Abstract
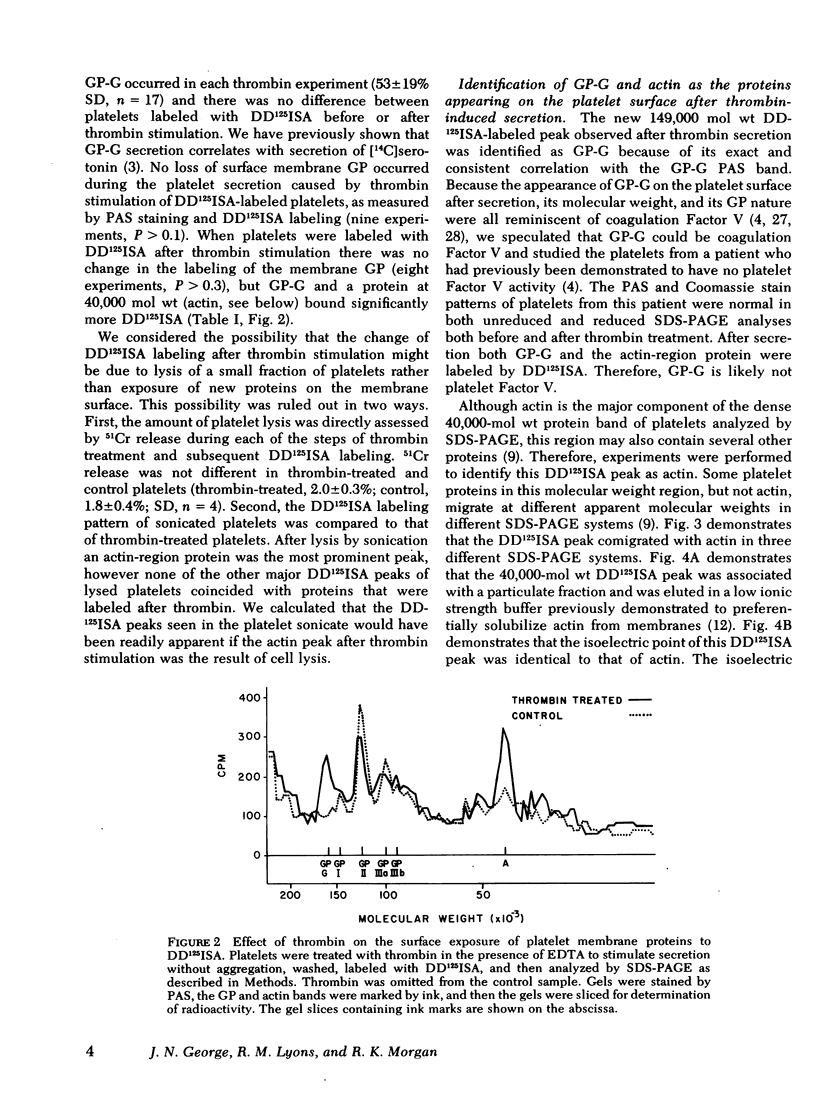
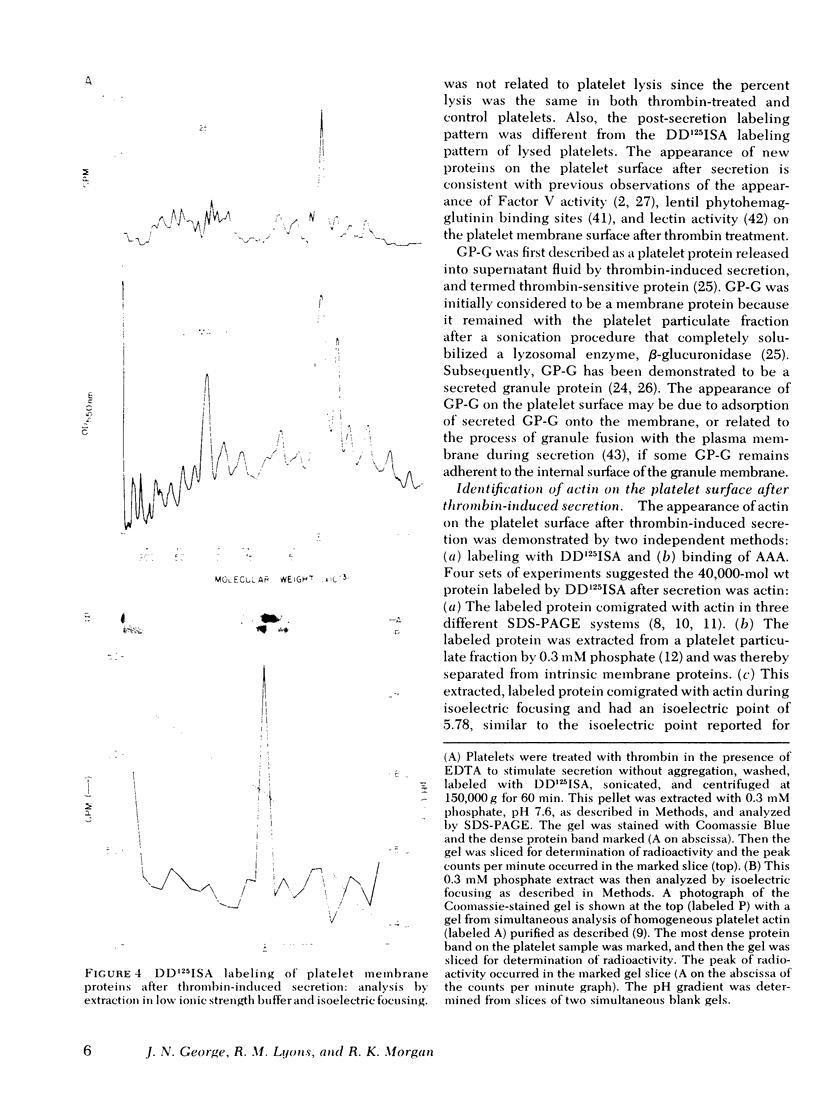
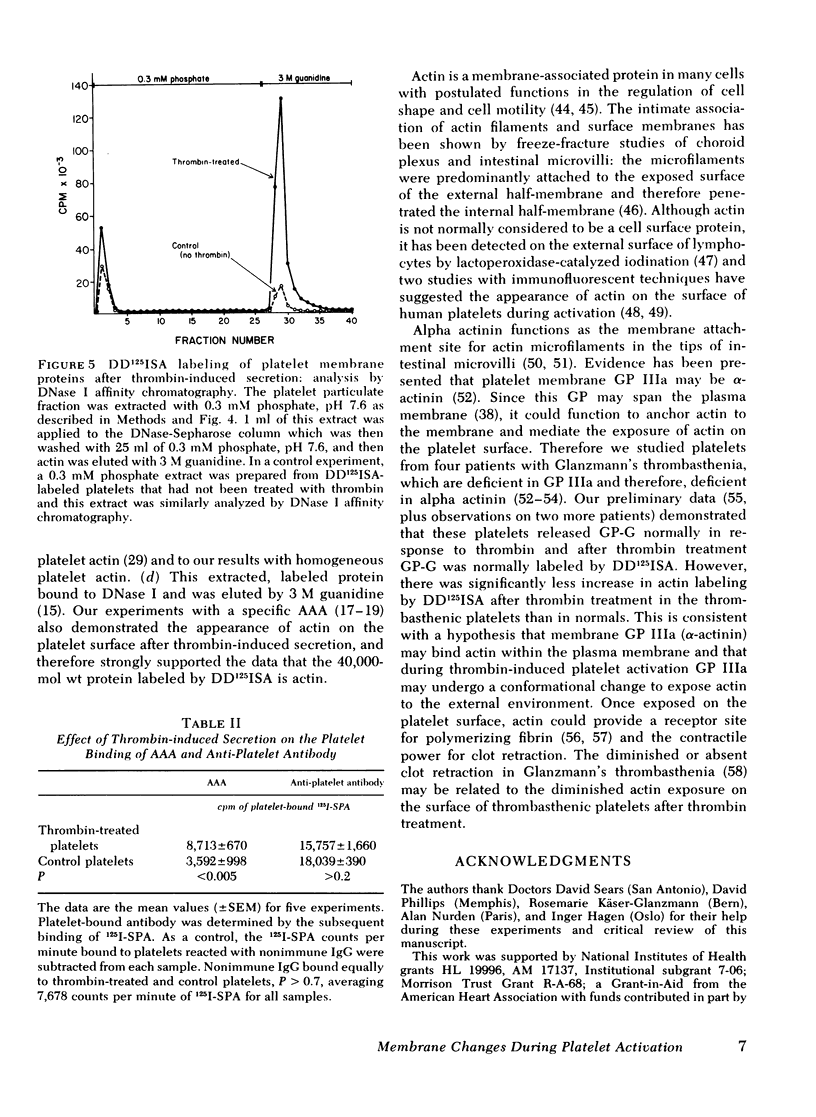
The effect of aggregation and secretion on membrane proteins was studied in washed human platelets. Reversible aggregation without secretion was stimulated by ADP and secretion without aggregation was stimulated by thrombin in the presence of EDTA. No loss of platelet surface glycoproteins occurred during reversible ADP-induced platelet aggregation, as measured by quantitative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of platelets that were labeled with 125I-diazotized diiodosulfanilic acid (DD125ISA) before ADP stimulation. Also, no new proteins became exposed on the platelet surface after ADP aggregation, as determined by DD125ISA labeling after stimulation. Thrombin-induced platelet secretion also caused no loss of platelet surface glycoproteins. However, after platelet secretion two new proteins were labeled by DD125ISA: (a) actin and (b) the 149,000-mol wt glycoprotein (termed GP-G), which is contained in platelet granules and secreted in response to thrombin. The identity of DD125ISA-labeled actin was confirmed by four criteria: (a) comigration with actin in three different sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis systems, (b) elution from a particulate fraction in low ionic strength buffer, (c) co-migration with actin in isoelectric focusing, and (d) binding to DNase I. The identity of actin and its appearance on the platelet surface after thrombin-induced secretion was also demonstrated by the greater binding of an anti-actin antibody to thrombin-treated platelets, measured with 125I-staphylococcal protein A.
Therefore, major platelet membrane changes occur after secretion but not after reversible aggregation. The platelet surface changes occurring with secretion may be important in the formation of irreversible platelet aggregates and in the final retraction of the blood clot.
Full text
PDF

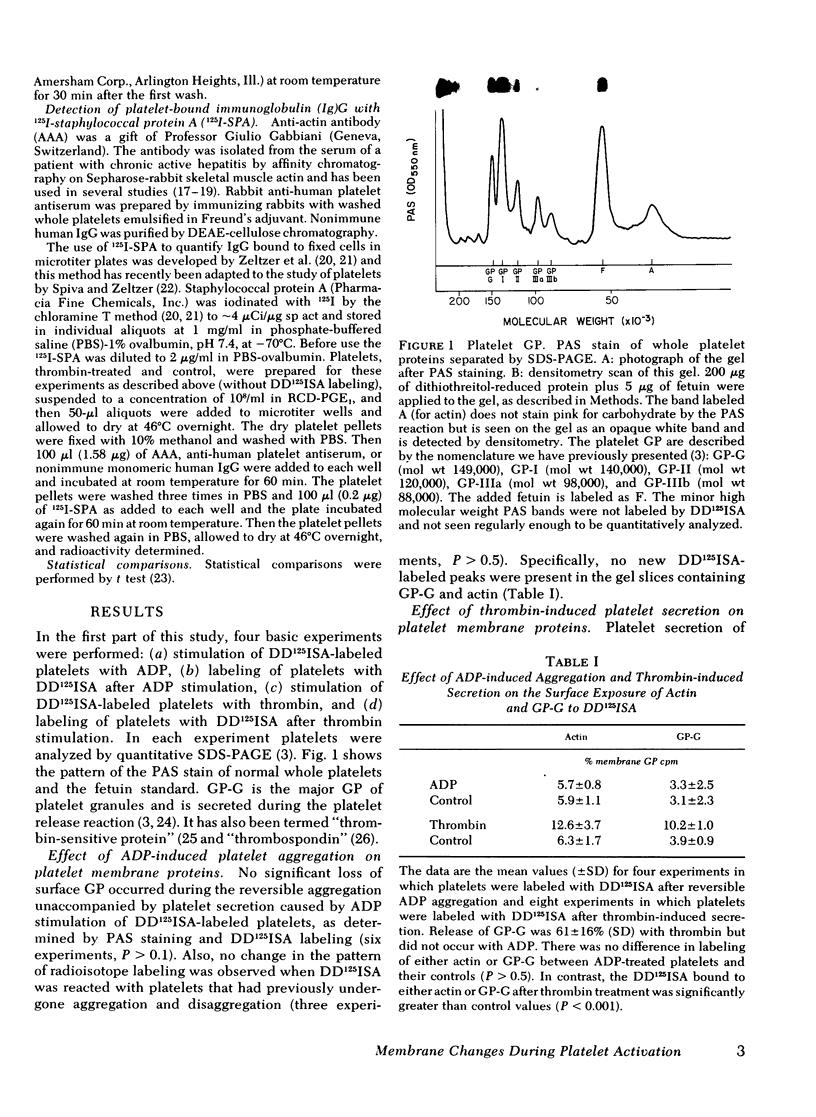



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aster R. H., Enright S. E. A platelet and granulocyte membrane defect in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: usefulness for the detection of platelet antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1199–1210. doi: 10.1172/JCI106084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. Isolation and properties of a thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2723–2731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Branton D. Selective association of spectrin with the