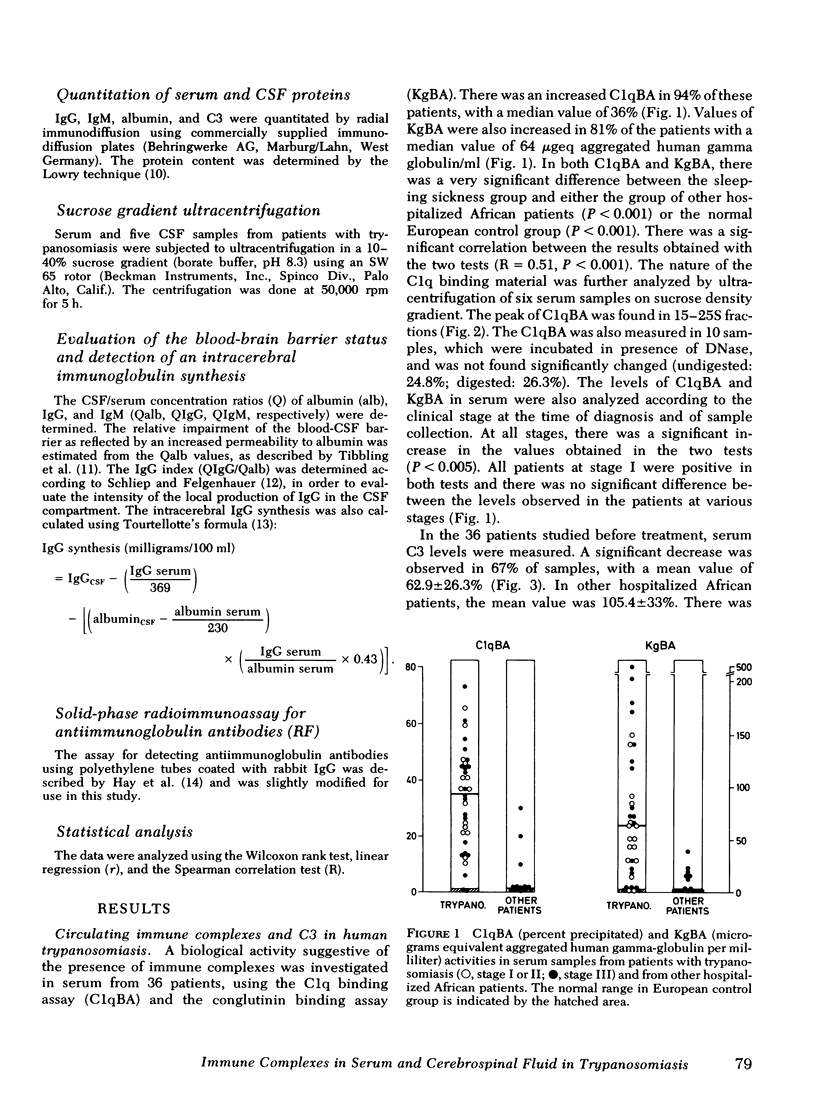
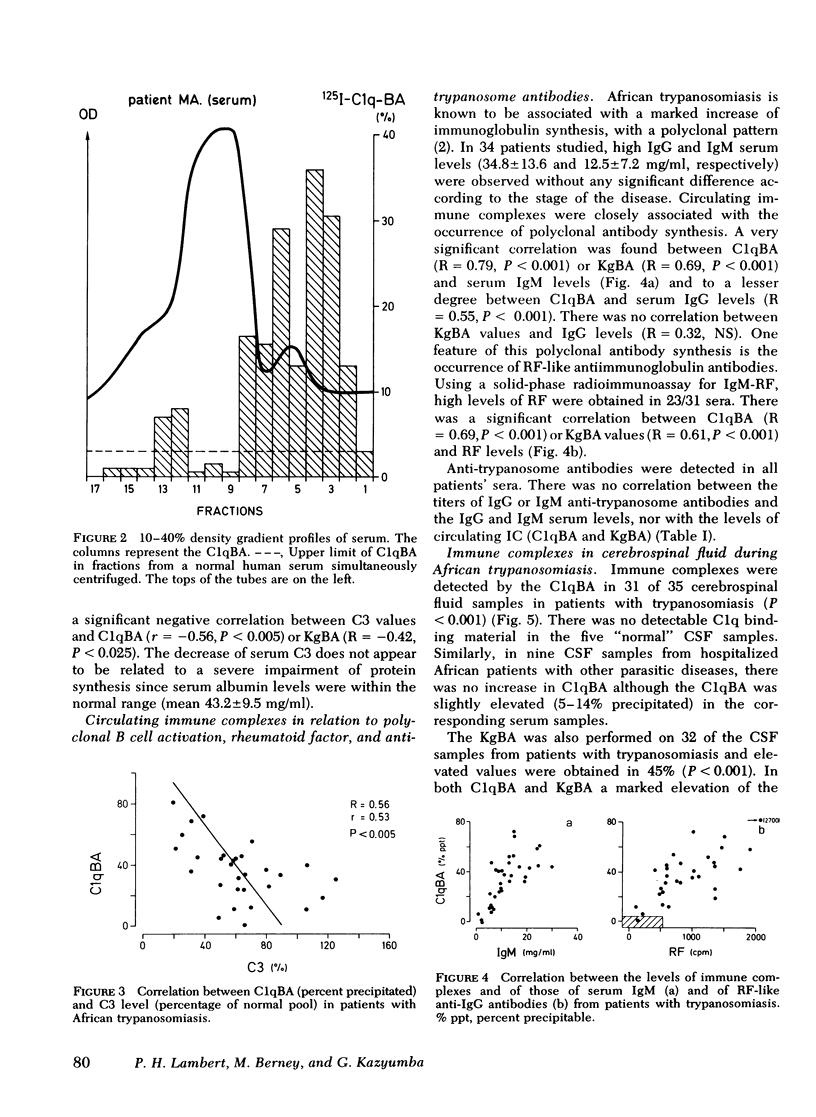
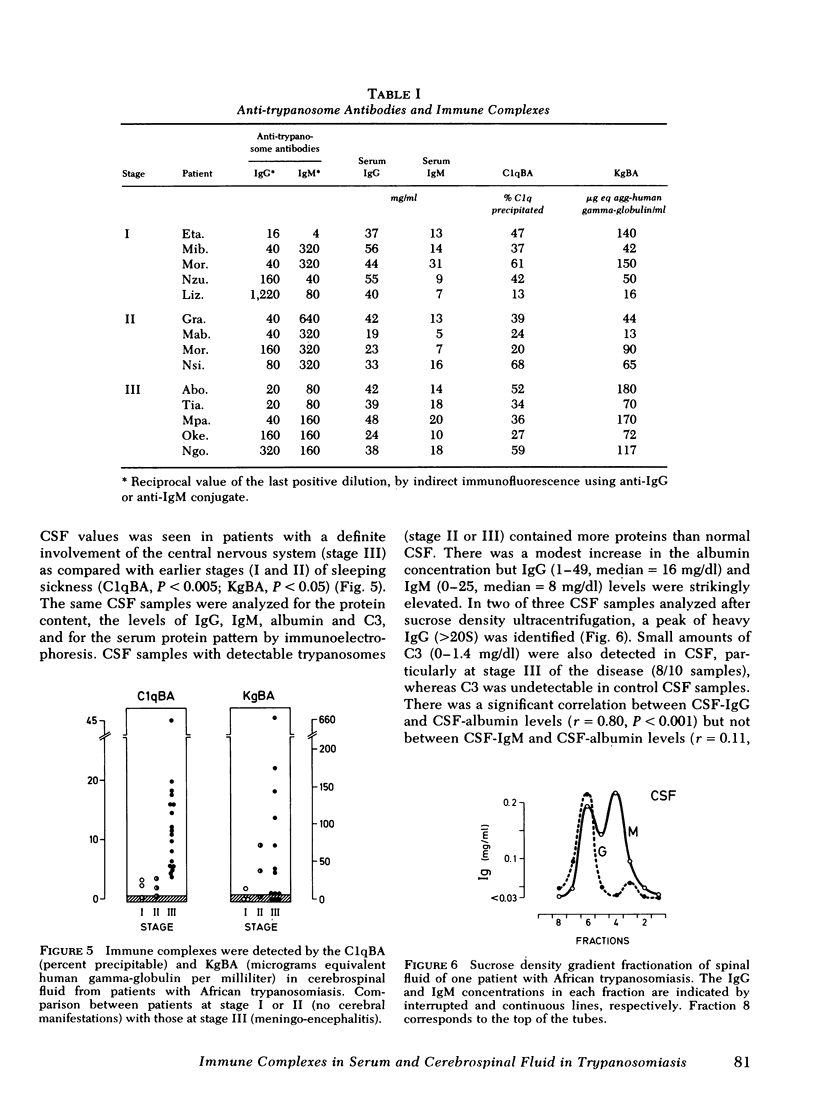
Abstract
The possible occurrence of immune complexes (IC) in serum and in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has been studied in 36 patients with African trypanosomiasis (Trypanosoma brucei gambiense). In serum, very high levels of IC were detectable by the 125I-C1q-binding and by the conglutinin-binding assays with positive results in 94 and 87%, respectively, of untreated patients. Circulating IC were found in both early and late stages of the disease, without significant quantitative differences; their size was 15-25S. There was a significant negative correlation between C3 values and C1qBA. Our studies suggest that circulating IC occurring during trypanosomiasis may be the expression of a polyclonal B cell activation. Indeed, there was a significant correlation (P < 0.001) between the levels of circulating IC and either the levels of IgM (mean value 12.5±7.2 mg/ml) or with the levels of rheumatoid factor-like antiimmunoglobulin antibodies that were detected by solid phase radioimmunoassay in 74% of the patients.
