Abstract
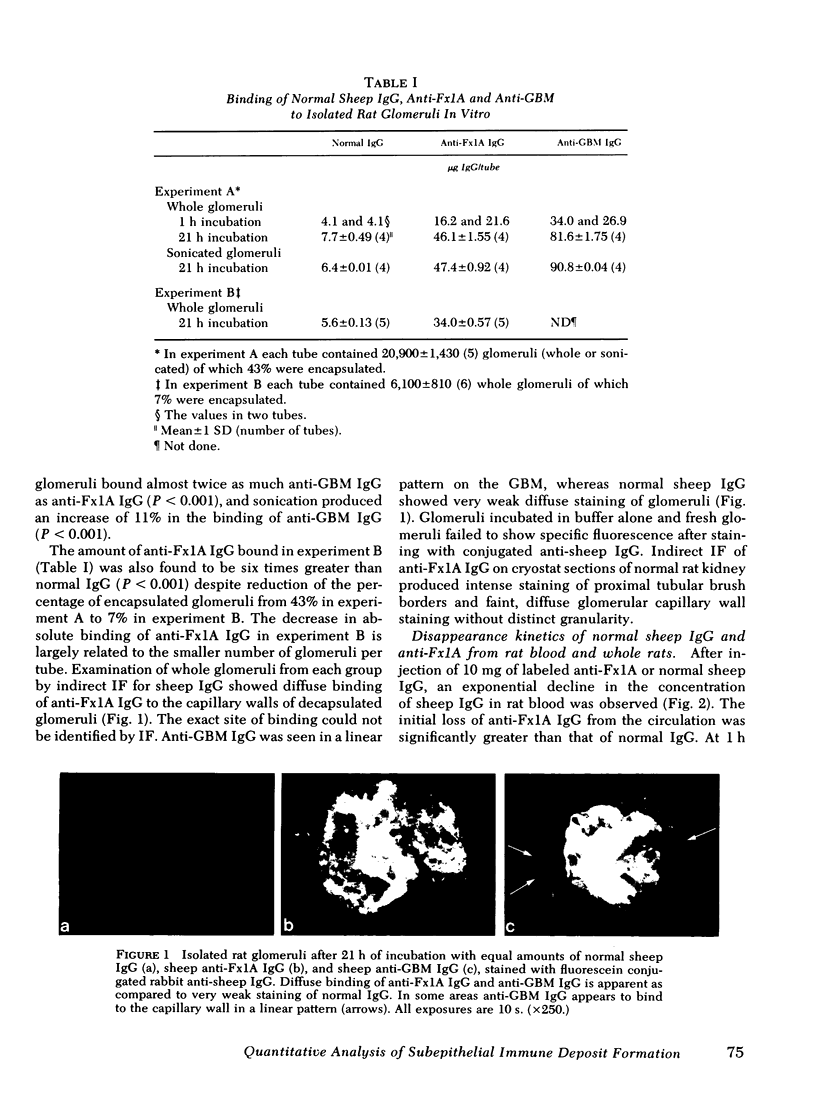
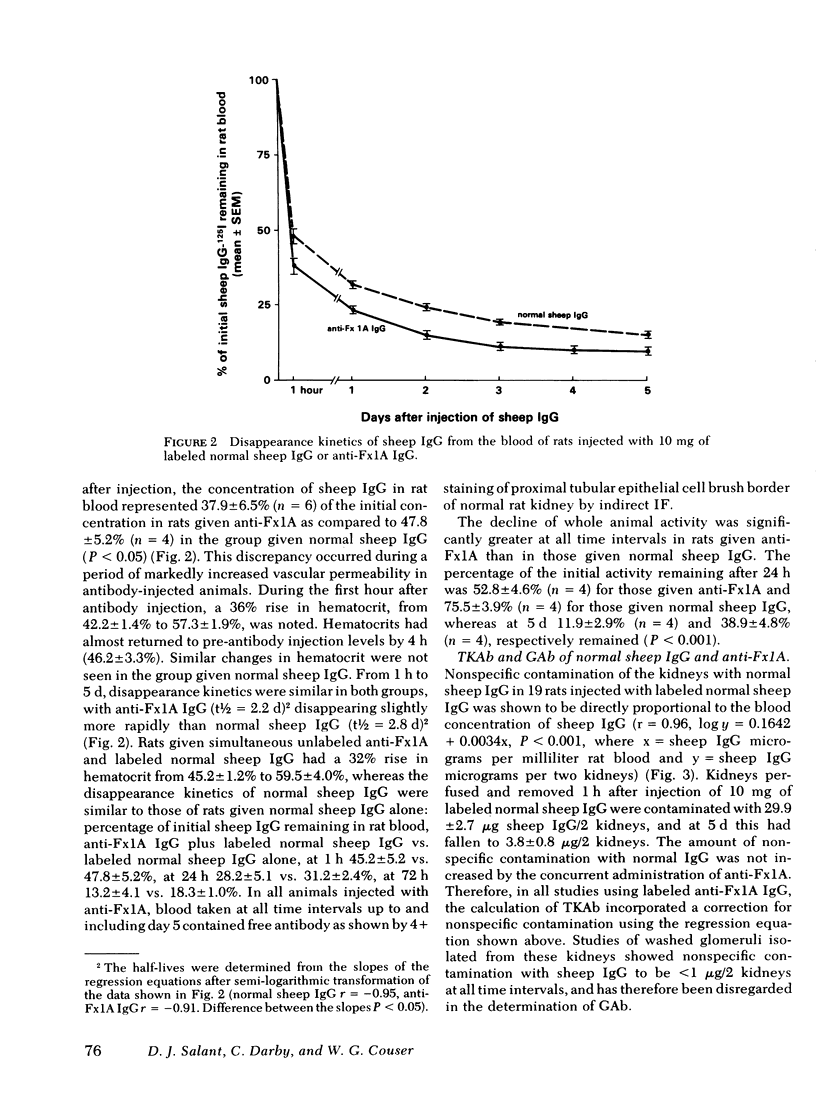
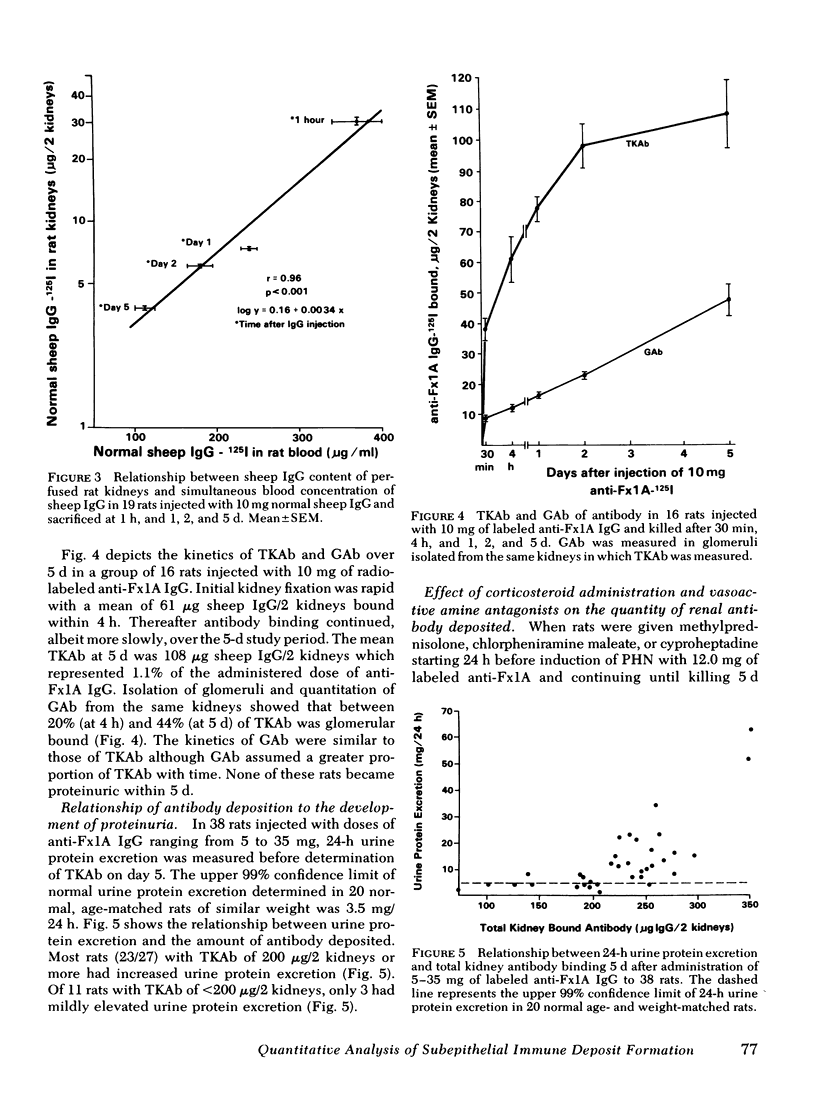
Quantitation of immune deposit formation in glomeruli and correlation with immunohistologic and functional changes has been accomplished only in models of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody-induced nephritis, or indirectly in immune complex disease by measuring radiolabeled antigen deposition. The kinetics of subepithelial immune deposit formation and the relationship between the quantity of antibody deposited and proteinuria are defined here for the first time in an established model of membranous immune complex nephritis (passive Heymann nephritis) induced by a single intravenous injection of 125I-labeled sheep immunoglobulin (Ig)G antibody to rat tubular brush border antigen (Fx1A). Measurement of antibody deposition in glomeruli (GAb) isolated from rats injected with 10 mg of anti-Fx1A demonstrated a mean of 12 μg GAb in 4 h, which increased linearly to 48 μg in 5 d. GAb represented only 20 and 44% of total kidney antibody binding at these times. Proteinuria occurred only after 4-5 d of antibody deposition in rats with total kidney antibody binding exceeding ∼200 μg/2 kidneys. Steroid treatment and vasoactive amine blockade did not significantly alter the quantity or localization of immune deposits. It was also demonstrated that isolated rat glomeruli specifically bound nephritogenic quantities of anti-Fx1A in vitro within hours. Analysis of the quantitative aspects of glomerular antibody deposition in vivo and glomerular antibody binding in vitro provides additional evidence that subepithelial immune deposits in passive Heymann nephritis may form in situ by reaction of free antibody with antigenic constitutents of the normal rat glomerulus. The observed kinetics of deposit formation differ markedly from those in anti-glomerular basement membrane disease and suggest a role for factors in addition to antigen-antibody interaction in determining this unique pattern of glomerular immune deposit formation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann U. Apparent escape rate of RIHSA and 51Cr-labeled erythrocytes from the blood of volume-expanded rats. Am J Physiol. 1978 May;234(5):F386–F392. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.5.F386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barabas A. Z., Lannigan R. Induction of an autologous immune-complex glomerulonephritis in the rat by intravenous injection of heterologous anti-rat kidney tubular antibody. I. Production of chronic progressive immune-complex glomerulonephritis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Feb;55(1):47–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barratt L. J., Wallin J. D., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Influence of volume expansion on single-nephron filtration rate and plasma flow in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1973 Mar;224(3):643–650. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.3.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Wilson C. B. Acute effects of antiglomerular basement membrane antibody on the process of glomerular filtration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):899–911. doi: 10.1172/JCI108543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Jermanovich N. B., Belok S., Stilmant M. M., Hoyer J. R. Effect of aminonucleoside nephrosis on immune complex localization in autologous immune complex nephropathy in rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):561–572. doi: 10.1172/JCI108967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Lewis E. J. Laboratory suggestion. A method for preservation of immunofluorescence in renal tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;61(6):873–876. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.6.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Steinmuller D. R., Stilmant M. M., Salant D. J., Lowenstein L. M. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1275–1287. doi: 10.1172/JCI109248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., FELDMAN J. D., VAZQUEZ J. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. The pathogenesis of a laboratory model resembling the spectrum of human glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:899–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. I. Identification and isolation of the pathogenetic antigen. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):555–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleuren G. J., vd Lee R., Greben H. A., Van Damme B. J., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. IV. Investigations into the pathogenesis of the model. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):496–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gang N. F., Mautner W., Kalant N. Nephrotoxic serum nephritis. II. Chemical, morphologic, and functional correlates of glomerular basement membrane at the onset of proteinuria. Lab Invest. 