Abstract
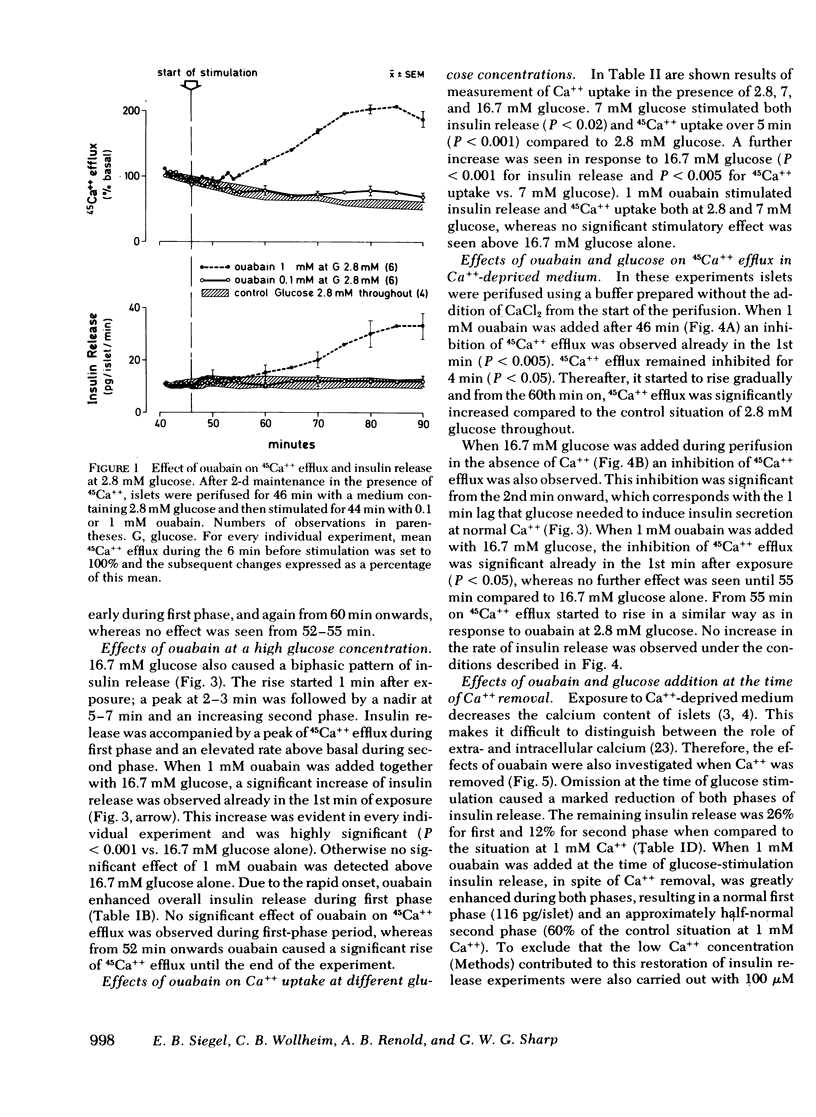
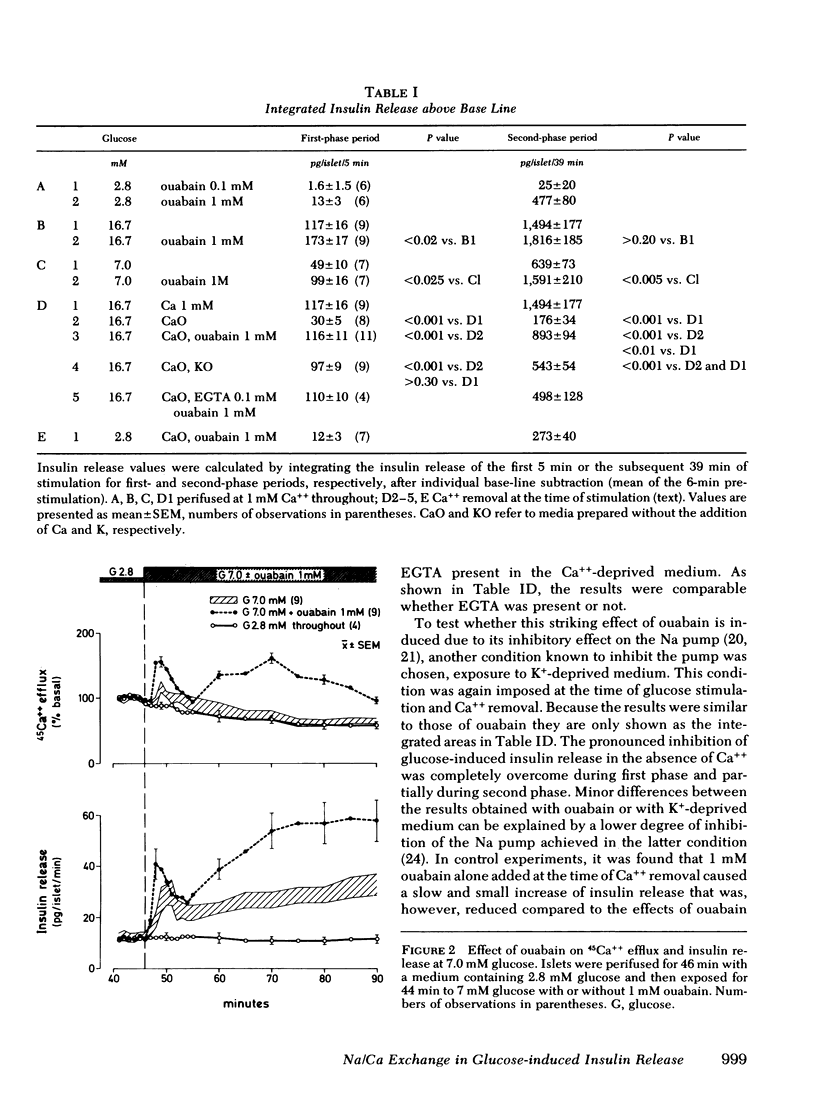
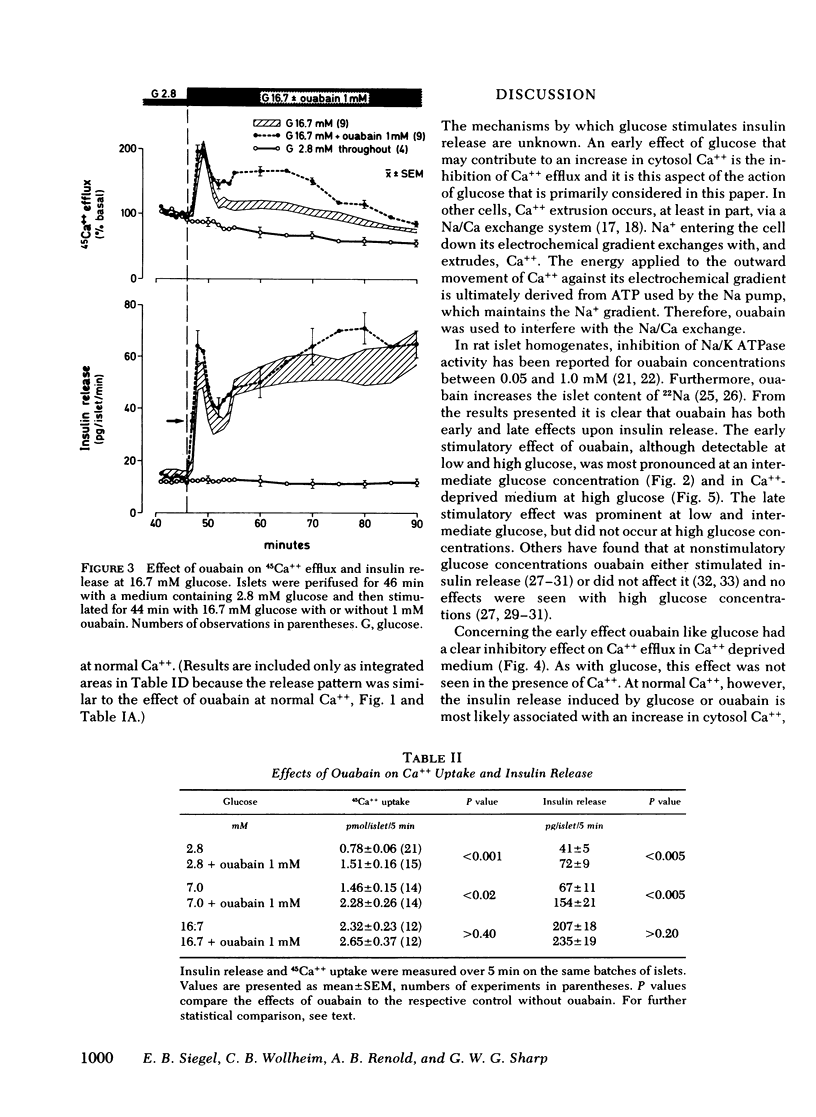
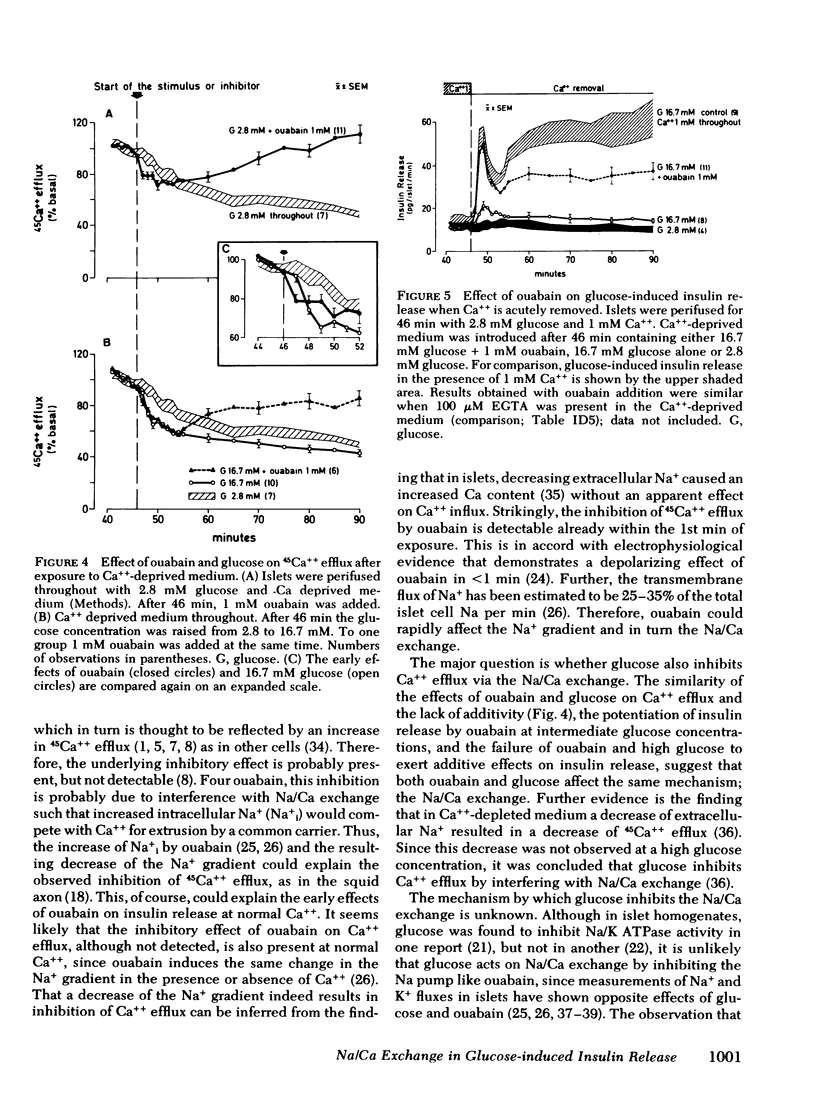
Glucose-induced inhibition of Ca++ extrusion from the β-cell may contribute to the rise in cytosol Ca++ that leads to insulin release. To study whether interference with Na/Ca exchange is involved in this inhibition the effects of glucose were compared to those of ouabain. This substance inhibits Na/K ATPase, decreases the transmembrane Na+ gradient in islets, and thus interferes with Na/Ca exchange. Collagenase isolated rat islets were maintained for 2 d in tissue culture with a trace amount of 45Ca++. Insulin release and 45Ca++ efflux were then measured during perifusion. In Ca++-deprived medium (to avoid changes in tissue specific radioactivity) 16.7 mM glucose inhibited 45Ca++ efflux. Initially 1 mM ouabain inhibited 45Ca++ efflux in a similar fashion, the onset being even faster than that of glucose. The effects of 16.7 mM glucose and ouabain were not additive, indicating that both substances may interfere with Na/Ca exchange. In the presence of Ca++, 16.7 mM glucose induced biphasic insulin release. Ouabain alone caused a gradual increase of insulin release. Again, the effects of ouabain and 16.7 mM glucose were not additive. In contrast, at a submaximal glucose concentration (7 mM) ouabain enhanced both phases of release. An important role for Na/Ca exchange is suggested from experiments in which Ca++ was removed at the time of glucose-stimulation (16.7 mM). The resulting marked inhibition of insulin release was completely overcome during first phase by ouabain added at the time of Ca++ removal; second phase was restored to 60%. This could be due to the rapid inhibitory action of ouabain on Ca++ efflux thereby preventing loss of cellular calcium critical for glucose to induce insulin release. It appears, therefore, that interference with Na/Ca exchange is an important event in the stimulation of insulin release by glucose.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F. The regulation of intracellular calcium in giant axons of Loligo and Myxicola. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:250–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Russell J. M. Sodium-calcium exchange and calcium-calcium exchange in internally dialyzed squid giant axons. J Membr Biol. 1975 Jul 24;22(3-4):285–312. doi: 10.1007/BF01868176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borle A. B. On the difficulty of assessing the role of extracellular calcium in cell function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:431–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschero A. C., Kawazu S., Duncan G., Malaisse W. J. Effect of glucose on K+ handling by pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80662-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Marliss E. B., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Differential effect of ouabain on glucose-induced biphasic insulin release in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1971 Sep;221(3):943–947. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.3.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Crompton M. The regulation of intracellular calcium by mitochondria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:269–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donatsch P., Lowe D. A., Richardson B. P., Taylor P. The functional significance of sodium channels in pancreatic beta-cell membranes. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):357–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formby B., Capito K., Egeberg J., Hedeskov C. J. Ca-activated ATPase activity in subcellular fractions of mouse pancreatic islets. Am J Physiol. 1976 Feb;230(2):441–448. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel B. J., Imagawa W. T., O'Connor M. D., Lundquist I., Kromhout J. A., Fanska R. E., Grodsky G. M. Glucose-stimulated 45Calcium efflux from isolated rat pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):525–531. doi: 10.1172/JCI109156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagerman E., Hellman B., Täljedal I. B. Effects of ouabain on insulin release, adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanine 3',5'-monophosphate in pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1979 Apr;104(4):1000–1002. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-4-1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Milner R. D. The role of sodium and potassium in insulin secretion from rabbit pancreas. