Abstract
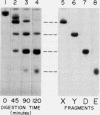
We have examined rotary shadowed, purified plasmic fragments of human fibrinogen with the electron microscope and have determined the relation of these fragments to the intact fibrinogen molecule. Both intact fibrinogen and its earliest cleavage product, fragment X, are trinodular. The next largest product, fragment Y, consists of two linked nodules. The two terminal products, fragments D and E, are single nodules. From measurements of simultaneously shadowed specimens of these different species, we conclude that the outer nodules of the trinodular fibrinogen molecule are the fragment D-containing regions and the central nodule is the fragment E-containing region.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blakey P. R., Groom M. J., Turner R. L. The conformation of fibrinogen and fibrin: an electron microscopy study. Br J Haematol. 1977 Mar;35(3):437–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzynski A. Z. Difference in conformation of fibrinogen degradation products as revealed by hydrogen exchange and spectropolarimetry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 23;229(3):663–671. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. P., Shurley H. M., Vickroy M. A facile separation of fragments D and E from the fibrinogen-fibrin degradation products of three mammalian species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 6;61(1):66–71. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell B. A., Doolittle R. F. The amino acid sequence of a 27-residue peptide released from the alpha-chain carboxy-terminus during the plasmic digestion of human fibrinogen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 9;71(3):754–761. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90895-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. W., Mihalyi E. Conformation of fibrinogen: calorimetric evidence for a three-nodular structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4125–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Structural aspects of the fibrinogen to fibrin conversion. Adv Protein Chem. 1973;27:1–109. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60446-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Structure and function of fibrinogen. Horiz Biochem Biophys. 1977;3:164–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson E. W., Fretto L. J., McKee P. A. A re-examination of the cleavage of fibrinogen and fibrin by plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7210–7218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. E., Erickson H. P. Trinodular structure of fibrinogen. Confirmation by both shadowing and negative stain electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL C. E., SLAYTER H. S. The fibrinogen molecule: its size, shape, and mode of polymerization. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):11–16. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkate F., Timan G. Protective effect of calcium in the plasmin degradation of fibrinogen and fibrin fragments D. Thromb Res. 1977 Jun;10(6):803–812. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopec M. Biological properties of fibrinogen derivatives relevant to the function of cardiovascular system and immuno-inflammatory reaction. New Istanbul Contrib Clin Sci. 1977 Sep;12(1):43–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köppel G. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur Gestalt und zum makromolekularen Bau des Fibrinogen molekïls und der Fibrinfasern. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;77(4):443–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R., Carroll W. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. I. Physicochemical and immunological characterization. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2111–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. II. Mechanism of their anticoagulant activity. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2120–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSENZWEIG V., SELIGMANN M., PELMONT J., GRABAR P. [The products of degradation of human fibrinogen by plasmin. I. Separation and physicochemical properties]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Mar;100:377–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Stewart G. J., Marder V. J. Formation of highly ordered polymers from fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 17;221(2):326–341. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouit L., Marcille G., Suscillon M., Hollard D. Etude en microscopie électronique de différentes etapes de la fibrinoformation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Jul 31;27(3):559–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayter H. S. High-resolution metal replication of macromolecules. Ultramicroscopy. 1976 Sep-Oct;1(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(76)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachurska J., Lopaciuk S., Gerdin B., Saldeen T., Korościk A., Kopeć M. Effects of proteolytic degradation products of human fibrinogen and of human factor VIII on platelet aggregation and vascular permeability. Thromb Res. 1979;15(5-6):663–672. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]