Abstract
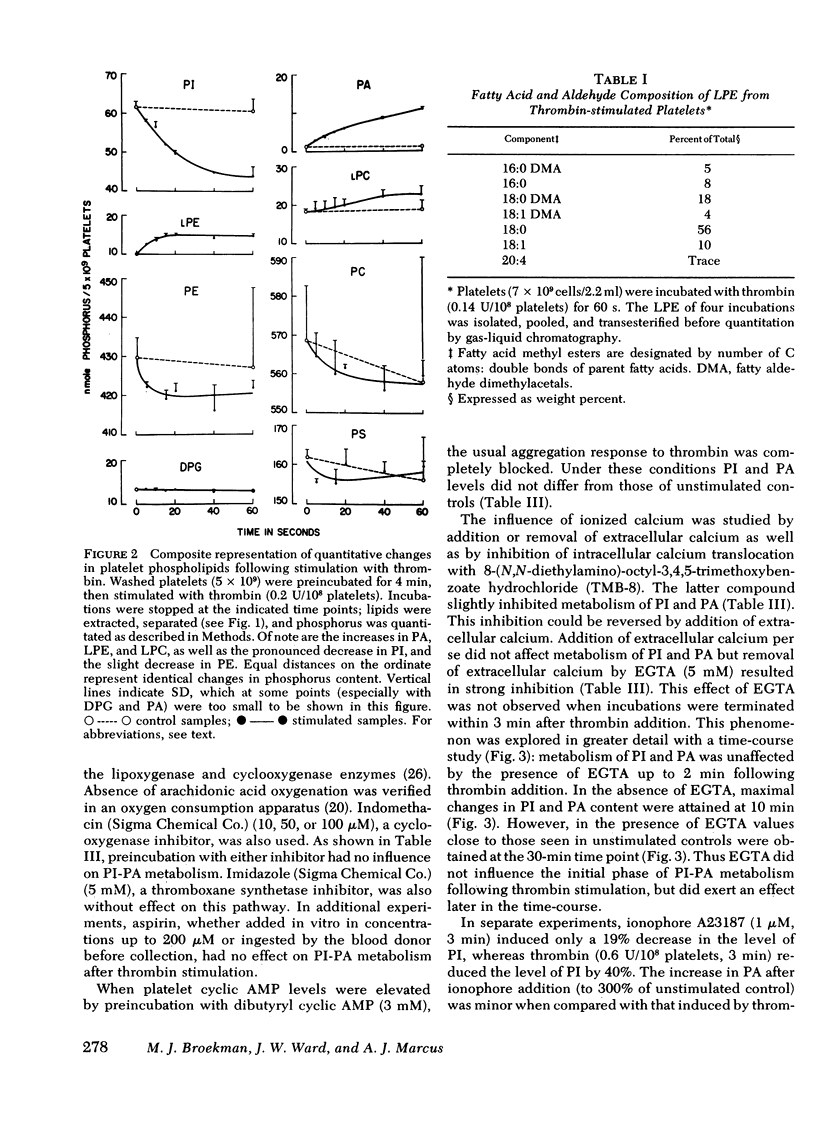
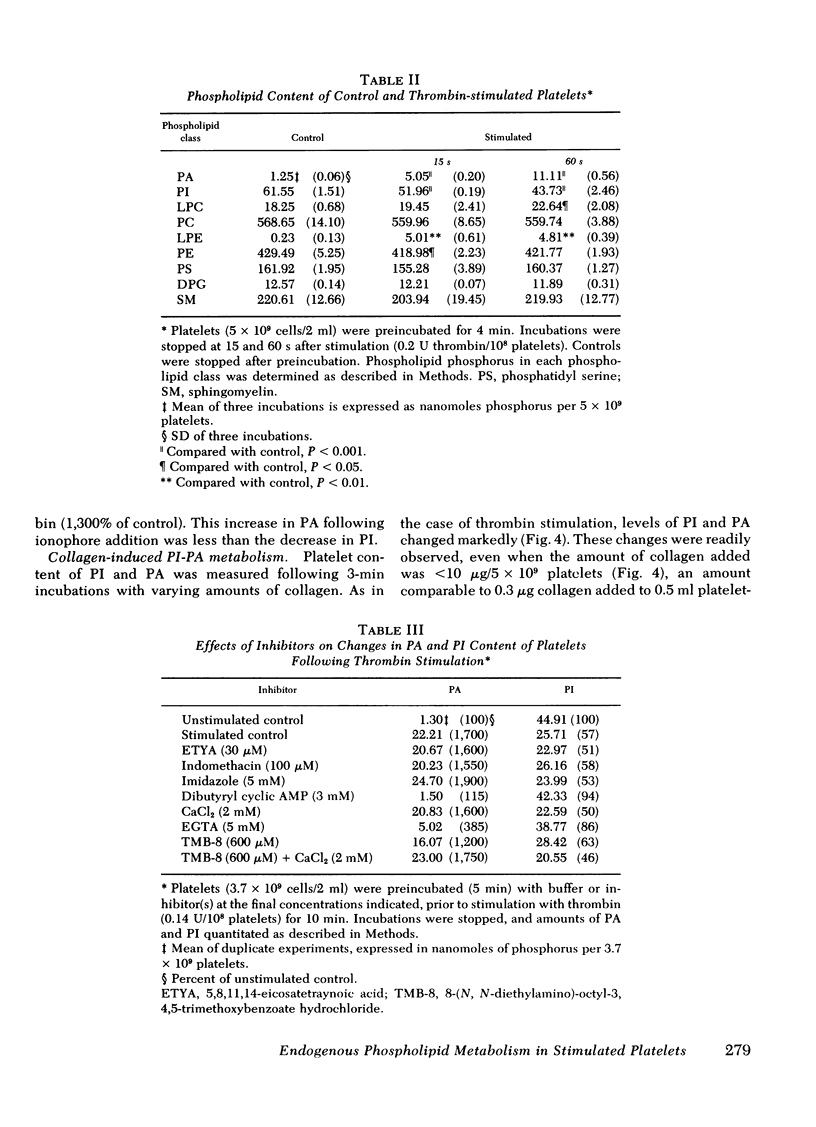
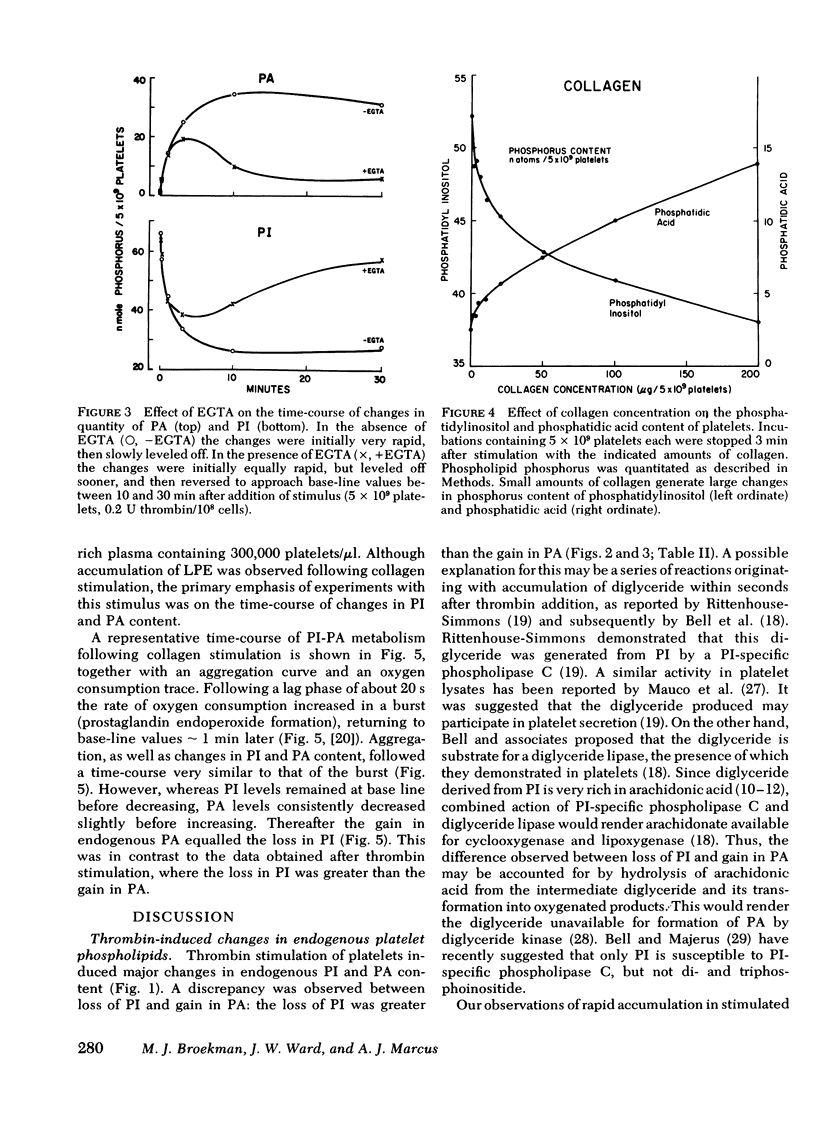
Endogenous phospholipid metabolism in stimulated human platelets was studied by phosphorus assay of major and minor components following separation by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. This procedure obviated the use of radioactive labels. Extensive changes were found in quantities of phosphatidylinositol (PI) and phosphatidic acid (PA) as a consequence of thrombin or collagen stimulation. Thrombin addition was followed by rapid alterations in the amount of endogenous PI and PA. The decrease in PI was not precisely reciprocated by an increase in PA