Abstract
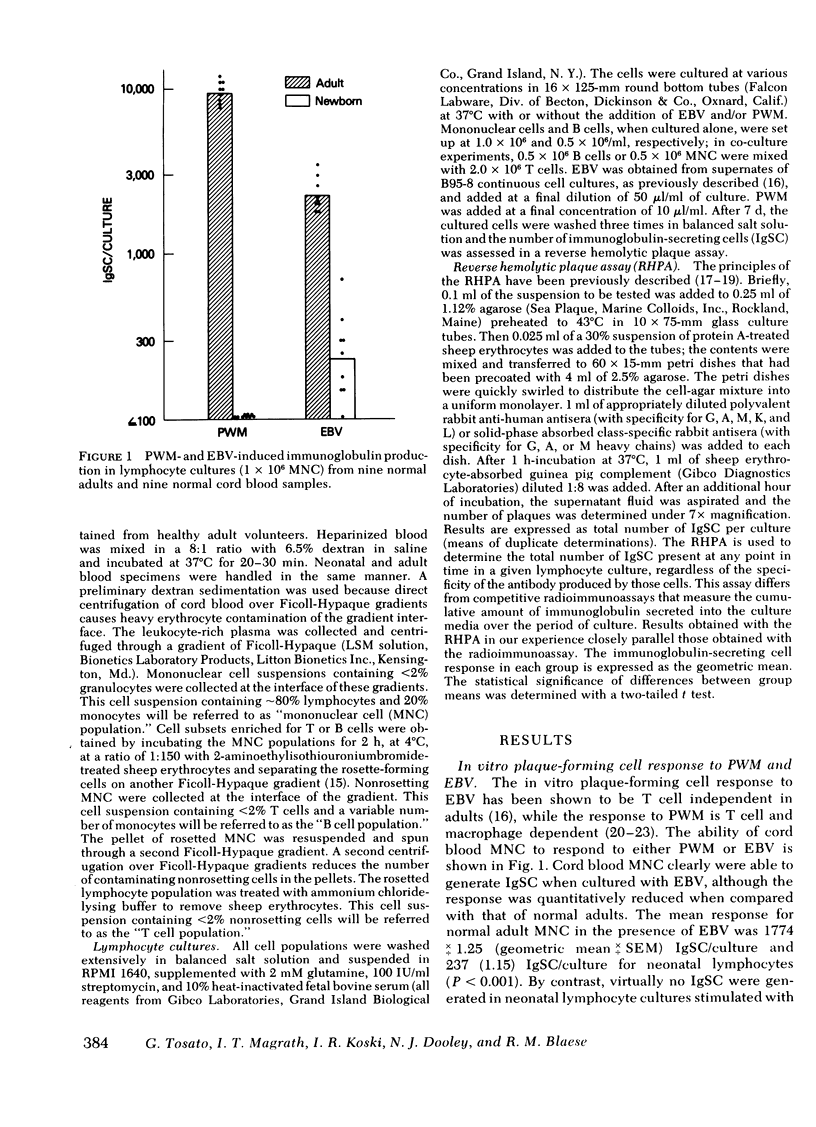
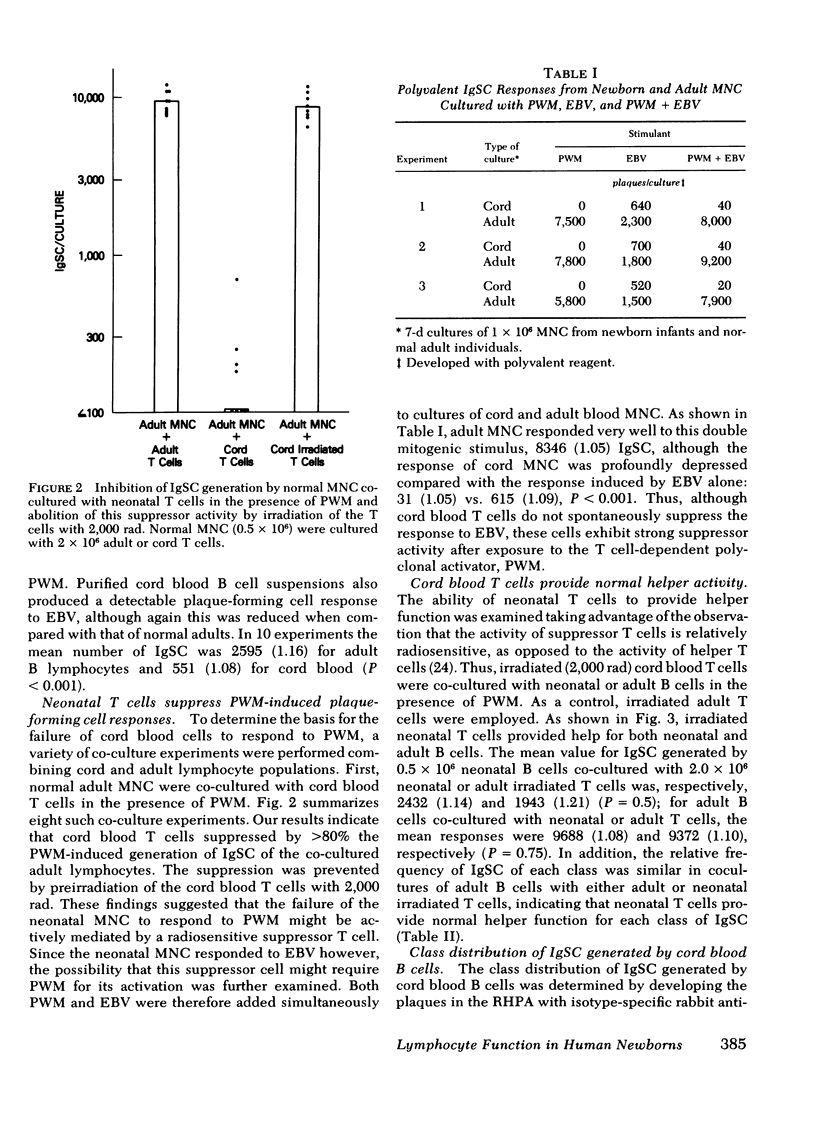
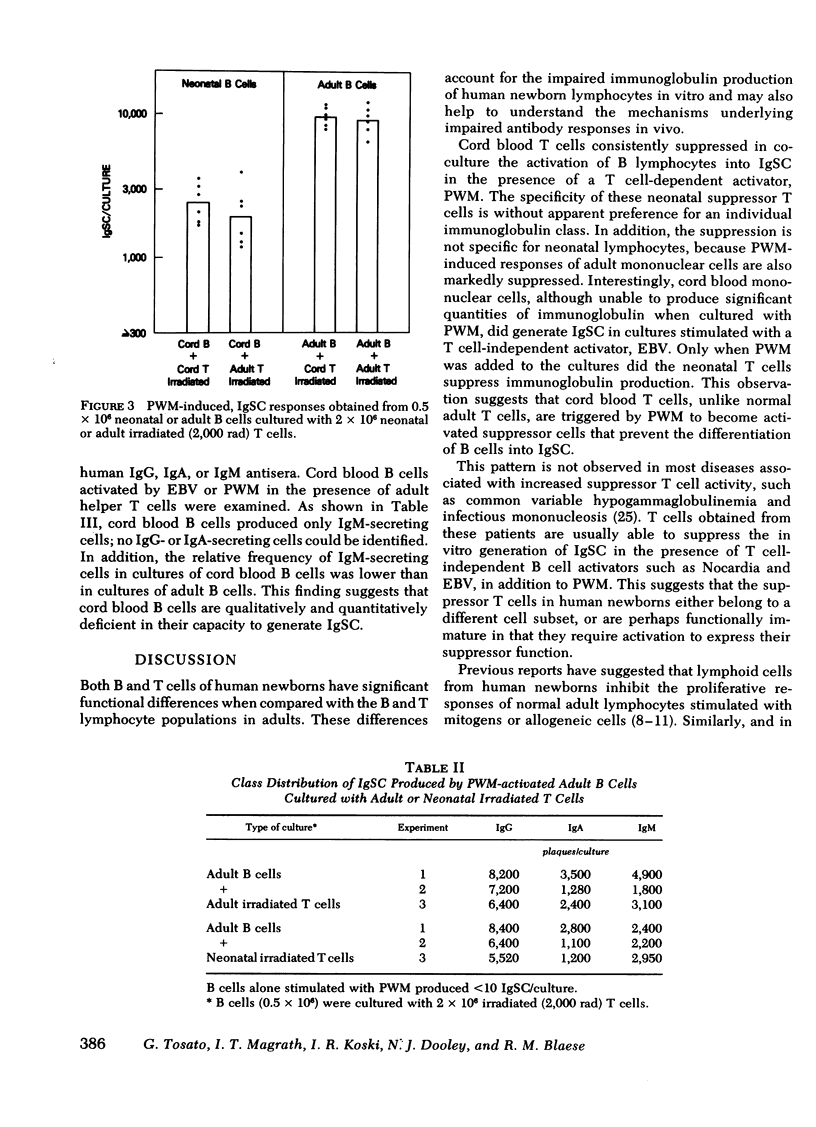
The functional maturity of T and B lymphocyte populations from human newborns was evaluated using a reverse hemolytic plaque assay to detect immunoglobulin-secreting cells generated in in vitro cultures stimulated with pokeweed mitogen (PWM), a T cell-dependent polyclonal activator, and the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a T cell-independent B cell activator. Cord blood lymphocytes failed to produce immunoglobulin in response to PWM, but did respond with immunoglobulin synthesis to stimulation with EBV. Co-culture experiments demonstrated that cord blood T cells would inhibit immunoglobulin production by adult cells stimulated with PWM, but not with EBV. Cord blood T cells did suppress immunoglobulin production by cord blood B cells when stimulated with a mixture of EBV and PWM, indicating that cord blood, in contrast to adult blood, contains a population of suppressor T cell precursors that are easily activated by PWM. Irradiation of the cord blood T cells with 2,000 rad eliminated the suppressor activity and revealed normal helper function for immunoglobulin (Ig) G, A, and M when these T cells were co-cultured with adult B cells. Cord blood B cells co-cultured with adult T cells or irradiated cord blood T cells did produce immunoglobulin in response to PWM, but the response was significantly lower than that of adult B cells, and only IgM was produced in these cultures. These studies demonstrate that both the T and B cells of the human newborn have significant functional differences compared with the functions of T and B lymphocyte populations in adults.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Durandy A., Fischer A., Griscelli C. Active suppression of B lymphocyte maturation by two different newborn T lymphocyte subsets. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2644–2650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gathings W. E., Lawton A. R., Cooper M. D. Immunofluorescent studies of the development of pre-B cells, B lymphocytes and immunoglobulin isotype diversity in humans. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Nov;7(11):804–810. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg W. W., Finkelman F. D., Lipsky P. E. Circulating and mitogen-induced immunoglobulin-secreting cells in human peripheral blood: evaluation by a modified reverse hemolytic plaque assay. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):33–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Lawton A. R. Induction of plasma cell differentiation of human fetal lymphocytes: evidence for functional immaturity of T and B cells. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1213–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R., Lydyard P. M. Suppression of B lymphocyte differentiation by newborn T lymphocytes with an Fc receptor for IgM. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Dec;34(3):374–378. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Greaves M. Functional analysis of murine and human B lymphocyte subsets. Transplant Rev. 1975;24:177–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keightley R. G., Cooper M. D., Lawton A. R. The T cell dependence of B cell differentiation induced by pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1538–1544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H., Tosato G., Blaese R. M., Broder S., Magrath I. T. Polyclonal immunoglobulin secretion by human B lymphocytes exposed to Epstein-Barr virus in vitro. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1310–1313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp W., Baumgartner G. Monocyte-mediated suppression of human B lymphocyte differentiation in vitro. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1177–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler S. D., Ukaejiofo E. O., Reeves B. R. Interaction of maternal and neonatal cells in mixed-lymphocyte cultures. Lancet. 1975 Dec 13;2(7946):1185–1187. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence E. C., Blaese R. M., Martin R. R., Stevens P. M. Immunoglobulin secreting cells in normal human bronchial lavage fluids. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):832–835. doi: 10.1172/JCI109195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgrom H., Shore S. L. Assessment of monocyte function in the normal newborn infant by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Pediatr. 1977 Oct;91(4):612–614. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki T., Seki H., Kubo M., Taniguchi N. Suppressor activity of T lymphocytes from infants assessed by co-culture with unfractionated adult lymphocytes in the pokeweed mitogen system. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1092–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morito T., Bankhurst A. D., Williams R. C., Jr Studies of human cord blood and adult lymphocyte interactions with in vitro immunoglobulin production. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):990–995. doi: 10.1172/JCI109565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Murgita R. A., Wigzell H. Mitogen-stimulated lymphoid cells from human newborns suppress the proliferation of maternal lymphocytes actoss a cell-impermeable membrane. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1109–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Oldstone B. A. Thymus-derived peripheral lymphocytes from human newborns inhibit division of their mothers' lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):682–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Oldstone M. B. Lymphocytes from human newborns abrogate mitosis of their mother's lymphocytes. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):161–162. doi: 10.1038/249161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Tishon A., Moretta L. Active thymus derived suppressor lymphocytes in human cord blood. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):333–335. doi: 10.1038/269333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S., Dierich M. P., Reisfeld R. A. Enhancement of sheep red blood cell human lymphocyte rosette formation by the sulfhydryl compound 2-amino ethylisothiouronium bromide. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Jan;3(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter B., Handzel Z. T., Altman Y., Nir E., Levin S. Cellular immunity in newborn infants and children: stimulation of lymphocyte protein synthesis as a measure of immune competence. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):478–484. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Siegal M. Enhancement by irradiated T cells of human plasma cell production: dissection of helper and suppressor functions in vitro. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):642–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Magrath I., Koski I., Dooley N., Blaese M. Activation of suppressor T cells during Epstein-Barr-virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 22;301(21):1133–1137. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911223012101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. Y., Blanco A., Cooper M. D., Lawton A. R. Ontogeny of B-lymphocyte differentiation induced by pokeweed mitogen. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Mar;5(2):208–217. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