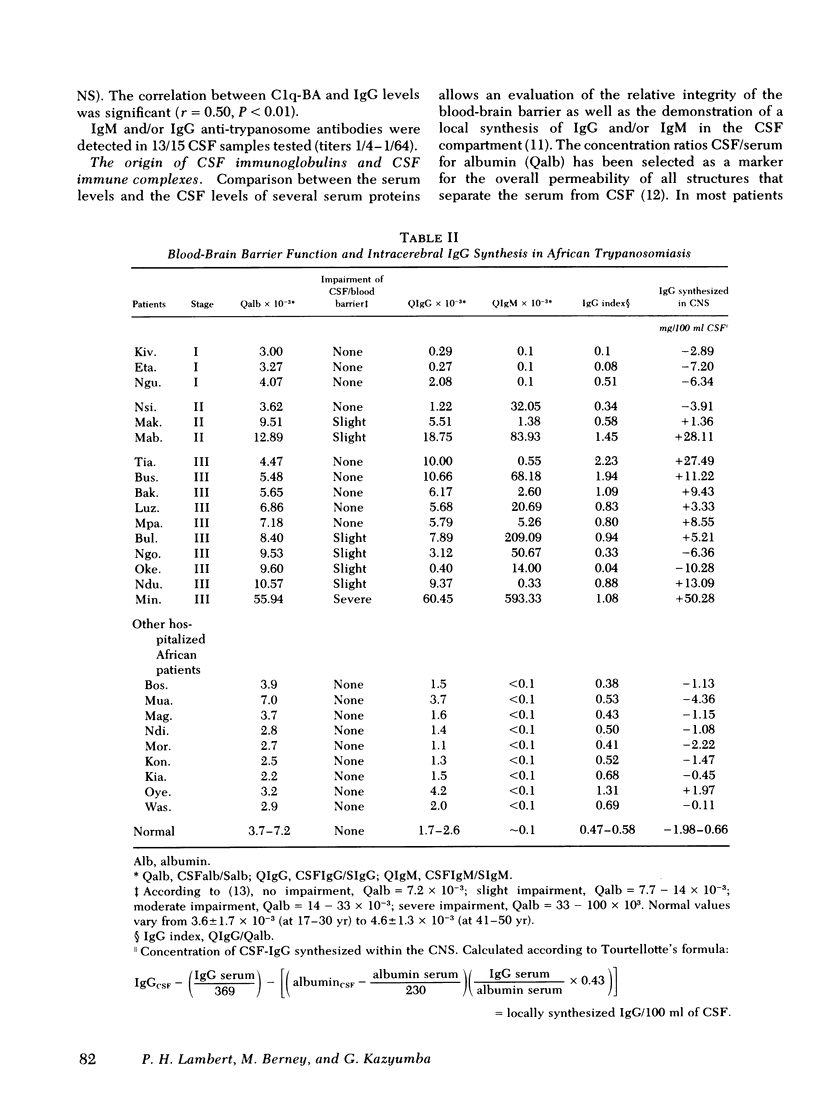
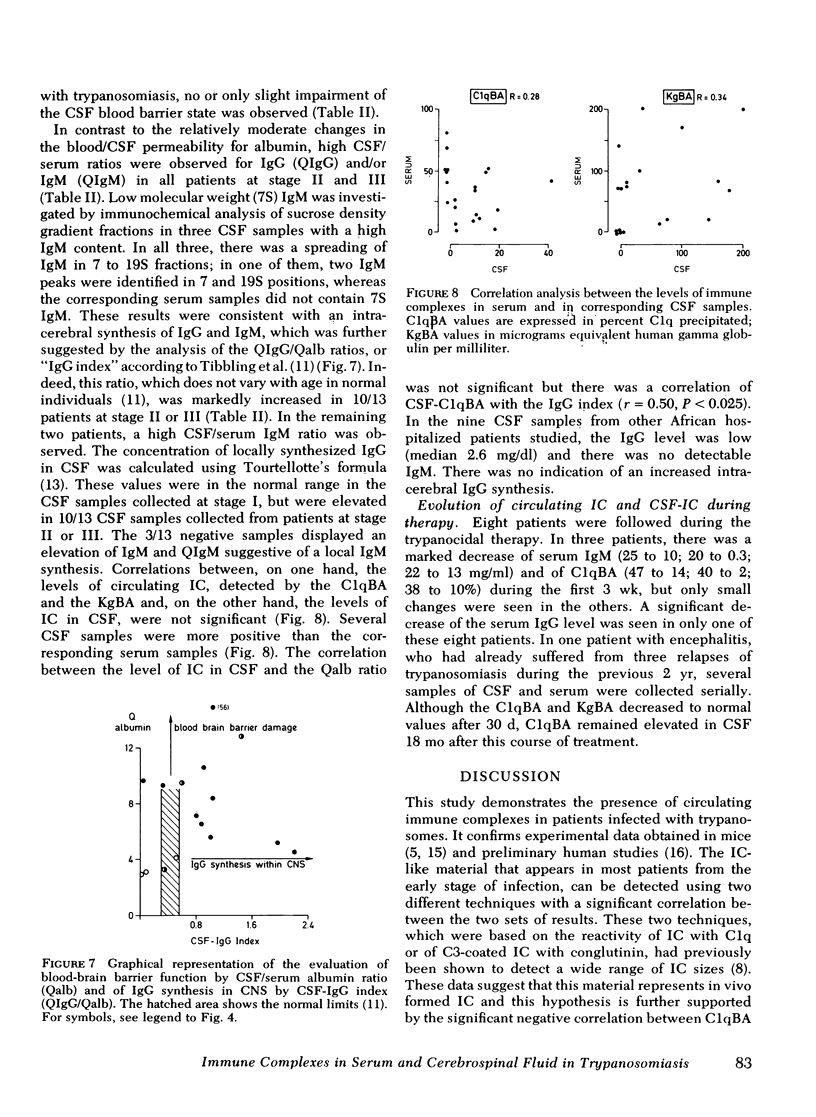
IC were detected in 31 of 35 CSF samples, with a marked elevation in patients with definite involvement of the central nervous system as compared with earlier stages of sleeping sickness. The occurrence of IC in CSF was not related to an impairment of the blood-brain barrier as shown by analysis of CSF/serum albumin ratios. The level of IC in CSF did not correlate with the serum level and, therefore, circulating IC do not appear to cross efficiently an unimpaired blood-brain barrier. The analysis of IgG, IgM, and albumin concentrations in serum and CSF demonstrates a marked intracerebral immunoglobulin synthesis in patients with manifestations of meningoencephalitis. There was a correlation between CSF-C1q binding assay and this local IgG synthesis.
These data are consistent with a local formation of IC in CSF in patients with active meningoencephalitis. The results obtained in eight patients followed during therapy suggest that the presence of IC in CSF may be an indicator of a continuing central nervous system disease and that the quantitation of CSF-IC may be useful for monitoring patient care.