Abstract
Insulin and such insulinlike growth factors as multiplication stimulating activity (MSA) are related polypeptides that have common biological activities. Both insulin and MSA produce acute metabolic responses (stimulation of glucose oxidation in isolated fat cells) as well as growth effects (stimulation of [3H]thymidine incorporation into DNA in cultured fibroblasts). In addition, most cells have separate receptors for insulin and insulinlike growth factors, and both peptides have weaker affinity for each other's specific receptors than for their own. To determine, therefore, whether these effects are mediated by receptors for insulin, insulinlike growth factors, or both, we have selectively blocked insulin receptors with a specific antagonist, namely Fab fragments derived from naturally occurring antibodies to the insulin receptor.
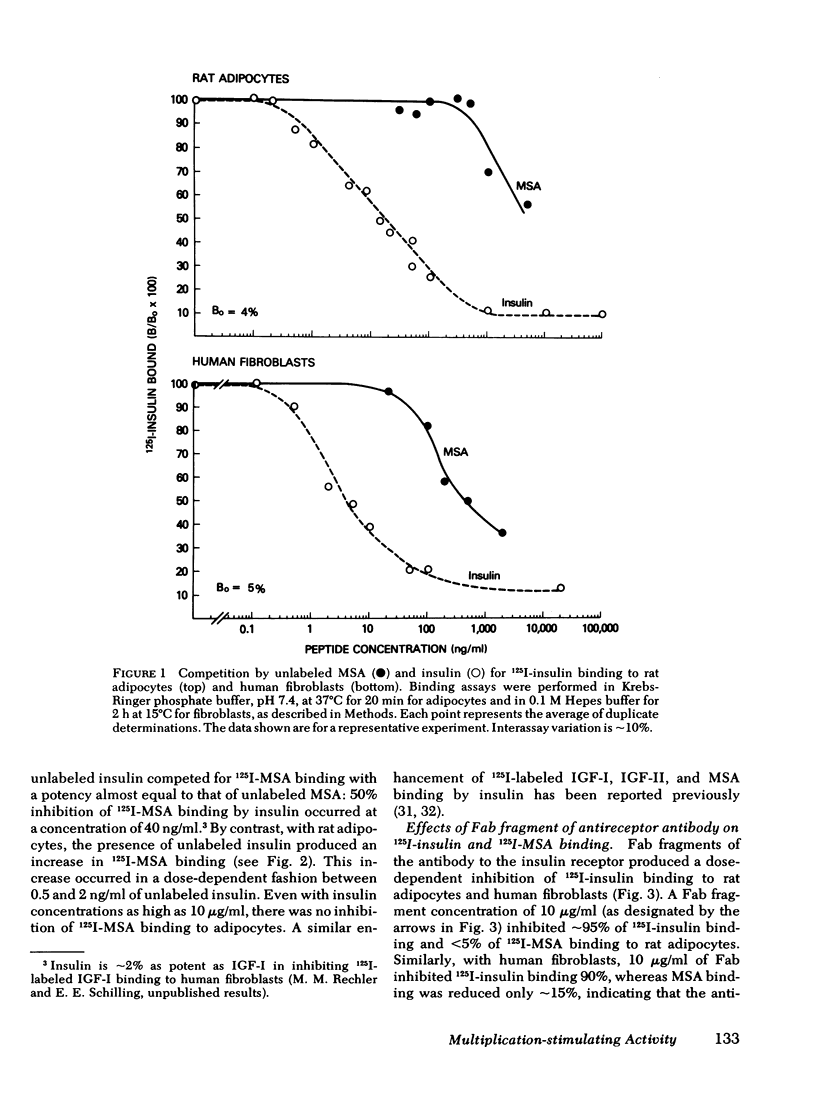
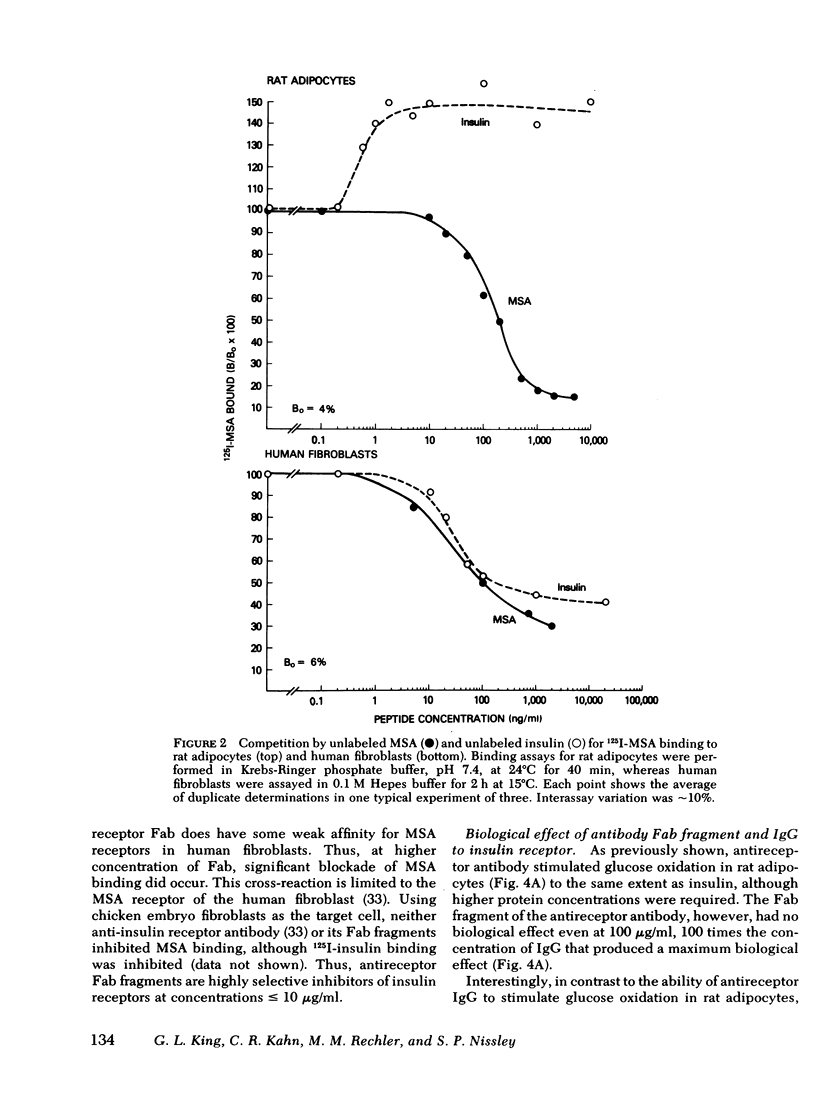
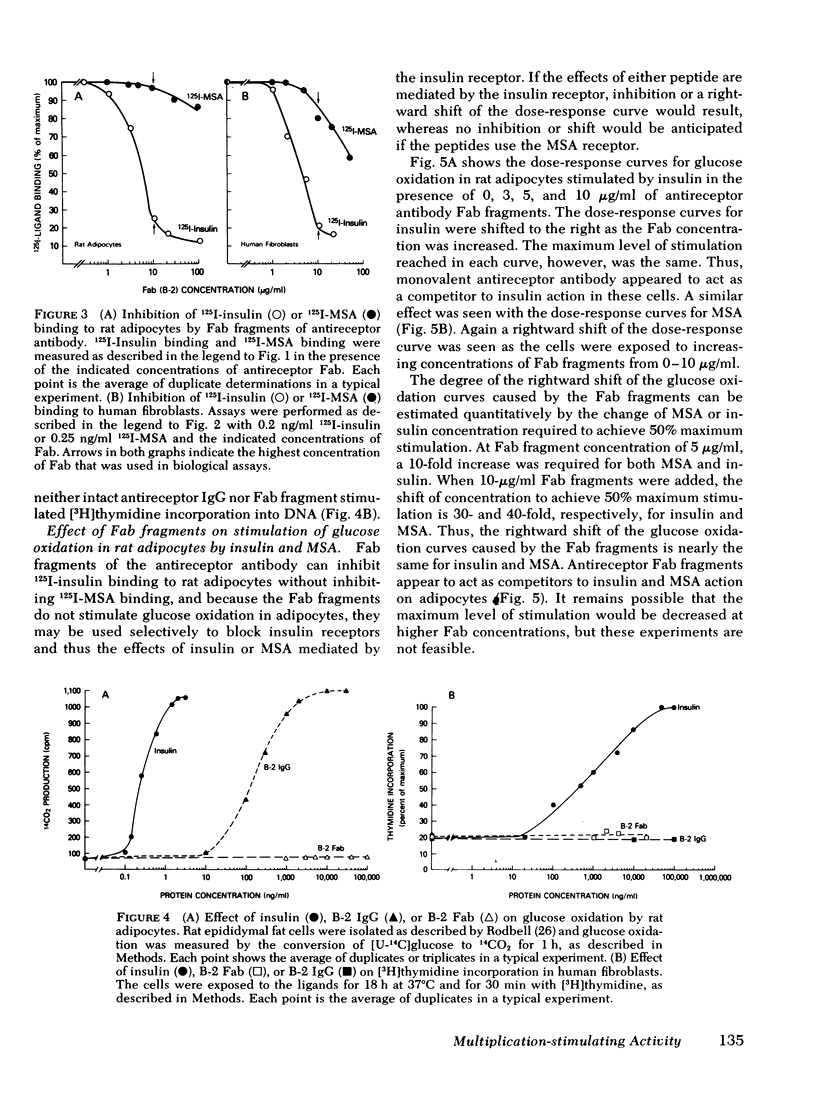
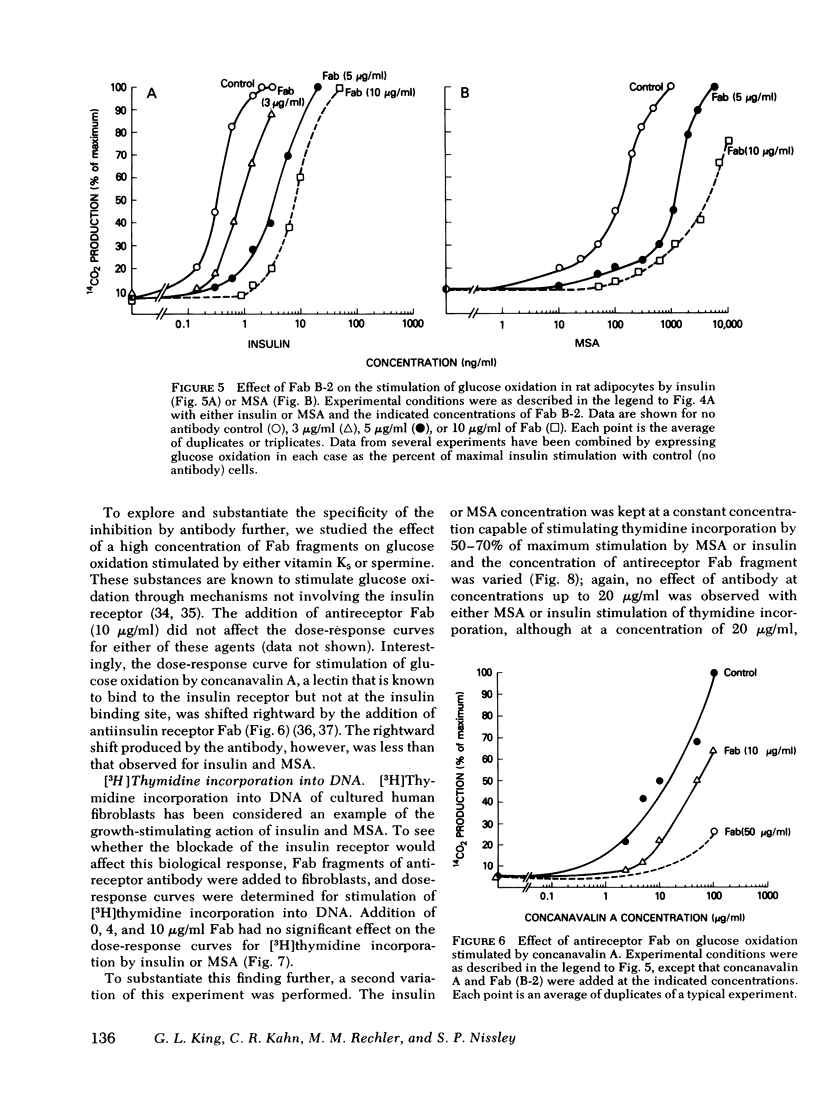
In rat adipocytes, 10 μg/ml of antireceptor Fab inhibited insulin binding by 90%, whereas it inhibited MSA binding <5%. The anti-insulin receptor Fab is without intrinsic biological activity, but acts as a competitive inhibitor of insulin receptors. Blockade of insulin receptors with Fab fragments produced a 30-fold rightward shift in the dose response for stimulation of glucose oxidation by both insulin and MSA. The dose-response curves for stimulation of oxidation by vitamin K5 and spermine, agents that stimulate glucose oxidation through noninsulin receptor pathways, were not affected by the blockade of insulin receptors with Fab antibody fragments. These data suggest that this acute metabolic effect of both insulin and MSA is mediated via the insulin receptor.
