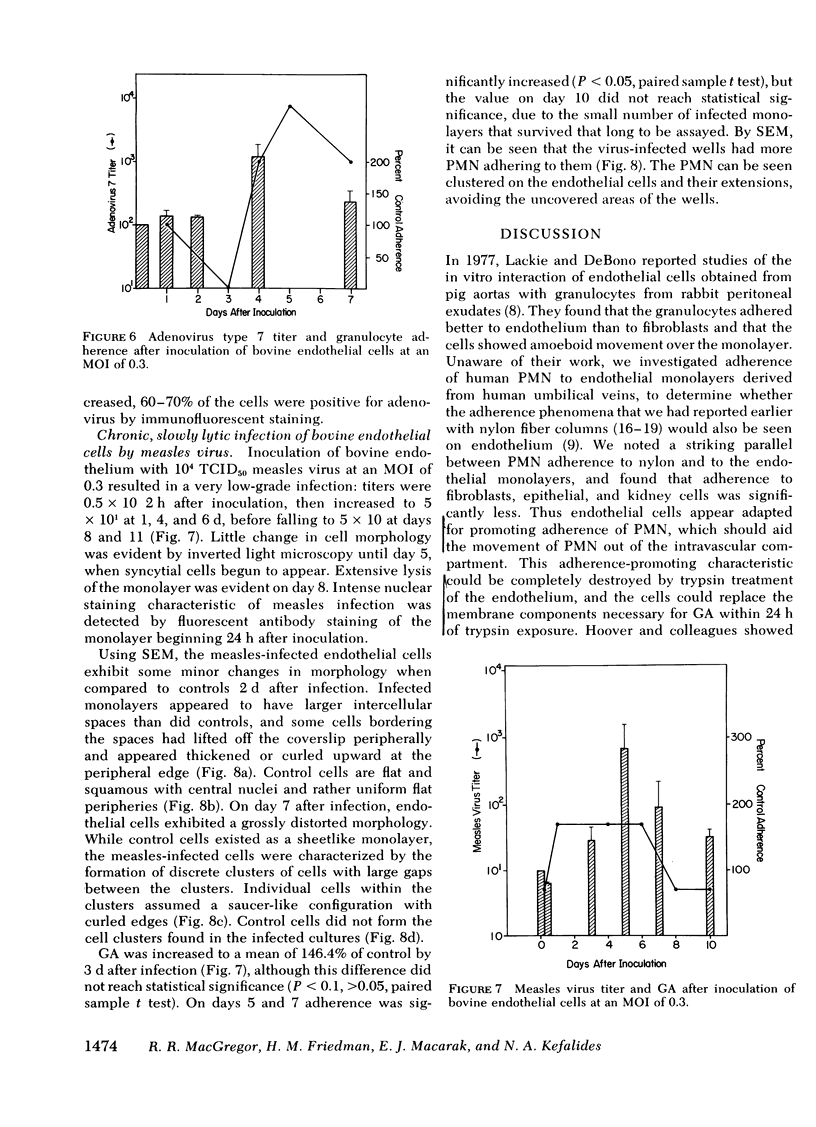
Adherence of human granulocytes was measured on endothelial monolayers of human and bovine origin, grown in 35-mm Diam petri dishes and in cluster wells. Adherence to human endothelium in petri dishes using 1.0 ml of whole blood averaged 17.9±3.7%, and to bovine endothelium was 20.3±3.7%. Cluster wells required only 1/5 the endothelial cells needed for petri dishes, and 0.25 ml of whole blood yielded average adherence of 26.2±3.4 to human cells and 28.0±3.7 to bovine in the wells. The impact of infection of the endothelium by different viruses on subsequent granulocyte adherence was measured. Polio virus produced an acute lytic infection of human endothelial cells, with associated increased adherence to 185.4% of control 24 h after inoculation. Significantly increased adherence was noted at 6 h, before detectable cytopathic effect. Herpes simplex type I caused a similar rapidly lytic infection of bovine endothelium associated with increased adherence to 213.7% of control 6 h after inoculation. This augmented adherence could be demonstrated when granulocytes were suspended in physiologic saline solution, showing that antibody and complement need not be present. Trypsin treatment of infected monolayers did not prevent the augmentation, and supernate from infected monolayers increased the adherence of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to normal, uninfected monolayers. Chronic, slowly lytic infections, lasting 7 d or more, were induced with adenovirus in human endothelium and with measles virus in bovine cells. Adherence increased as virus was noted in the cell cultures on day 4, several days before cytotoxicity was seen. Thus, chronic viral infection of the endothelium appears possible, and results in increased granulocyte adherence. In naturally occurring disease, such an infection may act synergistically with adherent granulocytes to damage the endothelium, and may represent an in vitro model of vasculitis.