when thrombin was the stimulus. This apparent discrepancy could be explained by removal of a transient intermediate in PI metabolism, such as diglyceride, formed by PI-specific phospholipase C (Rittenhouse-Simmons, S., J. Clin. Invest.63: 580-587, 1979). Diglyceride would be unavailable for PA formation by diglyceride kinase, if hydrolyzed by diglyceride lipase (Bell, R. L., D. A. Kennerly, N. Stanford, and P. W. Majerus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.76: 3238-3241, 1979) to yield arachidonate for prostaglandin endoperoxide formation. Thrombin-treated platelets also accumulated lysophospho-glycerides. Specifically, lysophosphatidyl ethanolamines accumulated within 15s following thrombin addition. Fatty acid and aldehyde analysis indicated phospholipase A2 activity, with an apparent preference for diacyl ethanolamine phosphoglycerides. In the case of collagen, these changes occurred concomitantly with aggregation and consumption of oxygen for prostaglandin endoperoxide formation.
These studies of endogenous phospholipid metabolism provide information supporting the existence of two previously postulated pathways for liberation of arachidonic acid from platelet phospholipids: (a) the combined action of PI-specific phospholipase C plus diglyceride lipase yielding arachidonate derived from PI; and (b) a phospholipase A2 acting primarily on diacyl ethanolamine phosphoglyceride.
