Abstract
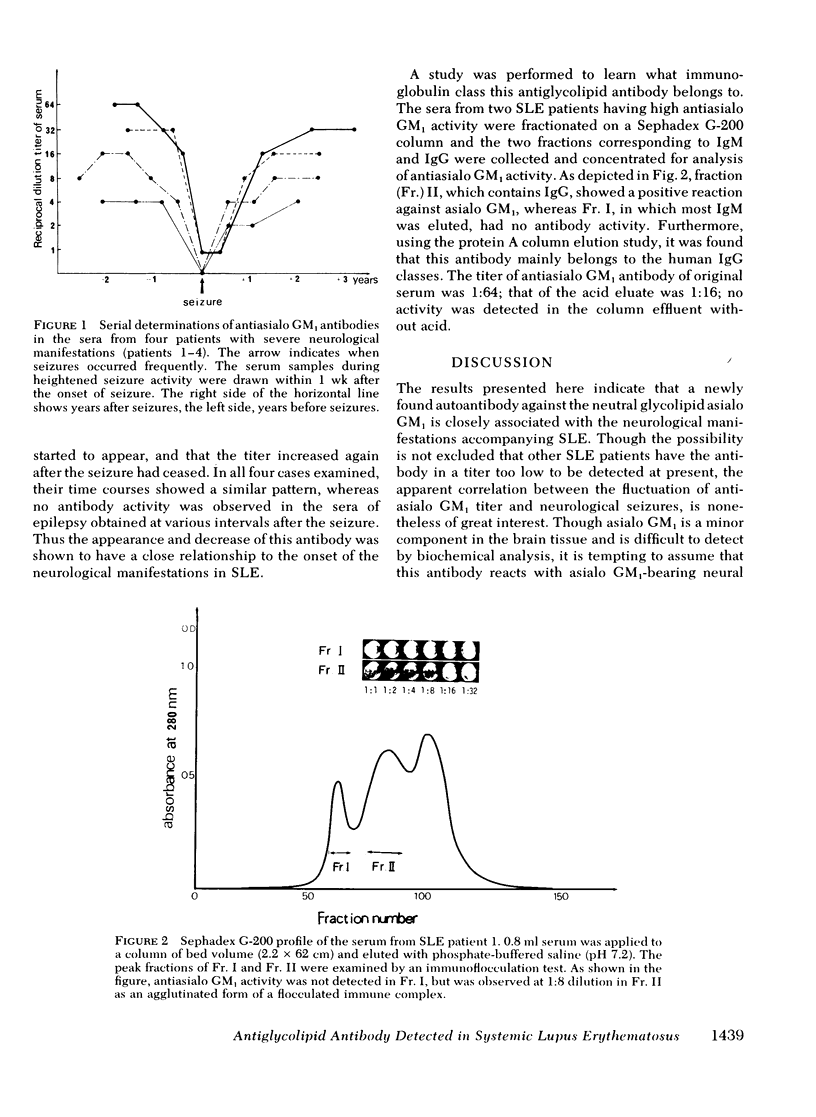
A high incidence of autoantibody against the neutral glycolipid "asialo GM1" was observed in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with neurological disorders, using an immunoflocculation test. The sera from 14 out of 17 cases of SLE with neurological disorders showed antibody activity against asialo GM1 but not against the following glycolipids: asialo GM2 GM1, and galactocerebroside. In another 87 cases of SLE without any history of seizures, as well as 61 cases of other autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, progressive systemic sclerosis, mixed connective tissue disease, etc.) and 20 cases of various neurological diseases (epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, etc.), no antibody could be detected. In general, the antibody titer was high several months, even years, before and/or after the seizure, though the titer was low at the time that patients showed definite neurological symptoms. Immunochemical characterization with Sephadex G-200 chromatogrphy and protein A-Sepharose CL-4B affinity column indicated that the antiasialo GM1 was probably an autoantibody belonging to the immunoglobulin G class. The above results suggest that this newly found autoantibody plays a role in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders accompanying SLE.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins C. J., Kondon J. J., Quismorio F. P., Friou G. J. The choroid plexus in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Jan;76(1):65–72. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestein H. G., Zvaifler N. J. Brain-reactive lymphocytotoxic antibodies in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):509–516. doi: 10.1172/JCI108303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Oliver M., Grigor R., Hughes G. R. Brain reactivity of lymphocytotoxic antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus with and without cerebral involvement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Dec;30(3):333–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg B., Keiser H. A Millipore filter assay for antibodies to native DNA in sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Mar-Apr;16(2):199–207. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Horiuchi Y., Okumura K., Tada T., Kawata M., Ohmori K. Immunological abnormalities of aging: an analysis of T lymphocyte subpopulations of Werner's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):695–699. doi: 10.1172/JCI109511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler N. M., Gerwin R. D., Frank M. M., Whitaker J. N., Baker M., Decker J. L. The fourth component of complement in the cerebrospinal fluid in systemic Lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Jul-Aug;16(4):507–521. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpiak S. E., Graf L., Rapport M. M. Antiserum to brain gangliosides produces recurrent epileptiform activity. Science. 1976 Nov 12;194(4266):735–737. doi: 10.1126/science.982041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tada T. A glycolipid on the surface of mouse natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Mar;10(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H. Preparation of 125I-labeled native DNA for use in radioimmunoassays for anti-native-DNA antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Jul-Aug;16(4):468–470. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Iwamori M. A new approach to the analysis of ganglioside molecular species. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1980;125:13–21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7844-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahara K., Ohashi T., Oda T., Hirano T., Kasai M., Okumura K., Tada T. Asialo GM1 as a cell-surface marker detected in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1980 Mar 20;302(12):674–677. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198003203021208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. A., Winfield J. B., Lahita R. G., Koffler D. Association of IgG anti-brain antibodies with central nervous system dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 May;22(5):458–462. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. W., Jr, Hakomori S. I., Durdik J. M., Henney C. S. Identification of ganglio-N-tetraosylceramide as a new cell surface marker for murine natural killer (NK) cells. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):199–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




