Abstract
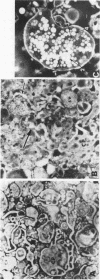
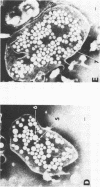
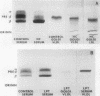
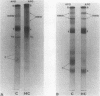
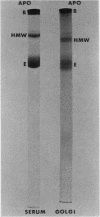
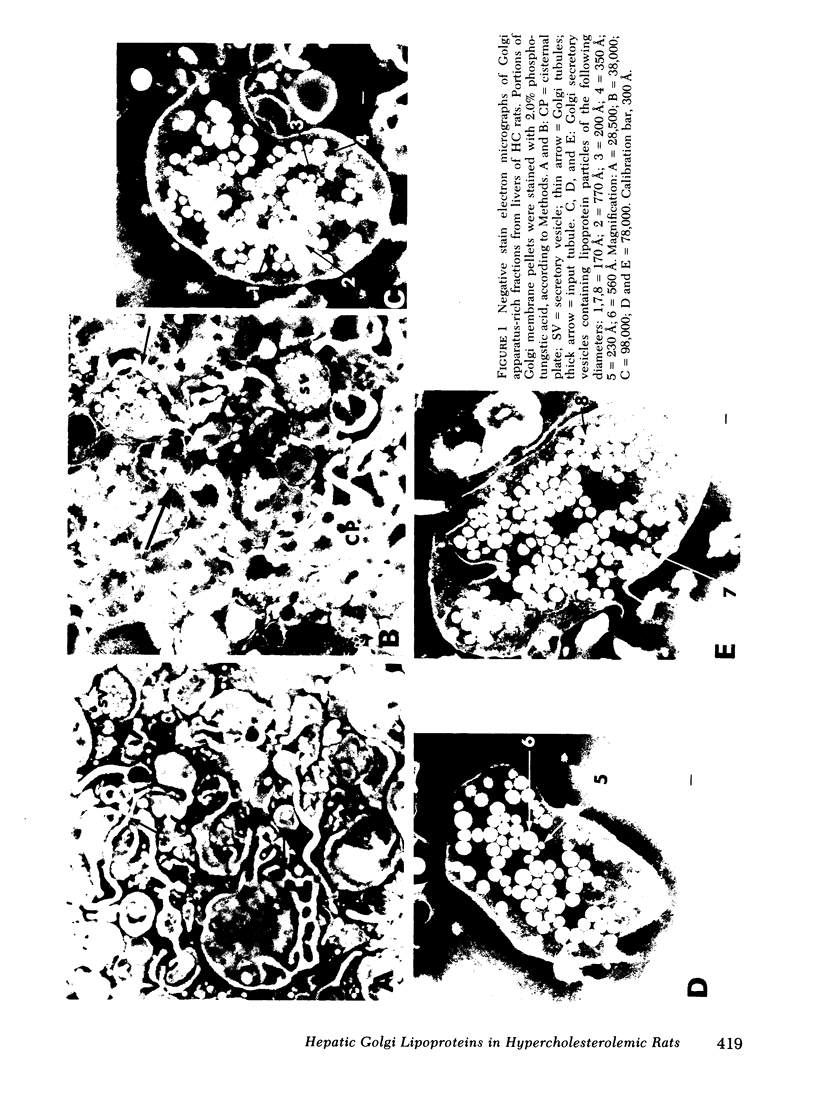
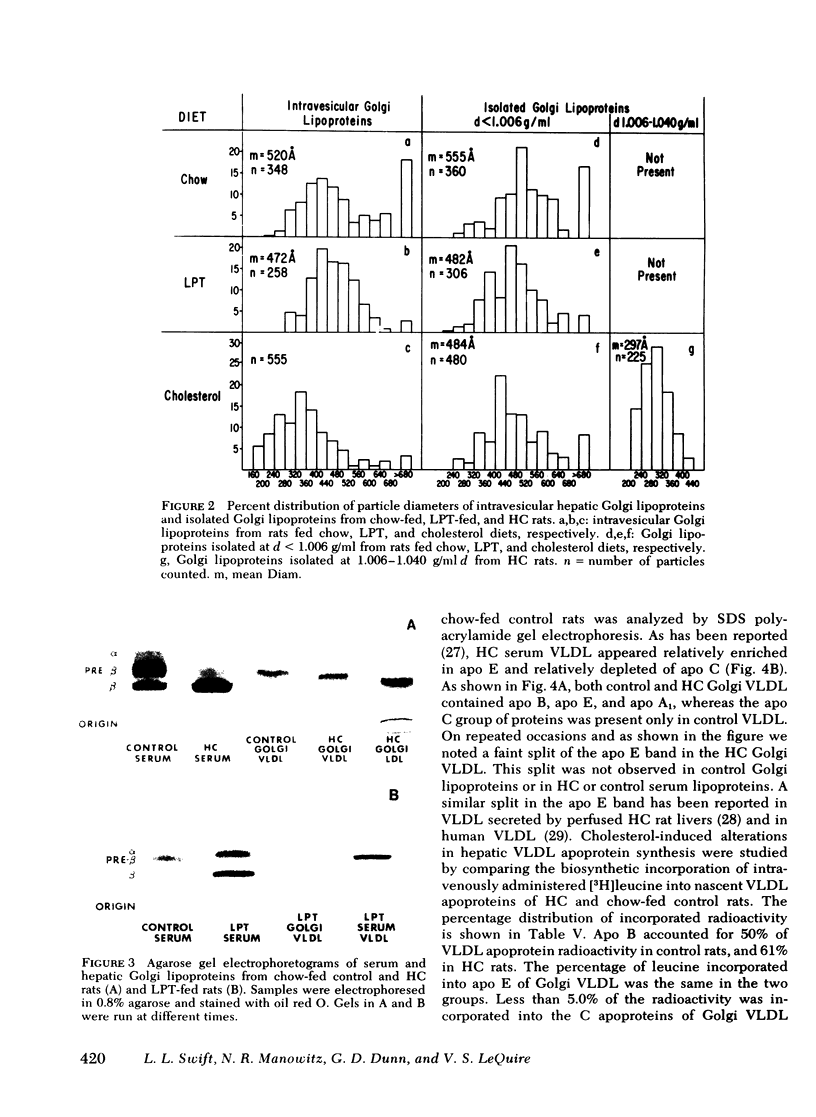
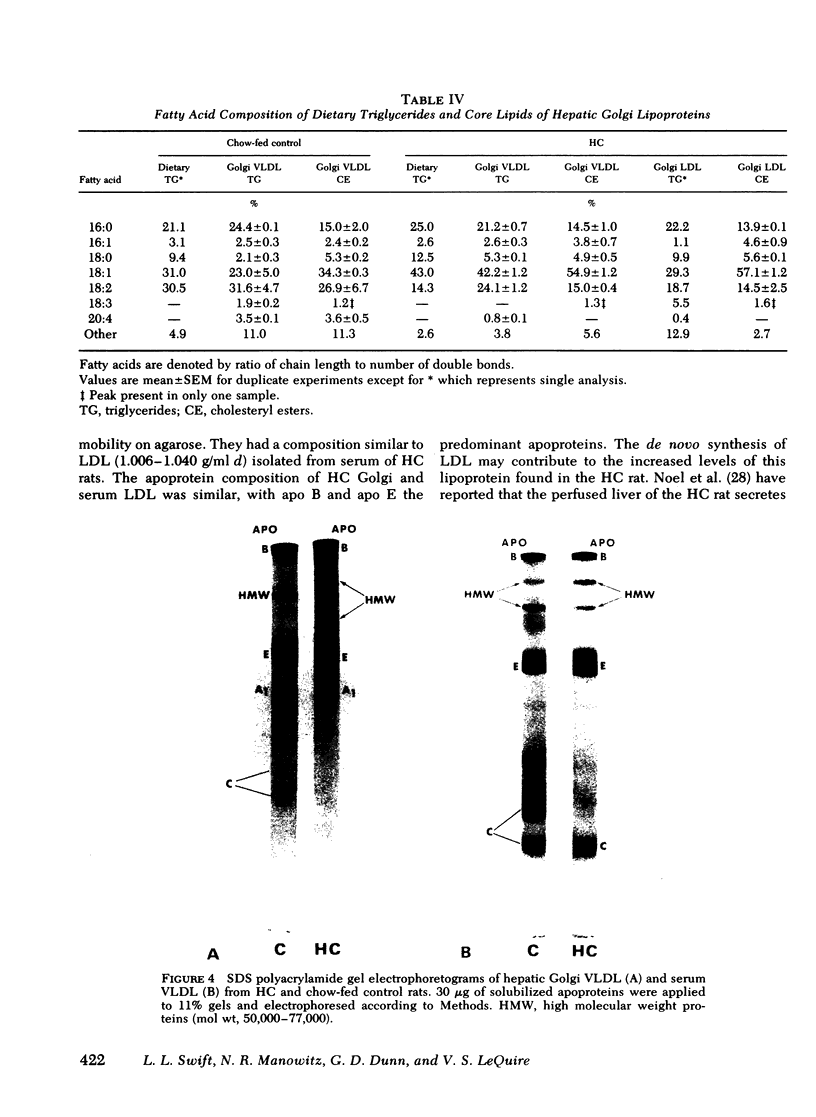
The feeding of cholesterol-rich diets alters the serum lipoproteins of a number of mammalian species. These lipoproteins are characterized by the presence of several classes of particles enriched in cholesteryl esters and apolipoprotein E (apo E). It was the aim of this study to determine whether one or more of these particles arises by de novo hepatic synthesis by characterizing nascent lipoproteins isolated from the hepatic Golgi apparatus of hypercholesterolemic rats. Characterization of these lipoproteins afforded the opportunity to assess morphologic, biochemical, and biophysical properties of newly synthesized lipoproteins before enzymatic alterations and apoprotein transfer known to occur after secretion into the plasma compartment. Golgi very low density lipoproteins (VLDL, d < 1.006 g/ml) from hypercholesterolemic rats contained nearly four times the total cholesterol mass found in control Golgi VLDL. They exhibited electrophoretic mobility intermediate between beta and pre-beta and were devoid of apo C. A second population of hepatic Golgi lipoproteins was isolated from hypercholesterolemic rats at 1.006--1.040 g/ml d. These low density lipoproteins were smaller than VLDL, displayed beta electrophoretic mobility, were enriched in cholesteryl esters, and contained apo E as well as apo B. The fatty acid composition of the core lipids of the nascent lipoproteins was found to reflect that of dietary triglyceride. The liver of the hypercholesterolemic rat thus plays an active role in dietary-induced hypercholesterolemia by synthesizing a modified VLDL and a low density lipoprotein resembling serum low density lipoprotein.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BABSON A. L., SHAPIRO P. O., PHILLIPS G. E. A new assay for cholesterol and cholesterol esters in serum which is not affected by bilirubin. Clin Chim Acta. 1962 Nov;7:800–804. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(62)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M., Hall M., 3rd, Levy R. I., Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Phair R. D., Goebel R. H. Metabolsim of apoB and apoC lipoproteins in man: kinetic studies in normal and hyperlipoproteininemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jan;19(1):38–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bersot T. P., Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Windmueller H. G., Fredrickson D. S., LeQuire V. S. Further characterization of the apolipoproteins of rat plasma lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1970 Aug 18;9(17):3427–3433. doi: 10.1021/bi00819a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G., Bosch V., Arreaza C., Mendez H. C. Early changes in plasma lipoprotein structure and biosynthesis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jan;14(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D., Yu P. Y. Rates of removal and degradation of chylomicron remnants by isolated perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jul;19(5):635–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin P. J., Wong L., Rubinstein D. A comparison of some immunological characteristics of very low density lipoproteins of normal and hypercholesterolemic rat sera. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jun;56(6):673–683. doi: 10.1139/o78-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn G. D., Wilcox H. G., Heimberg M. Temporal relationships between dietary, plasma, hepatic, and adipose tissue lipids after short-term feeding of safflower oil to rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Sep;86(3):369–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenreich J. H., Bergeron J. J., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Golgi fractions prepared from rat liver homogenates. I. Isolation procedure and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):45–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H., Poulis P. Metabolic heterogeneity in the formation of low density lipoprotein from very low density lipoprotein in the rat: evidence for the