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):725–743. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effect of Na+, K+ and Mg2+ on 45Ca+ uptake by pancreatic islets. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Dec 28;378(2):93–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00584440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Montague W., Tyhurst M. Calcium distribution in islets of Langerhans: a study of calcium concentrations and of calcium accumulation in B cell organelles. J Cell Sci. 1975 Nov;19(2):395–409. doi: 10.1242/jcs.19.2.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawazu S., Boschero A. C., Delcroix C., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXVIII. Effect of glucose on Na+ fluxes in isolated islets. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Jul 18;375(2):197–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00584244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmler W., Löffler G. NaK-ATPase in rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):235–238. doi: 10.1007/BF01219705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi M., Wollheim C. B., Cuendet G. S., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Studies on the dual effects of glucose on 45Ca++ efflux from isolated rat islets. Endocrinology. 1978 May;102(5):1339–1349. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-5-1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi M., Wollheim C. B., Siegel E. G., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Biphasic insulin release in rat islets of Langerhans and the role of Intracellular Ca++ stores. Endocrinology. 1979 Oct;105(4):1013–1019. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-4-1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klöppel G., Bommer G. Ultracytochemical calcium distribution in B cells in relation to biphasic glucose-stimulated insulin release by the perfused rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1979 Jun;28(6):585–592. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.6.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert A. E., Henquin J. C., Malvaux P. Cationic environment and dynamics of insulin secretion. IV. Effect of ouabain. Horm Metab Res. 1974 Nov;6(6):470–475. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin S. R., Kasson B. G., Driessen J. F. Adenosine triphosphatases of rat pancreatic islets: comparison with those of rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):692–701. doi: 10.1172/JCI109177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Boschero A. C., Kawazu S., Hutton J. C. The stimulus secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXVII. Effect of glucose on K+ fluxes in isolated islets. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Mar 20;373(3):237–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00580830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Herchuelz A., Devis G., Somers G., Boschero A. C., Hutton J. C., Kawazu S., Sener A., Atwater I. J., Duncan G. Regulation of calcium fluxes and their regulatory roles in pancreatic islets. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:562–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marliss E. B., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Orci L., Lambert A. E., Stauffacher W., Like A. A., Renold A. E. Insulin and glucagon release from monolayer cell cultures of pancreas from newborn rats. Eur J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;3(1):16–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1973.tb00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattews E. K., Sakamoto Y. Pancreatic islet cells: electrogenic and electrodiffusional control of membrane potential. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):439–457. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Goodman D. B. Relationships between calcium and cyclic nucleotides in cell activation. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jul;57(3):421–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J., Bürgin H. Calcium in human red blood cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:125–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Sodium uptake by microdissected pancreatic islets: effects of ouabain and chloromercuribenzene-p-sulphonic acid. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 15;39(2):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Transport of rubidium and sodium in pancreatic islets. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):505–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W. The adenylate cyclase-cyclic AMP system in islets of Langerhans and its role in the control of insulin release. Diabetologia. 