1970 Aug;23(2):150–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassock R. J., Edgington T. S., Watson J. I., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. II. The pathogenetic mechanism. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):573–588. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Case J. B., Mannik M. Effect of cortisone on the disappearance kinetics and tissue localization of soluble immune complexes. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1153–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Mannik M. The disappearance kinetics of soluble immune complexes prepared with reduced and alkylated antibodies and with intact antibodies in mice. Lab Invest. 1976 Sep;35(3):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Striker G. E., Mannik M. The glomerular deposition of soluble immune complexes prepared with reduced and alkylated antibodies and with intact antibodies in mice. Lab Invest. 1976 Sep;35(3):293–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoedemaeker P. J., Feenstra K., Nijkeuter A., Arends A. Ultrastructural localization of heterologous nephrotoxic antibody in the glomerular basement membrane of the rat. Lab Invest. 1972 May;26(5):610–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Arend W. P. Fate of preformed immune complexes in rabbits and rhesus monkeys. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):19s–31s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse T., Fukasawa T., Hirokawa N., Oike S., Miyakawa Y. The pathogenesis of experimental membranous glomerulonephritis induced with homologous nephritogenic tubular antigen. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1347–1362. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennke H. G., Cotran R. S., Venkatachalam M. A. Role of molecular charge in glomerular permeability. Tracer studies with cationized ferritins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):638–646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. Membranous glomerulonephritis: current status. Hum Pathol. 1971 Jun;2(2):209–231. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(71)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. B., Hein S. J., Karnovsky M. J. Glomerular permeability to proteins. Effects of hemodynamic factors on the distribution of endogenous immunoglobulin G and exogenous catalase in the rat glomerulus. Lab Invest. 