independent production of a low density lipoprotein subfraction. J Lipid Res. 1978 Mar;19(3):342–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frnka J., Reiser R. The effects of diet cholesterol on the synthesis of rat serum apolipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 19;360(3):322–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P. Primary dysbetalipoproteinemia: predominance of a specific apoprotein species in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2015–2019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth D. R. Metabolism of lipoproteins in nonhuman primates. Studies on the origin of low density lipoprotein apoprotein in the plasma of the squirrel monkey. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 18;388(1):38–51. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON W. R., SMITH L. M. PREPARATION OF FATTY ACID METHYL ESTERS AND DIMETHYLACETALS FROM LIPIDS WITH BORON FLUORIDE--METHANOL. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:600–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Hamilton R. L., Lequire V. S. Characterization of lipoprotein particles isolated from the Golgi apparatus of rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jul;10(4):433–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Holcombe K. S. Alterations of the plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins following cholesterol feeding in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):314–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morré D. J., Hamilton R. L., Mollenhauer H. H., Mahley R. W., Cunningham W. P., Cheetham R. D., Lequire V. S. Isolation of a Golgi apparatus-rich fraction from rat liver. I. Method and morphology. J Cell Biol. 1970 Mar;44(3):484–491. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestruck A. C., Rubinstein D. The synthesis of apoproteins of very low density lipoproteins isolated from the Golgi apparatus of rat liver. Can J Biochem. 1976 Jul;54(7):617–628. doi: 10.1139/o76-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel S. P., Wong L., Dolphin P. J., Dory L., Rubenstein D. Secretion of cholesterol-rich lipoproteins by perfused livers of hypercholesterolemic rats. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):674–683. doi: 10.1172/JCI109508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROHEIM P. S., HAFT D. E., GIDEZ L. I., WHITE A., EDER H. A. PLASMA LIPOPROTEIN METABOLISM IN PERFUSED RAT LIVERS. II. TRANSFER OF FREE AND ESTERIFIED CHOLESTEROL INTO THE PLASMA. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1277–1285. doi: 10.1172/JCI104812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G., Dunne K. B., Roberts D. C., West C. E. Chylomicron metabolism in rabbits fed diets with or without added cholesterol. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Sep;24(3):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. C., Zilversmit D. B. Chylomicron remnant cholesteryl esters as the major constituent of very low density lipoproteins in plasma of cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lipid Res. 1977 Mar;18(2):169–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soutar A. K., Myant N. B., Thompson G. R. Simultaneous measurement of apolipoprotein B turnover in very-low-and low-density lipoproteins in familial hypercholesterolaemia. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Nov;28(3):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Weber W., Beisiegel U. Different mobility in SDS--polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of apolipoprotein E from phenotypes apo E-N and Apo E-D. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HANDEL E., ZILVERSMIT D. B. Micromethod for the direct determination of serum triglycerides. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jul;50(1):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S., Wilson D. L., Gilliam J. J. Methods for fractionation and scintillation counting of radioisotope-labeled polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1970 Nov;38(1):90–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcow H. G., Dunn G. D., Heimberg M. Effects of several common long chain fatty acids on the properties and lipid composition of the very low density lipoprotein secreted by the perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 22;398(1):39–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]