Abstract
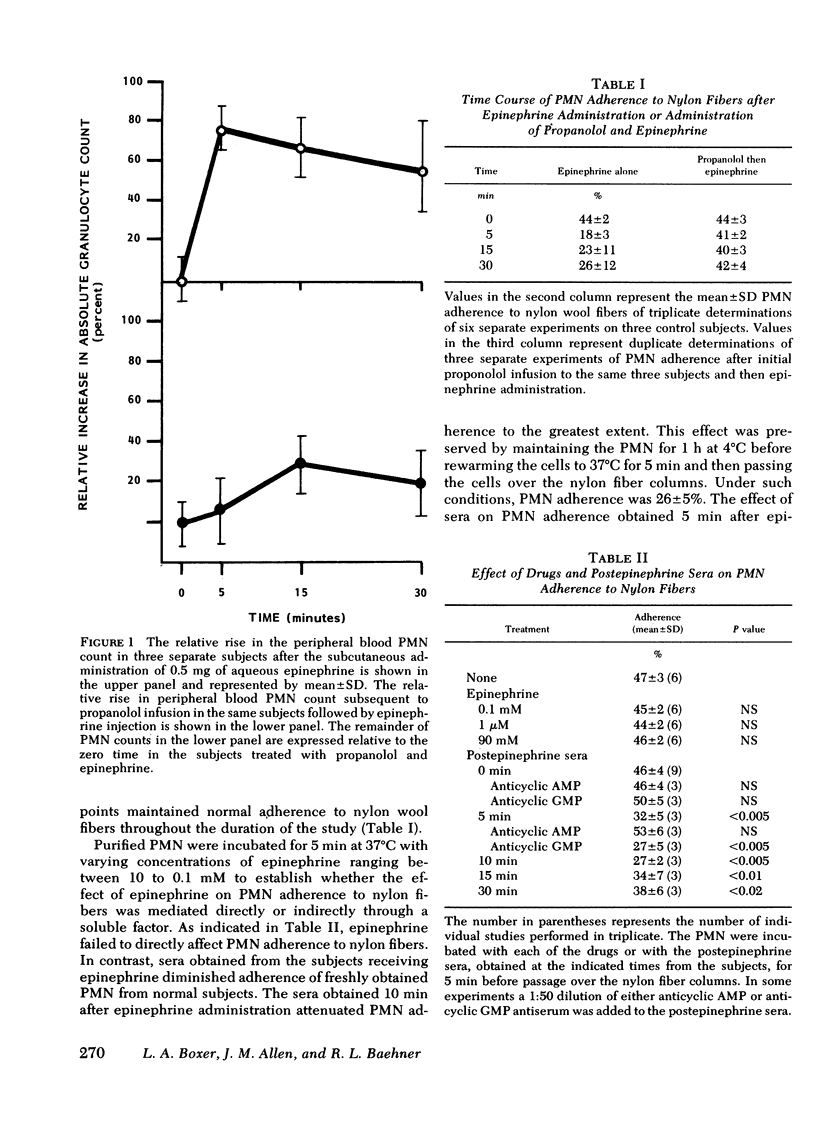
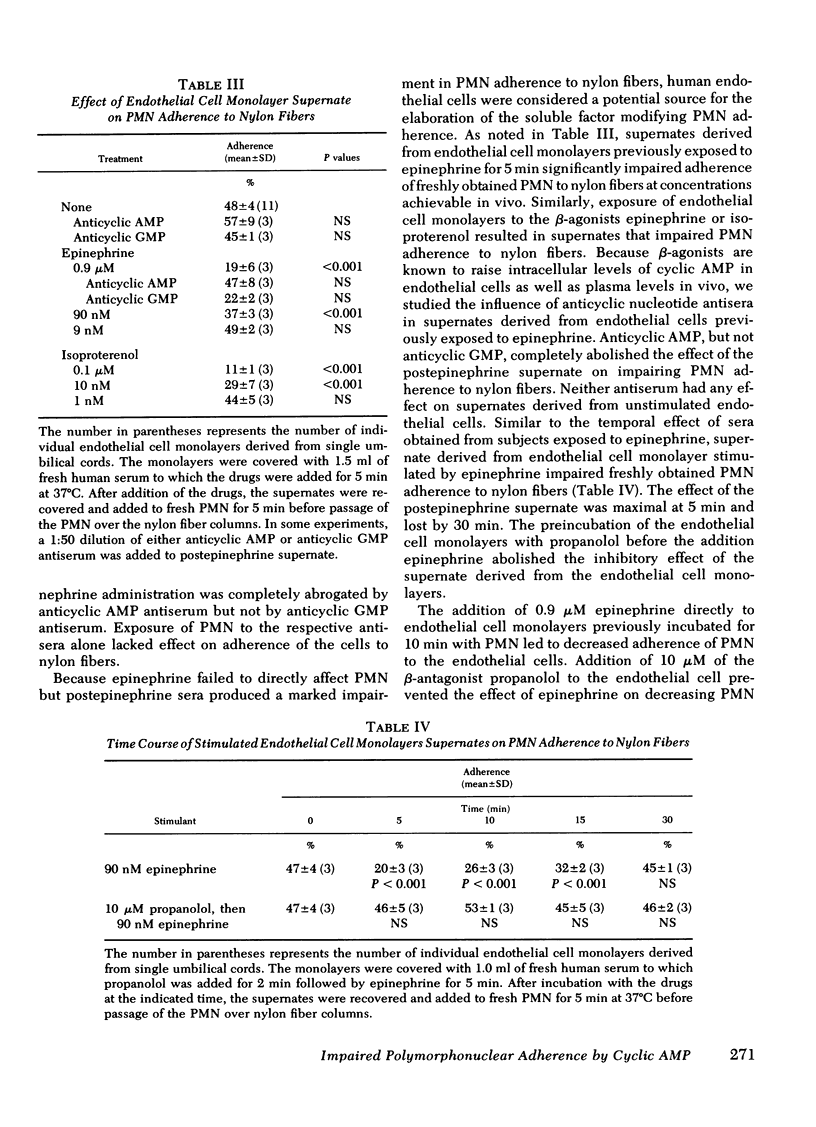
To investigate the biochemical and cellular basis for the rise in polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) count during epinephrine administration, PMN from subjects receiving epinephrine were studied for their capacity to adhere to nylon wool fibers and endothelial cell monolayers. After administration of epinephrine, the PMN count increased by 80% at 5 min, and isolated PMN adherence to nylon fibers fell from a base line of 44±2-18±3%. In contrast, when subjects were infused with the β-antagonist propanolol before receiving epinephrine, the PMN count failed to rise and PMN adherence was normal. Exposure of PMN endothelial cell monolayers to 0.1 μM epinephrine led to diminished PMN adherence that could be blocked by 10 μM propanolol but not by 10 μM phentolamine. Sera obtained from subjects 5 min after receiving epinephrine or from supernates derived from endothelial cell monolayers exposed to 90 nM epinephrine inhibited PMN adherence to nylon fibers. Addition of anticyclic AMP antisera but not anticyclic guanosine monophosphate antisera to the postepinephrine sera or to the postepinephrine supernate derived from the endothelial cell monolayers abolished their inhibitory effect of PMN adherence to nylon fibers. In contrast, direct exposure of PMN to epinephrine failed to affect their adherent properties. Because it has been previously shown that endothelial cells contain β-receptors and respond to catecholamines by raising their intracellular concentrations of cyclic AMP, and that PMN adherence is attenuated by cyclic AMP, it would appear that diminished PMN adherence after epinephrine administration is mediated through endothelial cell β-receptor activity, which in turn impairs PMN margination in vivo and could account for the rise in circulating PMN.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATHENS J. W., HAAB O. P., RAAB S. O., MAUER A. M., ASHENBRUCKER H., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Leukokinetic studies. IV. The total blood, circulating and marginal granulocyte pools and the granulocyte turnover rate in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jun;40:989–995. doi: 10.1172/JCI104338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Athens J. W. Granulocyte kinetics in health and disease. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1969 May;30:135–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton A., Born G. V. Quantitative investigations of the adhesiveness of circulating polymorphonuclear leucocytes to blood vessel walls. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):447–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson J. P., Sullivan T. J., Kelly J. P., Parker C. W. Stimulation by alcohols of cyclic AMP metabolism in human leukocytes. Possible role of cyclic AMP in the anti-inflammatory effects of ethanol. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):284–294. doi: 10.1172/JCI108776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball J. H., Kaminsky N. I., Hardman J. G., Broadus A. E., Sutherland E. W., Liddle G. W. Effects of catecholamines and adrenergic-blocking agents on plasma and urinary cyclic nucleotides in man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2124–2129. doi: 10.1172/JCI107019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley J. E., Pearson J. D., Carleton J. S., Hutchings A., Gordon J. L. Interaction of leukocytes with vascular cells in culture. J Cell Sci. 1978 Oct;33:85–101. doi: 10.1242/jcs.33.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan J. A., Duckles S. P. Evidence for alpha-adrenergic receptors on intimal endothelium. Blood Vessels. 1975;12(5):307–310. doi: 10.1159/000158066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Allen J. M., Watanabe A. M., Besch H. R., Jr, Baehner R. L. Role of microtubules in granulocyte adherence. Blood. 1978 Jun;51(6):1045–1050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. A., Yoder M., Bonsib S., Schmidt M., Ho P., Jersild R., Baehner R. L. Effects of a chemotactic factor, N-formylmethionyl peptide, on adherence, superoxide anion generation, phagocytosis, and microtubule assembly of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Mar;93(3):506–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonassisi V., Venter J. C. Hormone and neurotransmitter receptors in an established vascular endothelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1612–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czervionke R. L., Hoak J. C., Fry G. L. Effect of aspirin on thrombin-induced adherence of platelets to cultured cells from the blood vessel wall. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):847–856. doi: 10.1172/JCI109197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANT L., PALMER P., SANDERS A. G. The effect of heparin on the sticking of white cells to endothelium in inflammation. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:127–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbo H., Holst J. J., Christensen N. J. Glucagon and plasma catecholamine responses to graded and prolonged exercise in man. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Jan;38(1):70–76. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Cryer P. E., Santiago J. V., Haymond M. W., Pagliara A. S., Kipnis D. M. The role of adrenergic mechanisms in the substrate and hormonal response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):7–15. doi: 10.1172/JCI108460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst T. J., Raichle M. E., Ferrendelli J. A. beta-Adrenergic regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate concentration in brain microvessels. Science. 1979 Apr 20;204(4390):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.34879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. L., Briggs R. T., Karnovsky M. J. The adhesive interaction between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):423–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mac Gregor R. R. Granulocyte adherence changes induced by hemodialysis, endotoxin, epinephrine, and glucocorticoids. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jan;86(1):35–39. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Macarak E. J., Kefalides N. A. Comparative adherence of granulocytes to endothelial monolayers and nylon fiber. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):697–702. doi: 10.1172/JCI108981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Spagnuolo P. J., Lentnek A. L. Inhibition of granulocyte adherence by ethanol, prednisone, and aspirin, measured with an assay system. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 26;291(13):642–646. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409262911302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manhem P., Lecerof H., Hökfelt B. Plasma catecholamine levels in the coronary sinus, the left renal vein and peripheral vessels in healthy males at rest and during exercise. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Nov;104(3):364–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel C. M., French E. B., Aitchison W. R. Studies on adrenaline-induced leucocytosis in normal man. I. The role of the spleen and of the thoracic duct. Br J Haematol. 1971 Oct;21(4):413–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb02701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