1976 Apr;34(4):415–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salant D. J., Belok S., Stilmant M. M., Darby C., Couser W. G. Determinants of glomerular localization of subepithelial immune deposits: effects of altered antigen to antibody ratio, steroids, vasoactive amine antagonists, and aminonucleoside of puromycin on passive Heymann nephritis in rats. Lab Invest. 1979 Jul;41(1):89–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. J., Amos N., Evans D. J., Thomson N. M., Peters D. K. Guinea-pig nephrotoxic nephritis. I. The role of complement and polymorphonuclear leucocytes and the effect of antibody subclass and fragments in the heterologous phase. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Mar;19(3):499–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strassberg J., Paule J., Gonick H. C., Maxwell M. H., Kleeman C. R. The quantitative estimation of perfusible glomeruli and the collagen and non-collagen nitrogen of the normal kidney. Nephron. 1967;4(6):384–393. doi: 10.1159/000179597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E. R., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. V. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION OF NEPHROTOXIC ANTIBODIES WITH TISSUE OF THE RAT. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:697–714. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme B. J., Fleuren G. J., Bakker W. W., Vernier R. L., Hoedemaeker P. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1978 Apr;38(4):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A., Bockhorn H., Kozima K., Sasaki M. Electron microscopic localization of the nephrotoxic antibody in the glomeruli of the rat after intravenous application of purified nephritogenic antibody-ferritin conjugates. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):867–878. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolism of immunoglobulins. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:1–110. doi: 10.1159/000385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Quantitation of acute and chronic serum sickness in the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):7s–8s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Es L. A., Blok A. P., Schoenfield L., Glassock R. J. Chronic nephritis induced by antibodies reacting with glomerular-bound immune complexes. Kidney Int. 1977 Feb;11(2):106–115. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




