Abstract
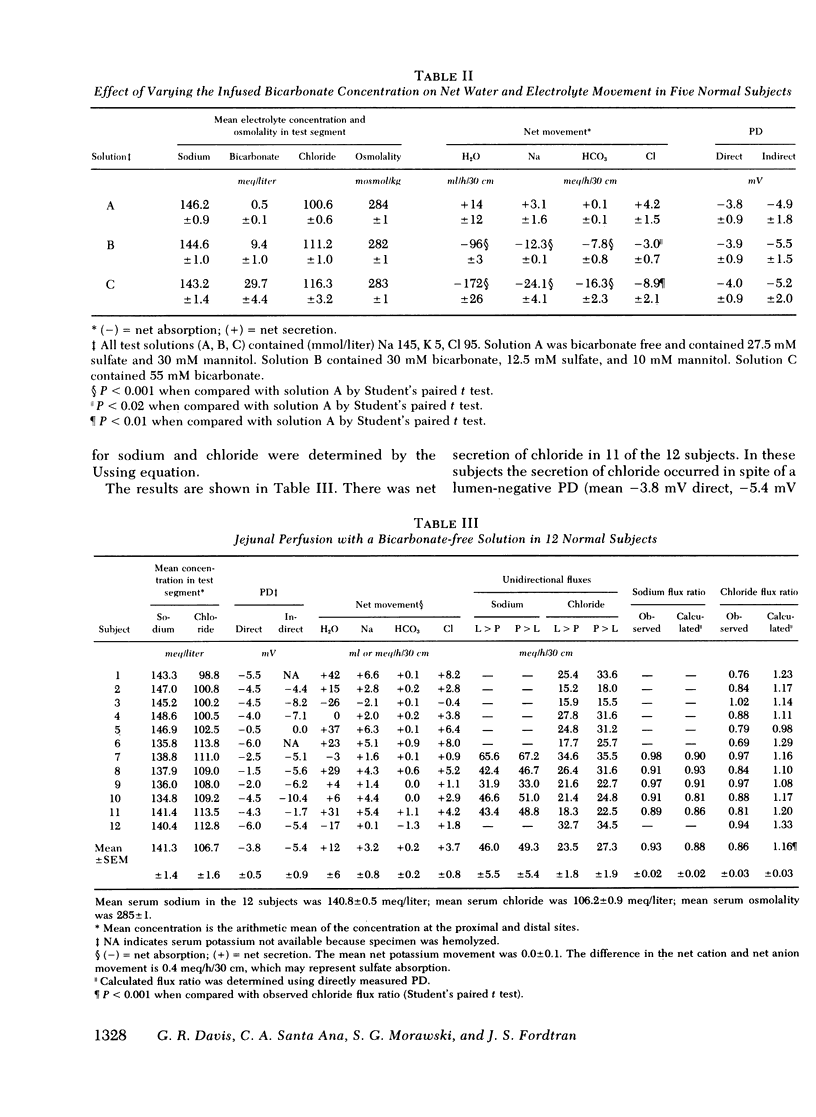
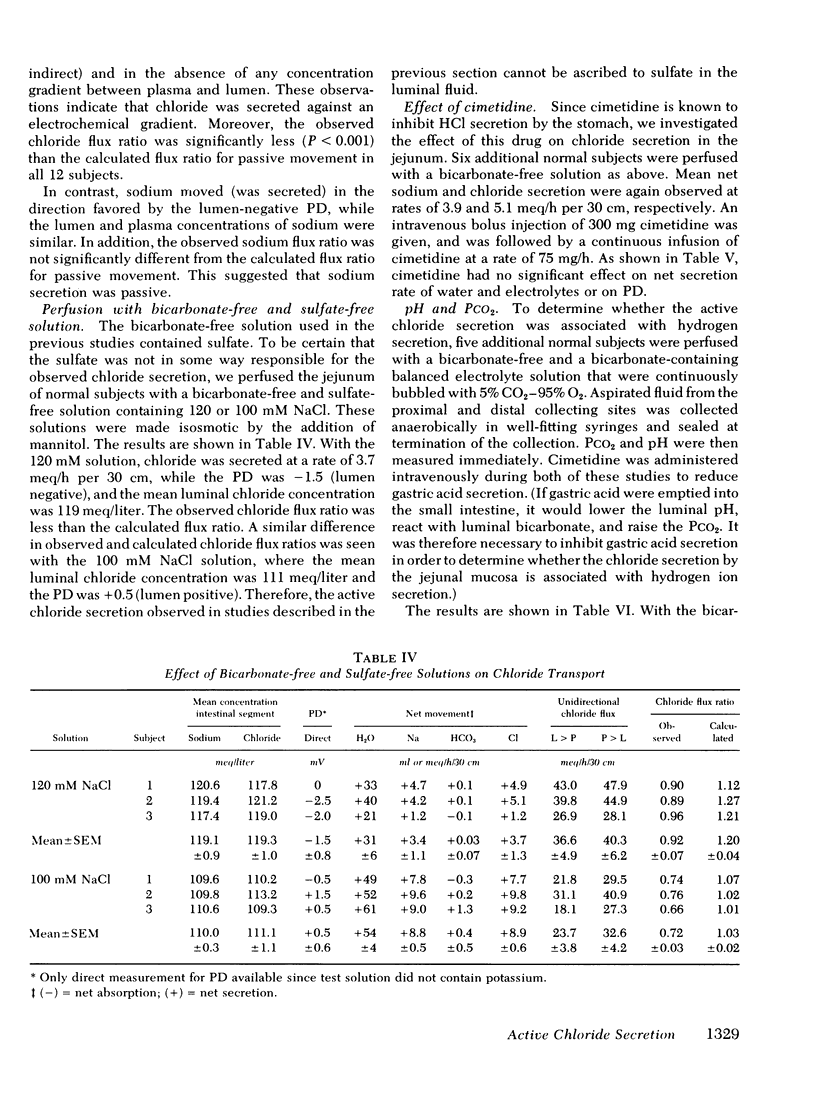
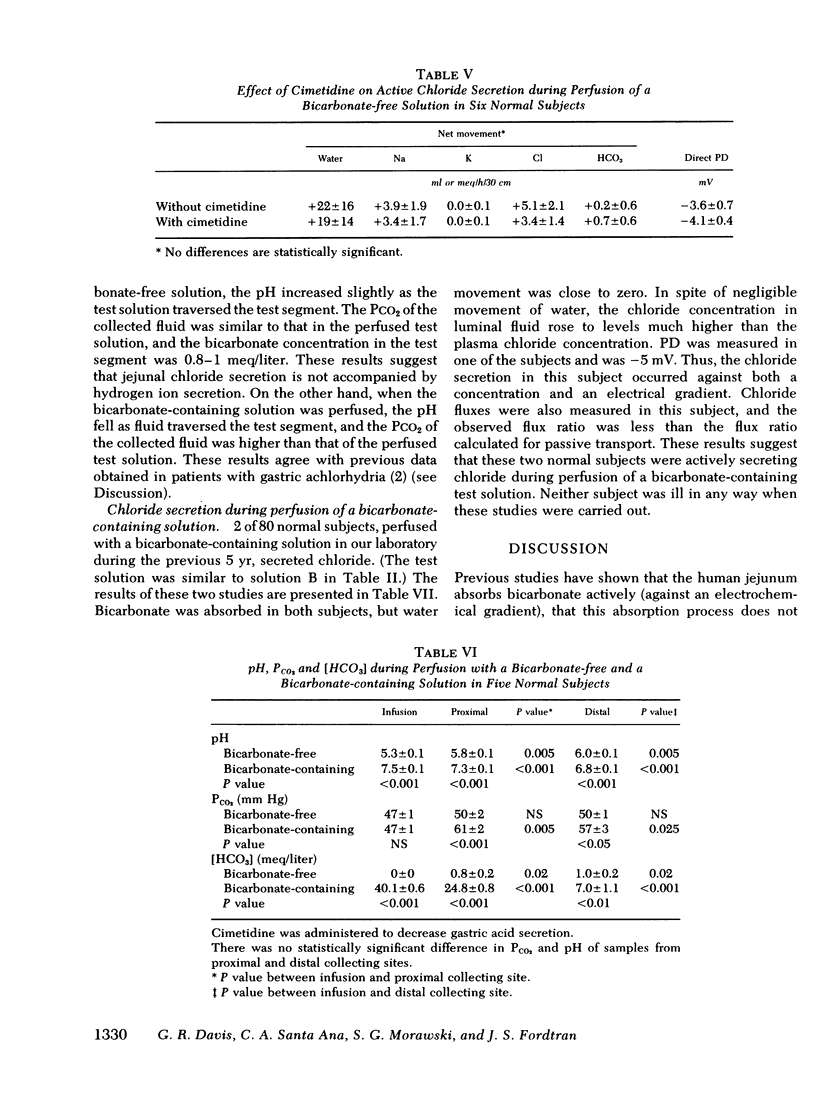
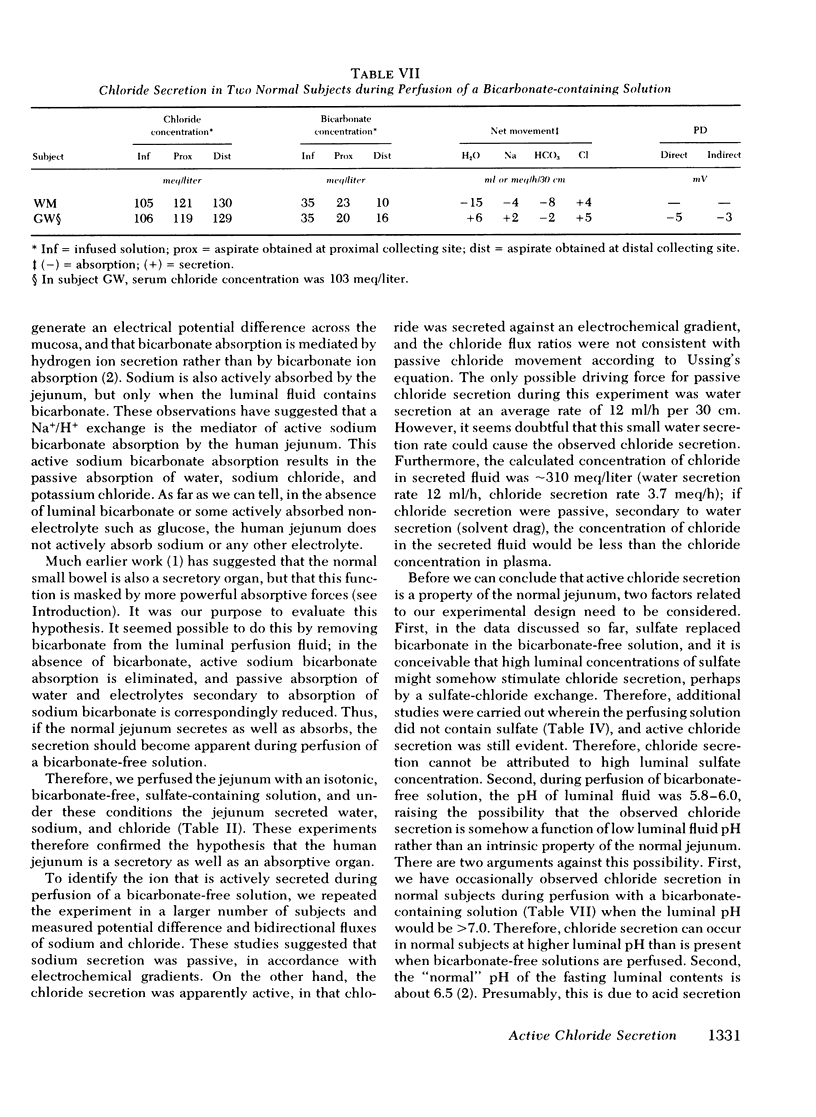
To determine whether the small intestine normally secretes fluid, it would be necessary to reduce or inhibit the greater absorptive processes that would otherwise mask such secretion if present. To do this, we perfused bicarbonate-free solutions in the jejunum of normal subjects, because it has been shown that active absorption from this part of the human small intestine is dependent on luminal bicarbonate. We found that the jejunum did secrete sodium chloride and water when isotonic bicarbonate-free solutions were perfused. Further studies revealed that the sodium secretion was passive, but that chloride was secreted against an electrochemical gradient and that observed chloride flux ratios did not agree with the flux ratios calculated for passive chloride movement. We conclude, therefore, that the normal jejunum actively secretes chloride, but that this is masked by greater absorptive processes when balanced electrolyte solutions are perfused. The rate of this active chloride secretion may be one of the factors that regulate the rate of fluid absorption in the normal human intestine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGER E. Y., STEELE J. M. The calculation of transfer rates in two compartment systems not in dynamic equilibrium. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Jul 20;41(6):1135–1152. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.6.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieberdorf F. A., Gorden P., Fordtran J. S. Pathogenesis of congenital alkalosis with diarrhea. Implications for the physiology of normal ileal electrolyte absorption and secretion. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1958–1968. doi: 10.1172/JCI107002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H., Levitan R., Fordtran J. S., Ingelfinger F. J. A method for studying absorption of water and solute from the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jan;50(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett C. L., Isaacs P. E., Riley A. K., Turnberg L. A. Human intestinal ion transport in vitro. Gut. 1977 Feb;18(2):136–140. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Locklear T. W. Ionic constituents and osmolality of gastric and small-intestinal fluids after eating. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Jul;11(7):503–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02233563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Carter N. W. The mechanisms of sodium absorption in the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):884–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI105781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Ewton M. F., Soter N., Kinney J. Permeability characteristics of the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1935–1944. doi: 10.1172/JCI105299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S. Stimulation of active and passive sodium absorption by sugars in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):728–737. doi: 10.1172/JCI107983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm D. Na and Cl transport across isolated proximal small intestine of the rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jan;224(1):110–116. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. L., Jr, Bieberdorf F. A., Morawski S. G., Finkelstein R. A., Fordtran J. S. Ion transport during cholera-induced ileal secretion in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):312–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI106496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck B. G. Effects of sugar and amino acid transport on transepithelial fluxes of sodium and chloride of short circuited rat jejunum. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(3):699–717. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W., Fordtran J. S. The role of intraluminal junction potentials in the generation of the gastric potential difference in man. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):932–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Fordtran J. S., Carter N. W., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):548–556. doi: 10.1172/JCI106265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A. Potassium transport in the human small bowel. Gut. 1971 Oct;12(10):811–818. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.10.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