1979 May;16(5):287–296. doi: 10.1007/BF01223617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E. G., Wollheim C. B., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Dependency of cyclic AMP-induced insulin release on intra- and extracellular calcium in rat islets of Langerhans. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):233–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI109665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E. G., Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W. Glucose-induced first phase insulin release in the absence of extracellular Ca2+ in rat islets. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 14;109(2):213–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E. G., Wollheim C. B., Sharp G. W., Herberg L., Renold A. E. Defective calcium handling and insulin release in islets from diabetic Chinese hamsters. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):233–236. doi: 10.1042/bj1800233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden M. C., Ashcroft S. J. Effects of phosphoenolpyruvate, other glycolytic intermediates and methylxanthines on calcium uptake by a mitochondrial fraction from rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1978 Sep;15(3):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00421235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Trueheart P. A., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Calcium-induced insulin release in monolayer culture of the endocrine pancreas. Studies with ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1354–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. Somatostatin- and epinephrine-induced modifications of 45Ca++ fluxes and insulin release in rat pancreatic islets maintained in tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1165–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI108869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Kikuchi M., Renold A. E., Sharp G. W. The roles of intracellular and extracellular Ca++ in glucose-stimulated biphasic insulin release by rat islets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):451–458. doi: 10.1172/JCI109146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



