Abstract
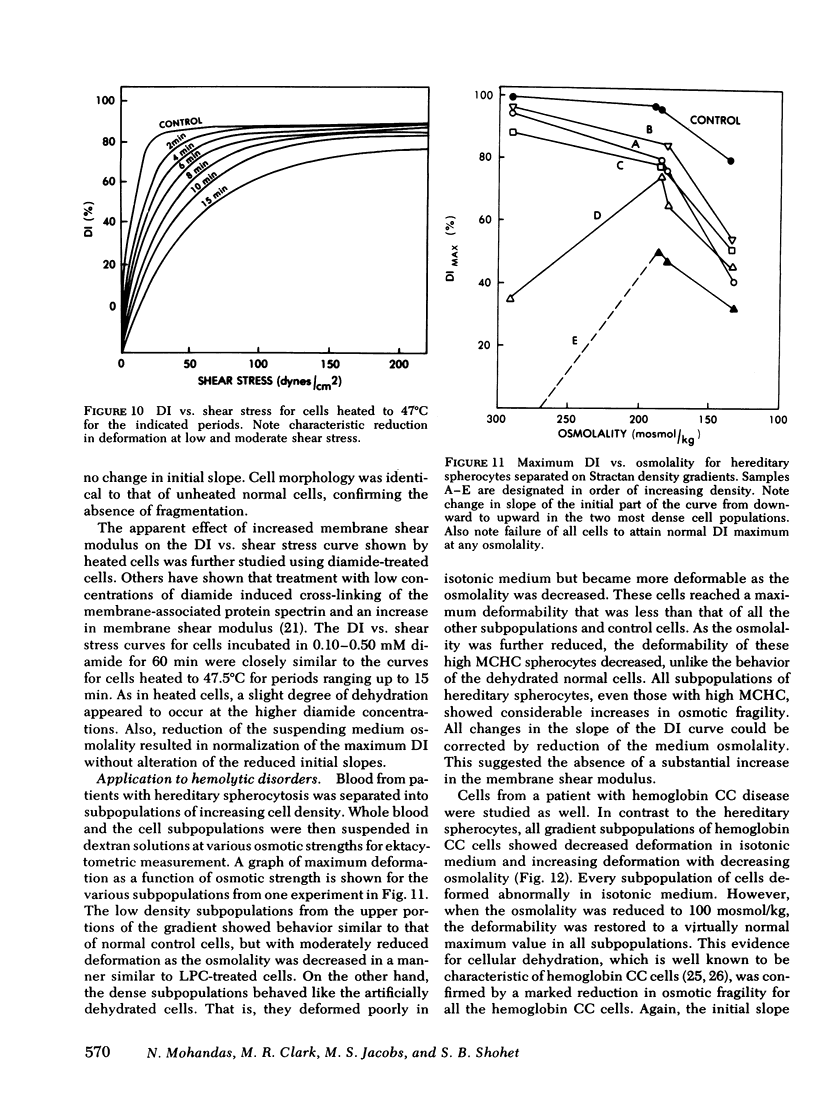
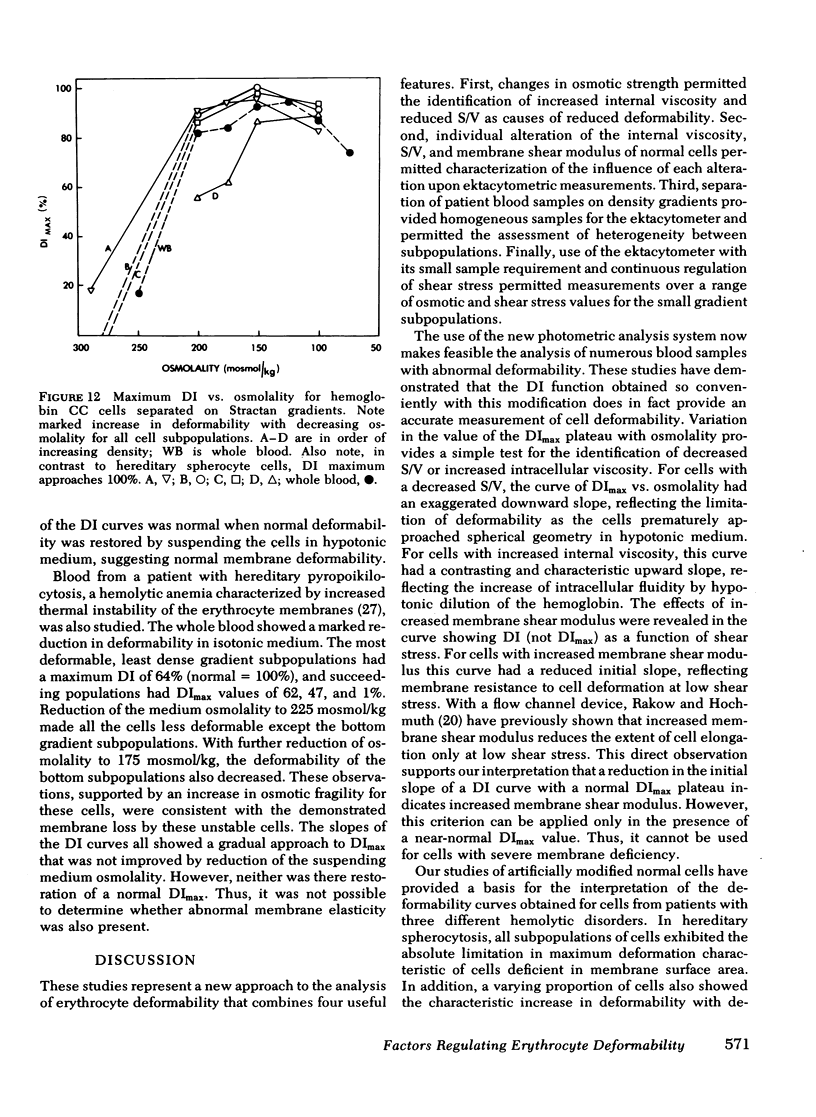
Using a laser diffraction technique, we have studied factors that influence the deformability of erythrocytes. Variations in suspending medium osmolality and applied shear stress were employed to isolate the individual contributions to whole cell deformability of internal viscosity, surface area-to-volume ratio, and viscoelastic properties of the membrane. An experimental system was devised in which normal cells were modified in vitro to induce specific alterations in each factor. Measurements of deformability as a function of medium osmolality showed characteristic behavior of the modified cells. Reduced surface area-to-volume ratio was detected by an exaggeration of the normal decrease in deformability as medium osmolality was decreased. In contrast, increased internal viscosity was detected by an increase in deformability as osmolality was decreased. Finally, decreased membrane flexibility was detected by reduced deformation at low shear stress. These methods of analysis were applied to cells from patients with hereditary spherocytosis, hereditary pyropoikilocytosis, and hemoglobin CC disease to define the basis of reduced deformability. Hereditary spherocytes showed the combined effects of reduced surface area and increased internal viscosity. Hereditary pyropoikilocytes revealed the effects of severely reduced surface area-to-volume ratio. Hemoglobin CC cells showed only the effects of high internal viscosity. An increase in the membrane shear modulus (decreased membrane deformability) was not evident in these disorders.