Full text
PDF


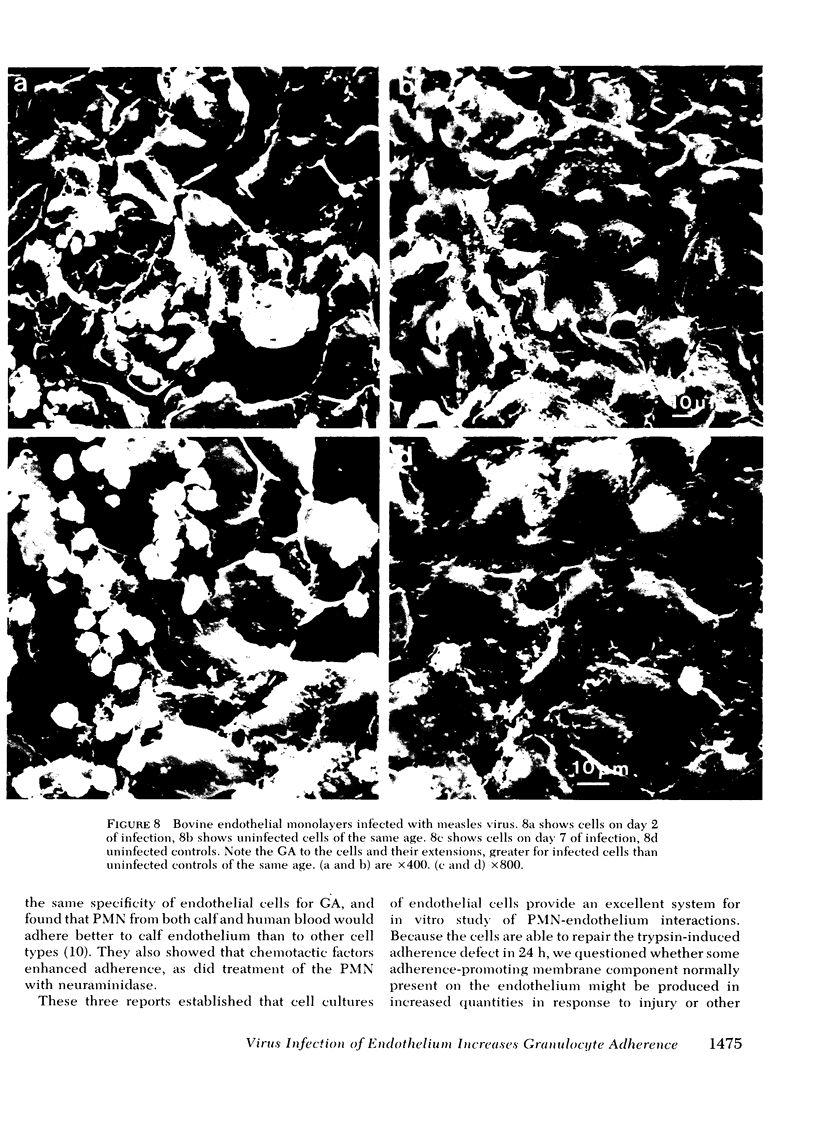


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON F., Jr, LANCASTER M. G. Studies on the pathogenesis of acute inflammation. II. The relationship of fibrinogen and fibrin to the leucocytic sticking reaction in ear chambers of rabbits injured by heat. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:45–64. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATHENS J. W., RAAB S. O., HAAB O. P., MAUER A. M., ASHENBRUCKER H., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Leukokinetic studies. III. The distribution of granulocytes in the blood of normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:159–164. doi: 10.1172/JCI104230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. S., Theofilopoulos A. N., Peters C. J., Loskutoff D. J., Brandt W. E., Dixon F. J. Replication of dengue and junin viruses in cultured rabbit and human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):776–781. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.776-781.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton A., Born G. V. Quantitative investigations of the adhesiveness of circulating polymorphonuclear leucocytes to blood vessel walls. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):447–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. L., Sheridan S. R. Blood leukocyte response to live measles vaccine. Am J Dis Child. 1967 Mar;113(3):301–304. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090180061002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTWRIGHT G. E., ATHENS J. W., WINTROBE M. M. THE KINETICS OF GRANULOPOIESIS IN NORMAL MAN. Blood. 1964 Dec;24:780–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D., White J. G., Dalmosso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement (C5-a)-induced granulocyte aggregation in vitro. A possible mechanism of complement-mediated leukostasis and leukopenia. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):260–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI108763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Growth and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa T. Further electron microscopic observations of herpes zoster virus. Arch Dermatol. 1971 Jan;103(1):45–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. L., Briggs R. T., Karnovsky M. J. The adhesive interaction between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):423–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackie J. M., de Bono D. Interactions of neutrophil granulocytes (PMNs) and endothelium in vitro. Microvasc Res. 1977 Jan;13(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentnek A. L., Schreiber A. D., MacGregor R. R. The induction of augmented granulocyte adherence by inflammation. Mediation by a plasma factor. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):1098–1103. doi: 10.1172/JCI108354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis L. J., Hoak J. C., Maca R. D., Fry G. L. Replication of human endothelial cells in culture. Science. 1973 Aug 3;181(4098):453–454. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4098.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T., FLOREY H. W. Electron micrographic observations on the emigration of leucocytes. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1960 Oct;45:343–348. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1960.sp001489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Macarak E. J., Kefalides N. A. Comparative adherence of granulocytes to endothelial monolayers and nylon fiber. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):697–702. doi: 10.1172/JCI108981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Spagnuolo P. J., Lentnek A. L. Inhibition of granulocyte adherence by ethanol, prednisone, and aspirin, measured with an assay system. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 26;291(13):642–646. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409262911302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R. The effect of anti-inflammatory agents and inflammation on granulocyte adherence. Evidence for regulation by plasma factors. Am J Med. 1976 Nov;61(5):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macarak E. J., Howard B. V., Kefalides N. A. Properties of calf endothelial cells in culture. Lab Invest. 1977 Jan;36(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraju M., Weitzman S., Baumann G. Viral hepatitis and agranulocytosis. Am J Dig Dis. 1973 Mar;18(3):247–252. doi: 10.1007/BF01071979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. P., Chiang W., Gale J. L., Chen N. S. A chick-embyo cell microtest for typing of Herpesvirus hominis (38531). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Feb;148(2):324–328. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]