cytoplasmic surface of human erythrocyte plasma membranes. Quantitative determination with purified (32P)spectrin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2753–2763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier C. A., Gabbiani G., Ryan G. B., Badonnel M. C., Majno G., Lüscher E. F. Binding of anti-actin autoantibodies to platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Apr 30;37(2):321–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M., Spudich J. A. Nonmuscle contractile proteins: the role of actin and myosin in cell motility and shape determination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:797–822. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. Factor V. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:109–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. W., Pardo J. V. alpha-Actinin localization in the junctional complex of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jan;80(1):203–210. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggle T. A., Toh B. H., Firkin B. G., Pfueller S. L. Human platelet actin: surface expression after platelet activation. Thromb Haemost. 1979 Aug 31;42(2):799–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagler J. R., Tillack T. W., Chaplin D. D., Majerus P. W. The effects of thrombin on phytohemagglutinin receptor sites in human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):541–553. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Chaponnier C., Hüttner I. Cytoplasmic filaments and gap junctions in epithelial cells and myofibroblasts during wound healing. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):561–568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Chaponnier C., Zumbe A., Vassalli P. Actin and tubulin co-cap with surface immunoglobulins in mouse B lymphocytes. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):697–698. doi: 10.1038/269697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Williams D. C., Minion F. C., Phillips D. R. Thrombin-induced platelet aggregation is mediated by a platelet plasma membrane-bound lectin. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1281–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.663608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Lewis P. C., Sears D. A. Studies on platelet plasma membranes. II. Characterization of surface proteins of rabbit platelets in vitro and during circulation in vivo using diazotized (125i)-diiodosulfanilic acid as a label. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Aug;88(2):247–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N. Studies on platelet plasma membranes. IV. Quantitative analysis of platelet membrane glycoproteins by (125I)-diazotized diiodosulfanilic acid labeling and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Sep;92(3):430–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Schollmeyer J. V., Phillips D. R., White J. G. alpha-Actinin deficiency in thrombasthenia: possible identity of alpha-actinin and glycoprotein III. Am J Pathol. 1979 Mar;94(3):509–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen I., Olsen T., Solum N. O. Studies on subcellular fractions of human platelets by the lactoperoxidase-iodination technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):214–225. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen I., Solum N. O., Olsen T. Membrane alterations in connection with the release reaction in human platelets as studied by the lactoperoxidase-iodination technique and by agglutination with bovine factor VIII-related protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 4;468(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Steckley S., Hammond D., Cheng C., Timmons S., Glick A. D., Des Prez R. M. Staphylococci-induced human platelet injury mediated by protein A and immunoglobulin G Fc fragment receptor. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):931–937. doi: 10.1172/JCI109559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. B., Smith G. M., Freuler F. The effect of intravenous adenosine diphosphate on the number of circulating platelets in experimental animals: inhibition by prostaglandin E1, dipyridamole, SH-869 and VK-774. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Feb 28;37(1):36–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymes K., Shulman S., Karpatkin S. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for bound anti-platelet antibody: studies on 45 patients with autoimmune platelet disorders. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Oct;94(4):639–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins C. S., Phillips D. R., Clemetson K. J., Meyer D., Larrieu M. J., Lüscher E. F. Platelet membrane glycoproteins implicated in ristocetin-induced aggregation. Studies of the proteins on platelets from patients with Bernard-Soulier syndrome and von Willebrand's disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):112–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laki K., Muszbek L. On the interaction of F-actin with fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 18;371(2):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon F., Huc C., Thomé F., Oriol C., Olomucki A. Human platelet actin. Evidence of beta and gamma forms and similarity of properties with sarcomeric actin. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec;81(3):571–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J. W., Slayter H. S., Coligan J. E. Isolation and characterization of a high molecular weight glycoprotein from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8609–8616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Lindberg U. Actin is the naturally occurring inhibitor of deoxyribonuclease I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4742–4746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Atherton R. M. Characterization of a platelet protein phosphorylated during the thrombin-induced release reaction. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):544–552. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNutt N. S. A thin-section and freeze-fracture study of microfilament-membrane attachments in choroid plexus and intestinal microvilli. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):774–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Majerus D. W., Majerus P. W. Patients with congenital factor V deficiency have decreased factor Xa binding sites on their platelets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):824–831. doi: 10.1172/JCI109194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Tilney L. G. Organization of an actin filament-membrane complex. Filament polarity and membrane attachment in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):725–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroff G., Jamieson G. A. Biochemical aspects of platelet function. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1978;28:25–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Vaheri A., Choate J. J., Gahmberg C. G. Action of thrombin on surface glycoproteins of human platelets. Blood. 1979 Mar;53(3):437–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Perry D. W., Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A. Preparation of suspensions of washed platelets from humans. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):193–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Perry D. W., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Packham M. A. Factors responsible for ADP-induced release reaction of human platelets. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1757–1765. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R., Levine R., Jaffe E. Synthesis of actin by cultured guinea pig megakaryocytes. Complex formation with fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 21;543(1):91–105. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. The different glycoprotein abnormalities in thrombasthenic and Bernard-Soulier platelets. Semin Hematol. 1979 Jul;16(3):234–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I., Lavine K. K. Factor V activity of platelets: evidence for an activated factor V molecule and for a platelet activator. Blood. 1977 May;49(5):819–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Auger J., Barber B. H., Edwards A. J., Walsh F. S., Crumpton M. J. Actin may be present on the lymphocyte surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4484–4488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet membrane defects in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Evidence for decreased amounts of two major glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):535–545. doi: 10.1172/JCI108805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet plasma membrane glycoproteins. Identification of a proteolytic substrate for thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 25;75(4):940–947. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Thrombin substrates and the proteolytic site of thrombin action on human-platelet plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):218–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Chaponnier C., Jeanrenaud B., Gabbiani G. Actin microfilaments, cell shape, and secretory processes in isolated rat hepatocytes. Effect of phalloidin and cytochalasin D. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):592–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Gerrard J. M. Platelet ultrastructure in relation to platelet function. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1978;28:5–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeltzer P. M., Pepose J. S., Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Microassay for immunoglobulin G antibodies to Treponema pallidum with radioiodinated protein A from staphylococcus aureus: immunoglobulin G response in experimental syphilis in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):163–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.163-170.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeltzer P. M., Seeger R. C. Microassay using radioiodinated protein A from Staphylococcus aureus for antibodies bound to cell surface antigens of adherent tumor cells. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(1-2):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]