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casali P., Bossus A., Carpentier N. A., Lambert P. H. Solid-phase enzyme immunoassay or radioimmunoassay for the detection of immune complexes based on their recognition by conglutinin: conglutinin-binding test. A comparative study with 125I-labelled Clq binding and Raji-cell RIA tests. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Aug;29(2):342–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewan P. W., Lachmann P. J. IgG synthesis within the brain in multiple sclerosis and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Feb;35(2):227–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruit J., Santoro F., Afchain D., Duvallet G., Capron A. Les immuncomplexes circulants dans la trypanosomiase africaine humaine et expérimentale. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1977;57(4-5):257–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvao-Castro B., Hochmann A., Lambert P. H. The role of the host immune response in the development of tissue lesions associated with African trypanosomiasis in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Jul;33(1):12–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M. Possible role of a B-cell mitogen in hypergammaglobulinaemia in malaria and trypanosomiasis. Lancet. 1974 Mar 16;1(7855):435–436. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Whittle H. C. Cerebrospinal-fluid IgM in patients with sleeping-sickness. Lancet. 1973 Sep 8;2(7828):525–527. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbeck R. J., Hoffman A. A., Hoffman S. A., Shucard D. W. Cerebrospinal fluid and the choroid plexus during acute immune complex disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Aug;13(4):413–425. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Torrigiani G., Roitt I. M. Hidden' IgG antiglobulins in normal human serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):185–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Host immunoglobulin G and complement deposits in the choroid plexus during spontaneous immune complex disease. Science. 1973 Apr 27;180(4084):408–410. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4084.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanham S. M., Godfrey D. G. Isolation of salivarian trypanosomes from man and other mammals using DEAE-cellulose. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Dec;28(3):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poltera A. A., Hochmann A., Rudin W., Lambert P. H. Trypanosoma brucei brucei: a model for cerebral trypanosomiasis in mice--an immunological, histological and electronmicroscopic study. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Jun;40(3):496–507. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliep G., Felgenhauer K. Serum-CSF protein gradients, the blood-GSF barrier and the local immune response. J Neurol. 1978 May 18;218(2):77–96. doi: 10.1007/BF02402169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbling G., Link H., Ohman S. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):385–390. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte W. On cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulin-G (IgG) quotients in multiple sclerosis and other diseases. A review and a new formula to estimate the amount of IgG synthesized per day by the central nervous system. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Mar;10(3):279–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