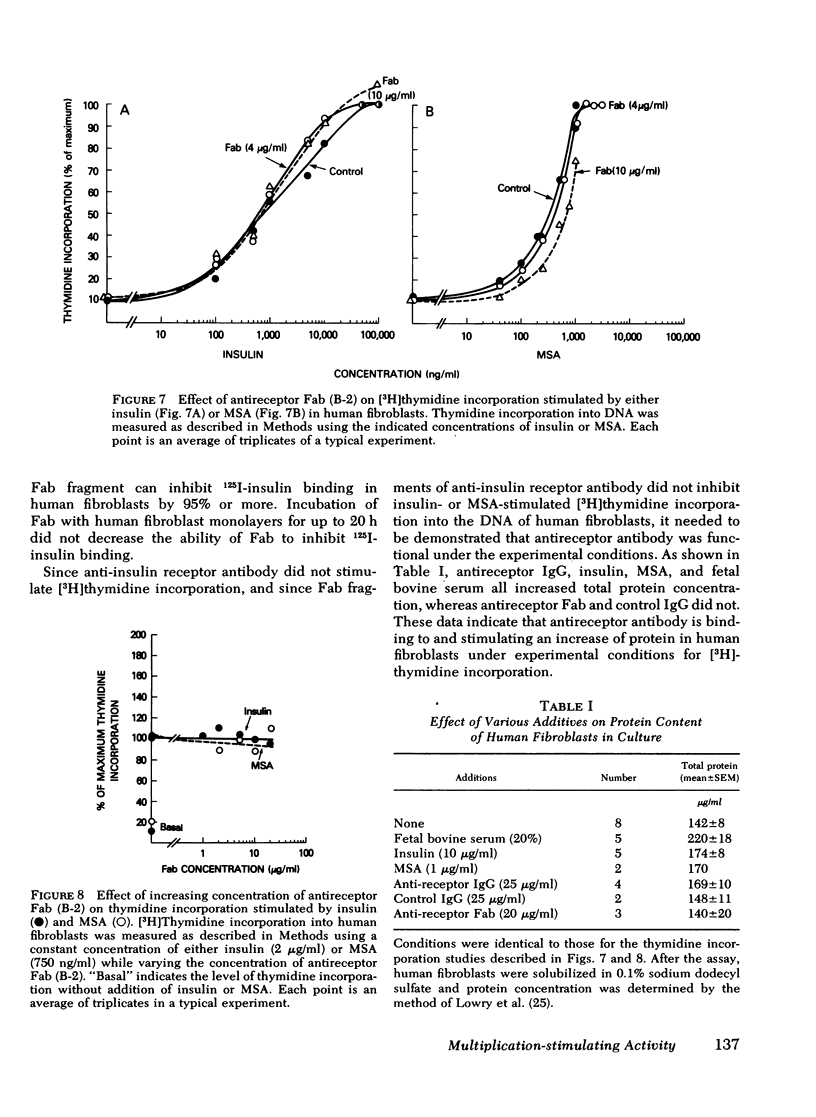
In cultured human fibroblasts, 10 μg/ml of Fab inhibited insulin binding by 90% and MSA binding by 15%. In fibroblasts, however, blockade of the insulin receptor did not alter the dose response for stimulation of thymidine incorporation into DNA by either insulin or MSA. Furthermore, intact antireceptor antibody immunoglobulin (Ig)G, which produces multiple other insulinlike effects, and Fab fragments of antireceptor antibody did not stimulate thymidine incorporation. These data demonstrate directly that the insulin receptor mediates the metabolic effects of insulin and MSA, whereas the growth-promoting action of both peptides is mediated by the MSA receptor or other growth factors.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buxtorf U. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. IV. Effects of purified nonsuppressible insulin-like activity and of insulin on protein synthesis of adipose tissue from [14C]glucose, [14C]pyruvate and [14C]glycine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 6;177(3):512–520. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Tell G. P. Insulin-like activity of concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin--direct interactions with insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Lynn W. S. Stimulation of glucose metabolism by lectins in isolated white fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 28;297(2):368–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Jarrett D. B., Roth J. Characterization of antibodies to the insulin receptor: a cause of insulin-resistant diabetes in man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1442–1449. doi: 10.1172/JCI108600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Bar R. S. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.170678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Gliemann J. Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Flier J. S., Roth J., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Immunoprecipitation of the insulin receptor: a sensitive assay for receptor antibodies and a specific technique for receptor purification. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jan;48(1):59–65. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Competitive binding of somatomedin to the insulin receptors of adipocytes, chondrocytes, and liver membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2351–2353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Hjelm K., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Its isolation by affinity chromatography and its use as an immunosorbent for isolation of immunoglobulins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80680-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. L., Jarrett D. B., Flier J. S. Direct demonstration that receptor crosslinking or aggregation is important in insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4209–4213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K., Filier J. S., Jarrett D. B. Effects of autoantibodies to the insulin receptor on isolated adipocytes. Studies of insulin binding and insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1094–1106. doi: 10.1172/JCI108861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Flier J. S., Bar R. S., Archer J. A., Gorden P., Martin M. M., Roth J. The syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Insulin-receptor disorders in man. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):739–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Amatruda J. M., Lockwood D. H. Studies of glucose transport system of fat cells: effects of insulin and insulin mimickers. Am J Physiol. 1978 May;234(5):E484–E488. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.5.E484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood D. H., East L. E. Studies of the insulin-like actions of polyamines on lipid and glucose metabolism in adipose tissue cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7717–7722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megyesi K., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Froesch E. R., Humbel R. E., Zapf J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin and non-suppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-s): evidence for separate plasma membrane receptor sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):307–315. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M. Purification and characterization of multiplication-stimulating activity. Insulin-like growth factors purified from rat-liver-cell-conditioned medium. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):387–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA): a somatomedin-like polypeptide from cultured rat liver cells. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1978 May;(48):167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Eisen H. J., Higa O. Z., Nissley P., Moses A. C., Schilling E. E., Fennoy I., Bruni C. B., Phillips L. S., Baird K. L. Characterization of a somatomedin (insulin-like growth factor) synthesized by fetal rat liver organ cultures. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7942–7950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Fryklund L., Nissley S., Hall K., Podskalny J. M., Skottner A., Moses A. C. Purified human somatomedin A and rat multiplication stimulating activity. Mitogens for cultured fibroblasts that cross-react with the same growth peptide receptors. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):5–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb11991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P., Podskalny J. M., Moses A. C., Fryklund L. Identification of a receptor for somatomedin-like polypeptides in human fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 May;44(5):820–831. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-5-820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Goldfine I. D., Wells C. A. DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts: stimulation by insulin and by nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Sep;39(3):512–521. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-3-512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M. Insulin receptors in cultured human fibroblasts. Diabetes. 1976 Apr;25(4):250–255. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.4.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Nissley S. P. Characterization of the binding of multiplication-stimulating activity to a receptor for growth polypeptides in chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3898–3910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Nissley S. P. Interaction of multiplication-stimulating activity with chick embryo fibroblasts demonstrates a growth receptor. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):134–136. doi: 10.1038/259134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Methods for assessing immunologic and biologic properties of iodinated peptide hormones. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:223–233. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Effects of insulin and NSILA on adipocytes of normal and diabetic rats: receptor binding, glucose transport and glucose metabolism. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):243–249. doi: 10.1007/BF01219707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano K., Hall K., Fryklund L., Holmgren A., Sievertsson H., Uthne K. The binding of insulin and somatomedin A to human placental membrane. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1975 Sep;80(1):14–31. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0800014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood L. E., Hintz R. L., Voina S. J., Van Wyk J. J. Human somatomedin, the growth hormone dependent sulfation factor, is antilipolytic. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Aug;35(2):194–198. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-2-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) from human serum: recent accomplishments and their physiologic implications. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12):1803–1828. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II: some biological actions and receptor binding characteristics of two purified constituents of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