Full text
PDF


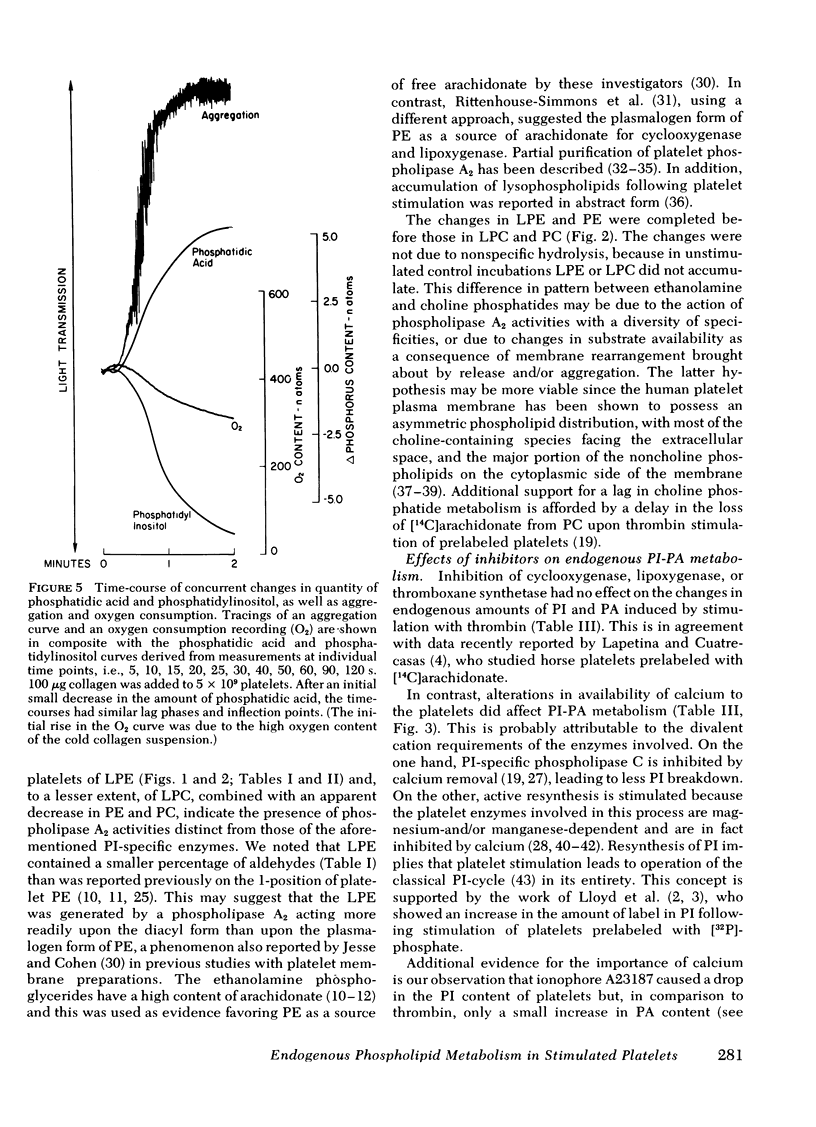


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apitz-Castro R. J., Mas M. A., Cruz M. R., Jain M. K. Isolation of homogeneous phospholipase A2 from human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1790–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase-C of platelets: association with 1,2-diacyglycerol-kinase and inhibition by cyclic-AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91594-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bills T. K., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Selective release of archidonic acid from the phospholipids of human platelets in response to thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI108745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler N. M., Broekman M. J., Marcus A. J. Concurrent studies of oxygen consumption and aggregation in stimulated human platelets. Blood. 1979 Feb;53(2):167–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Handin R. I., Derksen A., Cohen P. Distribution of phospholipids, fatty acids, and platelet factor 3 activity among subcellular fractions of human platelets. Blood. 1976 Jun;47(6):963–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call F. L., 2nd, Rubert M. Diglyceride kinase in human platelets. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jul;14(4):466–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call F. L., 2nd, Williams W. J. Biosynthesis of cytidine diphosphate diglyceride by human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):392–399. doi: 10.1172/JCI106248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chap H. J., Zwaal R. F., van Deenen L. L. Action of highly purified phospholipases on blood platelets. Evidence for an asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in the surface membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 2;467(2):146–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90192-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Broekman M. J., Verkley A., Lisman J. W., Derksen A. Quantification of human platelet inositides and the influence of ionic environment on their incorporation of orthophosphate-32P. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):762–772. doi: 10.1172/JCI106547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Derksen A. Comparison of phospholipid and fatty acid composition of human erythrocytes and platelets. Br J Haematol. 1969 Oct;17(4):359–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb01382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen A., Cohen P. Patterns of fatty acid release from endogenous substrates by human platelet homogenates and membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9342–9347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deykin D., Snyder D. Effect of epinephrine on platelet lipid metabolism. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Oct;82(4):554–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Prostaglandin endoperoxides. Novel transformations of arachidonic acid in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3400–3404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesse R. L., Cohen P. Arachidonic acid release from diacyl phosphatidylethanolamine by human platelet membranes. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 15;158(2):283–287. doi: 10.1042/bj1580283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesse R. L., Franson R. C. Modulation of purified phospholipase A2 activity from human platelets by calcium and indomethacin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 18;575(3):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi R., Koizumi K. Effect of different physical states of phospholipid substrates on partially purified platelet phospholipase A2 activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 5;556(3):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Stimulation of phosphatidic acid production in platelets precedes the formation of arachidonate and parallels the release of serotonin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 25;573(2):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung N. L., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Mustard J. F. Incorporation of 32PO4 into phospholipids of blood platelets. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jul;36(3):417–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis N., Majerus P. W. Lipid metabolism in human platelets. II. De novo phospholipid synthesis and the effect of thrombin on the pattern of synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2114–2123. doi: 10.1172/JCI106178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. V., Mustard J. F. Changes in 32P-content of phosphatidic acid and the phosphoinositides of rabbit platelets during aggregation induced by collagen or thrombin. Br J Haematol. 1974 Feb;26(2):243–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. V., Nishizawa E. E., Mustard J. F. Effect of ADP-induced shape change on incorporation of 32P into platelet phosphatidic acid and mono-, di- and triphosphatidyl inositol. Br J Haematol. 1973 Jul;25(1):77–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. T., Call F. L., 2nd, Williams W. J. The biosynthesis of phosphatidylinositol in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1949–1955. doi: 10.1172/JCI106414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS A. J., ULLMAN H. L., SAFIER L. B., BALLARD H. S. Platelet phosphatides. Their fatty acid and aldehyde composition and activity in different clotting systems. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2198–2212. doi: 10.1172/JCI104679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J. The role of lipids in platelet function: with particular reference to the arachidonic acid pathway. J Lipid Res. 1978 Sep;19(7):793–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Ullman H. L., Safier L. B. Lipid composition of subcellular particles of human blood platelets. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):108–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Characterization and properties of a phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase (phospholipase C) from platelet cytosol. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80371-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret B., Chap H. J., Douste-Blazy L. Asymmetric distribution of arachidonic acid in the plasma membrane of human platelets. A determination using purified phospholipases and a rapid method for membrane isolation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 5;556(3):434–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett W. C., Jesse R. L., Cohen P. Initiation of phospholipase A2 activity in human platelets by the calcium ion ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 18;486(1):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S., Deykin D. The activation by Ca2+ of platelet phospholipase A2. Effects of dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate and 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 1;543(4):409–422. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S., Deykin D. The mobilization of arachidonic acid in platelets exposed to thrombin or ionophore A23187. Effects of adenosine triphosphate deprivation. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):495–498. doi: 10.1172/JCI108801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S., Russell F. A., Deykin D. Mobilization of arachidonic acid in human platelets. Kinetics and Ca2+ dependency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):370–380. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu E. K., MacCoss M. Modification of the Dittmer-Lester reagent for the detection of phospholipid derivatives on thin-layer chromatograms. J Lipid Res. 1979 May;20(4):561–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick P. K., Kurica K. B., Chacko G. K. Location of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine in the human platelet plasma membrane. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1221–1226. doi: 10.1172/JCI108390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen D. M., Feagler J. R., Majerus P. W. The binding of thrombin to the surface of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2646–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. D., Rouser G. Precise quantitative determination of human blood lipids by thin-layer and triethylaminoethylcellulose column chromatography. I. Erythrocyte lipids. Anal Biochem. 1970 Dec;38(2):423–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida N., Aoki N. Release of arachidonic acid from human platelets. A key role for the potentiation of platelet aggregability in normal subjects as well as in those with nephrotic syndrome. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):969–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]