Abstract
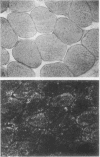
A patient with symptoms of easy fatigability, postexercise myalgias, and delayed recovery of muscle strength after activity is described. Skeletal muscle from this patient had <1.0% normal myoadenylate deaminase activity and NH3 was not released from muscle after ischemic exercise. In association with this enzyme deficiency, exercise led to a >90% reduction in muscle content of adenine nucleotides. No inosine monophosphate accumulated after exercise and total purine content of the muscle fell to 21% of control. Repletion of the adenine nucleotide pool in this patient was delayed compared to controls, and ATP content had only returned to 68% of control at 165 min after exercise. These studies demonstrate that disruption of the purine nucleotide cycle as a consequence of myoadenylate deaminase deficiency results in marked alterations in ATP content of muscle, and potentially, these changes in ATP content could account for muscle dysfunction in this patient.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ENGEL A. G., POTTER C. S., ROSEVEAR J. W. NUCLEOTIDES AND ADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE DEAMINASE ACTIVITY OF MUSCLE IN PRIMARY HYPOKALAEMIC PERIODIC PARALYSIS. Nature. 1964 May 16;202:670–672. doi: 10.1038/202670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein W. N., Armbrustmacher V. W., Griffin J. L. Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency: a new disease of muscle. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.644316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T., Sjøgaard G., Löllgen H., Saltin B. NAD in muscle of man at rest and during exercise. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Aug 25;376(1):35–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00585245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweinsberg P. D., Loo T. L. Simultaneous analysis of ATP, ADP, AMP, and other purines in human erythrocytes by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1980 Jan 11;181(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shumate J. B., Katnik R., Ruiz M., Kaiser K., Frieden C., Brooke M. H., Carroll J. E. Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. Muscle Nerve. 1979 May-Jun;2(3):213–216. doi: 10.1002/mus.880020309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solano C., Coffee C. J. Differential response of AMP deaminase isozymes to changes in the adenylate energy charge. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 29;85(2):564–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton J. R., Toews C. J., Ward G. R., Fox I. H. Purine metabolism during strenuous muscular exercise in man. Metabolism. 1980 Mar;29(3):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J., Lowenstein J. M. Adenylate deaminase from rat muscle. Regulation by purine nucleotides and orthophosphate in the presence of 150 mM KCl. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8994–8999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]