Full text
PDF


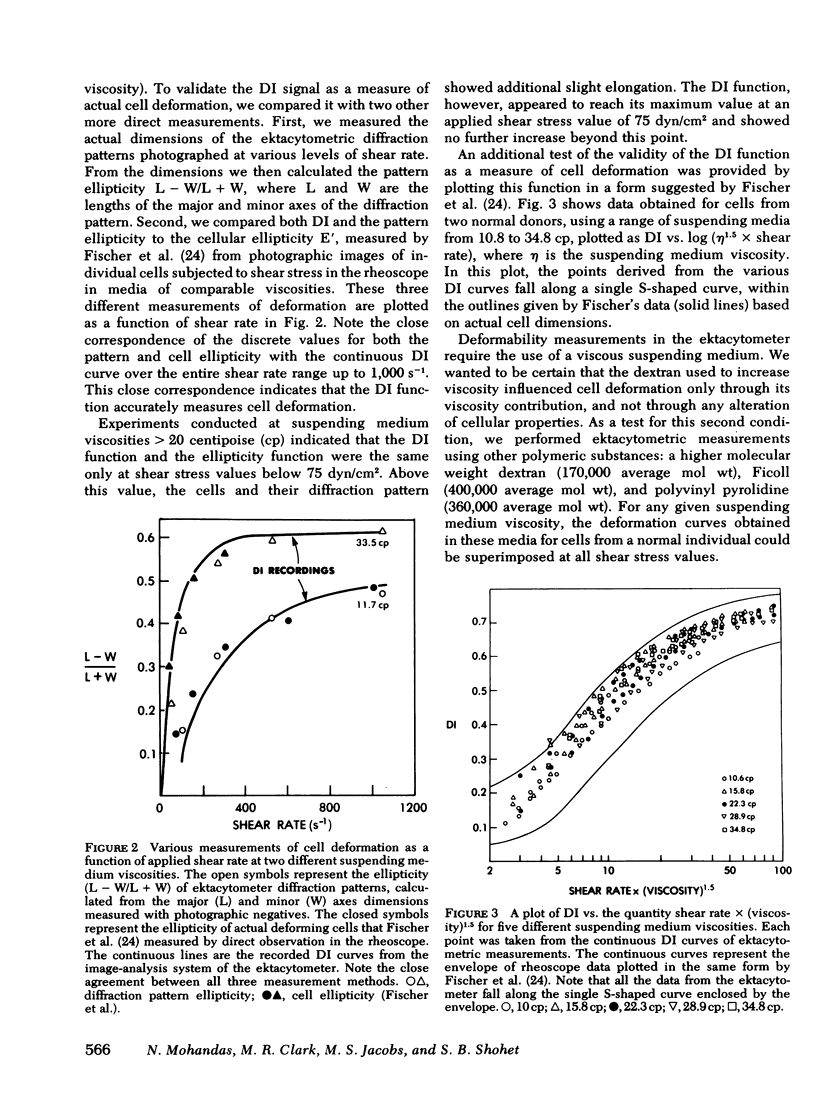
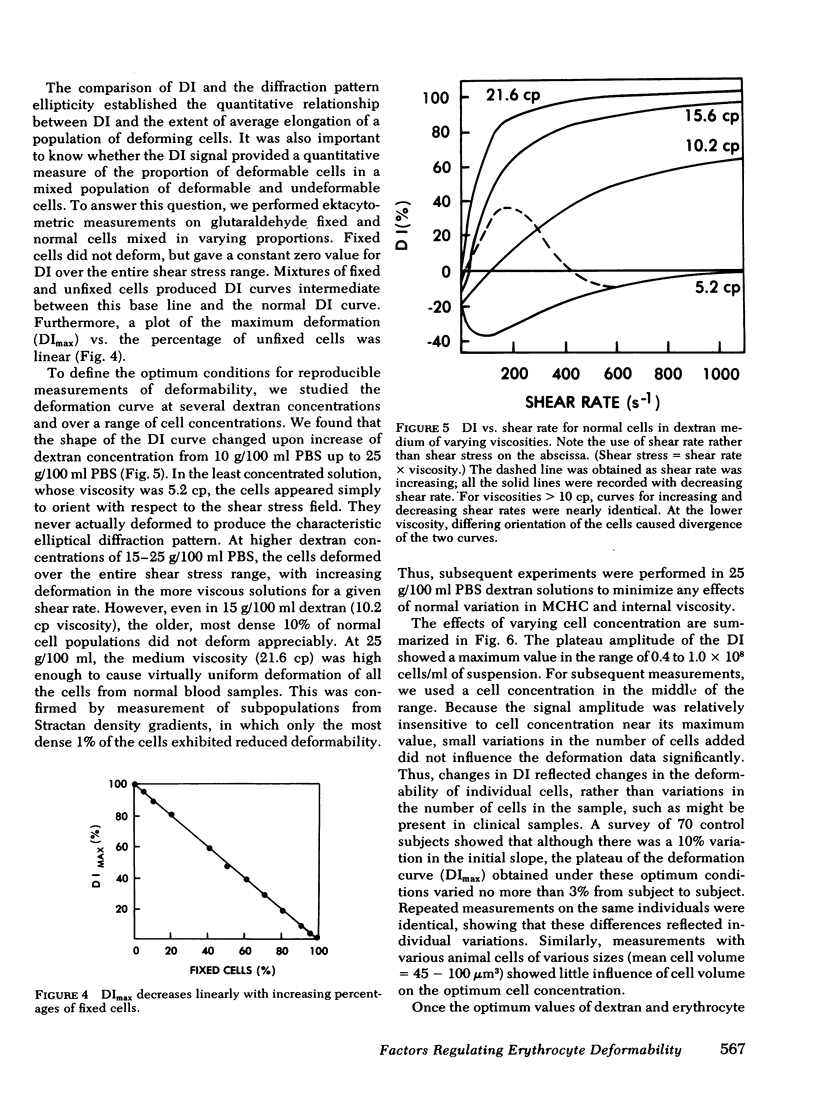
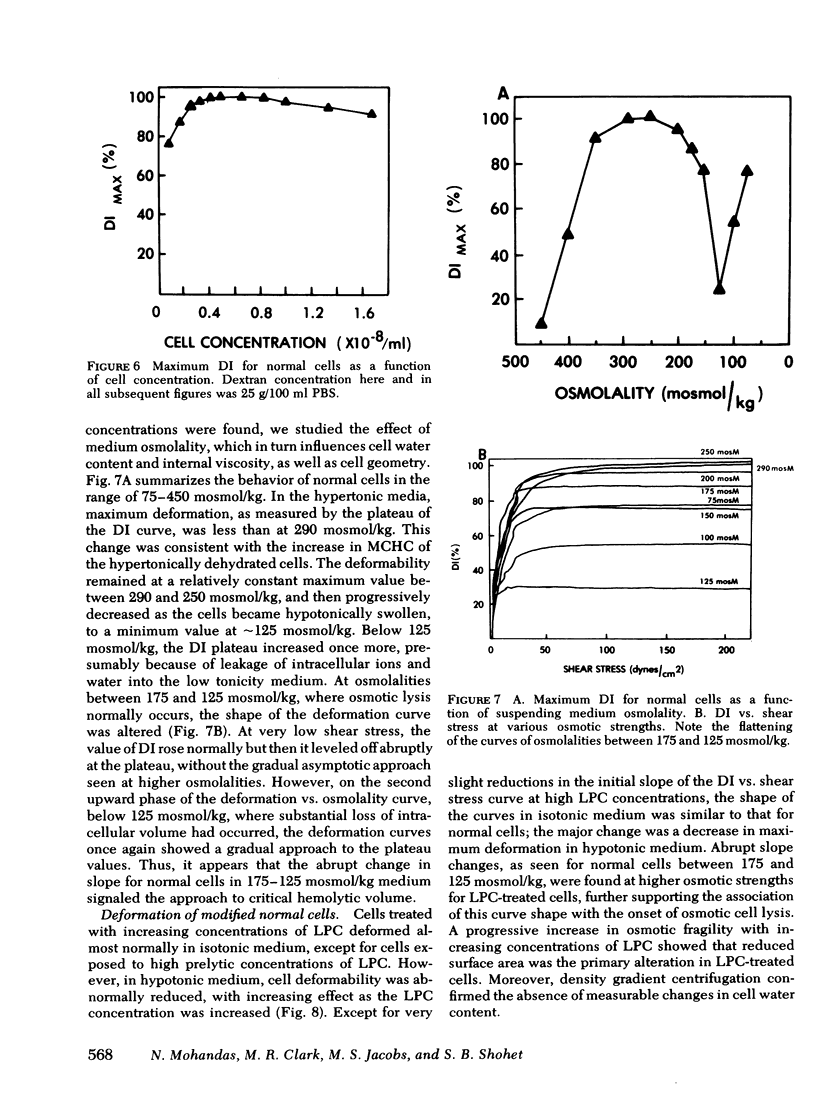



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bull B. S., Brailsford J. D. A new method of measuring the deformability of the red cell membrane. Blood. 1975 Apr;45(4):581–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charache S., Conley C. L., Waugh D. F., Ugoretz R. J., Spurrell J. R. Pathogenesis of hemolytic anemia in homozygous hemoglobin C disease. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1795–1811. doi: 10.1172/JCI105670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien S., Usami S., Bertles J. F. Abnormal rheology of oxygenated blood in sickle cell anemia. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):623–634. doi: 10.1172/JCI106273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Mohandas N., Caggiano V., Shohet S. B. Effects of abnormal cation transport on deformability of desiccytes. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(4):521–532. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Unger R. C., Shohet S. B. Monovalent cation composition and ATP and lipid content of irreversibly sickled cells. Blood. 1978 Jun;51(6):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Jandl J. H. The role of membrane lipids in the survival of red cells in hereditary spherocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):736–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI106031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombel L., Tchernia G., Mohandas N. Human reticulocyte maturation and its relevance to erythropoietic stress. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Sep;94(3):467–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERSLEV A. J., ATWATER J. EFFECT OF MEAN CORPUSCULAR HEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION ON VISCOSITY. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Sep;62:401–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., La Celle P. L. Intrinsic material properties of the erythrocyte membrane indicated by mechanical analysis of deformation. Blood. 1975 Jan;45(1):29–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer T. M., Haest C. W., Stöhr M., Kamp D., Deuticke B. Selective alteration of erythrocyte deformabiliby by SH-reagents: evidence for an involvement of spectrin in membrane shear elasticity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 4;510(2):270–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth R. M., Mohandas N., Blackshear P. L., Jr Measurement of the elastic modulus for red cell membrane using a fluid mechanical technique. Biophys J. 1973 Aug;13(8):747–762. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86021-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaCelle P. L. Alteration of membrane deformability in hemolytic anemias. Semin Hematol. 1970 Oct;7(4):355–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond P. F., Coulombe L. The measurement of erythrocyte deformability using micropore membranes. A sensitive technique with clinical applications. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jul;94(1):133–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Phillips W. M., Bessis M. Red blood cell deformability and hemolytic anemias. Semin Hematol. 1979 Apr;16(2):95–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R. Hemoglobin CC disease: rheological properties or erythrocytes and abnormalities in cell water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1483–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI105842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima K., Beutler E. Erythrocyte cellular and membrane deformability in hereditary spherocytosis. Blood. 1979 Mar;53(3):481–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakow A. L., Hochmuth R. M. Effect of heat treatment on the elasticity of human erythrocyte membrane. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1095–1100. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85885-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Variability in erythrocyte deformability among various mammals. Am J Physiol. 1979 May;236(5):H725–H730. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.5.H725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usami S., Chien S., Bertles J. F. Deformability of sickle cells as studied by microsieving. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Aug;86(2):274–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weed R. I., LaCelle P. L., Merrill E. W. Metabolic dependence of red cell deformability. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):795–809. doi: 10.1172/JCI106038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weed R. I. The importance of erythrocyte deformability. Am J Med. 1970 Aug;49(2):147–150. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkowsky H. S., Mohandas N., Speaker C. B., Shohet S. B. A congenital haemolytic anaemia with thermal sensitivity of the erythrocyte membrane. Br J Haematol. 1975 Apr;29(4):537–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb02740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]