Abstract
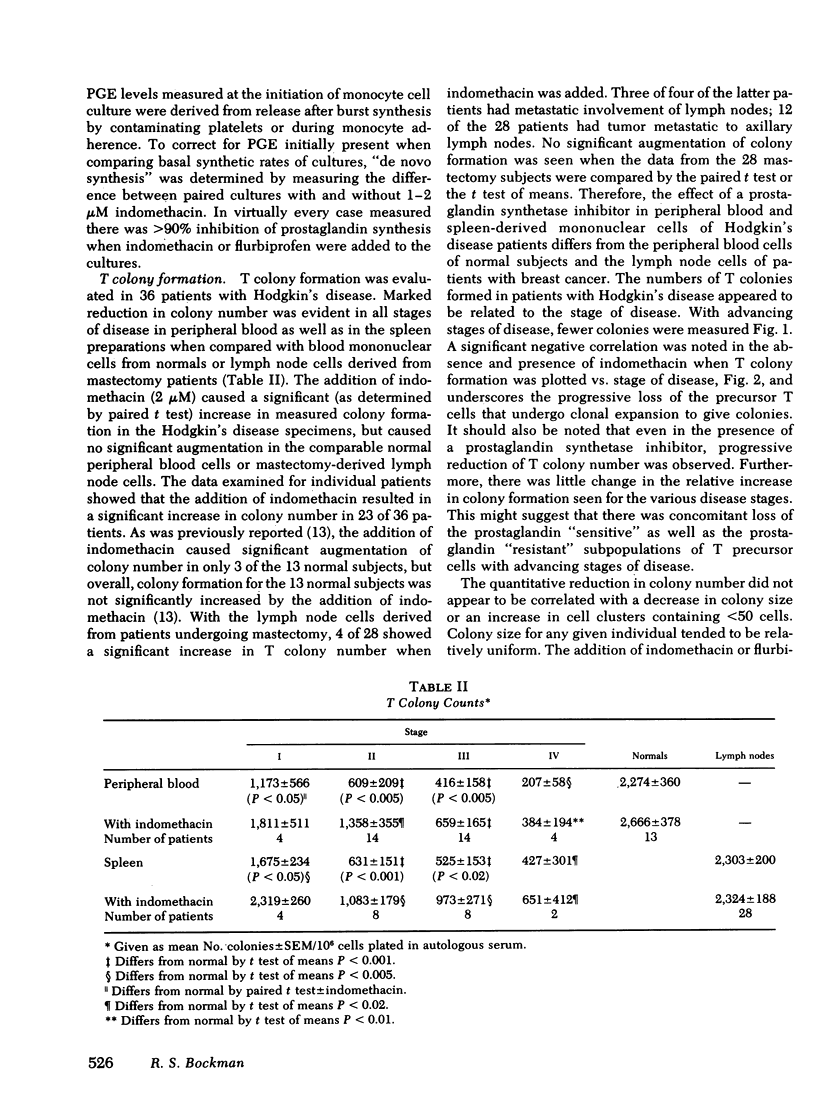
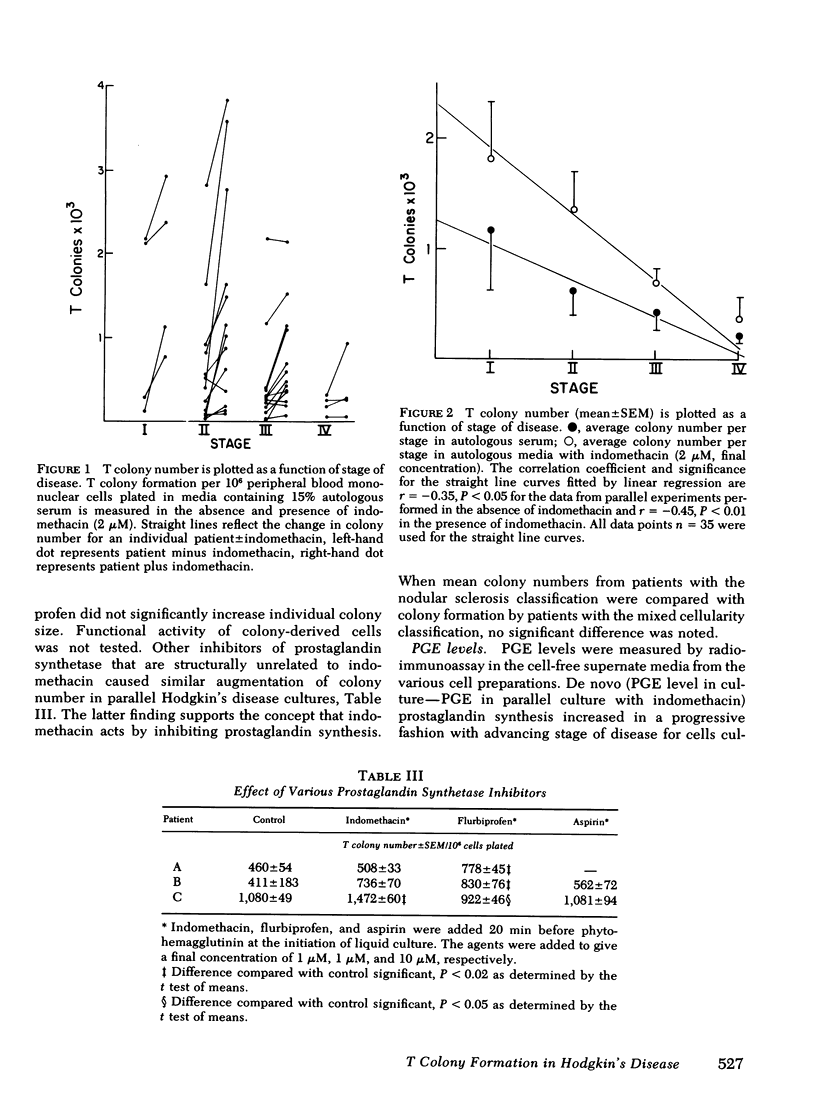
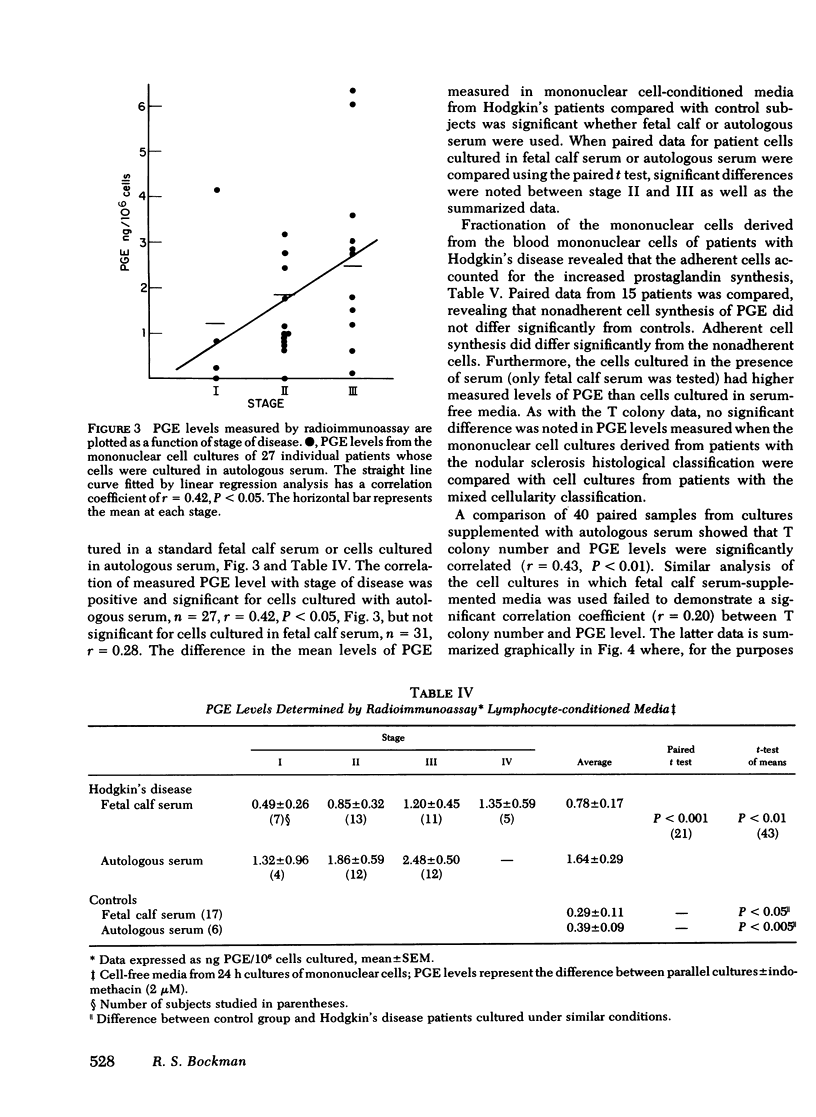
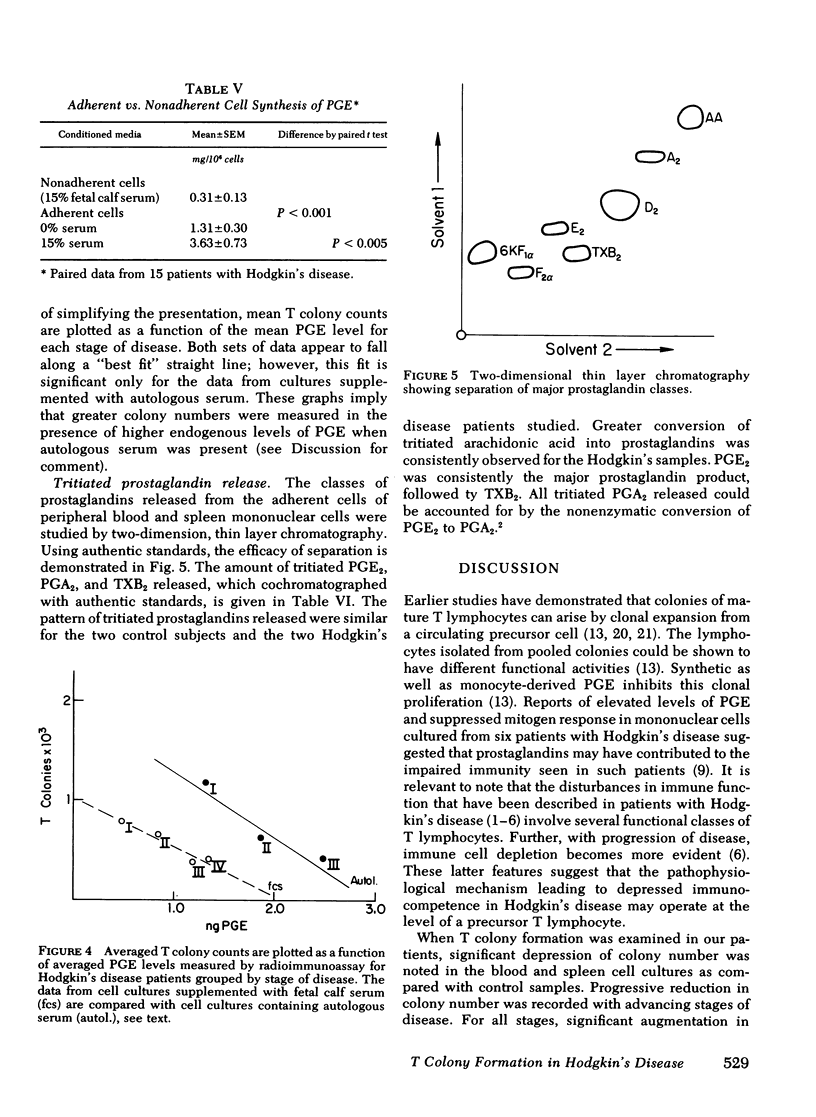
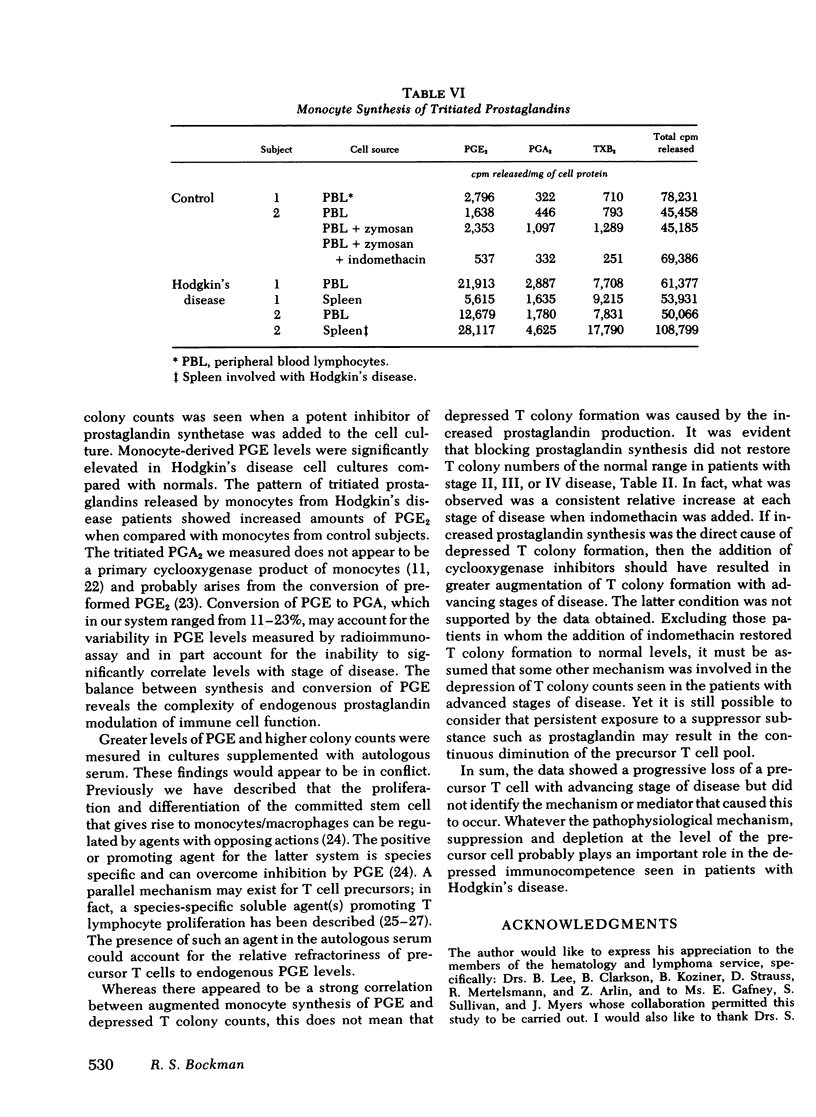
Prostaglandin synthesis and T lymphocyte colony formation have been examined in previously untreated patients with Hodgkin's disease. Mononuclear cells have been isolated from peripheral blood and spleens of these patients. Significant augmentation in prostaglandin E levels were noted in the mononuclear cell cutures from Hodgkin's disease patients compared with controls (1.64 +/- 0.29 vs. 0.39 +/- 0.09 ng/10(6) cells, P < 0.005). Measured prostaglandin E levels increased with advancing stage of disease. Virtually all of the prostaglandins were synthesized by the adherent monocyte cell population. Prostaglandin E was the major product. Clonal expansion of a T lymphocyte precursor cell, which gives rise to colonies > 50 cells, was determined by a layered soft agar method. T colony formation was significantly reduced in patients with stage II, III, and IV disease. There were progressively reduced colony numbers seen with advancing stage of disease (609 +/- 209, 416 +/- 158, 207 +/- 58 compared with normals 2,274 +/- 360 colonies/10(6) cells plated; P < 0.005). The addition of inhibitors of endogenous prostaglandin synthesis resulted in significant augmentation of T colony number. However, a consistent relative decrease in T colony number was seen even when endogenous prostaglandin E synthesis was blocked. It would appear that both the prostaglandin-dependent and independent T colony precursor cells are lost with progressive stage of disease. A causative role of augmented prostaglandin synthesis in this stage-dependent reduction of T colony formation could not be established.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bockman R. S., Rothschild M. Prostaglandin E inhibition of T-lymphocyte colony formation: a possible mechanism of monocyte modulation of clonal expansion. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):812–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI109528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonney R. J., Wightman P. D., Davies P., Sadowski S. J., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Humes J. L. Regulation of prostaglandin synthesis and of the selective release of lysosomal hydrolases by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):433–442. doi: 10.1042/bj1760433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. A one-stage procedure for isolation of granulocytes and lymphocytes from human blood. General sedimentation properties of white blood cells in a 1g gravity field. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:51–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone P. P., Kaplan H. S., Musshoff K., Smithers D. W., Tubiana M. Report of the Committee on Hodgkin's Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res. 1971 Nov;31(11):1860–1861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case D. C., Hansen J. A., Corrales E., Young C. W., Dupont B., Pinsky C. M., Good R. A. Comparison of multiple in vivo and in vitro parameters in untreated patients with Hodgkin's disease. Cancer. 1976 Oct;38(4):1807–1815. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197610)38:4<1807::aid-cncr2820380458>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droller M. J., Schneider M. U., Perlmann P. A possible role of prostaglandins in the inhibition of natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Aug;39(1):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Gerassi E., Sachs L. Induction of colony formation in vitro by human lymphocytes. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):127–129. doi: 10.1038/259127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith R. M., Goust J. M., Fudenberg H. H. Lymphocyte culture: induction of colonies by conditioned medium from human lymphoid cell lines. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1821–1826. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Messner R. P., Bankhurst A. D., Peake G. T., Saiki J. H., Williams R. C., Jr Prostaglandin-producing suppressor cells in Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 3;297(18):963–968. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711032971802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graze P. R., Perlin E., Royston I. In vitro lymphocyte dysfunction in Hodgkin's disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Feb;56(2):239–243. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillinger S. M., Herzig G. P. Impaired cell-mediated immunity in Hodgkin's disease mediated by suppressor lymphocytes and monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1620–1627. doi: 10.1172/JCI109082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland J. I., Bockman R. S., Broxmeyer H. E., Moore M. A. Limitation of excessive myelopoiesis by the intrinsic modulation of macrophage-derived prostaglandin E. Science. 1978 Feb 3;199(4328):552–555. doi: 10.1126/science.304600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland J. I., Bockman R. Prostaglandin E production by human blood monocytes and mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):952–957. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R., Kaplan H. S. Impaired lymphocyte function in untreated Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 24;290(4):181–186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401242900402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelus L. M., Bockman R. S. Increased prostaglandin synthesis by macrophages from tumor-bearing mice. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2118–2125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenszajn L. A., Shoham D., Kalechman I. Clonal proliferation of PHA-stimulated human lymphocytes in soft agar culture. Immunology. 1975 Dec;29(6):1041–1055. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter G. P., Soehnlen F. Monocyte-mediated inhibition of lymphocyte blastogenesis in Hodgkin disease. Blood. 1978 Aug;52(2):261–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Steiner A. L., Newberry W. M., Jr, Parker C. W. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in human lymphocytes. Alterations after phytohemagglutinin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):432–441. doi: 10.1172/JCI106510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava K. C., Clausen J. Stability of prostaglandin E compounds in solution. Lipids. 1973 Oct;8(10):592–594. doi: 10.1007/BF02532717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twomey J. J., Laughter A. H., Farrow S., Douglass C. C. Hodgkin's disease. An immunodepleting and immunosuppressive disorder. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):467–475. doi: 10.1172/JCI108113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeevi A., Goldman I., Rozenszajn L. A. Stimulation and inhibition of human T-lymphocyte colony cell proliferation by hemopoietic cell factors. Cell Immunol. 1977 Feb;28(2):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Raeburn J. A., van Zwet T. L. Characteristics of human mononuclear phagocytes. Blood. 1979 Aug;54(2):485–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


